|
Lampsacus
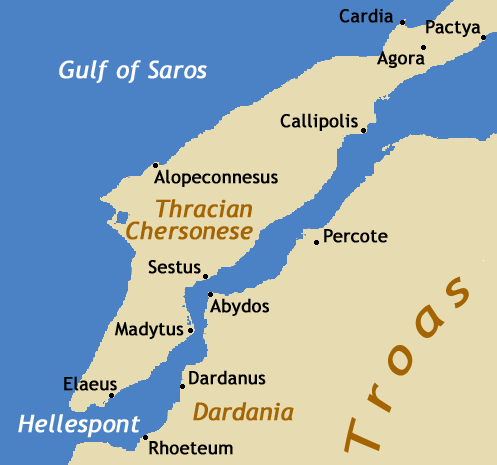
Lampsacus (; grc, Λάμψακος, translit=Lampsakos) was an ancient Greek city strategically located on the eastern side of the Hellespont in the northern Troad. An inhabitant of Lampsacus was called a Lampsacene. The name has been transmitted in the nearby modern town of Lapseki. Ancient history Originally known as Pityusa or Pityussa ( grc, Πιτυούσ(σ)α), it was colonized from Phocaea and Miletus. In the 6th century BC Lampsacus was attacked by Miltiades the Elder and Stesagoras, the Athenian tyrants of the nearby Thracian Chersonese. During the 6th and 5th centuries BC, Lampsacus was successively dominated by Lydia, Persia, Athens, and Sparta. The Greek tyrants Hippoclus and later his son Acantides ruled under Darius I. Artaxerxes I assigned it to Themistocles with the expectation that the city supply the Persian king with its famous wine. When Lampsacus joined the Delian League after the battle of Mycale (479 BC), it paid a tribute of twelve talents, a testimo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Themistocles
Themistocles (; grc-gre, Θεμιστοκλῆς; c. 524–459 BC) was an Athenian politician and general. He was one of a new breed of non-aristocratic politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy. As a politician, Themistocles was a populist, having the support of lower-class Athenians, and generally being at odds with the Athenian nobility. Elected archon in 493 BC, he convinced the polis to increase the naval power of Athens, a recurring theme in his political career. During the first Persian invasion of Greece he fought at the Battle of Marathon (490 BC) and was possibly one of the ten Athenian ''strategoi'' (generals) in that battle. In the years after Marathon, and in the run-up to the second Persian invasion of 480–479 BC, Themistocles became the most prominent politician in Athens. He continued to advocate for a strong Athenian Navy, and in 483 BC he persuaded the Athenians to build a fleet of 200 triremes; these prove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapseki
Lapseki (from Greek: Λάμψακος, ''Lampsakos'') is a town and district of Çanakkale Province, Turkey. In 2012 it had a population of 10,863. The mayor is Eyüp Yılmaz ( AKP). The district of Lapseki is known for its cherries, and a cherry festival is held annually in the town. History The town was founded by Greek colonists from Phocaea in the 6th century BC. Soon afterwards it became a competitor of Miletus, controlling the trade routes in the Dardanelles. The modern Turkish name derives from the original Greek name. Lapseki was founded about 500 BC, one of 4 settlements along the Dardanelles at that time. In ancient times, while the city was under the rule of King Mendrom and named Pityausa, the king, who defended the colonists from Foça from the attacks of the local people, minted coins for the first time in its history in the name of his daughter Lapseke and later the city was given this name by the colonists to express their indebtedness to him. In this way, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus. His name is cognate with the first element of his ancient Roman religion, Roman interpretatio graeca, equivalent Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter.''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. His mythology and powers are similar, though not identical, to those of Indo-European deities such as Jupiter, Perkūnas, Perun, Indra, Dyaus, and Zojz (deity), Zojz. Entry: "Dyaus" Zeus is the child of Cronus and Rhea (mythology), Rhea, the youngest of his siblings to be born, though sometimes reckoned the eldest as the others required disgorging from Cronus's stomach. In most traditions, he is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
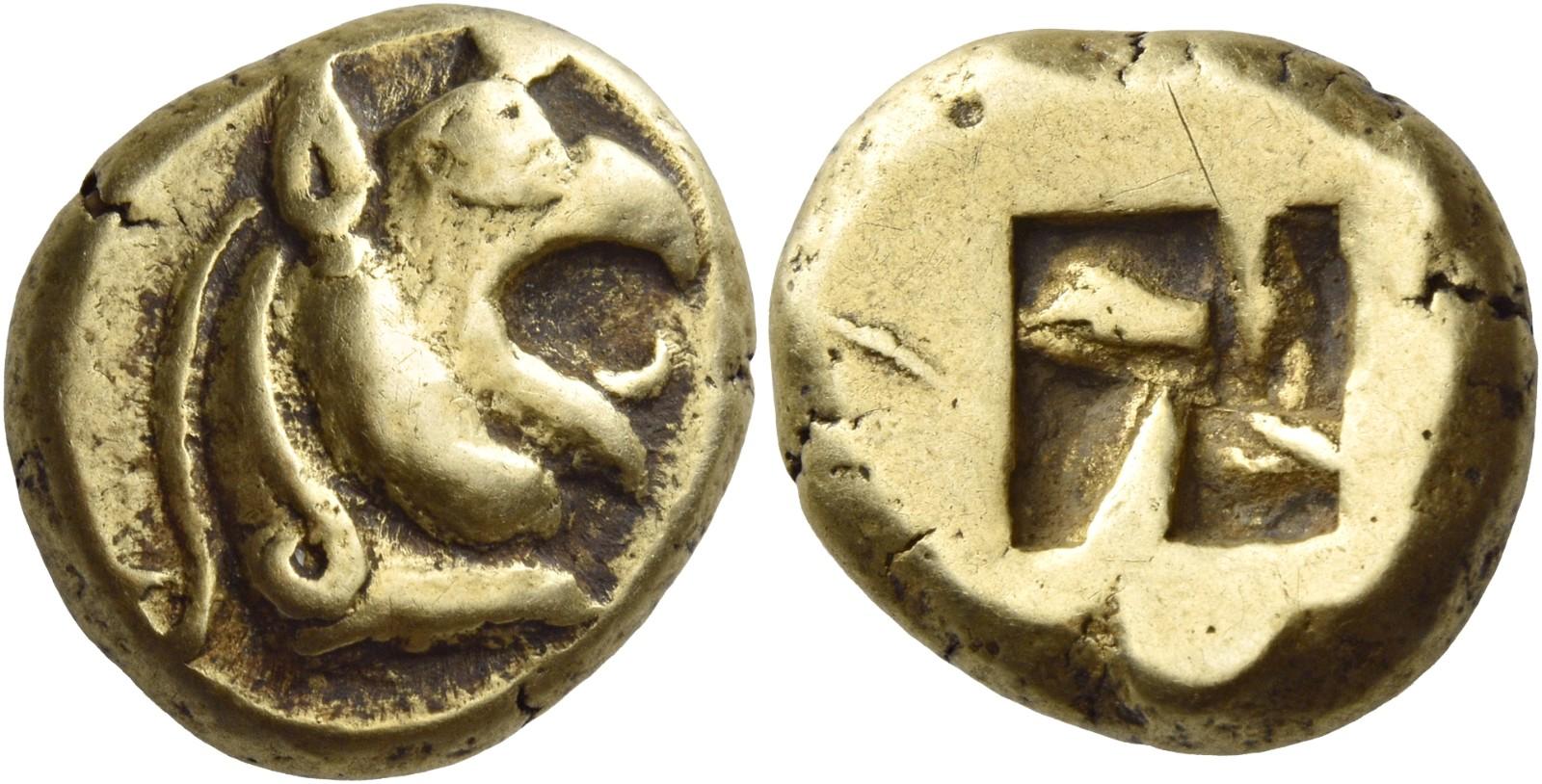
Stater
The stater (; grc, , , statḗr, weight) was an ancient coin used in various regions of Ancient Greece, Greece. The term is also used for similar coins, imitating Greek staters, minted elsewhere in ancient Europe. History The stater, as a Greek silver currency, first as ingots, and later as coins, circulated from the 8th century BC to AD 50. The earliest known stamped stater (having the mark of some authority in the form of a picture or words) is an electrum turtle coin, struck at Aegina that dates to about 650 BC. It is on display at the Bibliothèque Nationale in Paris. According to Robin Lane Fox, the stater as a weight unit was borrowed by the Euboean stater weighing from the Phoenician shekel, which had about the same weight as a stater () and was also one fiftieth of a Mina (unit), mina.Lane Fox, Robin. ''Travelling Heroes: Greeks and Their Myths in the Epic Age of Homer''. P. 94. London: Allen Lane, 2008. The silver stater minted at CorinthSmith, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; el, Στράβων ''Strábōn''; 64 or 63 BC 24 AD) was a Greek geographer, philosopher, and historian who lived in Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. Life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus (in present-day Turkey) in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics since at least the reign of Mithridates V. Strabo was related to Dorylaeus on his mother's side. Several other family members, including his paternal grandfather had served Mithridates VI during the Mithridatic Wars. As the war drew to a close, Strabo's grandfather had turned several Pontic fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the List of largest empires, largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus River, Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miltiades The Elder
Miltiades the Elder (ca. 590 – 525 BC) was an Athenian politician from the Philaid family. He is most famous for travelling to the Thracian Chersonese (modern-day Gallipoli) where, at the behest of the local peoples, he ruled as a tyrant. During his reign, Miltiades' best-attested action was the construction of a defensive wall across the peninsula. Miltiades was the uncle of Miltiades the Younger, who was a prominent commander in the Battle of Marathon. Early life and family Miltiades the Elder was born in Athens in around 590 BC. His father was Cypselus the archon; Miltiades also claimed descent from the mythological king Aeacus.Hammond, 117. During this time, the Philaids were one of the wealthiest families in the city. While living in Athens, Miltiades was a successful athlete. He owned a four-horse chariot,Herodotus, ''Histories,'' 6.35. and won an Olympic victory in the chariot race in 560 BC. In the Thracian Chersonese During this period, the Dolonci (a tribe from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artaxerxes I
Artaxerxes I (, peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης) was the fifth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, from 465 to December 424 BC. He was the third son of Xerxes I. He may have been the " Artasyrus" mentioned by Herodotus as being a satrap of the royal satrapy of Bactria. In Greek sources he is also surnamed "long-handed" ( grc, μακρόχειρ ''Makrókheir''; la, Longimanus), allegedly because his right hand was longer than his left. Succession to the throne Artaxerxes was probably born in the reign of his grandfather Darius I, to the emperor's son and heir, Xerxes I. In 465 BC, Xerxes I was murdered by ''Hazarapat'' ("commander of thousand") Artabanus, the commander of the royal bodyguard and the most powerful official in the Persian court, with the help of a eunuch, Aspamitres. Greek historians give contradicting accounts of events. According to Ctesias (in ''Persica'' 20), Artabanus then accused Crown Prince Darius, X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' (exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Ionia. Its ruins are located near the modern village of Balat in Aydın Province, Turkey. Before the Persian rule that started in the 6th century BC, Miletus was considered among the greatest and wealthiest of Greek cities. Evidence of first settlement at the site has been made inaccessible by the rise of sea level and deposition of sediments from the Maeander. The first available evidence is of the Neolithic. In the early and middle Bronze Age the settlement came under Minoan influence. Legend has it that an influx of Cretans occurred displacing the indigenous Leleges, and the site was renamed Miletus after a place in Crete. Recorded history at Miletus begins with the records of the Hittite Empire, and the Mycenaean records of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stater Lampsacus 360-340BC Obverse CdM Paris
The stater (; grc, , , statḗr, weight) was an ancient coin used in various regions of Greece. The term is also used for similar coins, imitating Greek staters, minted elsewhere in ancient Europe. History The stater, as a Greek silver currency, first as ingots, and later as coins, circulated from the 8th century BC to AD 50. The earliest known stamped stater (having the mark of some authority in the form of a picture or words) is an electrum turtle coin, struck at Aegina that dates to about 650 BC. It is on display at the Bibliothèque Nationale in Paris. According to Robin Lane Fox, the stater as a weight unit was borrowed by the Euboean stater weighing from the Phoenician shekel, which had about the same weight as a stater () and was also one fiftieth of a mina.Lane Fox, Robin. ''Travelling Heroes: Greeks and Their Myths in the Epic Age of Homer''. P. 94. London: Allen Lane, 2008. The silver stater minted at CorinthSmith, William. ''A Dictionary of Greek an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phocaea
Phocaea or Phokaia (Ancient Greek: Φώκαια, ''Phókaia''; modern-day Foça in Turkey) was an ancient Ionia Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionian ...n Ancient Greece, Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia. Colonies in antiquity, Greek colonists from Phocaea founded the colony of Massalia (modern-day Marseille, in France) in 600 BC, Emporion (modern-day Empúries, in Catalonia, Spain) in 575 BC and Elea (modern-day Velia, in Campania, Italy) in 540 BC. Geography Phocaea was the northernmost of the Ionian cities, on the boundary with Aeolis. It was located near the mouth of the river Hermus (now Gediz River, Gediz), and situated on the coast of the peninsula separating the Gulf of Cyme (Aeolis), Cyme to the north, named for the largest of the Aeolis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus The Great
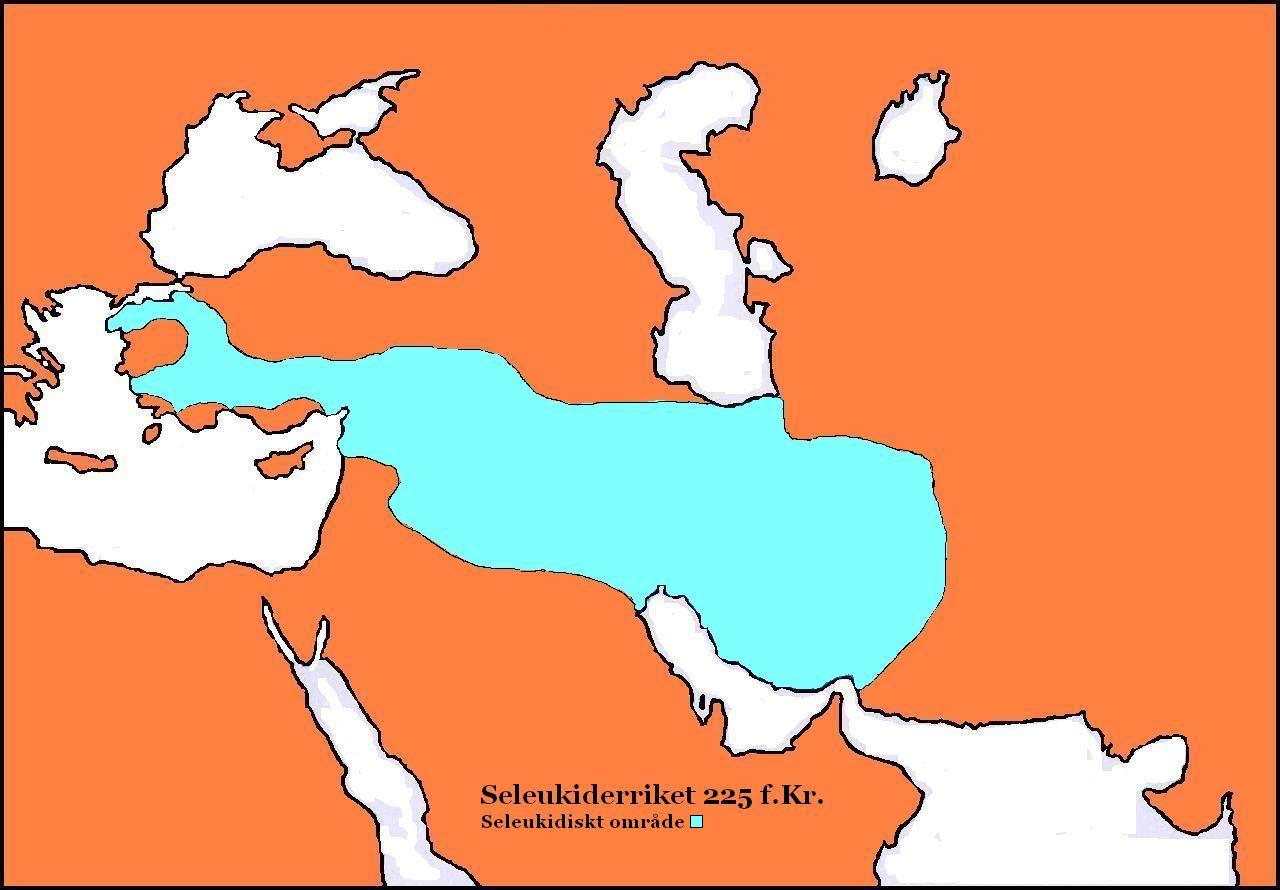
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |