|
Syntagmatic Analysis
In semiotics, syntagmatic analysis is analysis of syntax or surface structure (syntagmatic structure) as opposed to paradigms ( paradigmatic analysis). This is often achieved using commutation tests. "Syntagmatic" means that one element selects the other element either to precede it or to follow it. For example, the definitive article "the" selects a noun and not a verb. Of particular use in semiotic study, a syntagm is a chain which leads, through syntagmatic analysis, to an understanding of how a sequence of events forms a narrative. Alternatively, syntagmatic analysis can describe the spatial relationship of a visual text such as posters, photographs or a particular setting of a filmed scene. Roland Barthes was able to use metaphor in the form of various garments in order to display how the syntagm/paradigm relationship worked together to at once create and change meaning. Expanding on this form of explanation by Barthes, both David Lodge and Susan Spiggle have further devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiotics
Semiotics (also called semiotic studies) is the systematic study of sign processes ( semiosis) and meaning making. Semiosis is any activity, conduct, or process that involves signs, where a sign is defined as anything that communicates something, usually called a meaning, to the sign's interpreter. The meaning can be intentional such as a word uttered with a specific meaning, or unintentional, such as a symptom being a sign of a particular medical condition. Signs can also communicate feelings (which are usually not considered meanings) and may communicate internally (through thought itself) or through any of the senses: visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, or gustatory (taste). Contemporary semiotics is a branch of science that studies meaning-making and various types of knowledge. The semiotic tradition explores the study of signs and symbols as a significant part of communications. Unlike linguistics, semiotics also studies non-linguistic sign systems. Semiotics includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Analysis (linguistics)
In linguistics, semantic analysis is the process of relating syntactic structures, from the levels of phrases, clauses, sentences and paragraphs to the level of the writing as a whole, to their language-independent meanings. It also involves removing features specific to particular linguistic and cultural contexts, to the extent that such a project is possible. The elements of idiom and figurative speech, being cultural, are often also converted into relatively invariant meanings in semantic analysis. Semantics, although related to pragmatics, is distinct in that the former deals with word or sentence choice in any given context, while pragmatics considers the unique or particular meaning derived from context or tone. To reiterate in different terms, semantics is about universally coded meaning, and pragmatics, the meaning encoded in words that is then interpreted by an audience. Semantic analysis can begin with the relationship between individual words. This requires an und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradigm
In science and philosophy, a paradigm () is a distinct set of concepts or thought patterns, including theories, research methods, postulates, and standards for what constitute legitimate contributions to a field. Etymology ''Paradigm'' comes from Greek παράδειγμα (''paradeigma''), "pattern, example, sample" from the verb παραδείκνυμι (''paradeiknumi''), "exhibit, represent, expose" and that from παρά (''para''), "beside, beyond" and δείκνυμι (''deiknumi''), "to show, to point out". In classical (Greek-based) rhetoric, a paradeigma aims to provide an audience with an illustration of a similar occurrence. This illustration is not meant to take the audience to a conclusion, however it is used to help guide them get there. One way of how a ''paradeigma'' is meant to guide an audience would be exemplified by the role of a personal accountant. It is not the job of a personal accountant to tell a client exactly what (and what not) to spend money o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradigmatic Analysis
Paradigmatic analysis is the analysis of paradigms embedded in the text rather than of the surface structure (syntax) of the text which is termed syntagmatic analysis. Paradigmatic analysis often uses commutation tests, i.e. analysis by substituting words of the same type or class to calibrate shifts in connotation. Definition of terms In Semiotic literary criticism, a syntagm (or syntagma) is a building block of a text into which meaning is encoded by the writer and decoded by the reader, recalling past experience and placing the message in its appropriate cultural context. Individual syntagms can be arranged together to form more complex syntagms: groups of sounds (and the letters to represent them) form words, groups of words form sentences, sentences form narratives, and so on. A list of syntagms of the same type is called a ''paradigm''. So, in English, the alphabet is the paradigm from which the syntagms of words are formed. The set of words collected together in a le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commutation Test (semiotics)
In semiotics, the commutation test is used to analyze a signifying system. The test identifies signifiers as well as their signifieds, value and significance. The commutation test This test is a metalingual subjective system for analysing textual or other material. It has evolved from a limited method for investigating the structure of individual signs (per Roman Jakobson). Its primary uses are to: *identify distinctive signifiers, *define their significance, and *divide material into paradigmatic classes and identify the codes to which the signifiers belong (Roland Barthes). The initial assumption is that the communication to be analysed represents both a cognitive use of the sign system and a statement that refers to the values of the addresser. The purpose of the test is therefore to illuminate the addresser's intention in using the code in this particular way. It works through a process of substitution, assessing the extent to which a change in the signifier leads to a change i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Nelson Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Grand Canyon, utopia'', etc. * Actions: ''swimming, exercises, diffusions, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Qualities: ''colors, lengths, deafness, weights, roundness, symmetry, warp speed,'' etc. * Mental or physical states of existence: ''jealousy, sleep, heat, joy, stomachache, confusion, mind meld,'' etc. Lexical categories ( parts of speech) are defined in terms of the ways in which their members combine with other kinds of expressions. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntagma (linguistics)
In linguistics, a syntagma is an elementary constituent segment within a text. Such a segment can be a phoneme, a word, a grammatical phrase, a sentence, or an event within a larger narrative structure, depending on the level of analysis. Syntagmatic analysis involves the study of relationships (rules of combination) among syntagmas. At the lexical level, syntagmatic structure in a language is the combination of words according to the rules of syntax for that language. For example, English uses determiner + adjective + noun, e.g. ''the big house''. Another language might use determiner + noun + adjective (Spanish ) and therefore have a different syntagmatic structure. At a higher level, narrative structures feature a realistic temporal flow guided by tension and relaxation; thus, for example, events or rhetorical figures may be treated as syntagmas of epic structures. Syntagmatic structure is often contrasted with paradigmatic structure. In semiotics, " syntagmatic analysis" is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roland Barthes
Roland Gérard Barthes (; ; 12 November 1915 – 26 March 1980) was a French literary theorist, essayist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician. His work engaged in the analysis of a variety of sign systems, mainly derived from Western popular culture. His ideas explored a diverse range of fields and influenced the development of many schools of theory, including structuralism, anthropology, literary theory, and post-structuralism. Barthes is perhaps best known for his 1957 essay collection ''Mythologies'', which contained reflections on popular culture, and 1967 essay "The Death of the Author," which critiqued traditional approaches in literary criticism. During his academic career he was primarily associated with the École des Hautes Études en Sciences Sociales (EHESS) and the Collège de France. Biography Early life Roland Barthes was born on 12 November 1915 in the town of Cherbourg in Normandy. His father, naval officer Louis Barthes, was killed in a battle dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Lodge (author)
David John Lodge CBE (born 28 January 1935) is an English author and critic. A literature professor at the University of Birmingham until 1987, some of his novels satirise academic life, notably the "Campus Trilogy" – '' Changing Places: A Tale of Two Campuses'' (1975), '' Small World: An Academic Romance'' (1984) and '' Nice Work'' (1988). The second two were shortlisted for the Booker Prize. Another theme is Roman Catholicism, beginning from his first published novel '' The Picturegoers'' (1960). Lodge has also written television screenplays and three stage plays. After retiring, he continued to publish literary criticism. His edition of ''Twentieth Century Literary Criticism'' (1972) includes essays on 20th-century writers such as T. S. Eliot. Biography David Lodge was born in Brockley, south-east London. His family home until 1959 was 81 Millmark Grove, a residential street of 1930s terraced houses between Brockley Cross and Barriedale. His father, a violinist, played in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
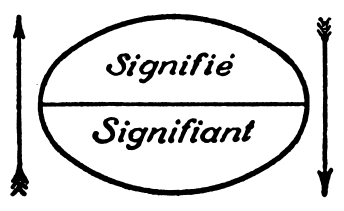
Signifier And Signified
In semiotics, signified and signifier (French: ''signifié'' and ''signifiant'') stand for the two main components of a sign, where ''signified'' pertains to the "plane of content", while ''signifier'' is the "plane of expression". The idea was first proposed in the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, one of the two founders of semiotics. Concept of signs The concept of signs has been around for a long time, having been studied by many classic philosophers such as Plato, Aristotle, Augustine, William of Ockham, and Francis Bacon, among others. The term ''semiotics'' derives from the Greek root ''seme'', as in ''semeiotikos'' (an 'interpreter of signs'). Berger, Arthur Asa. 2012. ''Media Analysis Techniques''. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications. It was not until the early part of the 20th century, however, that Saussure and American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce brought the term into more common use. While both Saussure and Peirce contributed greatly to the concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand De Saussure
Ferdinand de Saussure (; ; 26 November 1857 – 22 February 1913) was a Swiss linguist, semiotician and philosopher. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiotics in the 20th century. He is widely considered one of the founders of 20th-century linguistics and one of two major founders (together with Charles Sanders Peirce) of semiotics, or ''semiology'', as Saussure called it. One of his translators, Roy Harris, summarized Saussure's contribution to linguistics and the study of "the whole range of human sciences. It is particularly marked in linguistics, philosophy, psychoanalysis, psychology, sociology and anthropology." Although they have undergone extension and critique over time, the dimensions of organization introduced by Saussure continue to inform contemporary approaches to the phenomenon of language. As Leonard Bloomfield stated after reviewing the ''Cours'': "he has given us the theoretical basis for a science of human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |