|
Gamut
In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut , is a certain ''complete subset'' of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors which can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a certain output device. Another sense, less frequently used but still correct, refers to the complete set of colors found within an image at a given time. In this context, digitizing a photograph, converting a digitized image to a different color space, or outputting it to a given medium using a certain output device generally alters its gamut, in the sense that some of the colors in the original are lost in the process. Introduction The term ''gamut'' was adopted from the field of music, where in middle age Latin "gamut" meant the entire range of musical notes of which musical melodies are composed; Shakespeare's use of the term in ''The Taming of the Shrew'' is sometimes attributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIE 1931 Chromaticity Diagram
The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that define these color spaces are essential tools for color management, important when dealing with color inks, illuminated displays, and recording devices such as digital cameras. The system was designed in 1931 by the ''"Commission Internationale de l'éclairage"'', known in English as the International Commission on Illumination. The CIE 1931 RGB color space and CIE 1931 XYZ color space were created by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1931. They resulted from a series of experiments done in the late 1920s by William David Wright using ten observers and John Guild using seven observers. The experimental results were combined into the specification of the CIE RGB color space, from which the CIE XYZ color space was derived. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burned (image)
An image is said to be burned or burnt when its original gamut considerably exceeds the target gamut, or when the result of processing considerably exceeds the image's gamut, resulting in clipping.Langford, Fox, and Smith. ''Langford's Basic Photography'', p. 354 Colloquially, an image is burned when it contains uniform blobs of color, black, or white where there should actually be detail. All media for storing or capturing images, both analog and digital, are capable of storing only a limited number of color hues, and are bound to a certain gamut. Squeezing an image with a given gamut into a medium with a smaller gamut is done either by adapting the whole range of colors to the new gamut, or by ''trimming'' the colors out of gamut. Trimming colors at the extremes results in burning the image. While converting and capturing images is usually a "smart" process that tries to accommodate the entire gamut of the original into the target color space, extreme processing of an image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associated with objects or materials based on their physical properties such as light absorption, reflection, or emission spectra. By defining a color space, colors can be identified numerically by their coordinates. Because perception of color stems from the varying spectral sensitivity of different types of cone cells in the retina to different parts of the spectrum, colors may be defined and quantified by the degree to which they stimulate these cells. These physical or physiological quantifications of color, however, do not fully explain the psychophysical perception of color appearance. Color science includes the perception of color by the eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names (including discrete numbers infor examplethe Pantone collection), or structured with mathematical rigor (as with the NCS System, Adobe RGB and sRGB). A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised. A " color model" is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
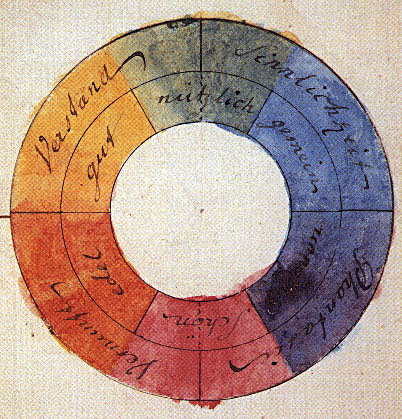
Color Theory
In the visual arts, color theory is the body of practical guidance for color mixing and the visual effects of a specific color combination. Color terminology based on the color wheel and its geometry separates colors into primary color, secondary color, and tertiary color. The understanding of color theory dates to antiquity. Aristotle (d. 322 BCE) and Claudius Ptolemy (d. 168 CE) already discussed which and how colors can be produced by mixing other colors. The influence of light on color was investigated and revealed further by al-Kindi (d. 873) and Ibn al-Haytham (d.1039). Ibn Sina (d. 1037), Nasir al-Din al-Tusi (d. 1274), and Robert Grosseteste (d. 1253) discovered that contrary to the teachings of Aristotle, there are multiple color paths to get from black to white. More modern approaches to color theory principles can be found in the writings of Leone Battista Alberti (c. 1435) and the notebooks of Leonardo da Vinci (c. 1490). A formalization of "color theory" bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
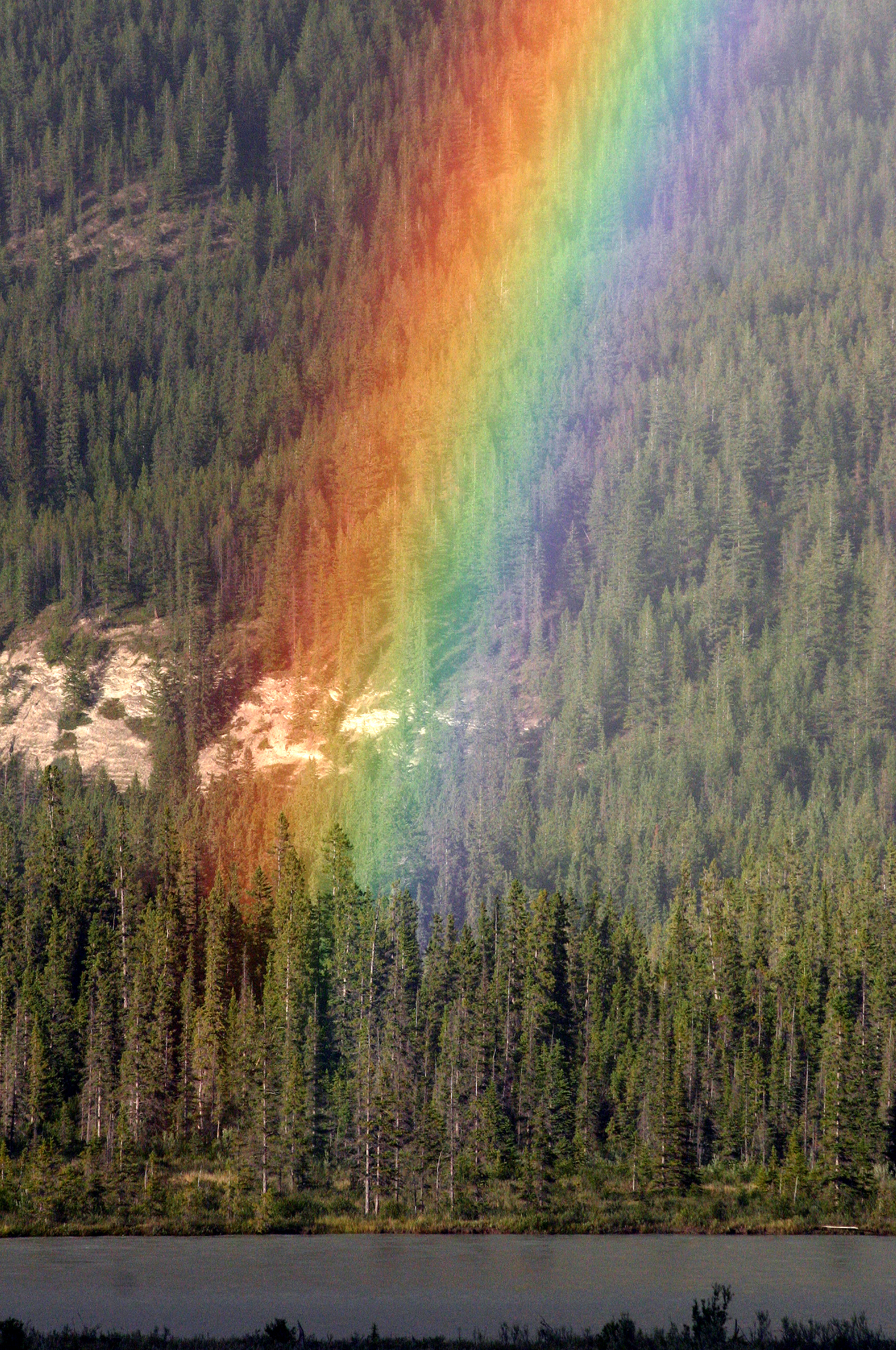
Spectral Color
A spectral color is a color that is evoked by '' monochromatic light'', i.e. either a single wavelength of light in the visible spectrum, or by a relatively narrow band of wavelengths (e.g. lasers). Every wavelength of visible light is perceived as a spectral color; when viewed as a continuous spectrum, these colors are seen as the familiar rainbow. All colors that do not qualify as a spectral color are called ''non-spectral colors'' or ''extra-spectral colors''. Extra-spectral colors cannot be evoked with a single wavelength of light, but rather by a combination of wavelengths. Likewise, light comprising several wavelengths cannot evoke a spectral color. In color spaces In color spaces which include all, or most spectral colors, they form a part of boundary of the set of all real colors. When considering a three-dimensional color space (which including luminance), the spectral colors form a surface. When excluding luminance and considering a two-dimensional color space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromaticity Diagram
Chromaticity is an objective specification of the quality of a color regardless of its luminance. Chromaticity consists of two independent parameters, often specified as hue (h) and colorfulness (s), where the latter is alternatively called saturation, chroma, intensity, or excitation purity. This number of parameters follows from trichromacy of vision of most humans, which is assumed by most models in color science. Quantitative description In color science, the white point of an illuminant or of a display is a neutral reference characterized by a chromaticity; all other chromaticities may be defined in relation to this reference using polar coordinates. The ''hue'' is the angular component, and the ''purity'' is the radial component, normalized by the maximum radius for that hue. Purity is roughly equivalent to the term " saturation" in the HSV color model. The property " hue" is as used in general color theory and in specific color models such as HSV and HSL color spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cie Chart With SRGB Gamut By Spigget
CIE may refer to: Organizations * Cambridge International Examinations, an international examination board * Center for International Education at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst * Cleveland Institute of Electronics, a private technical and engineering educational institution * International Commission on Illumination (''Commission internationale de l'éclairage'') * Companion of the Order of the Indian Empire (C.I.E.) * Computability in Europe, an international organization of computability theorists, computer scientists, mathematicians * CIÉ (Córas Iompair Éireann), the Irish state transport authority * Council on Islamic Education * Transportes Aéreos Cielos Andinos, ICAO code: CIE * Civil Information and Educational Section (CIE), General Headquarters, the Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers in Japan (1945–1952) Science and technology * CIE 1931 color space, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces, created by the International Commission on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monochromatic
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, monochromatic light refers to electromagnetic radiation that contains a narrow band of wavelengths, which is a distinct concept. Application Of an image, the term monochrome is usually taken to mean the same as black and white or, more likely, grayscale, but may also be used to refer to other combinations containing only tones of a single color, such as green-and-white or green-and-red. It may also refer to sepia displaying tones from light tan to dark brown or cyanotype ("blueprint") images, and early photographic methods such as daguerreotypes, ambrotypes, and tintypes, each of which may be used to produce a monochromatic image. In computing, monochrome has two meanings: *it may mean having only one color which is either on or off (also know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accomplishes most of the focussing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focussing of light i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, and cathodoluminescent substances which glow when struck by an electron beam ( cathode rays) in a cathode-ray tube. When a phosphor is exposed to radiation, the orbital electrons in its molecules are excited to a higher energy level; when they return to their former level they emit the energy as light of a certain color. Phosphors can be classified into two categories: fluorescent substances which emit the energy immediately and stop glowing when the exciting radiation is turned off, and phosphorescent substances which emit the energy after a delay, so they keep glowing after the radiation is turned off, decaying in brightness over a period of milliseconds to days. Fluorescent materials are used in applications in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |