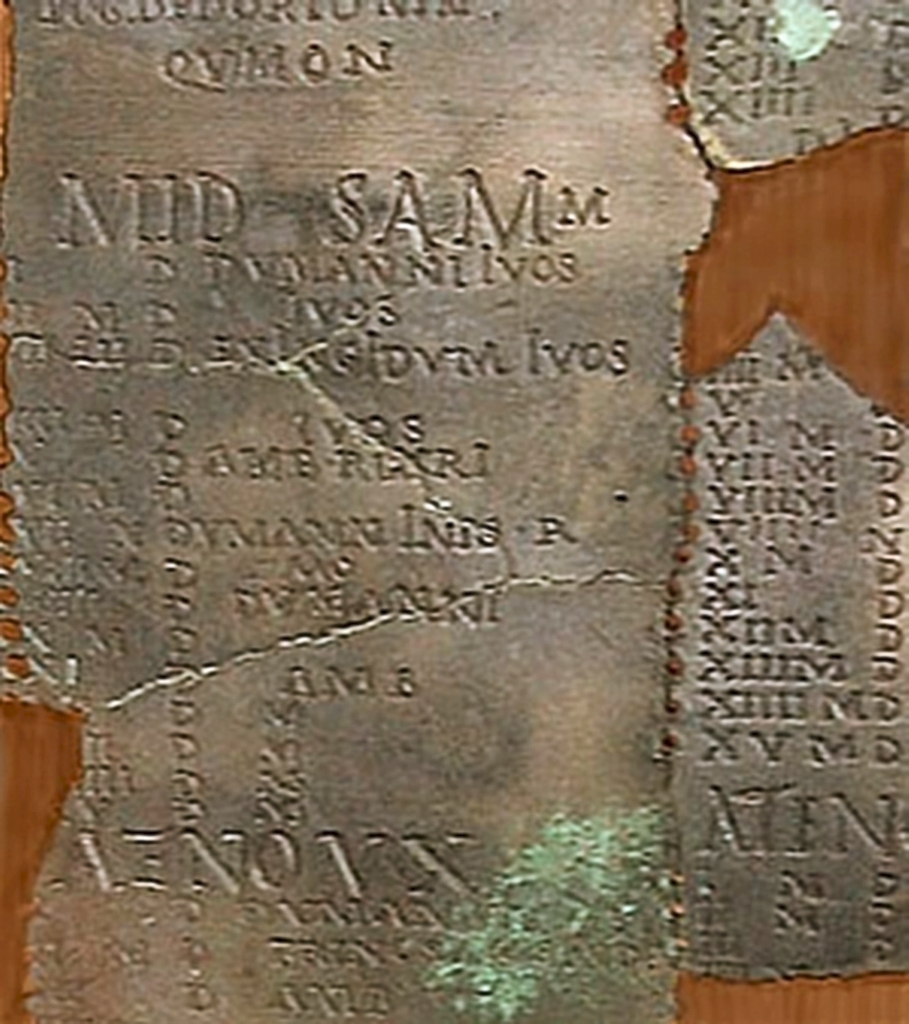|
Calan Gaeaf
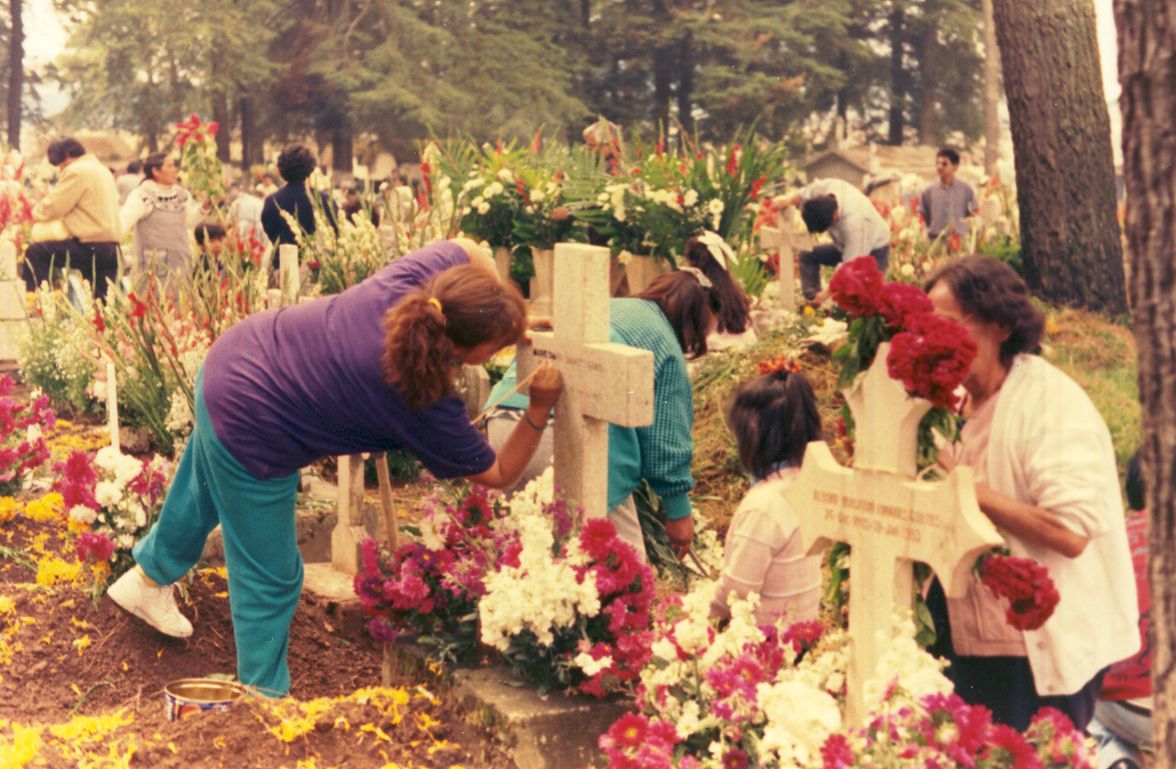
''Calan Gaeaf'' is the name of the first day of winter in Wales, observed on 1 November.Davies (2008), pg 107. The night before is ''Nos Galan Gaeaf'' or ''Noson Galan Gaeaf'', an ''Ysbrydnos'' ("spirit night"Jones (2020), pg 161.) when spirits are abroad. Traditionally, people avoid churchyards, stiles, and crossroads, since spirits are thought to gather there. The event was first recorded in literature as 'Kalan Gayaf' via a 13th century manuscript, known today as the Black Book of Carmarthen and due to the Welsh language originating from oral tradition, Calan Gaeaf may have existed far earlier. Traditions Dancing On Nos Galan Gaeaf, women and children would dance around a bonfire and everyone would write their names on, or otherwise mark, rocks and place them in and around said fire. When the fire started to die out,Jones (2020), pg 157. they would all run home, believing if they stayed, ''Yr Hwch Ddu Gwta'' (a bad omen that took the form of a tailless black sow with a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2021 of 3,107,500 and has a total area of . Wales has over of coastline and is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon (), its highest summit. The country lies within the Temperateness, north temperate zone and has a changeable, maritime climate. The capital and largest city is Cardiff. Welsh national identity emerged among the Celtic Britons after the Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was formed as a Kingdom of Wales, kingdom under Gruffydd ap Llywelyn in 1055. Wales is regarded as one of the Celtic nations. The Conquest of Wales by Edward I, conquest of Wales by Edward I of England was completed by 1283, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stile
A stile is a structure or opening that provides people passage over or through a boundary via steps, ladders, or narrow gaps. Stiles are often built in rural areas along footpaths, fences, walls, or hedges that enclose animals, allowing people to move freely. Types In the United Kingdom many stiles were built under legal compulsion (see Rights of way in the United Kingdom). Recent changes in UK government policy towards farming have encouraged upland landowners to make access more available to the public, and this has seen an increase in the number of stiles and an improvement in their overall condition. However stiles are deprecatedBritish Standard BS5709:2018 Gaps Gates & Stiles () and are increasingly being replaced by gates or kissing gates or, where the field is arable, the stile removed. Many legacy stiles remain, however, in a variety of forms (as is also the case in the US, where there is no standard). As well as having a variety of forms, stiles also sometimes include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Book Of Carmarthen
The Black Book of Carmarthen ( cy, Llyfr Du Caerfyrddin) is thought to be the earliest surviving manuscript written solely in Welsh. The book dates from the mid-13th century; its name comes from its association with the Priory of St. John the Evangelist and Teulyddog at Carmarthen, and is referred to as black due to the colour of its binding. It is currently part of the collection of the National Library of Wales, where it is catalogued as NLW Peniarth MS 1. This was one of the collection of manuscripts amassed at the mansion of Hengwrt, near Dolgellau, Gwynedd, by Welsh antiquary Robert Vaughan (c.1592–1667); the collection later passed to the newly established National Library of Wales as the Peniarth or Hengwrt-Peniarth Manuscripts. It is believed that the manuscript is first recorded when it came into the possession of Sir John Price of Brecon (1502?–1555), whose work was to search the monasteries dissolved by Henry VIII. It was given to him by the treasurer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Bobbing
Apple bobbing, also known as bobbing for apples, is a game often played on Halloween. The game is played by filling a tub or a large basin with water and putting apples in the water. Because apples are less dense than water, they will float at the surface. Players (usually children) then try to catch one with their teeth. Use of arms is not allowed, and the hands are often tied behind the back to prevent cheating. In Scotland, this may be called "dooking"Apple dookers make record attempt BBC News, 2 October 2008 (i.e., ducking). In northern England, the game is often called apple ducking or duck-apple. In |
Samhain
Samhain ( , , , ; gv, Sauin ) is a Gaelic festival on 1 NovemberÓ hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth Legend and Romance: An Encyclopaedia of the Irish Folk Tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. p. 402. Quote: "The basic Irish division of the year was into two parts, the summer half beginning at Bealtaine (May 1st) and the winter half at Samhain (November 1st) ... The festivals properly began at sunset on the day before the actual date, evincing the Celtic tendency to regard the night as preceding the day". marking the end of the harvest season and beginning of winter or "darker half" of the year. Celebrations begin on the evening of 31 October, since the Celtic day began and ended at sunset. This is about halfway between the autumnal equinox and winter solstice. It is one of the four Gaelic seasonal festivals along with Imbolc, Beltaine and Lughnasa. Historically it was widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland, Galicia and the Isle of Man (where it is spelled Sauin). A simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halloween
Halloween or Hallowe'en (less commonly known as Allhalloween, All Hallows' Eve, or All Saints' Eve) is a celebration observed in many countries on 31 October, the eve of the Western Christian feast of All Saints' Day. It begins the observance of Allhallowtide, the time in the liturgical year dedicated to remembering the dead, including saints ( hallows), martyrs, and all the faithful departed. One theory holds that many Halloween traditions were influenced by Celtic harvest festivals, particularly the Gaelic festival Samhain, which are believed to have pagan roots. Some go further and suggest that Samhain may have been Christianized as All Hallow's Day, along with its eve, by the early Church. Other academics believe Halloween began solely as a Christian holiday, being the vigil of All Hallow's Day. Celebrated in Ireland and Scotland for centuries, Irish and Scottish immigrants took many Halloween customs to North America in the 19th century,Brunvand, Jan (editor). ''Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Day Of The Dead
The Day of the Dead ( es, Día de Muertos or ''Día de los Muertos'') is a holiday traditionally celebrated on November 1 and 2, though other days, such as October 31 or November 6, may be included depending on the locality. It is widely observed in Mexico, where it largely developed, and is also observed in other places, especially by people of Mexican heritage. Although related to the simultaneous Christian remembrances for Hallowtide, it has a much less solemn tone and is portrayed as a holiday of joyful celebration rather than mourning. The multi-day holiday involves family and friends gathering to pay respects and to remember friends and family members who have died. These celebrations can take a humorous tone, as celebrants remember funny events and anecdotes about the departed. Traditions connected with the holiday include honoring the deceased using calaveras and marigold flowers known as ''cempazúchitl'', building home altars called '' ofrendas'' with the favorite fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allantide
Allantide ( kw, italic=yes, Kalan Gwav, meaning ''first day of winter'', or ''Nos Kalan Gwav'', meaning ''eve of the first day of winter'' and ''Dy' Halan Gwav'', meaning ''day of the first day of winter''), also known as Saint Allan's Day or the Feast of Saint Allan, is a Cornish festival that was traditionally celebrated on the night of 31 October, as well as the following day time, and known elsewhere as Allhallowtide. The festival in Cornwall is the liturgical feast day of St Allan (also spelled St Allen or St Arlan), who was the bishop of Quimper in the sixth century. As such, Allantide is also known as Allan Night and Allan Day. The origins of the name Allantide also probably stem from the same sources as Hollantide (Wales and the Isle of Man) and Hallowe'en itself. As with the start of the celebration of Allhallowtide in the rest of Christendom, church bells were rung in order to comfort Christian souls in the intermediate state. Another important part of this festiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holidays In Wales
This is a list of days celebrated in Wales. There are holidays traditionally celebrated in Wales that are not shared with the rest of the United Kingdom. Excluding those that fall at the same time as UK-wide public holidays, none of these traditional holidays are bank holidays. There is, however, much support for the recognition of St David's Day as a bank holiday in Wales, in the same way as St Patrick's Day in Northern Ireland, and St Andrew's Day in Scotland. Many of the historical seasonal festivals originate in the Celtic culture of Wales, as does the manner of their celebration. Historic Practice As recorded in the Laws of Hywel Dda, the three main holidays (''gwyliau'') of the medieval Welsh kingdoms were Christmas (''Nadolig''), Easter (''Pasg''), and Whitsuntide (''Sulgwyn''). Other important holidays were the feasts of St Patrick (''Gwyl Badric'') on 17 March; St. Quiricus (''Gwyl Giric'') on 16 June; the Beheading of John the Baptist (called in Welsh ''Gwyl Ieuan y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November Observances
November is the eleventh and penultimate month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian Calendars, the fourth and last of four months to have a length of 30 days and the fifth and last of five months to have a length of fewer than 31 days. November was the ninth month of the calendar of Romulus . November retained its name (from the Latin ''novem'' meaning "nine") when January and February were added to the Roman calendar. November is a month of late spring in the Southern Hemisphere and late autumn in the Northern Hemisphere. Therefore, November in the Southern Hemisphere is the seasonal equivalent of May in the Northern Hemisphere and vice versa. In Ancient Rome, Ludi Plebeii was held from November 4–17, Epulum Jovis was held on November 13 and Brumalia celebrations began on November 24. These dates do not correspond to the modern Gregorian calendar. November was referred to as Blōtmōnaþ by the Anglo-Saxons. Brumaire and Frimaire were the months on which November ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)