|
Exessive Case
The exessive case (abbreviated ) is a grammatical case that denotes a transition away from a state. It is a rare case found in certain dialects of Baltic-Finnic languages. It completes the series of "to/in/from a state" series consisting of the translative case, the essive case and the exessive case. The exessive case has been described in Estonian, South Estonian, Livonian, Votic, Ingrian, Ludic, Karelian, and Finnish. Estonian In the general pattern of the loss of a final vowel when compared to Finnish, the Estonian exessive ending is ''-nt''. Exessive case is unproductive in contemporary Estonian. It appears in words such as ''kodunt'' 'away from home' and ''tagant'' 'from behind', or South Estonian ''mant'' 'away from the vicinity of something'. The exessive is more common in the language of Estonian folk songs.Prillop, Külli et al. 2020. ''Eesti keele ajalugu''. Tartu Ülikooli Kirjastus. p. 201. Finnish The exessive is found only in Savo and southeastern dialec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Glossing Abbreviations
This article lists common abbreviations for grammatical terms that are used in linguistic interlinear glossing of oral languages in English. The list provides conventional glosses as established by standard inventories of glossing abbreviations such as the Leipzig Glossing Rules, Leipzig Glossing rules, the most widely known standard. Synonymous glosses are listed as alternatives for reference purposes. In a few cases, long and short standard forms are listed, intended for texts where that gloss is rare or uncommon. Conventions * Grammatical abbreviations are generally written in full or small caps to visually distinguish them from the translations of lexical words. For instance, capital or small-cap (frequently abbreviated to ) glosses a grammatical past-tense morpheme, while lower-case 'past' would be a literal translation of a word with that meaning. Similarly, (small) cap might be a locative suffix used in nominal inflections, prototypically indicating direction downward b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
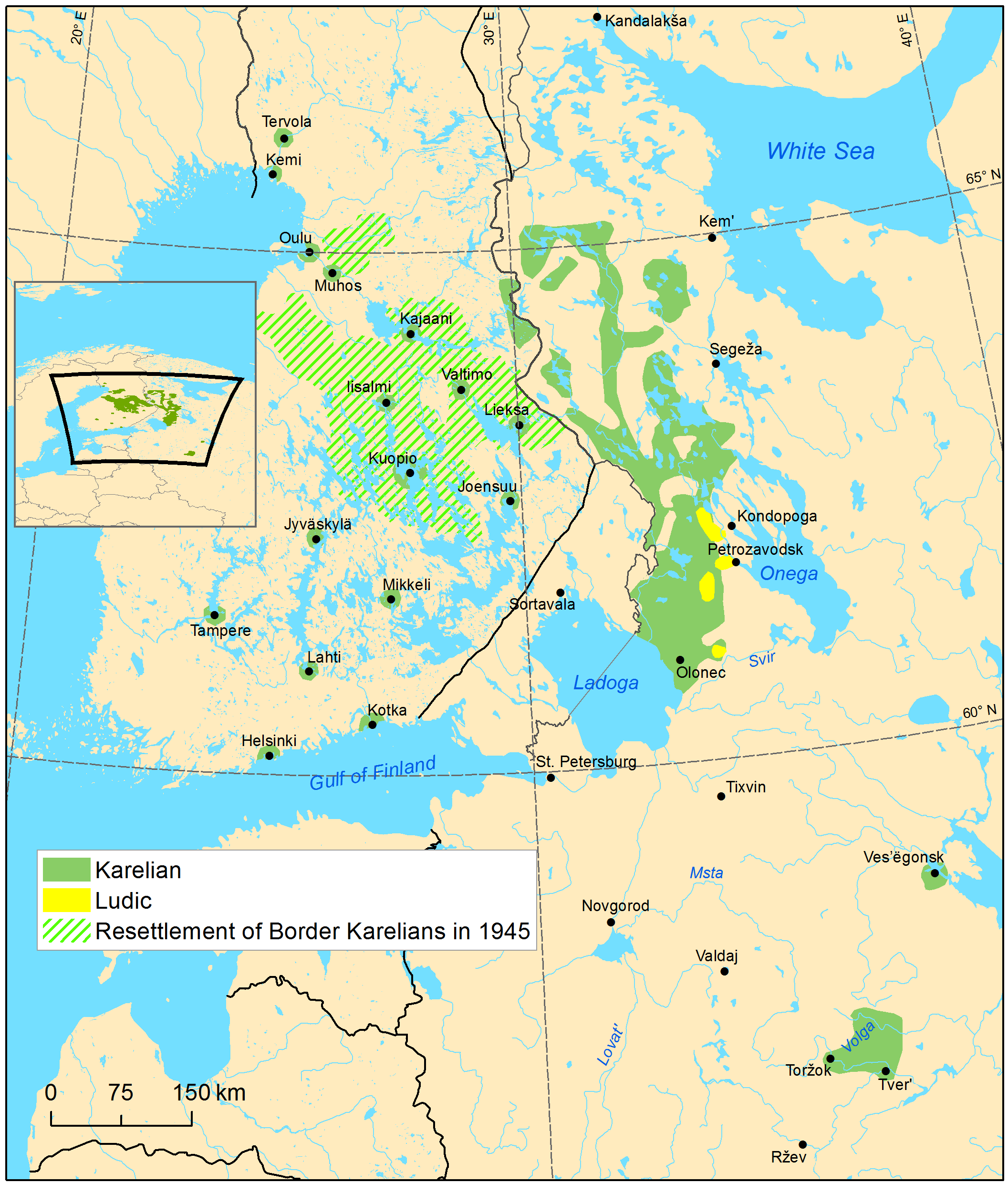
Ludic Language
Ludic, Ludian, or Ludic Karelian ( or ), is a Finnic language in the Uralic language family or a Karelian dialect. It is transitional between the Olonets Karelian language and the Veps language. It is spoken by 300 Karelians in the Republic of Karelia in Russia, near the southwestern shore of Lake Onega, including a few children. Classification In the Finnish research tradition, Ludic has been considered a transitional dialect area between Karelian and Veps, while in the Russian research tradition it is, on ethnographic grounds, normally considered a dialect of Karelian. A status as an independent language has been proposed in recent times. Ludic is characterised by a specific mixture of Karelian-like traits (such as the diphthongisation of the Proto-Finnic non-open long vowels: e.g. *pää > ''piä'' 'head', *soo > ''suo'' 'swamp', contrast Veps ''pä'', ''so'') and Veps-like traits (such as an almost complete loss of consonant gradation). Like Veps, Ludic has also partially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Locative Case
In grammar, the locative case ( ; abbreviated ) is a grammatical case which indicates a location. In languages using it, the locative case may perform a function which in English would be expressed with such prepositions as "in", "on", "at", and "by". The locative case belongs to the general local cases, together with the lative and ablative case. The locative case exists in many language groups. Indo-European languages The Proto-Indo-European language had a locative case expressing "place where", an adverbial function. The endings are reconstructed as follows: In most later Indo-European languages, the locative case merged into other cases (often genitive or dative) in form and/or function, but some daughter languages retained it as a distinct case. It is found in: * modern Balto-Slavic languages, except Bulgarian and Macedonian, although it is mostly used with prepositions in the other Slavic languages * some classical Indo-European languages, particularly Sanskrit and O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Savo Finnish
The Savo dialects (also called Savonian dialects or Savo Finnish) () are forms of the Finnish language spoken in Savo and other parts of Eastern Finland. Finnish dialects are grouped broadly into Eastern and Western varieties; Savo dialects are of the Eastern variety. Savo dialects are the most widely distributed Finnish dialect group (setting aside the higher-level east/west split mentioned above). They are spoken in Savo (both North and South Savo), but also in North Karelia, parts of Päijät-Häme, Central Finland, Kainuu, Koillismaa district of Northern Ostrobothnia, the lake section between Southern and Central Ostrobothnia as far north as Evijärvi and in the municipalities of Pudasjärvi and the Southern part of Ranua in Lapland. Also the language spoken by the Forest Finns in Värmland and Norwegian Hedmark of Central Scandinavia belonged to the old Savo dialects. The geographical area the Savo dialects cover makes up one-third the area of Finland. History The Savo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
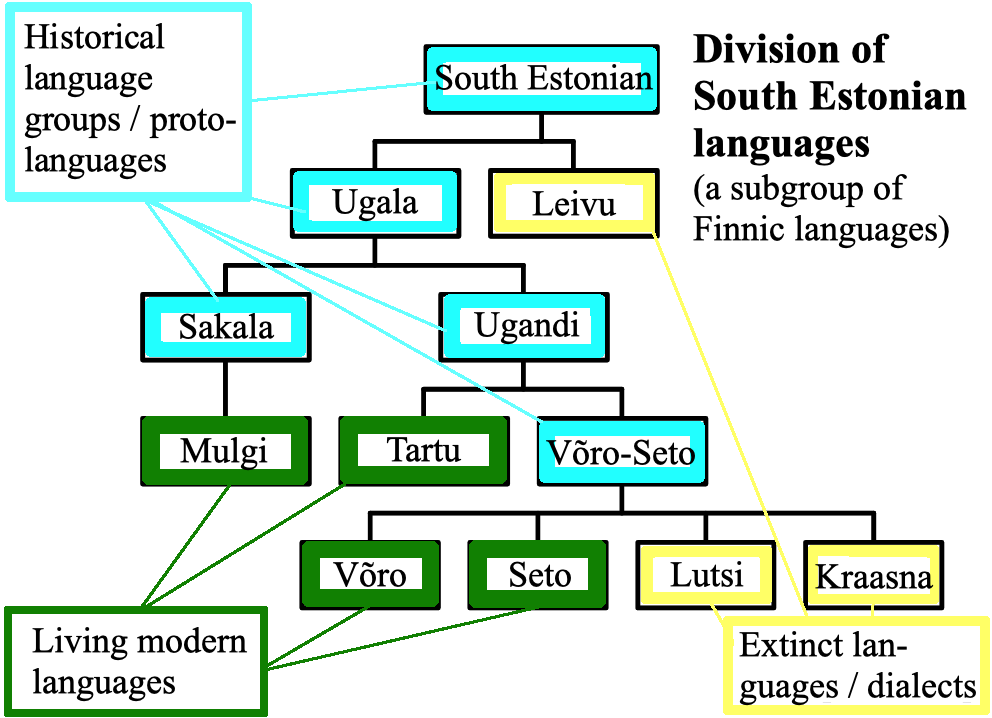
South Estonian Language
South Estonian, or Võro-Seto, is a Finnic language spoken in south-eastern Estonia, encompassing the Tartu, Mulgi, Võro and Seto dialects. Diachronically speaking, Estonian and South Estonian are in separate branches of the Finnic languages, with Estonian being more closely related to Finnish than it is to South Estonian. Note that reconstructed *č and *c stand for affricates , . Modern Standard Estonian has evolved on the basis of the dialects of Northern Estonian. However, from the 17th to the 19th centuries in Southern Estonia, literature was published in a standardized form of Southern Tartu and Northern Võro. That usage was called Tartu or literary South Estonian. The written standard was used in the schools, churches and courts of the Võro and Tartu linguistic area but not in the Seto and Mulgi areas. After Estonia gained independence in 1918, the standardized Estonian language policies were implemented further throughout the country. The government official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Standard Estonian
Estonian ( ) is a Finnic language and the official language of Estonia. It is written in the Latin script and is the first language of the majority of the country's population; it is also an official language of the European Union. Estonian is spoken natively by about 1.1 million people: 922,000 people in Estonia and 160,000 elsewhere. Classification By conventions of historical linguistics, Estonian is classified as a part of the Finnic (a.k.a. Baltic Finnic) branch of the Uralic (a.k.a. Uralian, or Finno-Ugric) language family. Other Finnic languages include Finnish and several endangered languages spoken around the Baltic Sea and in northwestern Russia. Estonian is typically subclassified as a Southern Finnic language, and it is the second-most-spoken language among all the Finnic languages. Alongside Finnish, Hungarian and Maltese, Estonian is one of the only four (out of 24) official languages of the European Union that are not Indo-European languages. In terms of lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paul Ariste
Paul Ariste (3 February 1905 – 2 February 1990) was an Estonian linguist renowned for his studies of the Finno-Ugric languages (especially Estonian and Votic), Yiddish and Baltic Romani language. He was born as Paul Berg, in Rääbise, Võtikvere Parish (now Jõgeva Parish), Kreis Dorpat, Governorate of Livonia, Russian Empire, but in 1927 Estonized his name to Ariste. He graduated from the University of Tartu and subsequently worked with it. Ariste wrote his M.A. thesis ("Eesti-rootsi laensõnad eesti keeles") on Swedish – viz. Estonian Swedish dialect – loanwords in Estonian, his doctoral thesis ("Hiiu murrete häälikud") treated the Hiiumaa dialect of Estonian language. From 1945 to 1946, Ariste was imprisoned by the Soviet authorities (for having been member of '' Veljesto'', a student association in independent Estonia) Since 1927 Paul Ariste eagerly participated in activities of Estonian Folklore Archives, where he established collections of Jewish, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Finnish Language
Finnish (endonym: or ) is a Finnic languages, Finnic language of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland, alongside Swedish language, Swedish. In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. Kven language, Kven, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norway, Norwegian counties of Troms and Finnmark by a minority of Finnish descent. Finnish is morphological typology, typologically agglutinative language, agglutinative and uses almost exclusively Suffix, suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, Numeral (linguistics), numerals and verbs are inflection, inflected depending on their role in the Sentence (linguistics), sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Karelian Language
Karelian (; ; ; ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly by the Karelians, Karelian people in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish language, Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, but nowadays it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the South Karelian dialects, Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as ("Karelian dialects") in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said they were able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland, and around 30,000 people in Finland have at least some knowledge of Karelian. The Karelian language is a group of two supradialects. The two supradialects are Karelian Proper language, Karelian Proper (which comprises Northern Karelian dialect, Northern Kareli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
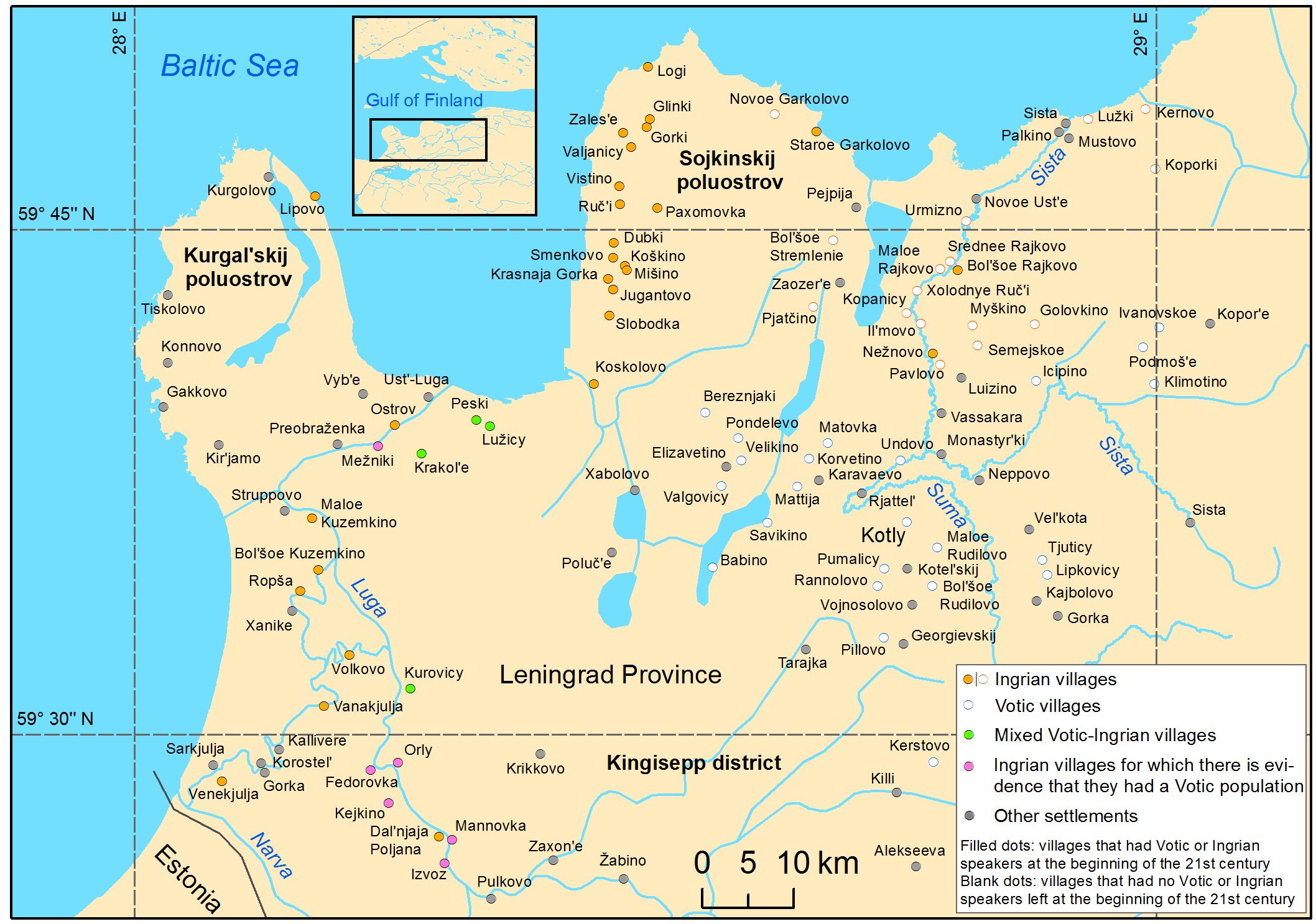
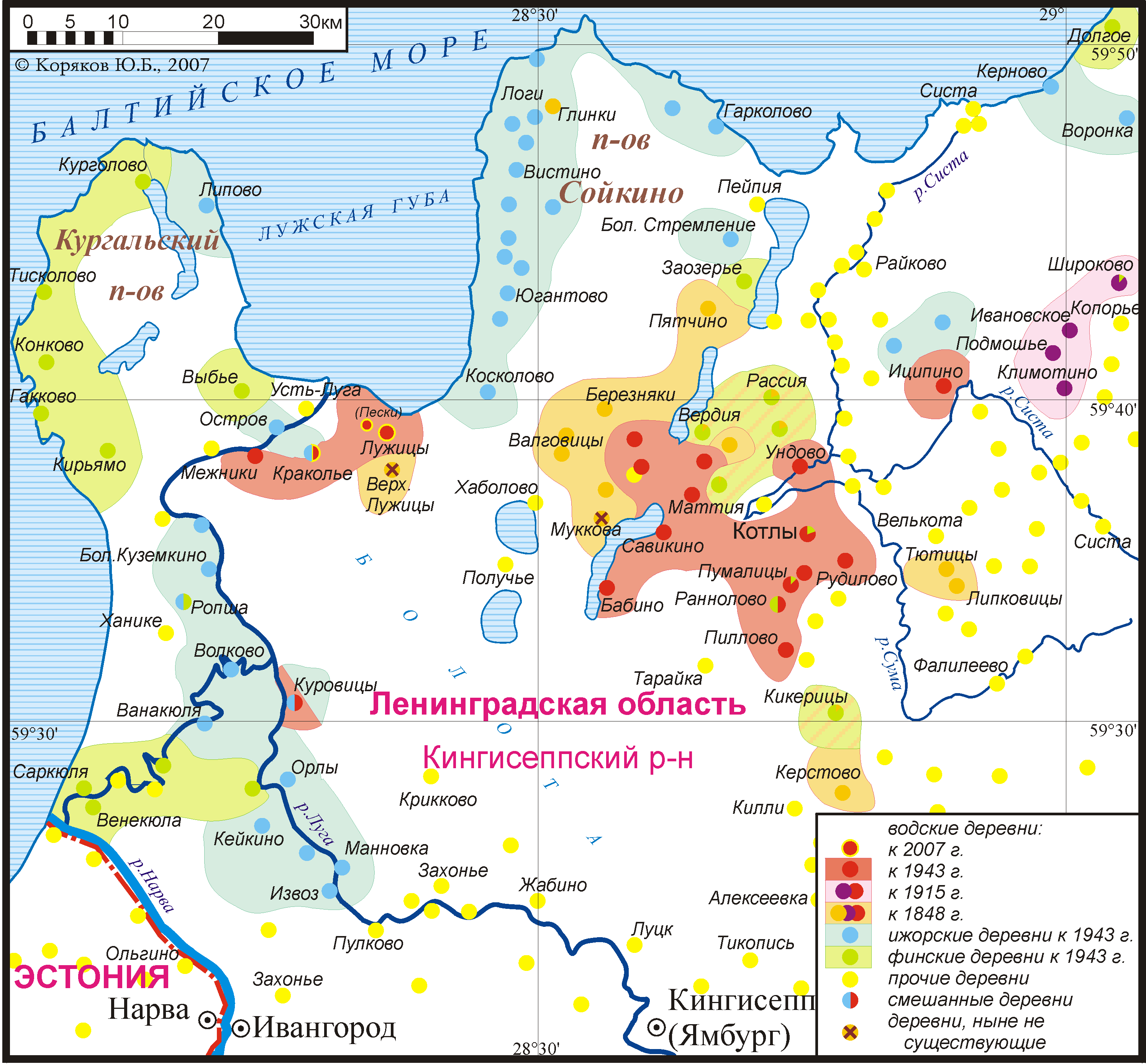
Ingrian Language
Ingrian (, ), also called Izhorian (, , ), is a Finnic language spoken by the (mainly Orthodox) Izhorians of Ingria. It has approximately 70 native speakers left, most of whom are elderly. The Ingrian language should be distinguished from the Ingrian dialect of the Finnish language, which became the majority language of Ingria in the 17th century with the influx of Lutheran Finnish immigrants; their descendants, the Ingrian Finns, are often referred to as Ingrians. The immigration of Lutheran Finns was promoted by Swedish authorities, who gained the area in 1617 from Russia, as the local population was (and remained) Orthodox. Dialects Four dialect groups of Ingrian have been attested, two of which are probably extinct by now: * Hevaha, spoken along Kovashi River and nearby coastal areas (†) * Soikkola, spoken on Soikinsky Peninsula and along Sista River * Ylä-Laukaa (Upper Luga or Oredezhi), spoken along Oredezh River and the upper Luga River (†) * Ala-Laukaa (Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Grammatical Case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and Numeral (linguistics), numerals) that corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a Nominal group (functional grammar), nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories. For instance, in English language, English, one says ''I see them'' and ''they see me'': the nominative case, nominative pronouns ''I/they'' represent the perceiver, and the accusative case, accusative pronouns ''me/them'' represent the phenomenon perceived. Here, nominative and accusative are cases, that is, categories of pronouns corresponding to the functions they have in representation. English has largely lost its inflected case system but personal pronouns still have three cases, which are simplified forms of the nominative, accusative (including functions formerly handled by the Dative case, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Votic Language
Votic or Votian (, ) , is a Finnic language spoken by the Vots of Ingria, belonging to the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. Votic is spoken only in Krakolye (now part of Ust-Luga) and Luzhitsy, two villages in Kingiseppsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. In the 2020–2021 Russian census, 21 people claimed to speak Votic natively, which is an increase from 4 in 2010. Arvo Survo also estimated that around 100 people have knowledge of the language to some degree. History Votic is one of numerous Finnic varieties known from Ingria. Votic shares some similarities with and has acquired loanwords from the adjacent Ingrian language, but also has deep-reaching similarities with Estonian to the west, which is considered its closest relative. Some linguists, including Tiit-Rein Viitso and Paul Alvre, have claimed that Votic evolved specifically from northeastern dialects of ancient Estonian. Votic regardless exhibits several features that indicate its distinction from Es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |