|
Sweden Proper
Sweden proper (, literally ''Actual Sweden'') is a term used to distinguish those territories that were fully integrated into the Kingdom of Sweden, as opposed to the dominions and possessions of, or states in union with, Sweden. Only the estates of the realm of Sweden proper were represented in the Riksdag of the Estates. Specifically this means that, from approximately 1155–1156 until the Treaty of Fredrikshamn in 1809, Sweden proper included the bulk of present-day Finland as a fully integrated part of the realm. After 1809, however, the term has been used to distinguish the western part from the former ''eastern half'' of the realm, i.e. Sweden from Finland. Skåne, Halland, Blekinge, and Bohuslän, formerly parts of Denmark and Norway, came under the Swedish Crown by the Treaty of Roskilde in 1658, but it was not until 1719 that they were fully integrated and became part of Sweden proper. Sweden proper, a geographical reference that has changed over time, contrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire or the Great Power era () was the period in Swedish history spanning much of the 17th and early 18th centuries during which Sweden became a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region. During this period it also held territories on the North Sea and some Swedish overseas colonies, overseas colonies, including New Sweden. The beginning of the period is usually taken as the reign of Gustavus Adolphus, who ascended the throne in 1611, and its end as the loss of territories in 1721 following the Great Northern War. After the death of Gustavus Adolphus in 1632, the empire was controlled for lengthy periods by part of the high Swedish nobility, nobility, such as the Oxenstierna family, acting as regents for minor monarchs. The interests of the high nobility contrasted with the uniformity policy (i.e., upholding the traditional equality in status of the Swedish estates favoured by the kings and peasantry). In territories ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland in the north Atlantic Ocean.* * * Metropolitan Denmark, also called "continental Denmark" or "Denmark proper", consists of the northern Jutland peninsula and an archipelago of 406 islands. It is the southernmost of the Scandinavian countries, lying southwest of Sweden, south of Norway, and north of Germany, with which it shares a short border. Denmark proper is situated between the North Sea to the west and the Baltic Sea to the east.The island of Bornholm is offset to the east of the rest of the country, in the Baltic Sea. The Kingdom of Denmark, including the Faroe Islands and Greenland, has roughly List of islands of Denmark, 1,400 islands greater than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Historical Regions
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geography Of Sweden
Sweden is a country in Northern Europe on the Scandinavian Peninsula. It borders Norway to the west (which is one of Sweden’s non- EU neighbours); Finland to the northeast; and the Baltic Sea and Gulf of Bothnia to the south and east. At , Sweden is the largest country in Northern Europe, the fifth largest in Europe, and the 55th largest country in the world. Sweden has a long coastline on its east, and the Scandinavian mountain chain (Skanderna) on its western border, separating it from Norway. It has maritime borders with Denmark, Germany, Poland, Russia (another non- EU neighbour) Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia, and it is also linked to Denmark (southwest) by the Öresund bridge. It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of . Terrain Much of Sweden is heavily forested, with 69% of the country being forest and woodland, while farmland constitutes only 8% of land use. Sweden consists of 39,960 km2 of water area, constituting around 95,700 lakes. The lakes are sometimes use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Political Geography
Political geography is concerned with the study of both the spatially uneven outcomes of political processes and the ways in which political processes are themselves affected by spatial structures. Conventionally, for the purposes of analysis, political geography adopts a three-scale structure with the study of the state at the centre, the study of international relations (or geopolitics) above it, and the study of localities below it. The primary concerns of the subdiscipline can be summarized as the inter-relationships between people, state, and territory. History The origins of political geography lie in the origins of human geography itself, and the early practitioners were concerned mainly with the military and political consequences of the relationships between physical geography, state territories, and state power. In particular there was a close association with both regional geography, with its focus on the unique characteristics of regions, and environmental det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Political History Of Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country by both area and population, and is the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. Its capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.6 million, and a low population density of ; 88% of Swedes reside in urban areas. They are mostly in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden's urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Sweden has a diverse Climate of Sweden, climate owing to the length of the country, which ranges from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times around 12,000 BC. The inhabitants emerged as the Geats () and Swedes (tribe), Swedes (), who formed part of the sea-faring peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Provinces Of Sweden
The 25 provinces of Sweden () are historical, geographical and cultural regions. They have no administrative function, but retain their own cultural identities, dialects and folklore. Several were administrative subdivisions until 1634, when they were replaced by the counties of Sweden (). Some were conquered later on from Denmark–Norway. Others, like the provinces of Finland, have been lost. In some cases, the county and province borders correspond almost exactly, as with Blekinge and Blekinge County. The island of Gotland is both a province, a county and a municipality (''kommun''). The only other province to share a name with a modern municipality is Härjedalen, though the borders are not quite the same. Administrative borders are subject to change – for example, several of today's counties were created in the 1990s – while the provincial borders have remained stable for centuries. All the provinces are also ceremonial duchies, but as such have no administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
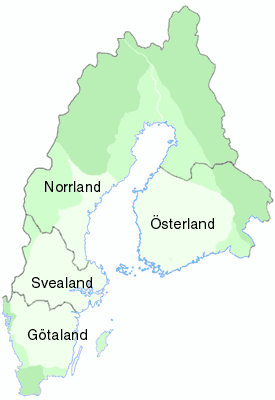
Svealand
Svealand (), or Swealand, is the historical core region of Sweden. It is located in south-central Sweden and is one of the three historical lands of Sweden, bounded to the north by Norrland and to the south by Götaland. Deep forests, Tiveden, Tylöskog, and Kolmården, separated Svealand from Götaland. Historically, its inhabitants were called , from which is derived the English 'Swedes'. Svealand consists of the capital region Mälardalen in the east, Roslagen in the north-east, the former mining district Bergslagen in the center, and Dalarna and Värmland in the west. It includes an extensive archipelago of thousands of small islands in Södermanland and Uppland and has lakeshores on the four largest lakes in the country. In the interior, there are several ski resorts in the southern parts of the Scandinavian Mountains. Two large rivers run through Svealand. Klarälven originates in Norway and enters lake Vänern through Värmland, whereas Dalälven runs from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Finland Proper (historical Province)
Finland Proper or Southwest Finland (; ) is a historical province in southwestern Finland, administered by its historic capital of Turku (). Before the Treaty of Fredrikshamn in 1809, it was part of Sweden. It borders Satakunta, Tavastia (Häme), and Uusimaa. It is also bounded by the Baltic Sea facing Åland. The modern region of Southwest Finland largely corresponds to the historical province. However, the modern region includes Loimaa, which was historically part of Satakunta, and Somero, which historically belonged to Tavastia. Southwest Finnish dialects are spoken in Southwest Finland. Administration Southwest Finland was within the boundaries of the administrative province of Turku and Pori from 1917 to 1997 and that of Western Finland from 1997 to 2009, when the provinces of Finland were abolished. History The province, which had been a part of Sweden from the 13th century, separated when Finland was ceded to the Russian Empire in 1809. The provinces have no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Treaty Of Roskilde
The Treaty of Roskilde was negotiated at Høje Taastrup Church and was concluded on 26 February ( OS) or 8 March 1658 ( NS) during the Second Northern War between Frederick III of Denmark–Norway and Karl X Gustav of Sweden in the Danish city of Roskilde. After a devastating defeat, Denmark–Norway was forced to give up a third of its territory to save the rest, the ceded lands comprising Blekinge, Bornholm, Bohuslän, Scania and Trøndelag, as well as Halland. After the treaty entered into force, Swedish forces continued to campaign in the remainder of Denmark–Norway, but had to withdraw from the Danish isles and Trøndelag in the face of a Dano–Norwegian and Dutch alliance. The Treaty of Copenhagen restored Bornholm to Denmark and Trøndelag to Norway in 1660, while the other provinces transferred in Roskilde remained Swedish. Background As the Northern Wars progressed, Charles X Gustav of Sweden crossed the frozen straits from Jutland and occupied the Danis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monarchy Of Sweden
The monarchy of Sweden is centred on the monarchical head of state of Sweden,See the #IOG, Instrument of Government, Chapter 1, Article 5. by law a constitutional monarchy, constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system.Parliamentary system: see the #IOG, Instrument of Government, Chapter 1, Article 1. There have been kings in what now is the Sweden, Kingdom of Sweden for more than a millennium. Originally an elective monarchy, it became a hereditary monarchy in the 16th century during the reign of Gustav Vasa, though virtually all monarchs before that belonged to a limited and small number of political families which are considered to be the royal dynasties of Sweden. The official continuous count usually begins with the kings who ruled both Svealand and Götaland as one kingdom. Sweden's monarchy is amongst the oldest in the world, with a regnal list stretching back to the tenth century, starting with Eric the Victorious; the Swedish monarchy has, for the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a Dependencies of Norway, dependency, and not a part of the Kingdom; Norway also Territorial claims in Antarctica, claims the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. Norway has a population of 5.6 million. Its capital and largest city is Oslo. The country has a total area of . The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden, and is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast. Norway has an extensive coastline facing the Skagerrak strait, the North Atlantic Ocean, and the Barents Sea. The unified kingdom of Norway was established in 872 as a merger of Petty kingdoms of Norway, petty kingdoms and has existed continuously for years. From 1537 to 1814, Norway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |