|
Ponza
Ponza (Italian: ''isola di Ponza'' ) is the largest island of the Italian Pontine Islands archipelago, located south of Cape Circeo in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is also the name of the commune of the island, a part of the province of Latina in the Lazio region. History The island was inhabited from neolithic through Roman times. According to local legends, Ponza was named after Pontius Pilate, Roman governor of Judea who tried Jesus of Nazareth for sedition against Roman rule. Pontius Pilate's family owned a grotto on Ponza, which is still named after him. The Pontius Pilate legend of Ponza's name has recently come into dispute amongst historians, because the name "Pontia" appears in Strabo's ''Geography''. This pre-dates the birth of Pilate. It is not known if this is the same name as Ponza or a similar name. Also, ''Pontia'' means "Land of Bridges" in Latin, a name which could have been applied for Ponza's many naturally occurring arches and bridge-like landforms. Another theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponza
Ponza (Italian: ''isola di Ponza'' ) is the largest island of the Italian Pontine Islands archipelago, located south of Cape Circeo in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is also the name of the commune of the island, a part of the province of Latina in the Lazio region. History The island was inhabited from neolithic through Roman times. According to local legends, Ponza was named after Pontius Pilate, Roman governor of Judea who tried Jesus of Nazareth for sedition against Roman rule. Pontius Pilate's family owned a grotto on Ponza, which is still named after him. The Pontius Pilate legend of Ponza's name has recently come into dispute amongst historians, because the name "Pontia" appears in Strabo's ''Geography''. This pre-dates the birth of Pilate. It is not known if this is the same name as Ponza or a similar name. Also, ''Pontia'' means "Land of Bridges" in Latin, a name which could have been applied for Ponza's many naturally occurring arches and bridge-like landforms. Another theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
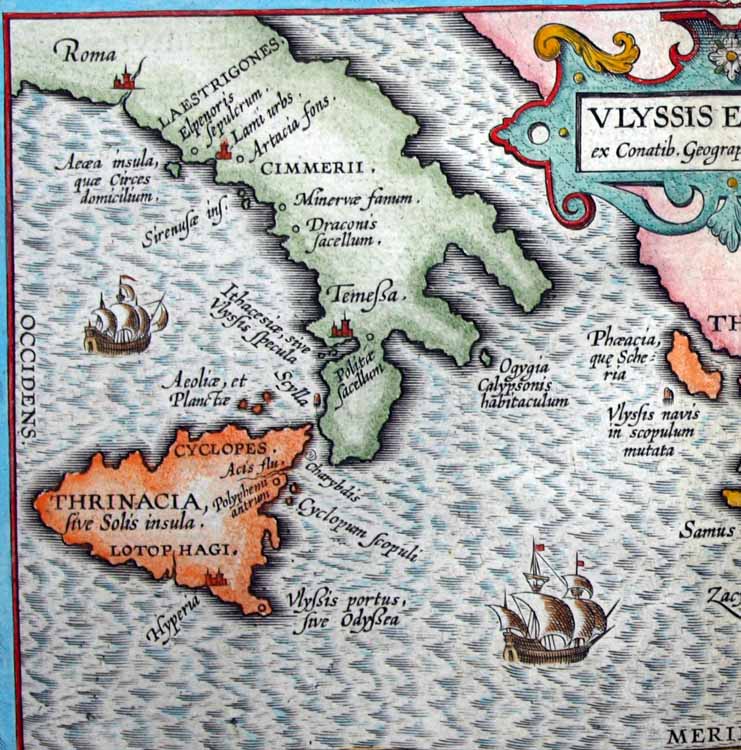
Pontine Islands
The Pontine Islands (, also ; it, Isole Ponziane ) are an archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the coast of Lazio region, Italy. The islands were collectively named after the largest island in the group, Ponza. The other islands in the archipelago are Palmarola, Zannone, and Gavi to the northwest and Ventotene and Santo Stefano to the southeast. These two groups are separated by . From Sabaudia-Cape Circeo peninsula to Zannone the distance is , while Ventotene faces Gaeta (21 miles). The minimum distance between Santo Stefano and the isle of Ischia is . The archipelago is volcanic and has been inhabited for thousands of years. Neolithic artefacts and Bronze Age obsidians have been excavated on the islands. The islands were used by the Etruscans who carved the "Blue Grottos". The earliest recorded history of the islands occurs with the Roman victory over the Volsci at 338 BC. According to a local legend, this was once the lost Kingdom of Tyrrhenia which sank with a narrow stri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea (; it, Mar Tirreno , french: Mer Tyrrhénienne , sc, Mare Tirrenu, co, Mari Tirrenu, scn, Mari Tirrenu, nap, Mare Tirreno) is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy. It is named for the Tyrrhenian people identified with the Etruscans of Italy. Geography The sea is bounded by the islands of Corsica and Sardinia (to the west), the Italian Peninsula (regions of Tuscany, Lazio, Campania, Basilicata, and Calabria) to the north and east, and the island of Sicily (to the south). The Tyrrhenian Sea also includes a number of smaller islands like Capri, Elba, Ischia, and Ustica. The maximum depth of the sea is . The Tyrrhenian Sea is situated near where the African and Eurasian Plates meet; therefore mountain chains and active volcanoes such as Mount Marsili are found in its depths. The eight Aeolian Islands and Ustica are located in the southern part of the sea, north of Sicily. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeaea
__NOTOC__ Aeaea, Ææa or Eëä ( or ; grc, Αἰαία, Aiaíā ) was a Greek mythology, mythological island said to be the home of the goddess-sorceress Circe. In Homer's ''Odyssey'', Odysseus tells Alcinous that he stayed here for one year on his way home to Homer's Ithaca, Ithaca. He says that he could not resist the need to be on this island, not so much for Circe but so that he does not resist the pull. Before leaving Aeaea, Odysseus was given instructions by Circe about how to cross the ocean and assisted by the North Wind to reach the Greek underworld, underworld: Description Homer describes Aeaea as covered with a mixture of pasture and dense woodland of oak and beech. There were high hills or bluffs from which the sea could be seen encircling the island in all directions. Circe's stone house was located in a "dense forest of trees" "in a place that could be seen from far." Location The somewhat inconsistent geography of the Odyssey, geography of Homer's ''Odyssey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Circeo
Monte Circeo or Cape Circeo ( it, Promontorio del Circeo , la, Mons Circeius) is a mountain promontory that marks the southwestern limit of the former Pontine Marshes.located on the southwest coast of Italy near San Felice Circeo. At the northern end of the Gulf of Gaeta, it is about long by wide at the base, running from east to west and surrounded by the sea on all sides except the north. The land to the northeast is the former ancient Pontine Marshes. Most of the ancient swamp has been reclaimed for agriculture and urban areas. The mountain, the coastal zone as far north as Latina, including the only remaining remnant of the swamp, and two of the Pontine Islands offshore, Zannone and Ponza, have been included in the Circeo National Park. Geology Although a headland, it was not formed by coastal erosion – as headlands are usually formed – but is a remnant of the orogenic processes that created the Apennines. The entire coast of Lazio, on which the mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Latina
The Province of Latina ( it, Provincia di Latina) is an area of local government at the level of province in the Republic of Italy. It is one of five provinces that form the region of Lazio. The provincial capital is the city of Latina. It is bordered by the provinces of Frosinone to the north-east and by the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital to the north-west. It has an area of and a population of 561,189 (2012). There are 33 ''comuni'' (singular: ''comune'') in the province Sub-divisions of the province The most populous ''comuni'' are: History The province of Latina was founded on 18 December 1934, encompassing mainly the drained areas of the Agro Pontino previously part of the province of Rome. Apart from the Pontine lands, it includes the Aurunci, Lepini and Ausoni mountain ranges, as well as the Pontine islands archipelago. The port of Gaeta and Formia, in the southernmost part of the province, belonged traditionally and linguistically to Campania. In Bronze Age, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters. The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, and the fruit has been used as human food over history. Eaten fresh or in dried form (as raisins, currants and sultanas), grapes also hold cultural significance in many parts of the world, particularly for their role in winemaking. Other grape-derived products include various types of jam, juice, vinegar and oil. History The Middle East is generally described as the homeland of grape and the cultivation of this plant began there 6,000–8,000 years ago. Yeast, one of the earliest domesticated microorganisms, occurs naturally on the skins of grapes, leading to the discovery of alcoholic drinks such as wine. The earliest archeological evidence for a dominant position of wine-making in human culture dates from 8,000 years ago in Georg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir), Buddhism, Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Islam (whose temples are called mosques), Judaism (whose temples are called synagogues), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baha'i Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baha'i House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are sometimes called Jinja), Confucianism (which are sometimes called the Temple of Confucius), and ancient religions such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. The form and function of temples are thus very variable, though they are often considered by believers to be, in some sense, the "house" of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region. Etruscan civilization endured until it was assimilated into Roman society. Assimilation began in the late 4thcenturyBC as a result of the Roman–Etruscan Wars; it accelerated with the grant of Roman citizenship in 90 BC, and became complete in 27 BC, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrace (agriculture)
In agriculture, a terrace is a piece of sloped plane that has been cut into a series of successively receding flat surfaces or platforms, which resemble steps, for the purposes of more effective farming. This type of landscaping is therefore called terracing. Graduated terrace steps are commonly used to farm on hilly or mountainous terrain. Terraced fields decrease both erosion and surface runoff, and may be used to support growing crops that require irrigation, such as rice. The Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras have been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of the significance of this technique. Uses Terraced paddy fields are used widely in rice, wheat and barley farming in east, south, southwest, and southeast Asia, as well as the Mediterranean Basin, Africa, and South America. Drier-climate terrace farming is common throughout the Mediterranean Basin, where they are used for vineyards, olive trees, cork oak, and other crops. Ancient history Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontine Islands Map
Pontine may refer to: * Having to do with the pons, a structure located in the brain stem (from ''pons'', "bridge") * Pontine Marshes, a region of Italy near Rome * Pontine Islands The Pontine Islands (, also ; it, Isole Ponziane ) are an archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the coast of Lazio region, Italy. The islands were collectively named after the largest island in the group, Ponza. The other islands in the archipe ..., islands of Italy near Circeo See also {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |