|
Nova
A nova ( novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems, but causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. This type is usually created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. If the orbital period of the system is a few days or less, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to draw accreted matter onto its surface, creating a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmosphere, mostly consisting of hydrogen, is heated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. The last supernova directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appearing not long after Tycho's Supernova in 1572, both of which were visible to the naked eye. The supernova remnant, remnants of more recent supernovae have been found, and observations of supernovae in other galaxies suggest they occur in the Milky Way on average about three times every century. A supernova in the Milky Way would almost certainly be observable through mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Type Ia Supernova
A Type Ia supernova (read: "type one-A") is a type of supernova that occurs in binary systems (two stars orbiting one another) in which one of the stars is a white dwarf. The other star can be anything from a giant star to an even smaller white dwarf. Physically, carbon–oxygen white dwarfs with a low rate of rotation are limited to below 1.44 solar masses (). Beyond this "Chandrasekhar limit, critical mass", they reignite and in some cases trigger a supernova explosion; this critical mass is often referred to as the Chandrasekhar mass, but is marginally different from the absolute Chandrasekhar limit, where electron degeneracy pressure is unable to prevent catastrophic collapse. If a white dwarf gradually accretes mass from a binary companion, or merges with a second white dwarf, the general hypothesis is that a white dwarf's core will reach the ignition temperature for Carbon burning process, carbon fusion as it approaches the Chandrasekhar mass. Within a few seconds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
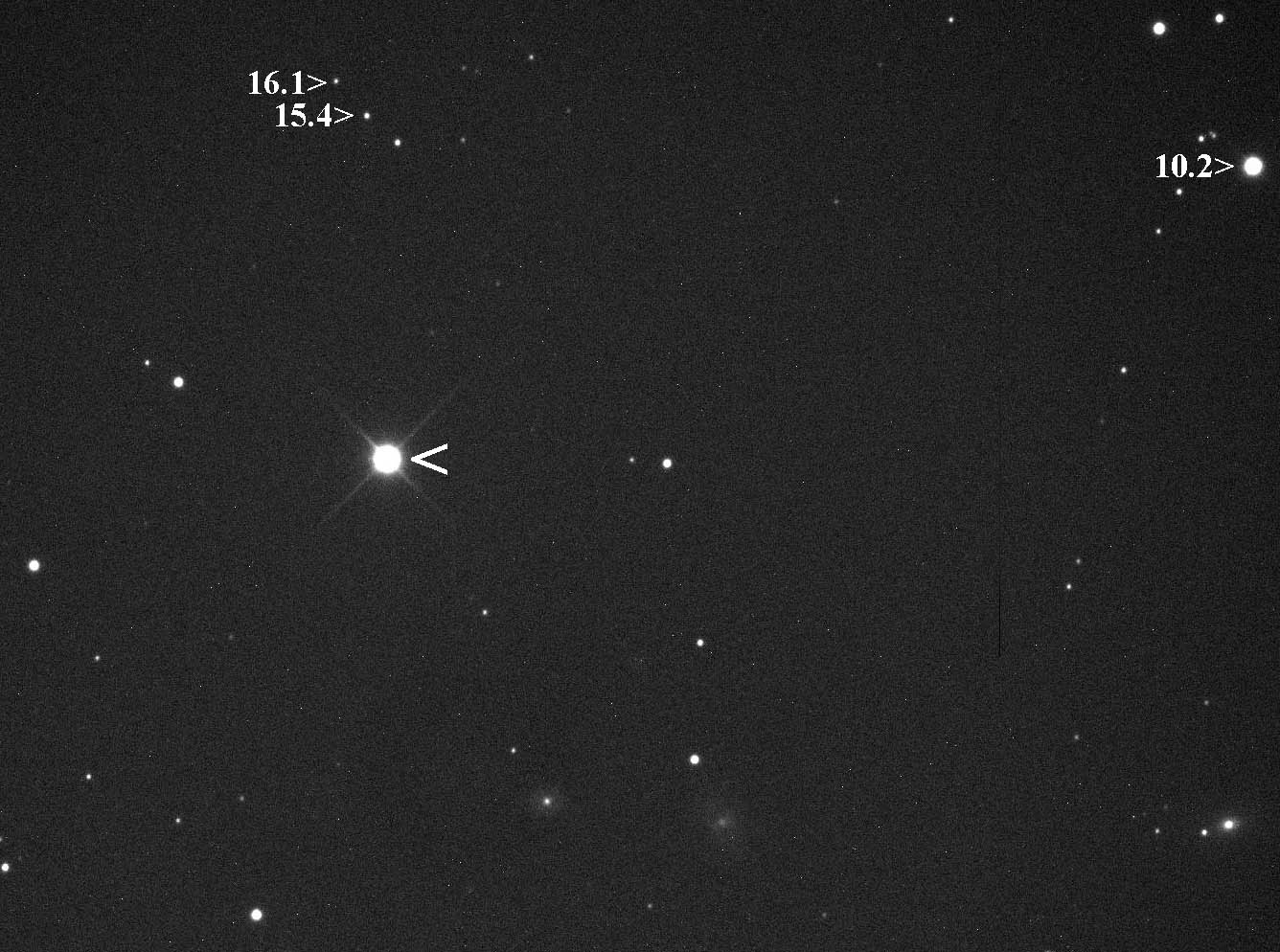
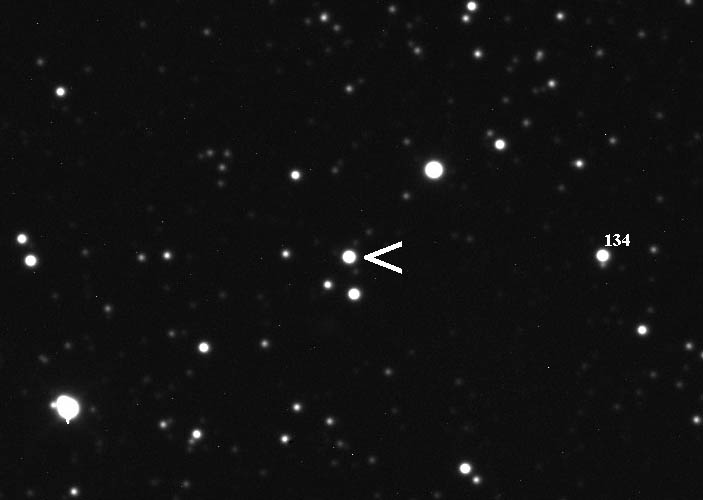
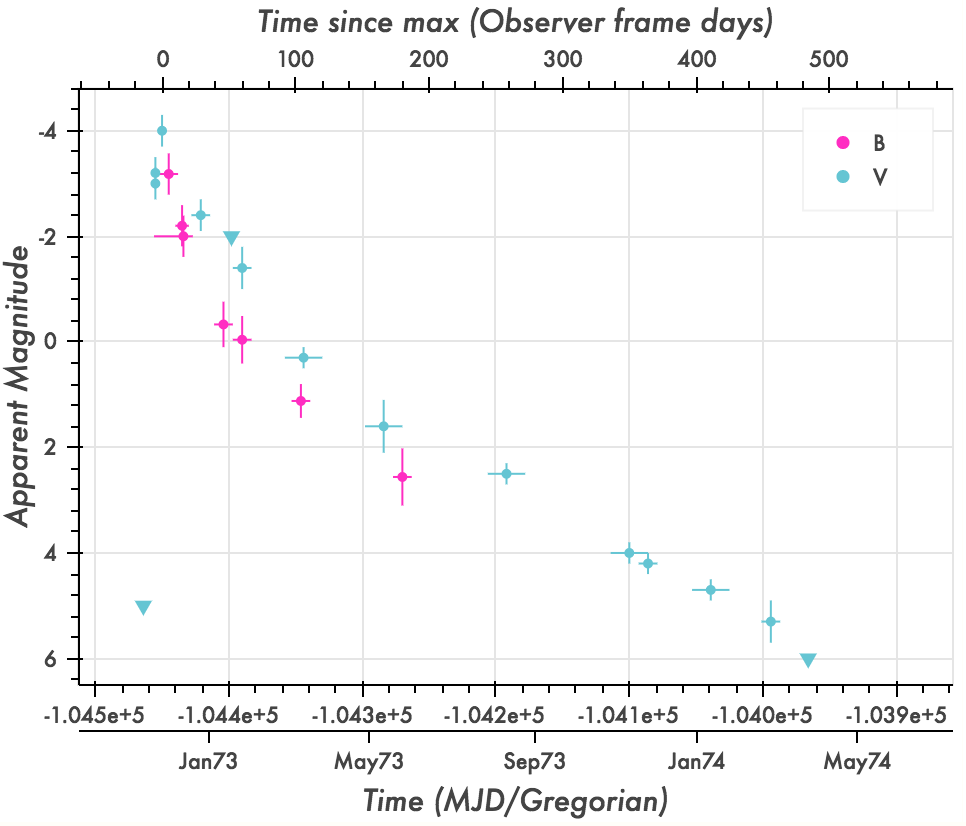
SN 1572
SN 1572 ('' Tycho's Star'', ''Tycho's Nova'', ''Tycho's Supernova''), or B Cassiopeiae (B Cas), was a supernova of Type Ia in the constellation Cassiopeia, one of eight supernovae visible to the naked eye in historical records. It appeared in early November 1572 and was independently discovered by many individuals. Its supernova remnant has been observed optically but was first detected at radio wavelengths. It is often known as 3C 10, a radio-source designation, although increasingly as Tycho's supernova remnant. Historic description The appearance of the Milky Way supernova of 1572 belongs among the most important observation events in the history of astronomy. The appearance of the " new star" helped to revise ancient models of the heavens and to speed on a revolution in astronomy that began with the realisation of the need to produce better astrometric star catalogues, and thus the need for more precise astronomical observing instruments. It also challenged the Aristot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
White Dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place in a white dwarf; what light it radiates is from its residual heat. The nearest known white dwarf is Sirius B, at 8.6 light years, the smaller component of the Sirius binary star. There are currently thought to be eight white dwarfs among the hundred star systems nearest the Sun. The unusual faintness of white dwarfs was first recognized in 1910. The name ''white dwarf'' was coined by Willem Jacob Luyten in 1922. White dwarfs are thought to be the final stellar evolution, evolutionary state of stars whose mass is not high enough to become a neutron star or black hole. This includes over 97% of the stars in the Milky Way. After the hydrogen-stellar nucleosynthesis, fusing period of a main sequence, main-sequence star of Stellar mass, lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stellar Evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the current age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are formed from Gravitational collapse, collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main sequence star. Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its existence. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the stellar core, core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
T Coronae Borealis
T Coronae Borealis (''T CrB''), nicknamed the Blaze Star, is a binary star and a recurrent nova about away in the constellation Corona Borealis. It was first discovered in outburst in 1866 by John Birmingham (astronomer), John Birmingham, though it had been observed earlier in quiescence as a 10th magnitude star. It may have been observed in 1217 and in 1787 as well. In February 1946, Michael Woodman, a 15-year-old schoolboy from Wales, observed a flare up, subsequently writing to the Astronomer Royal and leading to the theory that the star Variable star, flares every 80 years. Description T CrB normally has a apparent magnitude, magnitude of about 10, which is near the limit of typical binoculars. Well documented outbursts have been seen twice, reaching magnitude 2.0 on May 12, 1866 and magnitude 3.0 on February 9, 1946, though a more recent paper shows the 1866 outburst with a possible peak range of magnitude 2.5 ± 0.5. Even when at peak magnitude of 2.5, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, ; 14 December 154624 October 1601), generally called Tycho for short, was a Danish astronomer of the Renaissance, known for his comprehensive and unprecedentedly accurate astronomical observations. He was known during his lifetime as an astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist. He was the last major astronomer before the invention of the telescope. Tycho Brahe has also been described as the greatest pre-telescopic astronomer. In 1572, Tycho noticed a completely SN 1572, new star that was brighter than any star or planet. Astonished by the existence of a star that ought not to have been there, he devoted himself to the creation of ever more accurate instruments of measurement over the next fifteen years (1576–1591). Frederick II of Denmark, King Frederick II granted Tycho an estate on the island of Hven and the money to build Uraniborg, the first large observatory in Christian Europe. He later worked underground at Stjerneborg, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Novae In The Milky Way Galaxy
This is a partial list of novae in the Milky Way galaxy that have been discovered and recorded since 1891. Novae are stars that undergo dramatic explosions, but unlike supernovae, these do not result in the destruction of the original star. The likely rate of novae in the Milky Way is about 40 per year,Prialnik, Dina. "Novae", pp. 1846-56, in Paul Murdin, ed. ''Encyclopedia of Astronomy and Astrophysics.'' London: Institute of Physics Publishing Ltd and Nature Publishing Group, 2001. but of these only about 10 per year are discovered by observers as of the 2000s (decade).CBAT List of Novae in the Milky Way discovered since 1612 This list attempts to include only the brighter or more notable novae. The |
Thermal Runaway
Thermal runaway describes a process that is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing Thermal energy, energy that further increases temperature. Thermal runaway occurs in situations where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result. It is a kind of uncontrolled positive feedback. In chemistry (and chemical engineering), thermal runaway is associated with strongly exothermic reactions that are accelerated by temperature rise. In electrical engineering, thermal runaway is typically associated with increased Electric current, current flow and power dissipation. Thermal runaway can occur in civil engineering, notably when the heat released by large amounts of Concrete#Curing, curing concrete is not controlled. In astrophysics, runaway nuclear fusion reactions in stars can lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions, and also occur as a less dramatic event in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nova Remnant
A nova remnant is made up of the material either left behind by a sudden explosive fusion eruption by classical novae, or from multiple ejections by recurrent novae. Over their short lifetimes, nova shells show expansion velocities of around 1000 km/s, whose faint nebulosities are usually illuminated by their progenitor stars via light echos as observed with the spherical shell of Nova Persei 1901 or the energies remaining in the expanding bubbles like T Pyxidis. Form Most novae require a close binary system, with a white dwarf and a main sequence, sub-giant, or red giant star, or the merging of two red dwarfs, so probably all nova remnants must be associated with binaries. This theoretically means these nebula shapes might be affected by their central progenitor stars and the amount of matter ejected by novae. The shapes of these nova nebulae are of much interest to modern astrophysicists. Nova remnants when compared to supernova remnants or planetary nebulae generate much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cataclysmic Variable Star
In astronomy, cataclysmic variable stars (CVs) are stars which irregularly increase in brightness by a large factor, then drop back down to a quiescent state. They were initially called novae (), since those with an outburst brightness visible to the naked eye and an invisible quiescent brightness appeared as new stars in the sky. Cataclysmic variable stars are binary stars that consist of two components; a white dwarf primary, and a mass transferring secondary. The stars are so close to each other that the gravity of the white dwarf distorts the secondary, and the white dwarf accretes matter from the companion. Therefore, the secondary is often referred to as the ''donor star'', and it is usually less massive than the primary. The infalling matter, which is usually rich in hydrogen, forms in most cases an accretion disk around the white dwarf. Strong UV and X-ray emission is often detected from the accretion disc, powered by the loss of gravitational potential energy from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dwarf Nova
A dwarf nova (pl. wiktionary:nova, novae), or U Geminorum variable, is one of several types of cataclysmic variable star, consisting of a close binary star system in which one of the components is a white dwarf that accretion disk, accretes matter from its companion. Dwarf novae are dimmer and repeat more often than "classical" novae. Overview The first one to be observed was U Geminorum in 1855; however, the mechanism was not known until 1974, when Brian Warner (astronomer), Brian Warner showed that the nova is due to the increase of the luminosity of the accretion disk. They are similar to classical novae in that the white dwarf is involved in periodic outbursts, but the mechanisms are different. nova, Classical novae result from the fusion and detonation of accreted hydrogen on the primary's surface. Current theory suggests that dwarf novae result from instability in the accretion disk, when gas in the disk reaches a critical temperature that causes a change in viscosity, result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |