|
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30-nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biology, 58,'' 95–104. https://doi.o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin Structures
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA repair#DNA damage, DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30-nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleosome
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. The structure of a nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight histone proteins and resembles thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Each nucleosome is composed of a little less than two turns of DNA wrapped around a set of eight proteins called histones, which are known as a histone octamer. Each histone octamer is composed of two copies each of the histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. DNA must be compacted into nucleosomes to fit within the cell nucleus. In addition to nucleosome wrapping, eukaryotic chromatin is further compacted by being folded into a series of more complex structures, eventually forming a chromosome. Each human cell contains about 30 million nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones. Nucleosome positions in the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division (where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form). Before this happens, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and both copies are joined by a centromere, resulting either in an X-shaped structure (pictured above), if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-arm structure, if the centromere is located distally. The joined copies are now called si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Condensation
DNA condensation refers to the process of compacting DNA molecules ''in vitro'' or ''in vivo''. Mechanistic details of DNA packing are essential for its functioning in the process of gene regulation in living systems. Condensed DNA often has surprising properties, which one would not predict from classical concepts of dilute solutions. Therefore, DNA condensation ''in vitro'' serves as a model system for many processes of physics, biochemistry and biology. In addition, DNA condensation has many potential applications in medicine and biotechnology. DNA diameter is about 2 nm, while the length of a stretched single molecule may be up to several dozens of centimetres depending on the organism. Many features of the DNA double helix contribute to its large stiffness, including the mechanical properties of the sugar-phosphate backbone, electrostatic repulsion between phosphates (DNA bears on average one elementary negative charge per each 0.17 nm of the double helix), stackin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30-nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers. There are five families of histones which are designated H1/H5 (linker histones), H2, H3, and H4 (core histones). The nucleosome core is formed of two H2A-H2B dimers and a H3-H4 tetramer. The tight wrapping of DNA around histones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malignant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
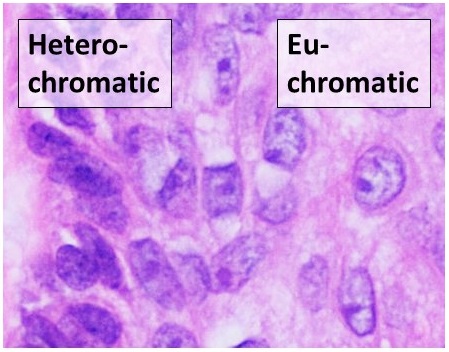
Euchromatin
Euchromatin (also called "open chromatin") is a lightly packed form of chromatin ( DNA, RNA, and protein) that is enriched in genes, and is often (but not always) under active transcription. Euchromatin stands in contrast to heterochromatin, which is tightly packed and less accessible for transcription. 92% of the human genome is euchromatic. In eukaryotes, euchromatin comprises the most active portion of the genome within the cell nucleus. In prokaryotes, euchromatin is the ''only'' form of chromatin present; this indicates that the heterochromatin structure evolved later along with the nucleus, possibly as a mechanism to handle increasing genome size. Structure Euchromatin is composed of repeating subunits known as nucleosomes, reminiscent of an unfolded set of beads on a string, that are approximately 11 nm in diameter. At the core of these nucleosomes are a set of four histone protein pairs: H3, H4, H2A, and H2B. Each core histone protein possesses a 'tail' str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beads On A String
Euchromatin (also called "open chromatin") is a lightly packed form of chromatin ( DNA, RNA, and protein) that is enriched in genes, and is often (but not always) under active transcription. Euchromatin stands in contrast to heterochromatin, which is tightly packed and less accessible for transcription. 92% of the human genome is euchromatic. In eukaryotes, euchromatin comprises the most active portion of the genome within the cell nucleus. In prokaryotes, euchromatin is the ''only'' form of chromatin present; this indicates that the heterochromatin structure evolved later along with the nucleus, possibly as a mechanism to handle increasing genome size. Structure Euchromatin is composed of repeating subunits known as nucleosomes, reminiscent of an unfolded set of beads on a string, that are approximately 11 nm in diameter. At the core of these nucleosomes are a set of four histone protein pairs: H3, H4, H2A, and H2B. Each core histone protein possesses a 'tail' structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone H2B
Histone H2B is one of the 5 main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Featuring a main globular domain and long N-terminal and C-terminal tails, H2B is involved with the structure of the nucleosomes. Structure Histone H2B is a lightweight structural protein made of 126 amino acids. Many of these amino acids have a positive charge at cellular pH, which allows them to interact with the negatively charged phosphate groups in DNA. Along with a central globular domain, histone H2B has two flexible histone tails that extend outwards – one at the N-terminal end and one at C-terminal end. These are highly involved in condensing chromatin from the beads-on-a-string conformation to a 30-nm fiber. Similar to other histone proteins, histone H2B has a distinct histone fold that is optimized for histone-histone as well as histone-DNA interactions. Two copies of histone H2B come together with two copies each of histone H2A, histone H3, and histone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterochromatin
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or '' condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continue between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a role in the expression of genes. Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; however, according to Volpe et al. (2002), and many other papers since, much of this DNA is in fact transcribed, but it is continuously turned over via RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS). Recent studies with electron microscopy and OsO4 staining reveal that the dense packing is not due to the chromatin. Constitutive heterochromatin can affect the genes near itself (e.g. position-effect variegation). It is usually repetitive and forms structural functions such as centromeres or telomeres, in addition to acting as an attractor for other gene-expression or repression signals. Facultative hete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservative rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there are two distinct types of cell division: a vegetative division (mitosis), producing daughter cells genetically identical to the parent cell, and a cell division that produces Haploidisation, haploid gametes for sexual reproduction (meiosis), reducing the number of chromosomes from two of each type in the diploid parent cell to one of each type in the daughter cells. In cell biology, mitosis (Help:IPA/English, /maɪˈtoʊsɪs/) is a part of the cell cycle, in which, replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is preceded by the S stage of interph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |