|
Polyspora
Theaceae (), the tea family, is a family of flowering plants comprising shrubs and trees, including the economically important tea plant, and the ornamental camellias. It can be described as having from seven to 40 genera, depending on the source and the method of circumscription used. The family Ternstroemiaceae has been included within Theaceae;Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. ''Vascular Plant Families and Genera''TheaceaeWatson, L., & Dallwitz, M. J. (1992 onwards). ''The families of flowering plants''/ref> however, the APG III system of 2009 places it instead in Pentaphylacaceae. Most but not all species are native to China and East Asia. Family traits Plants in this family are characterized by simple leaves that are alternate spiral to distichial, serrated, and usually glossy. Most of the genera have evergreen foliage, but '' Stewartia'' and ''Franklinia'' are deciduous. The toothed margins are generally associated with a characteristic Theoid leaf tooth, which is crowned by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordonia (plant)
''Gordonia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Theaceae, related to '' Franklinia'', ''Camellia'' and ''Stewartia''. Of the roughly 40 species, all but two are native to southeast Asia in southern China, Taiwan and Indochina. The remaining species, ''G. lasianthus'' (Loblolly-bay), is native to southeast North America, from Virginia south to Florida and west to Louisiana; ''G. fruticosa'' is native to the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, from Costa Rica to Brazil. They are evergreen trees, growing to 10–20 m tall. The bark is thick and deeply fissured. The leaves are alternately arranged, simple, serrated, thick, leathery, glossy, and 6–18 cm long. The flowers are large and conspicuous, 4–15 cm diameter, with 5 (occasionally 6-8) white petals; flowering is in late winter or early spring. The fruit is a dry five-valved capsule, with 1-4 seeds in each section. The species are adapted to acidic soils, and do not grow well on chalk or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyspora
Theaceae (), the tea family, is a family of flowering plants comprising shrubs and trees, including the economically important tea plant, and the ornamental camellias. It can be described as having from seven to 40 genera, depending on the source and the method of circumscription used. The family Ternstroemiaceae has been included within Theaceae;Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. ''Vascular Plant Families and Genera''TheaceaeWatson, L., & Dallwitz, M. J. (1992 onwards). ''The families of flowering plants''/ref> however, the APG III system of 2009 places it instead in Pentaphylacaceae. Most but not all species are native to China and East Asia. Family traits Plants in this family are characterized by simple leaves that are alternate spiral to distichial, serrated, and usually glossy. Most of the genera have evergreen foliage, but '' Stewartia'' and ''Franklinia'' are deciduous. The toothed margins are generally associated with a characteristic Theoid leaf tooth, which is crowned by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camellia Sinensis
''Camellia sinensis'' is a species of evergreen shrub or small tree in the flowering plant family Theaceae. Its leaves and leaf buds are used to produce the popular beverage, tea. Common names include tea plant, tea shrub, and tea tree (not to be confused with '' Melaleuca alternifolia'', the source of tea tree oil, or the genus ''Leptospermum'' commonly called tea tree). White tea, yellow tea, green tea, oolong, dark tea (which includes pu-erh tea) and black tea are all harvested from one of two major varieties grown today, ''C. sinensis'' var. ''sinensis'' and ''C. s.'' var. ''assamica'', but are processed differently to attain varying levels of oxidation with black tea being the most oxidized and green being the least. Kukicha (twig tea) is also harvested from ''C. sinensis'', but uses twigs and stems rather than leaves. Nomenclature and taxonomy The generic name ''Camellia'' is taken from the Latinized name of Rev. Georg Kamel, SJ (1661–1706), a Moravian-bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiosperm Phylogeny Website
The Angiosperm Phylogeny Website (or APweb) is a website dedicated to research on angiosperm phylogeny and taxonomy. The site is hosted by the Missouri Botanical Garden website and maintained by researchers, Peter F. Stevens and Hilary M. Davis. Peter F. Stevens is a member of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) is an informal international group of systematic botanists who collaborate to establish a consensus on the taxonomy of flowering plants (angiosperms) that reflects new knowledge about plant relationships disc ... (APG). The taxonomy presented is broadly based on the work of the APG, with modifications to incorporate new results. References External links * , hosted by thMissouri Botanical Garden Plant taxonomy American science websites Angiosperm taxonomy Angiosperm Phylogeny Group Online taxonomy databases Missouri Botanical Garden {{botany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camellia Ptilophylla
''Camellia ptilophylla'', also called the cocoa tea plant (not to be confused with the chocolate plant ''Theobroma cacao''), is a species of ''Camellia'' plant found in Southern Asia. It has insignificant levels of naturally occurring caffeine, unlike other varieties of the plant used to make tea. History For many years, it has been widely consumed by local inhabitants in the Longmen area of Guangdong Province Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) ... of China but has only started attracting scientific interest since 1988. It was first scientifically documented in the 1980s. Preparation for tea A recommendation for consuming cocoa tea is like steeping most other teas, in which to infuse tea leaves with boiling water for 3 min. The aroma profile of Cocoa tea is differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Selection
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together. Domesticated animals are known as breeds, normally bred by a professional breeder, while domesticated plants are known as varieties, cultigens, cultivars, or breeds. Two purebred animals of different breeds produce a crossbreed, and crossbred plants are called hybrids. Flowers, vegetables and fruit-trees may be bred by amateurs and commercial or non-commercial professionals: major crops are usually the provenance of the professionals. In animal breeding, techniques such as inbreeding, linebreeding, and outcrossing are utilized. In plant breeding, similar methods are used. Charles Darwin discussed how selective breeding had been successful in producing change over time in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
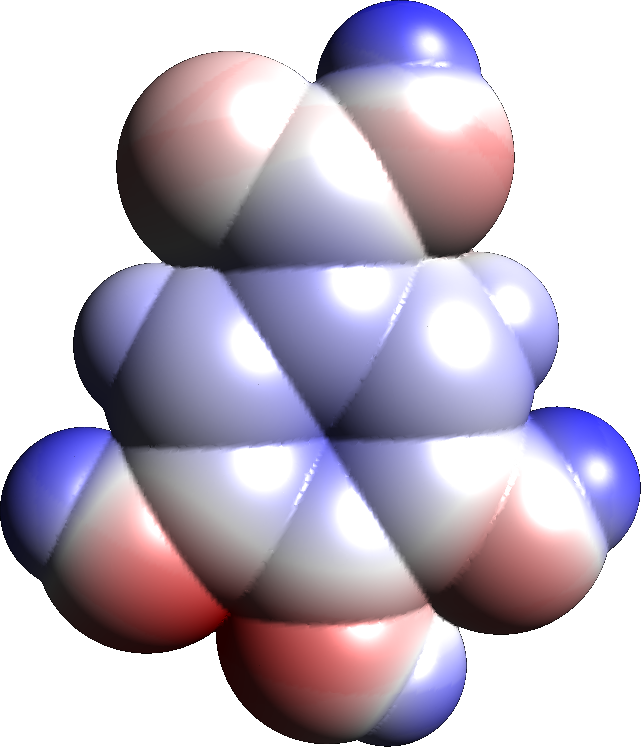
Catechin
Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids. The name of the catechin chemical family derives from ''catechu'', which is the tannic juice or boiled extract of ''Mimosa catechu'' (''Acacia catechu'' L.f). Chemistry Catechin possesses two benzene rings (called the A- and B-rings) and a dihydropyran heterocycle (the C-ring) with a hydroxyl group on carbon 3. The A-ring is similar to a resorcinol moiety while the B-ring is similar to a catechol moiety. There are two chiral centers on the molecule on carbons 2 and 3. Therefore, it has four diastereoisomers. Two of the isomers are in trans configuration and are called ''catechin'' and the other two are in cis configuration and are called ''epicatechin''. The most common catechin isomer is (+)-catechin. The other stereoisomer is (-)-catechin or ''ent''-catechin. The most common epicatechin isomer is (-)-epicatech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Acid
Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6 H2( OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates". Isolation and derivatives Gallic acid is easily freed from gallotannins by acidic or alkaline hydrolysis. When heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, gallic acid converts to rufigallol. Hydrolyzable tannins break down on hydrolysis to give gallic acid and glucose or ellagic acid and glucose, known as gallotannins and ellagitannins, respectively. Biosynthesis Gallic acid is formed from 3-dehydroshikimate by the action of the enzyme shikimate dehydrogenase to produce 3,5-didehydroshikimate. This latter compound aromatizes. Reactions Oxidation and oxidative coupling Alkaline solutions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellagic Acid
Ellagic acid is a polyphenol found in numerous fruits and vegetables. It is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid. Name The name comes from the French term ''acide ellagique'', from the word ''galle'' spelled backwards because it can be obtained from ''noix de galle'' ( galls), and to distinguish it from ''acide gallique'' (gallic acid). The molecule structure resembles to that of two gallic acid molecules being assembled "head to tail" and bound together by a C–C bond (as in biphenyl, or in diphenic acid) and two lactone links (cyclic carboxylic esters). Metabolism Biosynthesis Plants produce ellagic acid from hydrolysis of tannins such as ellagitannin and geraniin. Biodegradation Urolithins are gut flora human metabolites of dietary ellagic acid derivatives. Ellagic acid has low bioavailability, with 90% remaining unabsorbed from the intestines until metabolized by microflora to the more bioavailable urolintins. History Ellagic acid was first discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schima
''Schima'' is a genus of evergreen trees belonging to the tea family, Theaceae. The genus inhabits warm temperate to subtropical climates across southern and southeastern Asia, from the eastern Himalaya of Nepal and eastern India across Indochina, southern China, Taiwan, and the Ryukyu Islands. There are about 20 species, including six species endemic to China. Fossil record Fossil fruits of ''Schima'' have been described as †''Schima nanlinensis'', from the Miocene of Nanlin Formation in Longchuan Basin, Dehong Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan Province, China. The fossil fruits are 5-loculed capsules with flat reniform seeds. The genus ''Schima'' is known as fossils from the Palaeogene and Neogene of Germany and Austria. †''Schima nanlinensis'' represents the first fossil record of the genus in Asia.Fruits of Schima (Theaceae) and seeds of Toddalia (Rutaceae) from the Miocene of Yunnan Province, China by Ya Li, Jian Yang, Nilamber Awasthi and Cheng-Sen Li in†... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)