|
Vijñāna
''Vijñāna'' ( sa, विज्ञान) or ''viññāa'' ( pi, विञ्ञाण)As is standard in WP articles, the Pali term ''viññāa'' will be used when discussing the Pali literature, and the Sanskrit word ''vijñāna'' will be used when referring to either texts chronologically subsequent to the Pali canon or when discussing the topic broadly, in terms of ''both'' Pali and non-Pali texts. is translated as "consciousness," "life force," "mind,"See, for instance, Rhys Davids & Stede (1921-25), p. 618, entry for "Viññāa," retrieved on 2007-06-17 from the University of Chicago's "Digital Dictionaries of South Asia"University of Chicago/ref> or "discernment."See, for instanceApte (1957-59) , p. 1434, entry for "vijñānam," retrieved from "U. Chicago" a; andMonier-Williams (rev. 2008) , p. 961, The term ''vijñāna'' is mentioned in many early Upanishads, where it has been translated by terms such as understanding, knowledge, and intelligence. In the Pāli Canon's ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vijñāna
''Vijñāna'' ( sa, विज्ञान) or ''viññāa'' ( pi, विञ्ञाण)As is standard in WP articles, the Pali term ''viññāa'' will be used when discussing the Pali literature, and the Sanskrit word ''vijñāna'' will be used when referring to either texts chronologically subsequent to the Pali canon or when discussing the topic broadly, in terms of ''both'' Pali and non-Pali texts. is translated as "consciousness," "life force," "mind,"See, for instance, Rhys Davids & Stede (1921-25), p. 618, entry for "Viññāa," retrieved on 2007-06-17 from the University of Chicago's "Digital Dictionaries of South Asia"University of Chicago/ref> or "discernment."See, for instanceApte (1957-59) , p. 1434, entry for "vijñānam," retrieved from "U. Chicago" a; andMonier-Williams (rev. 2008) , p. 961, The term ''vijñāna'' is mentioned in many early Upanishads, where it has been translated by terms such as understanding, knowledge, and intelligence. In the Pāli Canon's ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
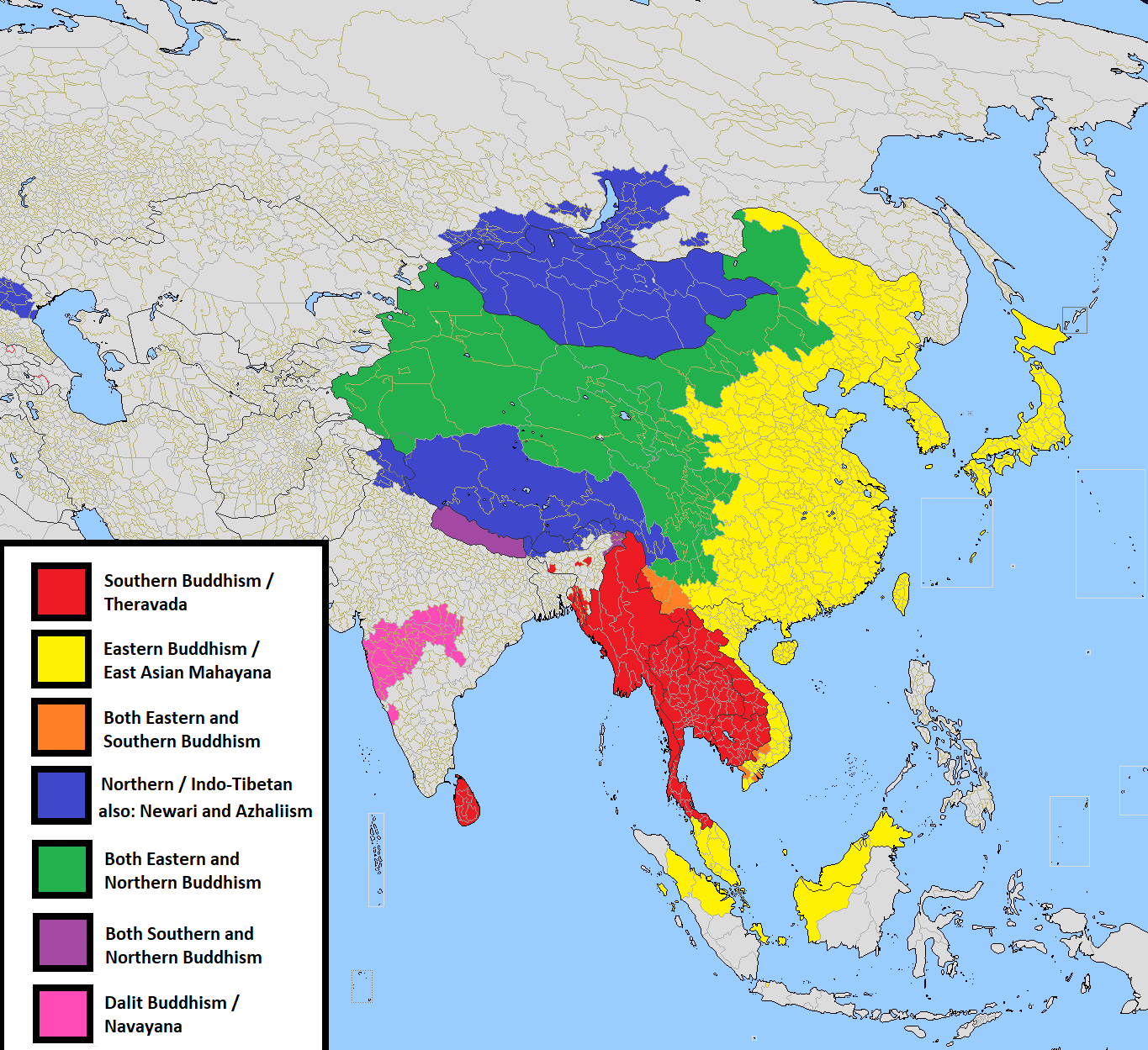
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manas (early Buddhism)
''Manas'' (Pali: मनस्) is one of three overlapping terms used in the nikayas to refer to the mind, the others being ''citta'' and '' viññāṇa''. Comparison with ''citta'' and ''viññāṇa'' ''Manas'', ''citta'', and ''viññāṇa'' are each sometimes used in the generic and non-technical sense of "mind" in general, and the three are sometimes used in sequence to refer to one's mental processes as a whole. Their primary uses are, however, distinct. In the distinction of Abhidhamma Pitaka of Theravada Buddhism, mana or mano is sort of the notion of mind as a whole, whereas a citta is each of instant steps or processes of mind, and viññāṇa is one of the several forms of citta, also being a step of a vithi or mental procedure, which is an orderly sequence of citta. Relationship with thinking and volition Manas often indicates the general thinking faculty. Thinking is closely associated with volitions, because mental activity is one of the ways that volit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skandha
(Sanskrit) or ( Pāḷi) means "heaps, aggregates, collections, groupings". In Buddhism, it refers to the five aggregates of clinging (), the five material and mental factors that take part in the rise of craving and clinging. They are also explained as the five factors that constitute and explain a sentient being’s person and personality, but this is a later interpretation in response to sarvastivadin essentialism. The five aggregates or heaps of clinging are: # form (or material image, impression) () # sensations (or feelings, received from form) () # perceptions () # mental activity or formations () # consciousness (). In the Theravada tradition, suffering arises when one identifies with or clings to the aggregates. This suffering is extinguished by relinquishing attachments to aggregates. The Mahayana tradition asserts that the nature of all aggregates is intrinsically empty of independent existence. Etymology () is a Sanskrit word that means "multitude, quant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
āyatana
''Āyatana'' (Pāli; Sanskrit: आयतन) is a Buddhist term that has been translated as "sense base", "sense-media" or "sense sphere". In Buddhism, there are six ''internal'' sense bases (Pali: ''ajjhattikāni āyatanāni''; also known as, "organs", "gates", "doors", "powers" or "roots"Pine 2004, p. 102) and six ''external'' sense bases (''bāhirāni āyatanāni'' or "sense objects"; also known as ''vishaya'' or "domains"Pine 2004, p. 103). There are six internal-external (organ-object) ' (Pāli; Skt. '), pairs of sense bases: :* eye and visible objects :* ear and sound :* nose and odor :* tongue and taste :* body and touch :* mindThe Pāli word translated here as "mind" is ''mano''. Other common translations include "intellect(e.g., Thanissaro, 2001a)and "consciousness In the Suttapitaka, ''mano'' does not necessarily refer to all mental processing. Other oft-mentioned complementary mental processes include "consciousness" ('' viññāṇa'') and "mental states" (''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schools Of Buddhism
The schools of Buddhism are the various institutional and doctrinal divisions of Buddhism that have existed from ancient times up to the present. The classification and nature of various doctrinal, philosophical or cultural facets of the schools of Buddhism is vague and has been interpreted in many different ways, often due to the sheer number (perhaps thousands) of different sects, subsects, movements, etc. that have made up or currently make up the whole of Buddhist traditions. The sectarian and conceptual divisions of Buddhist thought are part of the modern framework of Buddhist studies, as well as comparative religion in Asia. From a largely English-language standpoint, and to some extent in most of Western academia, Buddhism is separated into two groups: Theravāda, literally "the Teaching of the Elders" or "the Ancient Teaching," and Mahāyāna, literally the "Great Vehicle." The most common classification among scholars is threefold: Theravāda, Mahāyāna and Vajrayā ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Sanskrit Words And Phrases
{{CatAutoTOC words A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no conse ... Words and phrases in Indo-Aryan languages Archaic words and phrases Buddhist terminology Indian words and phrases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atthakatha
Aṭṭhakathā (Pali for explanation, commentary) refers to Pali-language Theravadin Buddhist commentaries to the canonical Theravadin Tipitaka. These commentaries give the traditional interpretations of the scriptures. The major commentaries were based on earlier ones, now lost, in Prakrit and Sinhala, which were written down at the same time as the Canon, in the last century BCE. Some material in the commentaries is found in canonical texts of other schools of Buddhism, suggesting an early common source. According to K.R. Norman: There is no direct evidence that any commentarial material was in fact recited at the first council, but there is clear evidence that some parts of the commentaries are very old, perhaps even going back to the time of the Buddha, because they afford parallels with texts which are regarded as canonical by other sects, and must therefore pre-date the schisms between the sects. As has already been noted, some canonical texts include commentarial pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overlapping Pali Terms For Mind
Overlap may refer to: * In set theory, an overlap of elements shared between sets is called an intersection, as in a Venn diagram. * In music theory, overlap is a synonym for reinterpretation of a chord at the boundary of two musical phrases * Overlap (railway signalling), the length of track beyond a stop signal that is proved to be clear of obstructions as a safety margin * Overlap (road), a place where multiple road numbers overlap * Overlap (term rewriting), in mathematics, computer science, and logic, a property of the reduction rules in term rewriting systems * Overlap add, an efficient convolution method using FFT * Overlap coefficient, a similarity measure between sets * Orbital overlap, important concept in quantum mechanics describing a type of orbital interaction that affects bond strength Overlapping can refer to: * "Reaching over", term in Schenkerian theory, see Schenkerian analysis#Lines between voices, reaching over See also * Overlay (other) * Overload ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pali Canon
The Pāli Canon is the standard collection of scriptures in the Theravada Buddhist tradition, as preserved in the Pāli language. It is the most complete extant early Buddhist canon. It derives mainly from the Tamrashatiya school. During the First Buddhist Council, three months after the parinibbana of Gautama Buddha in Rajgir, Ananda recited the Sutta Pitaka, and Upali recited the Vinaya Pitaka. The Arhats present accepted the recitations and henceforth the teachings were preserved orally by the Sangha. The Tipitaka that was transmitted to Sri Lanka during the reign of King Asoka were initially preserved orally and were later written down on palm leaves during the Fourth Buddhist Council in 29 BCE, approximately 454 years after the death of Gautama Buddha. The claim that the texts were "spoken by the Buddha", is meant in this non-literal sense. The existence of the bhanaka tradition existing until later periods, along with other sources, shows that oral tradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |