|
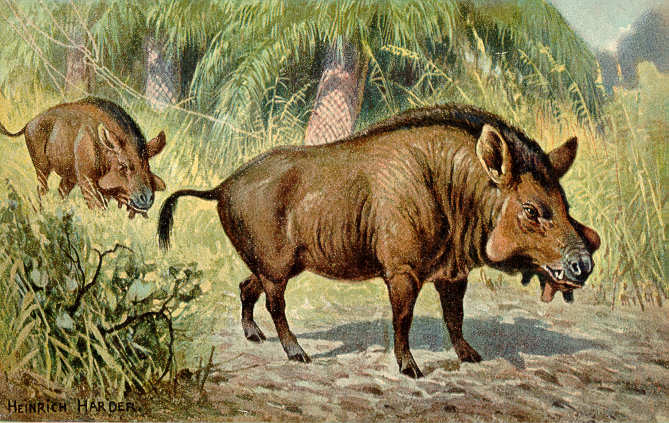
Entelodon
''Entelodon'' (meaning "complete teeth", from Ancient Greek ''entelēs'' "complete" and ''odōn'' "tooth", referring to its "complete" eutherian dentition), is an extinct genus of entelodont artiodactyl endemic to Eurasia. Fossils of species are found in Paleogene strata ranging in age from the Houldjinian (37.2–33.9 mya) until the Rupelian epoch of the early Oligocene (33.9–28.4 mya). Taxonomy It is one of four entelodont genera native to Eurasia, the other three being the primitive ''Eoentelodon'' of late Eocene China, '' Proentelodon'' of middle Eocene Mongolia and the gigantic '' Paraentelodon'' of mid to late Oligocene Central Asia. Description ''Entelodon'' was a fairly typical entelodont, with a large, bulky body, slender legs, and a long snout. Like other entelodonts, ''Entelodon'' had complete eutherian dentition (3 incisors, 1 canine, 3 premolars, and 3 molars per quadrant). It had only two toes on each foot, and its legs were built for fast running.Agus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entelodont
Entelodontidae, the entelodonts, are an extinct family of pig-like artiodactyls (even-toed ungulates) which inhabited the Northern Hemisphere (Asia, Europe, and North America) from the late Eocene to the Middle Miocene epochs, about 38-19 million years ago. Their large heads, low snouts, narrow gait, and proposed omnivorous diet inspires comparisons to suids (true pigs) and tayassuids (peccaries), and historically they have been considered closely related to these families purely on a morphological basis. However, studies which combine morphological and molecular (genetic) data on artiodactyls instead suggest that entelodonts are cetancodontamorphs, more closely related to hippos and cetaceans than to pigs or other ungulates. Description Entelodonts could get quite large, and in many cases are the largest mammals in their respective ecosystems. The largest entelodont known from a complete skeleton was '' Daeodon'', a North American entelodont which could reach an estimated we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Even-toed Ungulate
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proentelodon
''Proentelodon'' is an extinct genus of entelodont artiodactyl The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poster ... from the Middle Eocene of Mongolia. ''P. minutus'' is the oldest representative of the family Entelodontidae, ''P. minutus'' gen. et sp. nov, is described from the Middle Eocene Khaichin Ula II Fauna in Mongolia. References Entelodonts Eocene even-toed ungulates Fossils of Mongolia Fossil taxa described in 2008 Prehistoric even-toed ungulate genera {{Paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraentelodon
''Paraentelodon'' is an extinct entelodont from the Late Oligocene and Oligocene-Miocene boundary of Asia. The fossils of the type species ''P. intermedium'' were found in Georgia, Kazakhstan and China. An indeterminate species represents in Bugti Hills which is the late Oligocene of Pakistan.G. Métais, P.-O. Antoine, L. Marivaux, J.-L. Welcomme, and S. Ducrocq. 2003New artiodactyl ruminant mammal from the late Oligocene of Pakistan Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 48(3):375-382 Discovery and naming ''Paraentelodon'' was named by L. K. Gabunia in 1964 basing on molars and canine teeth that were found in Oligocene sites of Benara, Georgia (Georgian SSR at the time of discovery). It was assigned to Entelodontidae by Carroll (1988). In 1996 Lucas and Emry found ''Neoentelodon'' to be synonymous with ''Paraentelodon''. Although Gabunia did not explain the etymology, the name ''Paraentelodon'' is derived from the Greek ''para''/παρα "beside" or "near", ἐντελής en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Aymard
Auguste Aymard (5 December 1808 – 26 June 1889) was a French prehistorian and palaeontologist who lived and died in Puy-en-Velay Le Puy-en-Velay (, literally ''Le Puy in Velay''; oc, Lo Puèi de Velai ) is the prefecture of the Haute-Loire department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of south-central France. Located near the river Loire, the city is famous for its cat ... (Haute-Loire). He described the fossil '' Entelodon magnus'' and the fossil genera '' Anancus'' and '' Amphechinus''. Auguste Aymard was the archivist for the Departement Haute-Loire and Conservateur of Musée du Puy-en-Velay. He made archaeological discoveries in Puy-en-Velay, Polignac, Haute-Loire and Espaly-Saint-Marcel. Works * Aymard, A., 1848, Essai monographique sur un nouveau genre de Mammifère fossile trouvé dans la Haute-Loire, et nommé Entélodon, ''Annales de la Société d’Agriculture Sciences, Arts et Commerce du Puy'', Vol.12, 1848, pp. 227–268 * Aymard, A. 1854, Acquisiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eoentelodon
''Eoentelodon'' is a small, primitive entelodont, assigned as such by Carroll (1998), from the Middle Eocene of China. It was a very small entelodont, about the size of a modern pig, and was slightly smaller than its North American counterpart, '' Brachyhyops''. ''Eoentelodon'' was synonymized subjectively with ''Brachyhyops'' by Lucas and Emry (2004). However, in 2007, I. Vislobokova determined that ''Eoentelodon'' was not only distinct from ''Brachyhyops'', but more closely related to ''Proentelodon'', another primitive entelodont found in slightly older Middle Eocene strata of Mongolia Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million .... References Entelodonts Eocene even-toed ungulates Fossils of China Fossil taxa described in 1988 Prehistoric even-toed ungulate g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houldjinian
The Houldjinian age is a period of geologic time (37.2–33.9 Ma) within the Late Eocene epoch of the Paleogene used more specifically with Asian Land Mammal Ages. It follows the Ergilian and precedes the Kekeamuan age. The Houldjinian's lower boundary is the approximate base of the Priabonian age. The Houldjinian age is named after the Houldjin gravel beds in Mongolia Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ....Meng, Jin; Wang, YuanQing; Nik, Xijun, Beard, Christopher K.; Sun, Chengkai; Li, Qian; Jin, Xun; and Bai, Bin. Eocene {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canine Tooth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, or (in the context of the upper jaw) fangs, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. They can appear more flattened however, causing them to resemble incisors and leading them to be called ''incisiform''. They developed and are used primarily for firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally as weapons. They are often the largest teeth in a mammal's mouth. Individuals of most species that develop them normally have four, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, separated within each jaw by incisors; humans and dogs are examples. In most species, canines are the anterior-most teeth in the maxillary bone. The four canines in humans are the two maxillary canines and the two mandibular canines. Details There are generally four canine teeth: two in the upper (maxillary) and two in the lower (mandibular) arch. A canine is placed laterall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premolar
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two cusps. Premolars can be considered transitional teeth during chewing, or mastication. They have properties of both the canines, that lie anterior and molars that lie posterior, and so food can be transferred from the canines to the premolars and finally to the molars for grinding, instead of directly from the canines to the molars. Human anatomy The premolars in humans are the maxillary first premolar, maxillary second premolar, mandibular first premolar, and the mandibular second premolar. Premolar teeth by definition are permanent teeth distal to the canines, preceded by deciduous molars. Morphology There is always one large buccal cusp, especially so in the mandibular first premolar. The lower seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopotamidae
Hippopotamidae is a family of stout, naked-skinned, and semiaquatic artiodactyl mammals, possessing three-chambered stomachs and walking on four toes on each foot. While they resemble pigs physiologically, their closest living relatives are the cetaceans. They are formally referred to as hippopotamids. There are two living species of hippopotamid in two genera; the pygmy hippo, '' Choeropsis liberiensis'' of the forests of west Africa, and the common hippo, ''Hippopotamus amphibius''. The term ''hippopotamus'' can also be applied to hippopotamids in general, although it is most frequently used for the common hippo and its respective genus. Characteristics Hippopotamids are large mammals, with short, stumpy legs, and barrel-shaped bodies. They have large heads, with broad mouths, and nostrils placed at the top of their snouts. Like pigs, they have four toes, but unlike pigs, all of the toes are used in walking. Hippopotamids are unguligrade, although, unlike most other such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |