work breakdown structure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in
A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in
Earned Value Management Tutorial Module 2: Work Breakdown StructureOffice of Science, Tools & Resources for Project Management
science.energy.gov. Accessed 27. Dec 2011.
It includes WBS definitions for specific defense materiel commodity systems and addresses WBS elements that are common to all systems. Defense Materiel Item categories from MIL-STD-881F are: * Aircraft Systems * Electronic/Generic Systems * Missile/Ordnance Systems * Strategic Missile Systems * Sea Systems * Space Systems * Ground Vehicle Systems * Unmanned Maritime Systems * Launch Vehicle Systems * Information Systems/Defense Business Systems The common elements identified in MIL-STD-881F, Appendix K are: Integration, assembly, test, and checkout; Systems engineering; Program management; System test and evaluation; Data; Peculiar support equipment; Common support equipment; Operational/Site activation; Contractor Logistics Support; Industrial facilities; Initial spares and repair parts. The standard also includes additional common elements unique to Space Systems, Launch Vehicle Systems, and Strategic Missile Systems. In 1987, the
how to create work breakdown structure WBS using standard Division of workEverySpec.Com copies of MIL-HDBK-881 versionsASSIST entry for MIL-HDBK-881C
* ttps://www.workbreakdownstructure.com/how-to-make-a-work-breakdown-structure.php How to Make a Work Breakdown Structurebr>NASA Work Breakdown Structure Handbook, NASA/SP-2010-3404, January 2010
{{Systems Engineering Business process modelling Schedule (project management) Systems engineering
 A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in
A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
and systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering and engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage complex systems over their Enterprise life cycle, life cycles. At its core, systems engineering uti ...
is a breakdown of a project into smaller components. It is a key project management element that organizes the team's work into manageable sections. The Project Management Body of Knowledge defines the work-breakdown structure as a "hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables."
A WBS provides the necessary framework for detailed cost estimation and control while providing guidance for schedule
A schedule (, ) or a timetable, as a basic time-management tool, consists of a list of times at which possible tasks, events, or actions are intended to take place, or of a sequence of events in the chronological order in which such thing ...
development and control.Booz, Allen & HamiltoEarned Value Management Tutorial Module 2: Work Breakdown Structure
science.energy.gov. Accessed 27. Dec 2011.
Overview
WBS is a hierarchical and incremental decomposition of the project into deliverables (from major ones such as phases to the smallest ones, sometimes known as work packages). It is a tree structure, which shows a subdivision of effort required to achieve an objective, for example, a program,project
A project is a type of assignment, typically involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a specific objective.
An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of events: a "set of interrelated tasks to be ...
, and contract
A contract is an agreement that specifies certain legally enforceable rights and obligations pertaining to two or more parties. A contract typically involves consent to transfer of goods, services, money, or promise to transfer any of thos ...
. In a project or contract, the WBS is developed by starting with the end objective and successively subdividing it into manageable components in terms of size, duration, and responsibility (e.g., systems, subsystems, components, tasks, subtasks, and work packages) which include all steps necessary to achieve the objective.
The work breakdown structure provides a common framework for the natural development of the overall planning and control of a contract and is the basis for dividing work into definable increments from which the statement of work
A statement of work (SOW) is a document routinely employed in the field of project management. It is the narrative description of a project's work requirement. It defines project-specific activities, deliverables and timelines for a vendor providin ...
can be developed and technical, schedule, cost, and labor hour reporting can be established.
A work breakdown structure permits the summing of subordinate costs for tasks, materials, etc., into their successively higher level "parent" tasks, materials, etc. For each element of the work breakdown structure, a description of the task to be performed is generated. This technique (sometimes called a ''system breakdown structure'') is used to define and organize the total scope of a project
A project is a type of assignment, typically involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a specific objective.
An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of events: a "set of interrelated tasks to be ...
.
The WBS is organized around the primary products of the project (or planned outcomes) instead of the work needed to produce the products (planned actions). Since the planned outcomes are the desired ends of the project, they form a relatively stable set of categories in which the costs of the planned actions needed to achieve them can be collected. A well-designed WBS makes it easy to assign each project activity to one and only one terminal element of the WBS. In addition to its function in cost accounting, the WBS also helps map requirements from one level of system specification to another, for example, a cross-reference matrix mapping functional requirements to high level or low-level design documents.
The WBS may be displayed horizontally in outline form or vertically as a tree structure (like an organization chart).
The development of the WBS normally occurs at the start of a project and precedes detailed project and task planning. Through , an iterative process in project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
knowledge, the details of project management plan and amount of information will increase, and initial estimates of items such as project scope description, planning, budget, etc. will become more accurate. It also helps the project team to make the project plan with more details.
Types
PMI's Practice Standard for Work Breakdown Structures identifies two major types of work breakdown structures.
Deliverable
A deliverable is a tangible or intangible good or service produced as a result of a project that is intended to be delivered to a customer (either internal or external). A deliverable could be a report, a document, a software product, a server upgr ...
-oriented WBS
Deliverable-oriented WBS, also known as Product breakdown structure uses key deliverables to group each work in the project.
Phase-oriented WBS
Phase-oriented WBS groups the work under key phases or stages of project lifecycle.History
The concept of work breakdown structure was developed with the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) by theUnited States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and superv ...
(DoD). PERT was introduced by the U.S. Navy in 1957 to support the development of its Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris (Latinisation of names, Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an ...
missile program. While the term "work breakdown structure" was not used, this first implementation of PERT did organize the tasks into product-oriented categories.
By June 1962, DoD, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
, and the aerospace industry published a document for the PERT/COST system, which described the WBS approach. This guide was endorsed by the Secretary of Defense for adoption by all services. In 1968, the DoD issued "Work Breakdown Structures for Defense Materiel Items" (MIL-STD-881), a military standard requiring the use of work breakdown structures across the DoD.
The document has been revised several times. As of May 2023, the most recent revision is F, released 13 May 2022. The version history and current revision of the standard are posted on the Defense Logistics Agency (DLA) ASSIST web sitIt includes WBS definitions for specific defense materiel commodity systems and addresses WBS elements that are common to all systems. Defense Materiel Item categories from MIL-STD-881F are: * Aircraft Systems * Electronic/Generic Systems * Missile/Ordnance Systems * Strategic Missile Systems * Sea Systems * Space Systems * Ground Vehicle Systems * Unmanned Maritime Systems * Launch Vehicle Systems * Information Systems/Defense Business Systems The common elements identified in MIL-STD-881F, Appendix K are: Integration, assembly, test, and checkout; Systems engineering; Program management; System test and evaluation; Data; Peculiar support equipment; Common support equipment; Operational/Site activation; Contractor Logistics Support; Industrial facilities; Initial spares and repair parts. The standard also includes additional common elements unique to Space Systems, Launch Vehicle Systems, and Strategic Missile Systems. In 1987, the
Project Management Institute
The Project Management Institute (PMI, legally Project Management Institute, Inc.) is a U.S.-based not-for-profit professional organization for project management.
Overview
PMI serves more than five million professionals including over 680,0 ...
(PMI) documented expanding these techniques across non-defense organizations. The ''Project Management Body of Knowledge'' (PMBOK) Guide provides an overview of the WBS concept, while the "Practice Standard for Work Breakdown Structures" is comparable to the DoD standard but is intended for more general application.
Design principles
100% rule
An important design principle for work breakdown structures is called the 100% rule. It has been defined as follows: :The 100% rule states that the WBS includes 100% of the work defined by the project scope and captures all deliverables – internal, external, interim – in terms of the work to be completed, including project management. The 100% rule is one of the most important principles guiding the development, decomposition, and evaluation of the WBS. The rule applies at all levels within the hierarchy: the sum of the work at the "child" level must equal 100% of the work represented by the "parent", and the WBS should not include any work that falls outside the actual scope of the project, that is, it cannot include more than 100% of the work... It is important to remember that the 100% rule also applies to the activity level. The work represented by the activities in each work package must add up to 100% of the work necessary to complete the work package.Mutually exclusive elements
Mutually exclusive: In addition to the 100% rule, there must be no overlap in scope definition between different elements of a work breakdown structure. This ambiguity could result in duplicated work or miscommunications about responsibility and authority. Such overlap could also confuse project cost accounting.Plan outcomes, not actions
If the work breakdown structure designer attempts to capture any action-oriented details in the WBS, the designer will likely include either too many actions or too few actions. Too many actions will exceed 100% of the parent's scope, and too few will fall short of 100% of the parent's scope. The best way to adhere to the 100% rule is to define WBS elements in terms of outcomes or results, not actions. This also ensures that the WBS is not overly prescriptive of methods, allowing for greater ingenuity and creative thinking on the part of the project participants. When a project provides professional services, a common technique is to capture all planned deliverables to create a deliverable-oriented WBS. Work breakdown structures that subdivide work by project phases (e.g. preliminary design phase, critical design phase) must ensure that phases are clearly separated by a deliverable also used in defining entry and exit criteria (e.g., an approved preliminary or critical design review).Product breakdown structure (PBS)
For new product development projects, the most common technique to ensure an outcome-oriented WBS is to use a product breakdown structure (PBS).Feature-driven development
Feature-driven software projects may use a similar technique as the WBS, which is to use a feature breakdown structure.Level of detail
One must decide when to stop dividing work into smaller elements. For most projects, a hierarchy of two to four levels will suffice. This will assist in determining the duration of activities necessary to produce a deliverable defined by the WBS. There are several heuristics or "rules of thumb" used when determining the appropriate duration of an activity or group of activities necessary to produce a specific deliverable defined by the WBS. * The first is the "80-hour rule" which means that no single activity or group of activities at the lowest level of detail of the WBS to produce a single deliverable should be more than 80 hours of effort. * The second rule of thumb is that no activity or group of activities at the lowest level of detail of the WBS should be longer than a single reporting period. Thus if the project team is reporting progress monthly, then no single activity or series of activities should be longer than one month long. * The last heuristic is the "if it makes sense" rule. Applying this rule of thumb, one can apply "common sense" when creating the duration of a single activity or group of activities necessary to produce a deliverable defined by the WBS.Work package
According to theProject Management Institute
The Project Management Institute (PMI, legally Project Management Institute, Inc.) is a U.S.-based not-for-profit professional organization for project management.
Overview
PMI serves more than five million professionals including over 680,0 ...
, a work package is the "lowest level of the work breakdown structure for which cost and duration are estimated and managed."
A work package at the activity level is a task that:
* can be realistically and confidently estimated;
* makes no sense practically to break down any further;
* can be completed in accordance with one of the heuristics defined above;
* produces a deliverable which is measurable; and
* forms a unique package of work that can be outsourced or contracted out.
WBS dictionary
If the WBS element names are ambiguous, a WBS dictionary can help clarify the distinctions between WBS elements. The WBS Dictionary describes each component of the WBS with milestones, deliverables, activities, scope, and sometimes dates,resources
''Resource'' refers to all the materials available in our environment which are Technology, technologically accessible, Economics, economically feasible and Culture, culturally Sustainability, sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and want ...
, costs, quality.
According to the Project Management Institute
The Project Management Institute (PMI, legally Project Management Institute, Inc.) is a U.S.-based not-for-profit professional organization for project management.
Overview
PMI serves more than five million professionals including over 680,0 ...
, the WBS dictionary is defined as a "document that provides detailed deliverable, activity, and scheduling information about each component in the work breakdown structure."
Coding scheme
It is common for work breakdown structure elements to be numbered sequentially to reveal the hierarchical structure. The purpose of the numbering is to provide a consistent approach to identifying and managing the WBS across like systems regardless of vendor or service. For example, 1.1.2 Propulsion (in the example below) identifies this item as a Level 3 WBS element, since there are three numbers separated by two decimal points. A coding scheme also helps WBS elements to be recognized in any written context, such as progress tracking, scheduling, or billing, and allows for mapping to the WBS Dictionary. It is a preferred practice that theStatement of work
A statement of work (SOW) is a document routinely employed in the field of project management. It is the narrative description of a project's work requirement. It defines project-specific activities, deliverables and timelines for a vendor providin ...
or other contract descriptive include the same section terms and hierarchical structure as the WBS.
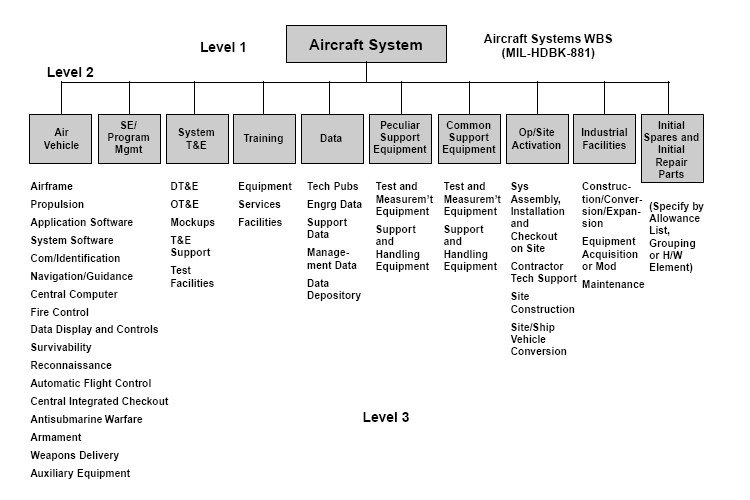
A practical example of the WBS coding scheme is
''1.0 Aircraft System''
:''1.1 Air Vehicle''
::''1.1.1 Airframe''
:::''1.1.1.1 Airframe Integration, Assembly, Test, and Checkout''
:::''1.1.1.2 Fuselage''
:::''1.1.1.3 Wing''
:::''1.1.1.4 Empennage''
:::''1.1.1.5 Nacelle''
:::''1.1.1.6 Other Airframe Components 1..n (Specify)''
::''1.1.2 Propulsion''
::''1.1.3 Vehicle Subsystems''
::''1.1.4 Avionics''
:''1.2 System Engineering''
:''1.3 Program Management''
:''1.4 System Test and Evaluation''
:''1.5 Training''
:''1.6 Data''
:''1.7 Peculiar Support Equipment''
:''1.8 Common Support Equipment''
:''1.9 Operational/Site Activation''
:''1.10 Industrial Facilities''
:''1.11 Initial Spares and Repair Parts''
Terminal element
The lowest element in a tree structure, a terminal element, is one that is not further subdivided. In a Work Breakdown Structure such elements (activity ordeliverable
A deliverable is a tangible or intangible good or service produced as a result of a project that is intended to be delivered to a customer (either internal or external). A deliverable could be a report, a document, a software product, a server upgr ...
), also known as work packages, are the items that are estimated in terms of resource requirements, budget
A budget is a calculation plan, usually but not always financial plan, financial, for a defined accounting period, period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including tim ...
and duration; linked by dependencies; and schedule. At the juncture of the WBS element and organization unit, control accounts and work packages are established, and performance is planned, measured, recorded, and controlled. A WBS can be expressed down to any level of interest. Three levels are the minimum recommended, with additional levels for and only for items of high cost or high risk, and two levels of detail at cases such as systems engineering or program management, with the standard showing examples of WBS with varying depth such as software development at points going to 5 levels or fire-control system to 7 levels.
Consistent to norms
The higher WBS structure should be consistent with whatever norms or template mandates exist within the organization or domain. For example, shipbuilding for the U.S. Navy must respect that the nautical terms and their hierarchy structure put into MIL-STD are embedded in Naval Architecture and that matching Navy offices and procedures have been built to match this naval architecture structure, so any significant change of WBS element numbering or naming in the hierarchy would be unacceptable.Example
The adjacent figure shows a work breakdown structure construction technique that demonstrates the 100% rule and the "progressive elaboration" technique. At WBS Level 1 it shows 100 units of work as the total scope of a project to design and build a custom bicycle. At WBS Level 2, the 100 units are divided into seven elements. The number of units allocated to each element of work can be based on effort or cost; it is not an estimate of task duration. The three largest elements of WBS Level 2 are further subdivided at Level 3. The two largest elements at Level 3 each represent only 17% of the total scope of the project. These larger elements could be further subdivided using the ''progressive elaboration'' technique described above. This is an example of the product-based approach (which might be end-product or deliverable or work-based), as compared to phased approach (which might be gated stages in a formal Systems development life cycle), or forced events (e.g. quarterly updates or a fiscal year rebudgeting), or a skills/roles based approach. WBS design can be supported by software (e.g. aspreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application for computation, organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets were developed as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The program operates on data entered in c ...
) to allow automatic rolling up of point values. Estimates of effort or cost can be developed through discussions among project team members. This collaborative technique builds greater insight into scope definitions, underlying assumptions, and consensus regarding the level of granularity required to manage the projects.
See also
* '' Common Arrangement of Work Sections'' * Charge code * List of project management topics * MECE principle * Product Breakdown Structure * Project anatomy * Project management software * Project planning * Structure chart * TimeblockingReferences
Further reading
* * (Note: The Second Edition is an extensive re-write of the Practice Standard.) * * * * (Note: This new book is essentially a facilitator's guide for planning a project based on the WBS.) *External links
*how to create work breakdown structure WBS using standard Division of work
* ttps://www.workbreakdownstructure.com/how-to-make-a-work-breakdown-structure.php How to Make a Work Breakdown Structurebr>NASA Work Breakdown Structure Handbook, NASA/SP-2010-3404, January 2010
{{Systems Engineering Business process modelling Schedule (project management) Systems engineering