|
Norman Paterson School Of International Affairs
The Norman Paterson School of International Affairs (NPSIA ( )) is a professional school of international affairs at Carleton University that was founded in 1965. The school is based at Richcraft Hall on Carleton's campus in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Students, alumni and faculty of NPSIA are referred to as 'NPSIAns' ( ). NPSIA is Canada's oldest school of international affairs, founded during what is commonly considered a golden age of Canadian diplomacy. The school offers an interdisciplinary approach to the study of global issues, divided into eight fields. In 2007, a poll of Canadian academics, intended to determine the best professional master's degree programs in international affairs, ranked NPSIA at number 2, tied with Georgetown University and ahead of programs at universities like Harvard and Columbia. A 2019 survey of Canadian academics in international affairs confirmed NPSIA as the most-recommended school in Canada for students seeking a career in policy. NPSIA is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman McLeod Paterson
Norman McLeod Paterson, KGStJ, DCL, LLD (August 3, 1883 – August 10, 1983) was a Canadian businessman and politician. Life and career Born in Portage la Prairie, Manitoba, the son of Hugh Savigny Paterson and Ella Snider, he started working with the Manitoba Railway and Canal Company in 1897. Paterson later worked for the Great Northern Railway of Canada as a telegrapher, eventually becoming a purchasing agent In 1903, he started working with his father in the grain business and founded a firm, N.M Paterson and Company, in 1908. Later, he started Paterson Steamships Limited. The two firms later became N.M. Paterson and Sons Limited, which is still run by the Paterson family.Norman McLeod Paterson biography patersonfoundation.ca; accessed 14 March 2018. According to the Manitoba marriage registration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Of Canada
The Senate of Canada (french: region=CA, Sénat du Canada) is the upper house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Crown and the House of Commons, they comprise the bicameral legislature of Canada. The Senate is modelled after the British House of Lords with members appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister. The explicit basis on which appointment is made and the chamber's size is set, at 105 members, is by province or territory assigned to 'divisions'. The Constitution divides provinces of Canada geographically among four regions, which are represented equally. Senatorial appointments were originally for life; since 1965, they have been subject to a mandatory retirement age of 75. While the Senate is the upper house of parliament and the House of Commons is the lower house, this does not imply the former is more powerful than the latter. It merely entails that its members and officers outrank the members and officers of the Commons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Secretary-General
The Commonwealth secretary-general is the head of the Commonwealth Secretariat, the central body which has served the Commonwealth of Nations since its establishment in 1965, and responsible for representing the Commonwealth publicly. The Commonwealth secretary-general should not be confused with the head of the Commonwealth. Role The position was created, along with the Secretariat itself, after the fourteenth Commonwealth Prime Ministers Conference in London in 1965, issued a memorandum describing the role of the Secretary-General: The headquarters of the secretary-general, as with the Secretariat generally, is Marlborough House, a former royal residence in London, which was placed at the disposal of the Secretariat by Queen Elizabeth II, who was the head of the Commonwealth. However, as the building cannot house all of the Secretariat's staff in London, additional space is rented elsewhere in London. From this operational base, a large part of the Secretary-General's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Cantwell Smith
Arnold Cantwell Smith (January 18, 1915 – February 7, 1994) was a Canadian diplomat. He was the first Commonwealth Secretary-General, serving from 1965–1975. A talented student, he won a Rhodes Scholarship to Christ Church, Oxford. From 1958 to 1961, he was the Canadian Ambassador to Egypt. From 1961 to 1963, he was the Canadian Ambassador to the USSR. During his time at the Commonwealth Secretariat, the Commonwealth flag was designed on his and Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau's initiative. In 1975 he was made a member of the Order of the Companions of Honour. In 1984, he was made an Officer of the Order of Canada for "a long and distinguished diplomatic career". Arnold Smith was the elder brother of Wilfred Cantwell Smith. His published work includes ''Stitches In Time; the Commonwealth in World Politics''.Smith, Arnold, and Clyde Sanger. ''Stitches in Time : The Commonwealth in World Politics''. Don Mills, Ont.: General Publishing, 1981. References Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maclaren Cemetery
Maclaren Cemetery is a small cemetery in the town of Wakefield, Quebec and the final resting place for Prime Minister Lester B. Pearson. Established near the 1870s, the cemetery is located in the clearing below the hills bordering the Gatineau River and is the resting place for Scottish settlers in the area. Notable persons interred here include: * David Maclaren – settler and namesake of the cemetery * Malak Karsh (1915–2001) – Canadian photographer * Ian Kerr (1965–2019) – law professor and privacy expert Ian Kerr (academic) * Geoffrey Pearson (1927–2008) – diplomat and son of Lester B. Pearson * Lester B. Pearson (1897–1972) – 14th Prime Minister of Canada and Nobel Peace Prize winner * Norman Robertson (1904–1968) – diplomat and friend of Pearson and Wrong * Humphrey Hume Wrong Humphrey Hume Wrong (September 10, 1894 – January 24, 1954) was a Canadian historian, professor, career diplomat, and Canada's ambassador to the United States. Backgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. The term "White House" is often used as a metonym for the president and his advisers. The residence was designed by Irish-born architect James Hoban in the neoclassical style. Hoban modelled the building on Leinster House in Dublin, a building which today houses the Oireachtas, the Irish legislature. Construction took place between 1792 and 1800, using Aquia Creek sandstone painted white. When Thomas Jefferson moved into the house in 1801, he (with architect Benjamin Henry Latrobe) added low colonnades on each wing that concealed stables and storage. In 1814, during the War of 1812, the mansion was set ablaze by British forces in the Burning of Washington, destroying the interior and charring much of the exterior. Reconstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was the 36th vice president from 1953 to 1961 under President Dwight D. Eisenhower. His five years in the White House saw reduction of U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War, détente with the Soviet Union and China, the first manned Moon landings, and the establishment of the Environmental Protection Agency and Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Nixon's second term ended early, when he became the only president to resign from office, as a result of the Watergate scandal. Nixon was born into a poor family of Quakers in a small town in Southern California. He graduated from Duke Law School in 1937, practiced law in California, then moved with his wife Pat to Washington in 1942 to work for the federal government. After active duty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
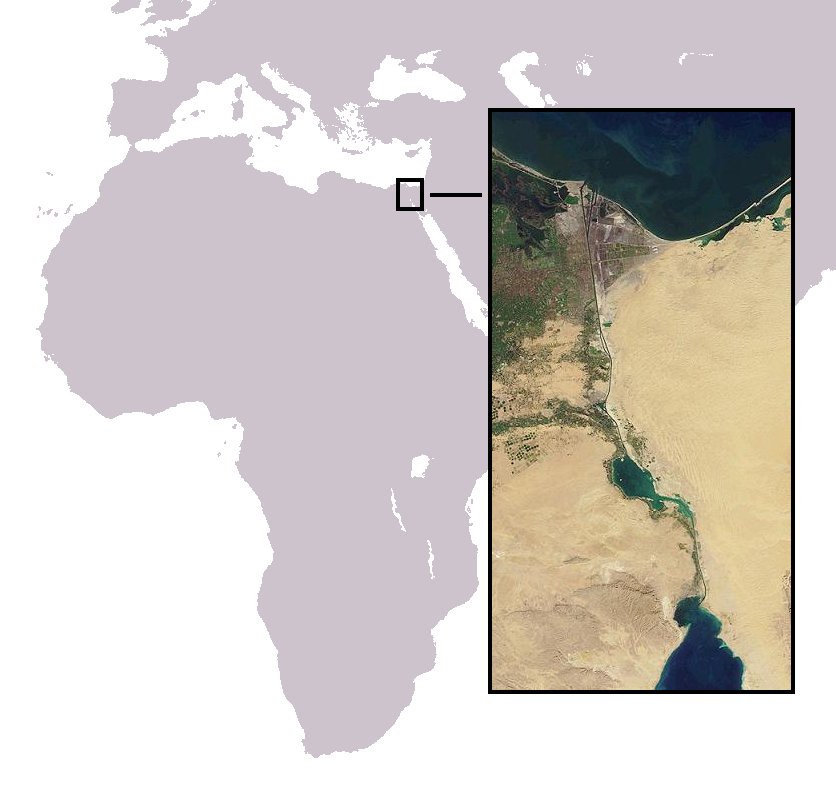
Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 War; other names include the ''Sinai war'', ''Suez–Sinai war'', ''1956 Arab–Israeli war'', the Second Arab–Israeli war, ''Suez Campaign'', ''Sinai Campaign'', ''Kadesh Operation'' and ''Operation Musketeer'' was an invasion of Egypt in late 1956 by Israel, followed by the United Kingdom and France. The aims were to regain control of the Suez Canal for the Western powers and to remove Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser, who had just swiftly nationalised the foreign-owned Suez Canal Company, which administered the canal. Israel's primary objective was to re-open the blocked Straits of Tiran. After the fighting had started, political pressure from the United States, the Soviet Union and the United Nations led to a withdrawal by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nobel Peace Prize Laureates
The Norwegian Nobel Committee awards the Nobel Peace Prize annually "to the person who shall have done the most or the best work for fraternity between nations, for the abolition or reduction of standing armies and for the holding and promotion of peace congresses". As dictated by Nobel's will, the award is administered by the Norwegian Nobel Committee and awarded by a committee of five people elected by the Parliament of Norway. Each recipient receives a medal, a diploma, and a monetary award prize (that has varied throughout the years). It is one of the five prizes established by the 1895 will of Alfred Nobel (who died in 1896), awarded for outstanding contributions in chemistry, physics, literature, peace, and physiology or medicine. Overview The Peace Prize is presented annually in Oslo, in the presence of the King of Norway, on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel's death, and is the only Nobel Prize not presented in Stockholm. Unlike the other prizes, the Peace Prize is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiology or Medicine and Literature. Since March 1901, it has been awarded annually (with some exceptions) to those who have "done the most or the best work for fraternity between nations, for the abolition or reduction of standing armies and for the holding and promotion of peace congresses". In accordance with Alfred Nobel's will, the recipient is selected by the Norwegian Nobel Committee, a five-member committee appointed by the Parliament of Norway. Since 2020 the prize is awarded in the Atrium of the University of Oslo, where it was also awarded 1947–1989; the Abel Prize is also awarded in the building. The prize was previously awarded in Oslo City Hall (1990–2019), the Norwegian Nobel Institute (1905–1946), and the Parliament (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lester B
Lester is an ancient Anglo-Saxon surname and given name. Notable people and characters with the name include: People Given name * Lester Bangs (1948–1982), American music critic * Lester W. Bentley (1908–1972), American artist from Wisconsin * Lester Bird (1938–2021), second prime minister of Antigua and Barbuda (1994–2004) * Lester Cotton (born 1996), American football player * Lester del Rey (1915–1993), American science fiction author and editor * Lester Flatt (1914–1979), American bluegrass musician * Lester Gillis (1908–1934), better known as Baby Face Nelson, American gangster * Lester Holt (born 1959), American television journalist * Lester Charles King (1907–1989), English geomorphologist * Lester Lanin (1907–2004), American jazz and pop music bandleader * Lester Lockett (1912–2005), American Negro League baseball player * Lester Maddox (1915–2003), governor and lieutenant governor of the U.S. state of Georgia * Lester Patrick (1883–196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Minister Of Canada
The prime minister of Canada (french: premier ministre du Canada, link=no) is the head of government of Canada. Under the Westminster system, the prime minister governs with the confidence of a majority the elected House of Commons; as such, the prime minister typically sits as a member of Parliament (MP) and leads the largest party or a coalition of parties. As first minister, the prime minister selects ministers to form the Cabinet, and serves as its chair. Constitutionally, the Crown exercises executive power on the advice of the Cabinet, which is collectively responsible to the House of Commons. Justin Trudeau is the 23rd and current prime minister of Canada. He took office on November 4, 2015, following the 2015 federal election where his Liberal Party won a majority of seats and was invited to form the 29th Canadian Ministry. Trudeau was subsequently re-elected following the 2019 and 2021 elections with a minority of seats. Not outlined in any constitutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




.jpg)