|
Agroecomyrmecinae
Agroecomyrmecinae is a subfamily of ants containing two extant and two fossil genera. The subfamily was originally classified in 1930 by Carpenter as Agroecomyrmecini, a Myrmicinae tribe. Bolton raised the tribe to subfamily status in 2003, suggesting that Agroecomyrmecinae might be the sister taxon to Myrmicinae. It has since been discovered to be one of the earliest lineages of ants, a clade from the basal polytomy for all ants. In 2014, the subfamily was expanded to two tribes. The tribe Ankylomyrmini was moved from the subfamily Myrmicinae to Agroemyrmecinae. Tribes and genera *Agroecomyrmecinae Carpenter, 1930 ** Agroecomyrmecini Carpenter, 1930 *** †''Agroecomyrmex'' Wheeler, 1910 **** †''Agroecomyrmex duisburgi'' Wheeler, 1910 *** †''Eulithomyrmex'' Carpenter, 1935 ****†''Eulithomyrmex rugosus'' Carpenter, 1930 ****†''Eulithomyrmex striatus'' Carpenter, 1930 *** ''Tatuidris'' Brown & Kempf, 1968 **** ''Tatuidris tatusia'' Brown & Kempf, 1968 (=''T. kapasi'' Lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatuidris Tatusia
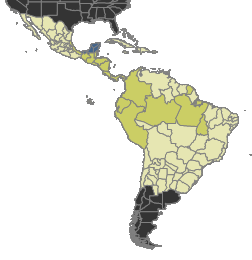
''Tatuidris'', or armadillo ant, is a rare genus of ants consisting of a single species, ''Tatuidris tatusia''. The ants are small in size and inhabit the leaf litter of Neotropical forests in Central and South America, from Mexico to Brazil. Workers are ferruginous-colored to dark red and present a distinctive morphology, consisting of a shield-like head with a broad vertex, ventrally-turned heavy mandibles which do not overlap at full closure, and unique among ants – an antenna socket apparatus sitting upside-down. Little is known about the biology of the ants, but they are likely nocturnal and specialist predators. ''Tatuidris'' was first described in 1968 and initially placed in the myrmicine tribe Agroecomyrmecini, together with two fossil genera. Since the original description, the systematic status of the tribe has been the focus of debate. Taxonomy ''Tatuidris tatusia'' is the only species in ''Tatuidris'', a monotypic genus and one of only two extant gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatuidris
''Tatuidris'', or armadillo ant, is a rare genus of ants consisting of a single species, ''Tatuidris tatusia''. The ants are small in size and inhabit the leaf litter of Neotropical forests in Central and South America, from Mexico to Brazil. Workers are ferruginous-colored to dark red and present a distinctive morphology, consisting of a shield-like head with a broad vertex, ventrally-turned heavy mandibles which do not overlap at full closure, and unique among ants – an antenna socket apparatus sitting upside-down. Little is known about the biology of the ants, but they are likely nocturnal and specialist predators. ''Tatuidris'' was first described in 1968 and initially placed in the myrmicine tribe Agroecomyrmecini, together with two fossil genera. Since the original description, the systematic status of the tribe has been the focus of debate. Taxonomy ''Tatuidris tatusia'' is the only species in ''Tatuidris'', a monotypic genus and one of only two extant gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eulithomyrmex
''Eulithomyrmex'' is an extinct genus of ant in the formicid subfamily Agroecomyrmecinae. The genus contains two described species, ''Eulithomyrmex rugosus'' and ''Eulithomyrmex striatus''. ''Eulithomyrmex'' is known from a group of Late Eocene fossils which were found in North America. History and classification When described the genus ''Eulithomyrmex'' was known from over forty separate fossils preserved as impressions in fine shales of the Florissant formation in Colorado. The formation is composed of successive lake deposits which have preserved a diverse assemblage of insects. The insects and plants suggest a climate similar to modern Southeastern North America, with a number of taxa represented that are now found in the subtropics to tropics and confined to the old world. When ''Eulithomyrmex'' was described, the Florissant formation was considered to be Miocene in age, based on the flora and fauna preserved. Successive research and fossil descriptions moved the ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylomyrma
''Ankylomyrma'' is a genus of large arboreal ants in the subfamily Agroecomyrmecinae. It contains the single species ''Ankylomyrma coronacantha'', the sole member of the tribe Ankylomyrmini. The genus is known from Africa Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area .... Nothing is known about their biology. The genus was moved from the subfamily Myrmicinae to Agroecomyrmecinae in 2014. References External links * Agroecomyrmecinae Monotypic ant genera Hymenoptera of Africa {{ant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agroecomyrmex
''Agroecomyrmex'' is an extinct genus of ants in the formicid subfamily Agroecomyrmecinae, for which it is the type genus. The genus contains a single described species, ''Agroecomyrmex duisburgi''. ''Agroecomyrmex'' is known from a group of Middle Eocene fossils which were found in Europe. History and classification When described ''Agroecomyrmex'' was known only from five separate fossils, the holotype worker, number 639/10246 plus three paratype workers and a single paratype female, which are fossilized as inclusions in transparent chunks of Baltic amber. Baltic amber is approximately forty six million years old, having been deposited during Lutetian stage of the Middle Eocene. There is debate on what plant family the amber was produced by, with evidence supporting relatives of either an '' Agathis'' relative or a ''Pseudolarix'' relative. All the type specimens were collected over 125 years ago, and when first described were part of the University of Königsberg amber c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalacromyrmecini
Fungus-growing ants (tribe Attini) comprise all the known fungus-growing ant species participating in ant–fungus mutualism. They are known for cutting grasses and leaves, carrying them to their colonies' nests, and using them to grow fungus on which they later feed. Their farming habits typically have large effects on their surrounding ecosystem. Many species farm large areas surrounding their colonies and leave walking trails that compress the soil, which can no longer grow plants. Attine colonies commonly have millions of individuals, though some species only house a few hundred. They are the sister group to the subtribe Dacetina. Leafcutter ants, including '' Atta'' and ''Acromyrmex'', make up two of the genera. Their cultivars mostly come from the fungal tribe Leucocoprineae of family Agaricaceae. Attine gut microbiota is often not diverse due to their primarily monotonous diets, leaving them at a higher risk than other beings for certain illnesses. They are especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraponerinae
''Paraponera'' is a genus of ants and the only genus in the subfamily Paraponerinae. The name means "near-''Ponera''". It consists of two species: the extant ''Paraponera clavata'', also known as a bullet ant, found in the Neotropics, and the very small fossil species ''Paraponera dieteri'' known from Dominican amber (Early Miocene; 16-19 million years ago). Bullet ants are so named for the pain caused by their venomous stings. The intensely painful sting is toxic to invertebrates as well as vertebrates and a major component is the neurotoxic peptide poneratoxin. Species * ''Paraponera clavata'' (Fabricius, 1775) * †''Paraponera dieteri ''Paraponera dieteri'' is an extinct species of Miocene ant Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in ...'' Baroni Urbani, 1994 References External links * Paraponerinae Ant genera Messini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades. Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, and synapomorphy, all mean a trait shared between species because they share an ancestral species. Apomorphic and synapomorphic characteristics convey much information about evolutionary clades and can be used to define taxa. However, plesiomorphic and symplesiomorphic characteristics cannot. The term ''symplesiomorphy'' was introduced in 1950 by German entomologist Willi Hennig. Examples A backbone is a plesiomorphic trait shared by birds and mammals, and does not help in placing an animal in one or the other of these two clades. Birds and mammals share this trait because both clades are descended from the same far distant ancestor. Other clades, e.g. snakes, lizards, turtles, fish, frogs, all have backbones and none are either birds no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poneromorph Subfamilies
In ants, the traditional subfamily Ponerinae has been subdivided into several Poneromorph subfamilies, with several former tribes now elevated to subfamily rank. According to this analysis, some ponerine groups may be more closely related to other subfamilies than to each other. The subfamilies of "poneromorph" Ant, Formicidae include: *Amblyoponinae *Ectatomminae (apparently related to the widely distributed and highly diverse Myrmicinae) *Heteroponerinae *Paraponerinae *Ponerinae (in a much more restricted sense) *Proceratiinae. Long considered primitive on the basis of retention of a typical hymenopteran Stinger, sting and pupae in Pupa#Cocoon, cocoons, some groups among the poneromorphs exhibit considerable specialization in predatory habits and mandibular form. These two evolutionary developments are often, but not necessarily, seen in association: elongated mandibles with modified teeth for handling large and potentially toxic prey in ''Amblyopone'' and ''Thaumatomyrmex'', an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |