thiazides on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of
Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of

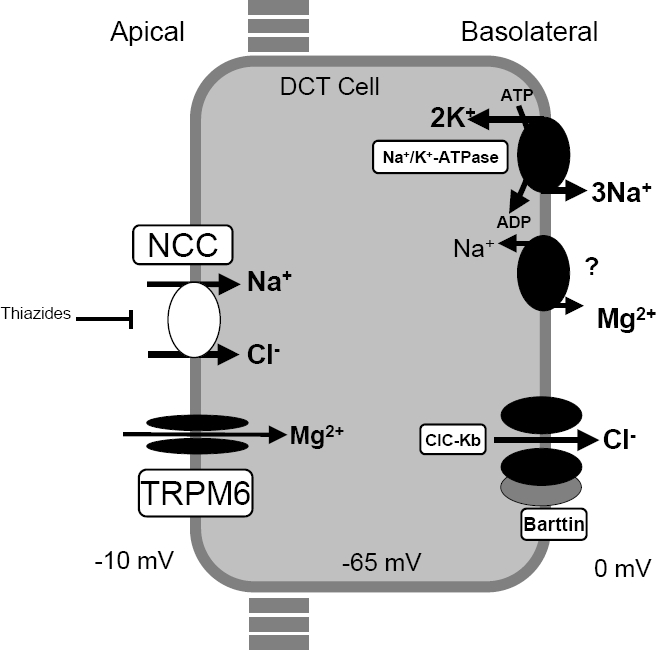 Thiazide diuretics control hypertension in part by inhibiting
Thiazide diuretics control hypertension in part by inhibiting
diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics in ...
s based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine
Benzothiadiazine is a bicyclic heterocyclic benzene derivative with the heterocycle containing two nitrogens and one sulfur.
Some benzothiadiazine derivatives are used as pharmaceutical drugs, including:
* bendroflumethiazide
* chlorothiazide
* ...
. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The first approved drug of this class, chlorothiazide
Chlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Diuril among others, is an organic compound used as a diuretic and as an antihypertensive.
It is used both within the hospital setting or for personal use to manage excess fluid associated with congestive ...
, was marketed under the trade name Diuril
Chlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Diuril among others, is an organic compound used as a diuretic and as an antihypertensive.
It is used both within the hospital setting or for personal use to manage excess fluid associated with congestive ...
beginning in 1958. In most countries, thiazides are the least expensive antihypertensive drug
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that r ...
s available.
Thiazide organic molecules are bi-cyclic structures that contain adjacent sulfur and nitrogen atoms on one ring. Confusion sometimes occurs because thiazide-like diuretic A thiazide-like diuretic is a sulfonamide diuretic that has similar physiological properties to a thiazide diuretic, but does not have the chemical properties of a thiazide, lacking the benzothiadiazine molecular structure. Examples include metolaz ...
s such as indapamide
Indapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used in the treatment of hypertension, as well as decompensated heart failure. Combination preparations with perindopril (an ACE inhibitor antihypertensive) are available. The thiazide-like diuretics ...
are referred to as thiazides despite not having the thiazide chemical structure. When used this way, "thiazide" refers to a drug which acts at the thiazide receptor. The thiazide receptor is a sodium-chloride transporter that pulls NaCl
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g/ ...
from the lumen in the distal convoluted tubule
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting tubule.
Physiology
It is partly responsible for the regulation of potassium, sodium, calcium, and pH.
On its apical surface (lum ...
. Thiazide diuretics inhibit this receptor, causing the body to release NaCl and water into the lumen, thereby increasing the amount of urine produced each day. An example of a molecule that is chemically a thiazide but not used as a diuretic is methylchloroisothiazolinone
Methylchloroisothiazolinone, also referred to as MCI, is the organic compound with the formula S(C2HCl)C(O)N(CH3). It is a white solid that melts near room temperature. The compound is an isothiazolinone, a class of heterocycles used as biocides ...
, often found as an antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals ar ...
in cosmetics.
Medical uses
Thiazide diuretics are primarily used to treat thehypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
(high blood pressure) and edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
(swelling) caused by water overload as well as certain conditions related to unbalanced calcium metabolism.
Water balance
Hypertension
There are many causes ofhypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
(high blood pressure), including advancing age, smoking and obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
. Sometimes the underlying cause of hypertension can not be determined, resulting in a diagnosis of idiopathic hypertension. Regardless of the cause, someone may have very high hypertension without any initial symptoms. Uncontrolled hypertension will eventually cause damage to the heart, kidneys and eyes. Lifestyle changes, including reducing dietary salt, increasing exercise and losing weight can help to reduce blood pressure.
Thiazides and thiazide-like diuretics have been in constant use since their introduction in 1958. Decades as a cornerstone of hypertension treatment show how well these drugs perform for most patients. Low-dose thiazides are tolerated as well as the other classes of medications for hypertension, including ACE inhibitor
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. They work by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decrease in blood volum ...
s, beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). They are al ...
s and calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s. In general, the thiazides and thiazide-like diuretic A thiazide-like diuretic is a sulfonamide diuretic that has similar physiological properties to a thiazide diuretic, but does not have the chemical properties of a thiazide, lacking the benzothiadiazine molecular structure. Examples include metolaz ...
s reduce the risk of death, stroke, heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
, and heart failure due to hypertension.
Clinical practice guideline
Clinical may refer to: Healthcare
* Of or about a clinic, a healthcare facility
* Of or about the practice of medicine Other uses
* ''Clinical'' (film), a 2017 American horror thriller
See also
*
*
* Clinical chemistry, the analysis of bodily flu ...
s regarding the use of thiazides vary by geographic region. Guidelines in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
recommend thiazides as a first-line treatment for hypertension (JNC VIII). A systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on t ...
by the Cochrane Collaboration
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health profess ...
specifically recommended that low-dose thiazides be used as the initial pharmacological therapy for high blood pressure. Low-dose thiazides are more effective at treating hypertension than beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). They are al ...
s and are similar to angiotensin-converting enzyme
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (), or ACE, is a central component of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), which controls blood pressure by regulating the volume of fluids in the body. It converts the hormone angiotensin I to the active vasoconstr ...
(ACE) inhibitors. Thiazides are a recommended treatment for hypertension in Europe (ESC/ESH). However, the UK National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence recommends ACE inhibitor
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. They work by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decrease in blood volum ...
and calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s for first-line treatment of hypertension in adults (CG127).National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guideline on the management of primary hypertension in adults (CG127) accessed 5/3/2012 at Thiazides should be considered as initial treatment if the patient has a high risk of developing heart failure. Thiazides have also been replaced by ACE inhibitor
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. They work by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decrease in blood volum ...
s in Australia due to the association between thaizide use and increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus type 2
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, ...
.Guide to management of hypertension 2008. National Heart Foundation Australia. 2008. accessed online at
Diabetes insipidus
Thiazides can be used to paradoxically decrease urine flow in people with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Thiazides may also be useful in treatinghyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be abs ...
(low blood sodium) in infants with central diabetes insipidus
Central diabetes insipidus, also called neurogenic diabetes insipidus, is a type of diabetes insipidus due to a lack of vasopressin (ADH) production in the brain. Vasopressin acts to increase the volume of blood (intravascularly), and decrease ...
.
Calcium balance
Urinary stones
Thiazides are useful in treatingkidney stones
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine ...
and bladder stones
A bladder stone is a stone found in the urinary bladder.
Signs and symptoms
Bladder stones are small mineral deposits that can form in the bladder. In most cases bladder stones develop when the urine becomes very concentrated or when one is ...
that result from hypercalciuria
Hypercalciuria is the condition of elevated calcium in the urine. Chronic hypercalciuria may lead to impairment of renal function, nephrocalcinosis, and chronic kidney disease. Patients with hypercalciuria have kidneys that put out higher levels ...
(high urine calcium levels). Thiazides increase the uptake of calcium in the distal tubules, to moderately reduce urinary calcium. Thiazides combined with potassium citrate
Potassium citrate (also known as tripotassium citrate) is a potassium salt of citric acid with the molecular formula K3C6H5O7. It is a white, hygroscopic crystalline powder. It is odorless with a saline taste. It contains 38.28% potassium by ma ...
, increased water intake and decreased dietary oxalate
Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate) is an anion with the formula C2O42−. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4), and several esters such as dimethyl ...
and sodium can slow or even reverse the formation of calcium-containing kidney stones. High-dose therapy with the thiazide-like diuretic indapamide
Indapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used in the treatment of hypertension, as well as decompensated heart failure. Combination preparations with perindopril (an ACE inhibitor antihypertensive) are available. The thiazide-like diuretics ...
can be used to treat idiopathic hypercalcinuria (high urine calcium with unknown cause).
Dent's disease
Thiazides may be used to treat the symptoms ofDent's disease
Dent's disease (or Dent disease) is a rare X-linked recessive inherited condition that affects the proximal renal tubules of the kidney. It is one cause of Fanconi syndrome, and is characterized by tubular proteinuria, excess calcium in the urin ...
, an X-linked genetic condition that results in electrolyte imbalance with repeated episodes of kidney stones. A case study of two brothers with the condition, two years of treatment with hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic medication often used to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build-up. Other uses include treating diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in tho ...
reduced the incidence of kidney stones and improved kidney function. The thiazide-like diuretic chlortalidone
Chlortalidone, also known as chlorthalidone, is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used to treat high blood pressure, swelling including that due to heart failure, liver failure, and nephrotic syndrome, diabetes insipidus, and renal tubular acido ...
reduced urine calcium oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate ...
in seven of the eight males with inactivated CLCN5
The ''CLCN5'' gene encodes the chloride channel Cl-/H+ exchanger ClC-5. ClC-5 is mainly expressed in the kidney, in particular in proximal tubules where it participates to the uptake of albumin and low-molecular-weight proteins, which is one of t ...
gene that participated in the study. Inactivation of the CLCN5 gene causes Dent's disease Type 1. The rare nature of Dent's disease makes it difficult to coordinate large controlled studies, so most evidence for thiazide use is with too few patients to make broad recommendations possible. Long-term thiazide use may not be advisable due to the risk of significant adverse side effects.
Osteoporosis
Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L) while levels less than 2.1 mmol ...
(low blood calcium) can be caused by a variety of conditions that reduce dietary calcium absorption, increase calcium excretion or both. Positive calcium balance occurs when calcium excretion is decreased and intake remains constant so that calcium is retained within the body.Aung K, Htay T. Thiazide diuretics and the risk of hip fracture. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 10. Art. No.: CD005185. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005185.pub2. Higher levels of retained calcium are associated with increased bone mineral density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optic ...
and fewer fractures in individuals with osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone am ...
. By a poorly understood mechanism, thiazides directly stimulate osteoblast
Osteoblasts (from the Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cells with a single nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts functio ...
differentiation and bone mineral formation, further slowing the course of osteoporosis.
Other uses
Bromine intoxication can be treated by givingintravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
saline with either thiazides or Loop diuretic
Loop diuretics are diuretics that act on the Na-K-Cl cotransporter along the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle in the kidney. They are primarily used in medicine to treat hypertension and edema often due to congestive heart failure or chr ...
s.
Contraindications
Contraindications include: *Hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
* Allergy to sulphur-containing medications
* Gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensi ...
* Kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as ei ...
* Lithium therapy
* Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an ab ...
* May worsen diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
Thiazides reduce the clearance of uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown o ...
since they compete for the same transporter, and therefore raise the levels of uric acid in the blood. Hence, they are prescribed with caution in patients with gout or hyperuricemia
Hyperuricaemia or hyperuricemia is an abnormally high level of uric acid in the blood. In the pH conditions of body fluid, uric acid exists largely as urate, the ion form. Serum uric acid concentrations greater than 6 mg/dL for females, 7&nbs ...
.
Chronic administration of thiazides is associated with the increase of insulin resistance which can lead to hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
.
Thiazides cause loss of blood potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
, while conserving blood calcium.
Thiazides can decrease placental perfusion and adversely affect the fetus, so should be avoided in pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
.
Adverse effects
*Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an ab ...
– Thiazide diuretics reduces potassium concentration in blood through two indirect mechanisms: inhibition of sodium-chloride symporter
The sodium-chloride symporter (also known as Na+-Cl− cotransporter, NCC or NCCT, or as the thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl− cotransporter or TSC) is a cotransporter in the kidney which has the function of reabsorbing sodium and chloride ions from t ...
at distal convoluted tubule
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting tubule.
Physiology
It is partly responsible for the regulation of potassium, sodium, calcium, and pH.
On its apical surface (lum ...
of a nephron
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure c ...
and stimulation of aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays a ...
that activates Na+/K+-ATPase at collecting duct
The collecting duct system of the kidney consists of a series of tubules and ducts that physically connect nephrons to a minor calyx or directly to the renal pelvis. The collecting duct system is the last part of nephron and participates in elect ...
. Inhibition of sodium-chloride symporter increases availability of sodium and chloride in urine. When the urine reaches the collecting duct, the increase in sodium and chloride availability activates Na+/K+-ATPase, which increases the absorption of sodium and excretion of potassium into the urine. Long term administration of thiazide diuretics reduces total body blood volume. This activates the renin–angiotensin system
The renin–angiotensin system (RAS), or renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance.
When renal blood flow is reduced, ju ...
, stimulates the secretion of aldosterone, thus activating Na+/K+-ATPase, increasing excretion of potassium in urine. Therefore, ACE inhibitor and thiazide combination is used to prevent hypokalemia.
* Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
* Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia is abnormally elevated levels of any or all lipids (fats, cholesterol, or triglycerides) or lipoproteins in the blood. citing: and The term ''hyperlipidemia'' refers to the laboratory finding itself and is also used as an umbr ...
* Hyperuricemia
Hyperuricaemia or hyperuricemia is an abnormally high level of uric acid in the blood. In the pH conditions of body fluid, uric acid exists largely as urate, the ion form. Serum uric acid concentrations greater than 6 mg/dL for females, 7&nbs ...
* Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcemia ...
* Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be abs ...
* Hypomagnesemia
Magnesium deficiency is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is a low level of magnesium in the body. It can result in multiple symptoms. Symptoms include tremor, poor coordination, muscle spasms, loss of appetite, personality changes, and ...
* Hypocalciuria Hypocalciuria is a low level of calcium in the urine. It is a significant risk factor for predicting eclampsia in pregnancy. The most common causes for hypocalciuria is either thiazide diuretics
Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-cont ...
Mechanism of action
 Thiazide diuretics control hypertension in part by inhibiting
Thiazide diuretics control hypertension in part by inhibiting reabsorption
In renal physiology, reabsorption or tubular reabsorption is the process by which the nephron removes water and solutes from the tubular fluid (pre-urine) and returns them to the circulating blood. It is called ''reabsorption'' (and not ''absorpt ...
of sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
(Na+) and chloride
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride salts ...
(Cl−) ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conv ...
s from the distal convoluted tubule
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting tubule.
Physiology
It is partly responsible for the regulation of potassium, sodium, calcium, and pH.
On its apical surface (lum ...
s in the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s by blocking the thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl− symporter. The term "thiazide" is also often used for drugs with a similar action that do not have the thiazide chemical structure, such as chlorthalidone and metolazone
Metolazone is a thiazide-like diuretic marketed under the brand names Zytanix, Metoz, Zaroxolyn, and Mykrox. It is primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure. Metolazone indirectly decreases the amount of water rea ...
. These agents are more properly termed thiazide-like diuretic A thiazide-like diuretic is a sulfonamide diuretic that has similar physiological properties to a thiazide diuretic, but does not have the chemical properties of a thiazide, lacking the benzothiadiazine molecular structure. Examples include metolaz ...
s.
Thiazide diuretics also increase calcium reabsorption at the distal tubule
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting tubule.
Physiology
It is partly responsible for the regulation of potassium, sodium, calcium, and pH.
On its apical surface (lumen ...
. By lowering the sodium concentration in the tubule epithelial cells, thiazides indirectly increase the activity of the basolateral Na+/Ca2+ antiporter to maintain intracellular Na+ level, facilitating Ca2+ to leave the epithelial cells into the renal interstitium. Thus, intracellular Ca2+ concentration is decreased, which allows more Ca2+ from the lumen of the tubules to enter epithelial cells via apical Ca2+-selective channels (TRPV5). In other words, less Ca2+ in the cell increases the driving force for reabsorption from the lumen.
Thiazides are also thought to increase the reabsorption of Ca2+ by a mechanism involving the reabsorption of sodium and calcium in the proximal tubule
The proximal tubule is the segment of the nephron in kidneys which begins from the renal pole of the Bowman's capsule to the beginning of loop of Henle. It can be further classified into the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and the proximal stra ...
in response to sodium depletion. Some of this response is due to augmentation of the action of parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone r ...
.
Breastfeeding
Thiazides pass intobreast milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by mammary glands located in the breast of a human female. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborns, containing fat, protein, carbohydrates ( lact ...
and can decrease the flow of breast milk. Thiazides have been associated with significant side effect
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
s in some nursing infants and should be administered to nursing mothers with caution.
History
The thiazide diuretics were developed by scientists Karl H. Beyer, James M. Sprague, John E. Baer, and Frederick C. Novello of Merck and Co. in the 1950s, and led to the marketing of the first drug of this class,chlorothiazide
Chlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Diuril among others, is an organic compound used as a diuretic and as an antihypertensive.
It is used both within the hospital setting or for personal use to manage excess fluid associated with congestive ...
, under the trade name Diuril in 1958. The research leading to the discovery of chlorothiazide, leading to "the saving of untold thousands of lives and the alleviation of the suffering of millions of victims of hypertension" was recognized by a special Public Health Award from the Lasker Foundation in 1975.
References
{{Membrane transport modulators * World Anti-Doping Agency prohibited substances Nephrotoxins