|
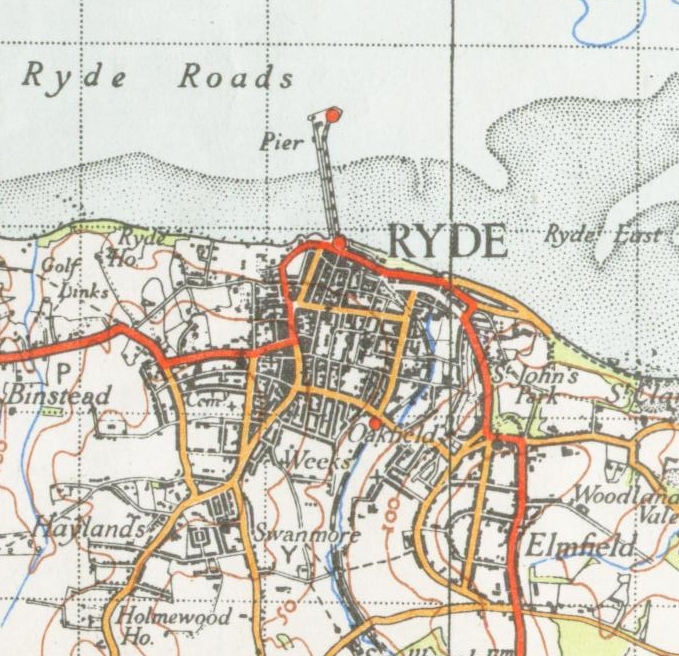
Ryde Pier
Ryde Pier is an early 19th century pier serving the town of Ryde, on the Isle of Wight, off the south coast of England. It is the world's oldest seaside pleasure pier. Ryde Pier Head railway station is at the sea end of the pier, and Ryde Esplanade railway station at the land end, both served by Island Line trains. Before the pier Before the pier was built, passengers had the uncomfortable experience of coming ashore on the back of a porter and then, depending on the state of the tide, having to walk as far as half a mile across wet sand before reaching the town. The need for a pier was obvious, especially if the town was to attract the wealthy and fashionable visitors who were beginning to patronise other seaside resorts. The original pier The pier was designed by John Kent of Southampton. It was authorised by the ( 52 Geo. 3. c. cxcvi), and its foundation stone laid on 29 June 1813. The pier opened on 26 July 1814, with, as it still has, a timber-planked promenade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ryde Pier Head Railway Station
Ryde Pier Head railway station is one of three stations in the town of Ryde on the Isle of Wight. Situated at the end of the town's pier, it is adjacent to the terminal for the Wightlink fast catamaran service connecting the island with Portsmouth on the English mainland. Passengers can use this to connect with the rest of the National Rail network at Portsmouth Harbour station, which is adjacent to the Portsmouth terminal. Through rail tickets for travel via Pier Head station are available to and from other stations on the Isle of Wight. These include travel on the catamaran service to or from Portsmouth as appropriate. Trains run down the eastern coast of the Isle of Wight to Shanklin (the Island Line), the last remnant of a network of railways on the island. Because of the restricted loading gauge, particularly through the tunnel under Ryde, services are operated by former London Underground stock. The ticket office at the station is run by Wightlink and not Island Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ryde
Ryde is an English seaside town and civil parish on the north-east coast of the Isle of Wight. The built-up area had a population of 24,096 according to the 2021 Census. Its growth as a seaside resort came after the villages of Upper Ryde and Lower Ryde were merged in the 19th century, as can still be seen in the town's central and seafront architecture. The resort's expansive sands are revealed at low tide. Their width means the regular ferry service to the mainland requires a long listed pier – the fourth longest in the United Kingdom, and the oldest surviving. History In 1782 numerous bodies of men, women and children from HMS ''Royal George'', which sank suddenly at Spithead, were washed ashore at Ryde. Many were buried on land that is now occupied by the Esplanade. A memorial to them was erected in June 2004. There are a series of Regency and Victorian buildings in the town with important buildings such as All Saints' Church, designed by the eminent George Gilbert Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Esplanade
An esplanade or promenade is a long, open, level area, usually next to a river or large body of water, where people may walk. The historical definition of ''esplanade'' was a large, open, level area outside fortress or city walls to provide clear fields of fire for the fortress's guns. In modern usage, the space allows the area to be paved as a pedestrian walk; esplanades are often on sea fronts and allow walking whatever the state of the tide, without having to walk on the beach. History In the 19th century, the razing of city fortifications and the relocation of port facilities made it possible in many cities to create promenade paths on the former fortresses and ramparts. The parts of the former fortifications, such as hills, viewpoints, ditches, waterways and lakes have now been included in these promenades, making them popular excursion destinations as well as the location of cultural institutions. The rapid development of artificial street lighting in the 19th century als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Southern Railway Act 1924
