|
Infix
An infix is an affix inserted inside a word stem (an existing word or the core of a family of words). It contrasts with '' adfix,'' a rare term for an affix attached to the outside of a stem, such as a prefix or suffix. When marking text for interlinear glossing, most affixes are separated with a hyphen, but infixes are separated with . English English has almost no true infixes (as opposed to tmesis) and those it does have are marginal. A few are heard in colloquial speech, and a few more are found in technical terminology. Colloquialisms None of the following are recognized in standard English. * The infix or is characteristic of hip-hop slang, for example ''h-iz-ouse'' for ''house'' and ''sh-izn-it'' for ''shit.'' * The infix (or "Homeric infix," after Homer Simpson), whose location in the word is described in , gives a word an ironic pseudo-sophistication, as in ''sophisti-ma-cated (sophisticated), saxo-ma-phone,'' (saxophone) and ''edu-ma-cation.'' (education) Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Infix
The nasal infix is a reconstructed nasal consonant or syllable that was inserted ( infixed) into the stem or root of a word in the Proto-Indo-European language. It has reflexes in several ancient and modern Indo-European languages. It is one of the affixes that mark the present tense. Proto-Indo-European In the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE), the nasal infix is one of several means to form the athematic present tense. It is inserted immediately before the last consonant of the zero-grade root. The infix appeared as in the forms where a full-grade stem would be expected, and as in forms where zero-grade would be expected. For example, the PIE root "to win" would yield a nasal-infixed present stem . These presents are called ''nasal infix presents'' or simply ''nasal presents'' and are typically active transitive verbs, often with durative aspect. Origins Since the linguistic ancestor of PIE is not known, there can only be speculations about the origins of the nasa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Infix
The nasal infix is a reconstructed nasal consonant or syllable that was inserted ( infixed) into the stem or root of a word in the Proto-Indo-European language. It has reflexes in several ancient and modern Indo-European languages. It is one of the affixes that mark the present tense. Proto-Indo-European In the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE), the nasal infix is one of several means to form the athematic present tense. It is inserted immediately before the last consonant of the zero-grade root. The infix appeared as in the forms where a full-grade stem would be expected, and as in forms where zero-grade would be expected. For example, the PIE root "to win" would yield a nasal-infixed present stem . These presents are called ''nasal infix presents'' or simply ''nasal presents'' and are typically active transitive verbs, often with durative aspect. Origins Since the linguistic ancestor of PIE is not known, there can only be speculations about the origins of the nasa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
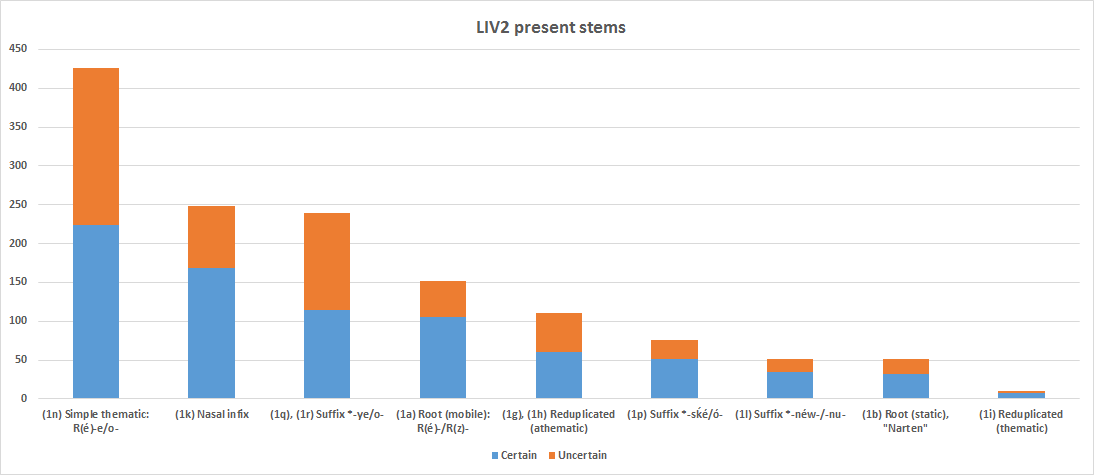
Proto-Indo-European Verb
Proto-Indo-European verbs reflect a complex system of morphology, more complicated than the substantive, with verbs categorized according to their aspect, using multiple grammatical moods and voices, and being conjugated according to person, number and tense. In addition to finite forms thus formed, non-finite forms such as participles are also extensively used.Beekes, 18.1.1. The verbal system is clearly represented in Ancient Greek and Vedic Sanskrit, which closely correspond, in nearly all aspects of their verbal systems, and are two of the most well-understood of the early daughter languages of Proto-Indo-European. Basics Verb conjugation in Proto-Indo-European involves the interplay of six dimensions (number, person, voice, mood, aspect and tense) with the following variables identified under the ''Cowgill-Rix'' system, which is one of the methodologies proposed and applies only to certain subfamilies: Further, participles can be considered part of the verbal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Notation
Polish notation (PN), also known as normal Polish notation (NPN), Łukasiewicz notation, Warsaw notation, Polish prefix notation or simply prefix notation, is a mathematical notation in which operators ''precede'' their operands, in contrast to the more common infix notation, in which operators are placed ''between'' operands, as well as reverse Polish notation (RPN), in which operators ''follow'' their operands. It does not need any parentheses as long as each operator has a fixed number of operands. The description "Polish" refers to the nationality of logician Jan Łukasiewicz, who invented Polish notation in 1924. The term ''Polish notation'' is sometimes taken (as the opposite of ''infix notation'') to also include reverse Polish notation. When Polish notation is used as a syntax for mathematical expressions by programming language interpreters, it is readily parsed into abstract syntax trees and can, in fact, define a one-to-one representation for the same. Because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affix
In linguistics, an affix is a morpheme that is attached to a word stem to form a new word or word form. Affixes may be derivational, like English ''-ness'' and ''pre-'', or inflectional, like English plural ''-s'' and past tense ''-ed''. They are bound morphemes by definition; prefixes and suffixes may be separable affixes. Affixation is the linguistic process that speakers use to form different words by adding morphemes at the beginning (prefixation), the middle (infixation) or the end (suffixation) of words. Positional categories of affixes ''Prefix'' and ''suffix'' may be subsumed under the term ''adfix'', in contrast to ''infix.'' When marking text for interlinear glossing, as in the third column in the chart above, simple affixes such as prefixes and suffixes are separated from the stem with hyphens. Affixes which disrupt the stem, or which themselves are discontinuous, are often marked off with angle brackets. Reduplication is often shown with a tilde. Affixes whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlinear Gloss
In linguistics and pedagogy, an interlinear gloss is a gloss (series of brief explanations, such as definitions or pronunciations) placed between lines, such as between a line of original text and its translation into another language. When glossed, each line of the original text acquires one or more corresponding lines of transcription known as an interlinear text or interlinear glossed text (IGT)interlinear for short. Such glosses help the reader follow the relationship between the source text and its translation, and the structure of the original language. In its simplest form, an interlinear gloss is simply a literal, word-for-word translation of the source text. History Interlinear glosses have been used for a variety of purposes over a long period of time. One common usage has been to annotate bilingual textbooks for language education. This sort of interlinearization serves to help make the meaning of a source text explicit without attempting to formally model the struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adfix
In linguistics, an affix is a morpheme that is attached to a word stem to form a new word or word form. Affixes may be derivational, like English ''-ness'' and ''pre-'', or inflectional, like English plural ''-s'' and past tense ''-ed''. They are bound morphemes by definition; prefixes and suffixes may be separable affixes. Affixation is the linguistic process that speakers use to form different words by adding morphemes at the beginning (prefixation), the middle (infixation) or the end (suffixation) of words. Positional categories of affixes ''Prefix'' and ''suffix'' may be subsumed under the term ''adfix'', in contrast to ''infix.'' When marking text for interlinear glossing, as in the third column in the chart above, simple affixes such as prefixes and suffixes are separated from the stem with hyphens. Affixes which disrupt the stem, or which themselves are discontinuous, are often marked off with angle brackets. Reduplication is often shown with a tilde. Affixes which can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expletive Infixation
Expletive infixation is a process by which an expletive or profanity is inserted into a word, usually for intensification. It is similar to tmesis, but not all instances are covered by the usual definition of ''tmesis'' because the words are not necessarily compounds. The most commonly inserted English expletives are adjectival: either participles (''fucking'', ''mother-fucking'', ''freaking'', ''blooming'', ''bleeding'', '' damned'', ''wretched'') or adjectives (''bloody''). Rules of formation in English Judgments of which formations of expletive infixation are acceptable are remarkably consistent. This suggests that the rules for the placement of the expletive are not arbitrary, but instead derive from fundamental aspects of English phonology. A simple rule is that the insertion occurs at a syllable boundary, usually just before the primary stressed syllable. Thus, one hears ''abso-fuckin'-lutely'' rather than *''ab-fuckin'-solutely''. This rule is insufficient to describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postfix Notation
Reverse Polish notation (RPN), also known as reverse Łukasiewicz notation, Polish postfix notation or simply postfix notation, is a mathematical notation in which operators ''follow'' their operands, in contrast to Polish notation (PN), in which operators ''precede'' their operands. It does not need any parentheses as long as each operator has a fixed number of operands. The description "Polish" refers to the nationality of logician Jan Łukasiewicz, who invented Polish notation in 1924. The first computer to use postfix notation, though it long remained essentially unknown outside of Germany, was Konrad Zuse's Z3 in 1941 as well as his Z4 in 1945. The reverse Polish scheme was again proposed in 1954 by Arthur Burks, Don Warren, and Jesse Wright and was independently reinvented by Friedrich L. Bauer and Edsger W. Dijkstra in the early 1960s to reduce computer memory access and use the stack to evaluate expressions. The algorithms and notation for this scheme were exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tmesis
In its strictest sense, tmesis (; plural tmeses ; Ancient Greek: ''tmēsis'' "a cutting" < ''temnō'', "I cut") is a word compound that is divided into two parts, with another word ed between the parts, thus constituting a separate word compound. In a broader sense, ''tmesis'' is a recognizable phrase (such as a ) or word that is divided into two parts, with one or more words interpolated between the parts, thus creating a separate phrase. Verbs Tmesis of ed verbs (whereby the prefix is s ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages#Old Indo- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Root
The roots of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) are basic parts of words that carry a lexical meaning, so-called morphemes. PIE roots usually have verbal meaning like "to eat" or "to run". Roots never occurred alone in the language. Complete inflected verbs, nouns, and adjectives were formed by adding further morphemes to a root and potentially changing the root's vowel in a process called ablaut. A root consists of a central vowel that is preceded and followed by at least one consonant each. A number of rules have been determined that specify which consonants can occur together, and in which order. The modern understanding of these rules is that the consonants with the highest sonority (') are nearest to the vowel, and the ones with the lowest sonority such as plosives are furthest away. There are some exceptions to these rules such as thorn clusters. Sometimes new roots were created in PIE or its early descendants by various processes such as root extensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |