|
Battle Of Dyrrhachium (48 BC)
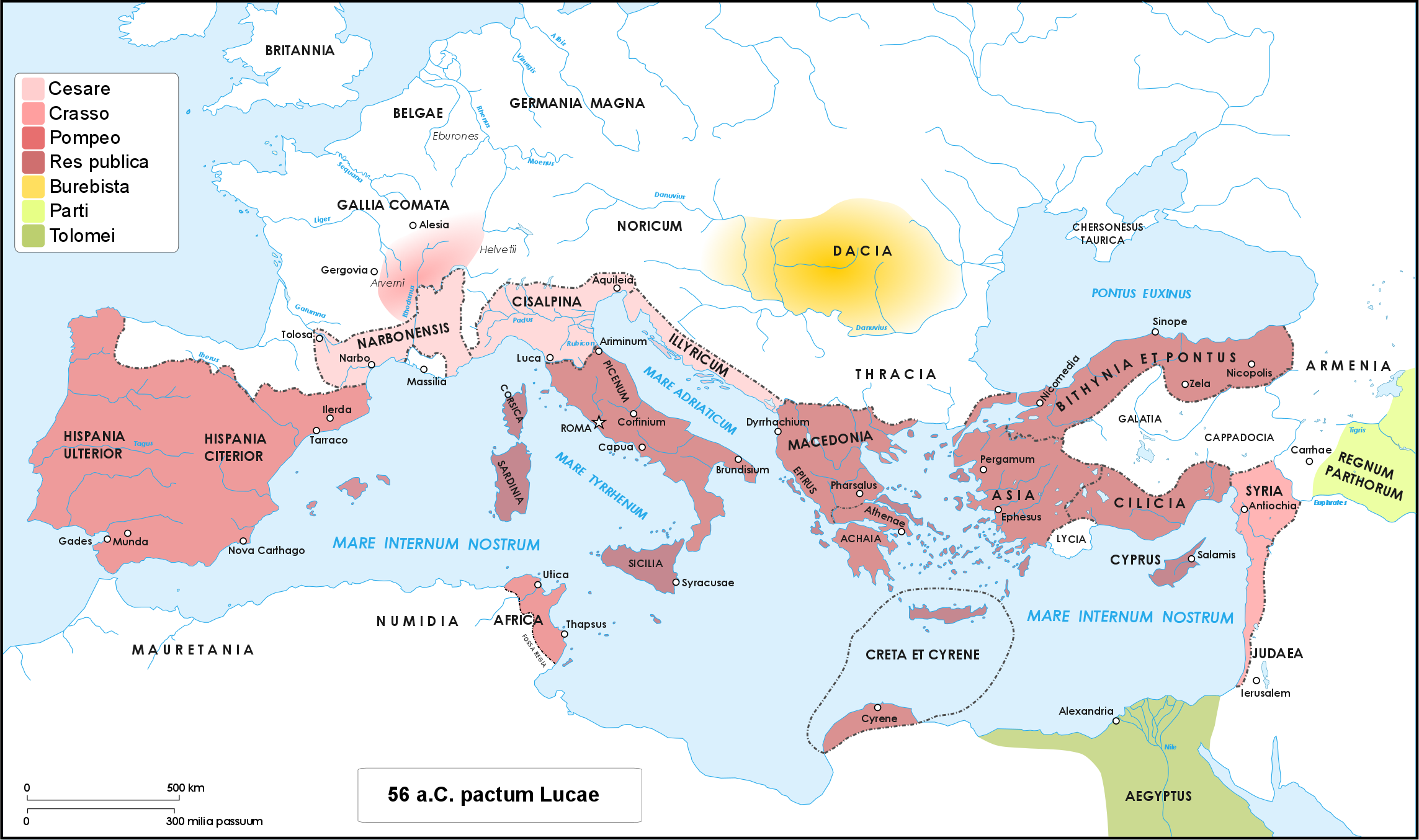
The Battle of Dyrrachium (or Dyrrhachium) took place from April to late July 48 BC near the city of Dyrrachium, modern day Durrës in what is now Albania. It was fought between Gaius Julius Caesar and an army led by Gnaeus Pompey during Caesar's civil war. Caesar attempted to capture the vital Pompeian logistics hub of Dyrrachium but was unsuccessful after Pompey occupied it and the surrounding heights. In response, Caesar besieged Pompey's camp and constructed a circumvallation thereof, until, after months of skirmishes, Pompey was able to break through Caesar's fortified lines, forcing Caesar to make a strategic retreat into Thessaly. After the battle, Pompey pursued Caesar into Thessaly and then towards Pharsalus, where the decisive battle of Caesar's Greek campaign would be fought. Background Starting in 49 BC, Julius Caesar had crossed the Rubicon and started a civil war in the Roman republic. Starting in January with a lightning advance against the Pomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the autocratic Roman Empire. Antony was a relative and supporter of Julius Caesar, and served as one of his generals during the conquest of Gaul and the Civil War. Antony was appointed administrator of Italy while Caesar eliminated political opponents in Greece, North Africa, and Spain. After Caesar's assassination in 44 BC, Antony joined forces with Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, another of Caesar's generals, and Octavian, Caesar's great-nephew and adopted son, forming a three-man dictatorship known to historians as the Second Triumvirate. The Triumvirs defeated Caesar's killers, the ''Liberatores'', at the Battle of Philippi in 42 BC, and divided the government of the Republic between themselves. Antony was assigned Rome's eastern provinces, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
48 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 48 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Vatia (or, less frequently, year 706 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 48 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Republic * Consuls: Gaius Julius Caesar and Publius Servilius Vatia Isauricus. Caesar is named consul for a period of five years. * Caesar's Civil War: ** January 4 – Julius Caesar lands at Dyrrhachium ( Durazzo). ** March – Mark Antony joins Julius Caesar. ** April – Siege of Dyrrhachium: Julius Caesar builds a fortified line of entrenchments and besieges Pompey the Great. ** The Roman temple to Bellona on the Capitolinus outside Rome is burnt to the ground. ** May – Publius Servilius Vatia Isauricus, co-consul with Julius Caesar, destroys Caelius's magistrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of Caesar's Civil War
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Durrës
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albania In The Roman Era
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares land borders with Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south. Tirana is its capital and largest city, followed by Durrës, Vlorë, and Shkodër. Albania displays varied climatic, geological, hydrological, and morphological conditions, defined in an area of . It possesses significant diversity with the landscape ranging from the snow-capped mountains in the Albanian Alps as well as the Korab, Skanderbeg, Pindus and Ceraunian Mountains to the hot and sunny coasts of the Albanian Adriatic and Ionian Sea along the Mediterranean Sea. Albania has been inhabited by different civilisations over time, such as the Illyrians, Thracians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Venetians, and Ottoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Roman Republic
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, wherea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus (consul 54 BC)
Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus, consul in 54 BC, was an enemy of Julius Caesar and a strong supporter of the aristocratic () party in the late Roman Republic. Biography Ahenobarbus was born as the son of consul Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus. His grandfather Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus was a general and consul who led a campaign to conquer southern Gaul against the Allobroges. He is first mentioned in 70 BC by Cicero as a witness against Verres. In 61, he was curule aedile, when he exhibited a hundred Numidian lions, and continued the games so long that the people were obliged to leave the circus before the exhibition was over, in order to take food, which was the first time they had done so. This pause in the games was called ''diludium''. He married Porcia, the sister of Cato the Younger, and in his aedileship supported the latter in his proposals against bribery at elections, which were directed against Pompey, who was purchasing votes for Afranius. The political opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Labienus
Titus Labienus (c. 10017 March 45 BC) was a high-ranking military officer in the late Roman Republic. He served as tribune of the Plebs in 63 BC. Although mostly remembered as one of Julius Caesar's best lieutenants in Gaul, mentioned frequently in the accounts of his military campaigns, Labienus chose to oppose him during the Civil War and was killed at Munda. He was the father of Quintus Labienus. Biography Early career As his praetorship was in 60 or 59 BC, Titus Labienus most likely was born around 100 BC.Tyrrell(3) Many sources suggest that he came from the town of Cingulum in Picenum. His family was of equestrian status. He most likely had early ties with Pompey during his time as a patron for Picenum and his desire to rise in military rank. His early service was c. 78–75 BC in Cilicia under Publius Servilius Vatia Isauricus fighting pirates and the Isaurian hill tribes. Tribune of the Plebs, Trial of Gaius Rabirius In 63 BC, Titus Labienus was a tribune of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubicon
The Rubicon ( la, Rubico; it, Rubicone ; rgn, Rubicôn ) is a shallow river in northeastern Italy, just north of Rimini. It was known as Fiumicino until 1933, when it was identified with the ancient river Rubicon, famously crossed by Julius Caesar in 49 BC. The river flows for around from the Apennine Mountains to the Adriatic Sea through the south of the Emilia-Romagna region, between the towns of Rimini and Cesena. History The Latin word comes from the adjective , meaning "red". The river was so named because its waters are colored red by iron deposits in the riverbed. During the Roman Republic, the Rubicon marked the boundary between the Roman province of Cisalpine Gaul and Italy proper, controlled directly by Rome and its (allies), to the south. On the north-western side, the border was marked by the river Arno, a much wider and more important waterway, which flows westward from the Apennine Mountains (the Arno and the Rubicon rise not far from each other) into the Ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