The Southern Railway (SR), sometimes shortened to 'Southern', was a British railway company established in the Railways Act 1921, 1923 Grouping. It linked London with the English Channel, Channel ports, South West England, Seaside resort#British seaside resorts, South coast resorts and Kent. The railway was formed by the amalgamation of several smaller railway companies, the largest of which were the London and South Western Railway (LSWR), the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) and the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR).Bonavia (1987) pp. 26–28 The construction of what was to become the Southern Railway began in 1838 with the opening of the London and Southampton Railway, which was renamed the London & South Western Railway. The railway was noted for its astute use of public relations and a coherent management structure headed by Herbert Ashcombe Walker, Sir Herbert Walker. At , the Southern Railway was the smallest of the Big Four (British railway comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eugénie De Montijo
Eugénie de Montijo (; born María Eugenia Ignacia Agustina de Palafox y Kirkpatrick; 5 May 1826 – 11 July 1920) was Second French Empire, Empress of the French from her marriage to Napoleon III on 30 January 1853 until he was overthrown on 4 September 1870. From 28 July to 4 September 1870, she was the ''de facto'' head of state of France. Born to prominent Spanish nobility, Eugénie was educated in France, Spain, and England. As Empress, she used her influence to champion "authoritarian and clerical policies"; her involvement in politics earned her much criticism from contemporaries.McQueen 2011, p. 3. Napoléon and Eugénie had one child together, Louis-Napoléon, Prince Imperial (1856–1879). After the fall of the Empire, the three lived in exile in England; Eugénie outlived both her husband and son and spent the remainder of her life working to commemorate their memories and the memory of the Second French Empire. Youth María Eugenia Ignacia Agustina was born on 5 Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Newport Railway Station (IoWCR Isle Of Wight)
Newport railway station was established in 1862 with the opening of the Cowes and Newport Railway. It was enlarged in December 1875 when the lines to Ryde and Ventnor were opened. The station was also used by the Freshwater, Yarmouth and Newport Railway from its opening in 1888 until 1913, when that company opened its own station nearby. Upon the formation of the Southern Railway in 1923 reverted to using this station. The station was closed by British Railways in 1966. It was then used as a base for the Wight Locomotive Society until January 1971, when it was demolished. Isle of Wight Central Railway station Newport railway station was a pivotal station within the unique railway network on the Isle of Wight, that began in 1862 when the Cowes and Newport Railway opened for business. Situated in the centre of the town, the station was enlarged in 1875 with the opening of the Ryde and Newport Railway in December 1875, which also connected the station to Ventnor. Traffic was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cowes Railway Station
Cowes railway station was a railway station in Cowes on the Isle of Wight, off the south coast of England. It took pride in being the "prettiest station on the Garden Isle". History Opened in 1862, the very first on the island, as part of the inaugural "Cowes and Newport" railway, it expanded to three platforms as the railway branched out towards Ryde in the years before the motor bus began to diminish trade. In its time prosperous enough to have a WH Smith bookstall, its latter years were considerably leaner as more and more people took their holidays abroad. The station has long since been demolished and today the area is a supermarket and municipal car park. The footbridge was salvaged and moved to Medstead and Four Marks railway station on the Watercress Line heritage railway. In its later years Cowes station was notable for an unusual operating procedure. The engine would propel its empty carriages backwards up the 1-in-95 gradient towards Mill Hill and then run forw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ventnor Railway Station
Ventnor railway station was the terminus of the Isle of Wight Railway line from Ryde. History The station occupied a ledge above sea level which had been quarried into the hill side. The station was at the end of a tunnel through St Boniface Down. A turntable was used to allow steam engines to runaround their trains. In later years it was replaced by a three way switch. The tracks merged just before the tunnel and the locomotives had to enter the tunnel during run round manoeuvres. The station had a platform connected to the station buildings and a narrow island platform. There was only one track between the side platform and the island platform. When this track was occupied, an incoming train arrived at the outer face of the island platform and passengers had to pass through the train on the inner track. When this train then departed, a temporary bridge that was a former ship's gangway, as used on the Portsmouth to Ryde ferries, was manually pushed across the intervening ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isle Of Wight Central Railway
The Isle of Wight Central Railway (IoWCR) was a railway company on the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom. It was formed in 1887 by the merging of three earlier railways, the Cowes and Newport Railway (opened 1862), the Ryde and Newport Railway (opened 1875) and the Isle of Wight (Newport Junction) Railway (opened in stages 1875 and 1879). Its network ran from near Ryde to Cowes and from Sandown to Newport. It also worked the Freshwater, Yarmouth and Newport Railway until 1913, and in that year it purchased the Newport, Godshill and St. Lawrence Railway. The was always short of money, and operated with antiquated equipment. The heavily seasonal traffic and, later, competition from buses and cars limited profitable income. In 1923, it was absorbed by the new Southern Railway (UK), Southern Railway, and the new owner put financial resources into worthwhile modernisation, but by the 1960s the financial situation became difficult and the whole of the former network was closed in 1966 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isle Of Wight Railway
The Isle of Wight Railway was a railway company on the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom; it operated of railway line between Ryde and Ventnor. It opened the first section of line from Ryde to Sandown in 1864, later extending to Ventnor in 1866. The Ryde station was at St Johns Road, some distance from the pier where the majority of travellers arrived. A tramway operated on the pier itself, and a street-running tramway later operated from the Pier to St Johns Road. It was not until 1880 that two mainland railways companies jointly extended the railway line to the Pier Head, and IoWR trains ran through, improving the journey arrangements. An independent company built a branch line from Brading to Bembridge, and the IoWR operated passenger trains on the line from 1882, and later absorbed the owning company. The IoWR was itself absorbed into the Southern Railway in the "grouping" of 1923. The Bembridge branch closed in 1953, and in 1966 the Ryde Pier Head to Ventnor line was tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
London And South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter and Plymouth, and to Padstow, Ilfracombe and Bude. It developed a network of routes in Hampshire, Surrey and Berkshire, including Portsmouth and Reading. The LSWR became famous for its express passenger trains to Bournemouth and Weymouth, and to Devon and Cornwall. Nearer London it developed a dense suburban network and was pioneering in the introduction of a widespread suburban electrified passenger network. It was the prime mover of the development of Southampton Docks, which became an important ocean terminal as well as a harbour for cross channel services and for Isle of Wight ferries. Although the LSWR's area of influence was not the home of large-scale heavy industry, the transport of goods and mineral traffic was a major activity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
London, Brighton And South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR (known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton)) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its apex, practically the whole coastline of Sussex as its base, covering a large part of Surrey. It was bounded on its western side by the London and South Western Railway (L&SWR), which provided an alternative route to Portsmouth. On its eastern side the LB&SCR was bounded by the South Eastern Railway (England), South Eastern Railway (SER)—later one component of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR)—which provided an alternative route to Bexhill-on-Sea, Bexhill, St Leonards-on-Sea, and Hastings. The LB&SCR had the most direct routes from London to the south coast seaside resorts of Brighton, Eastbourne, Worthing, Littlehampton and Bognor Regis, and to the ports of Newhaven, East Sussex, Newhaven and Shoreham-by-Sea. It served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |