shinmei-zukuri on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 is an ancient Japanese
is an ancient Japanese
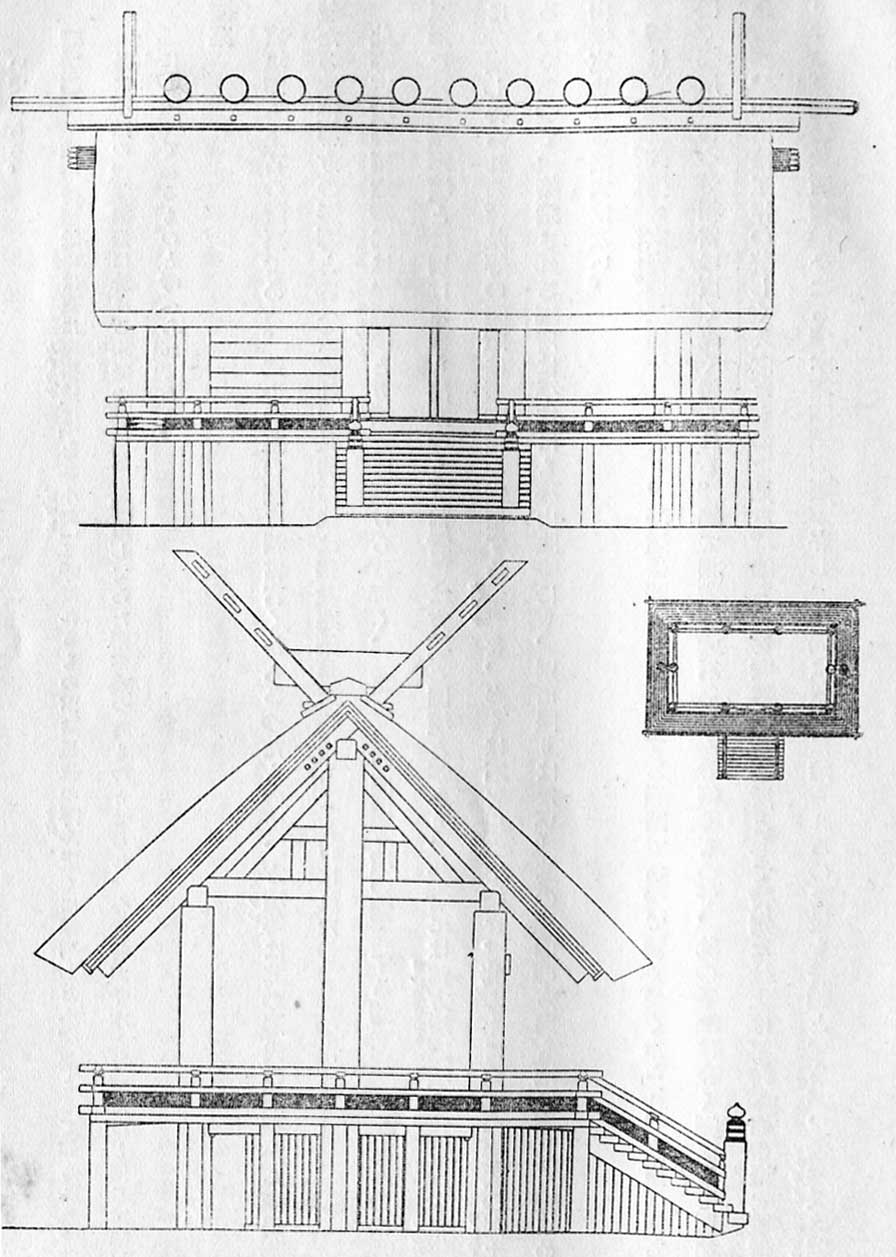
Shinmei-zukuri
accessed on December 1, 2009
History and Typology of Shrine Architecture
Encyclopedia of Shinto accessed on November 29, 2009 *, * {{Shinto shrine Shinto architecture
 is an ancient Japanese
is an ancient Japanese architectural style
An architectural style is a set of characteristics and features that make a building or other structure notable or historically identifiable. It is a sub-class of style in the visual arts generally, and most styles in architecture relate closely ...
typical of Ise Grand Shrine
The , located in Ise, Mie Prefecture of Japan, is a Shinto shrine dedicated to the sun goddess Amaterasu. Officially known simply as , Ise Jingū is a shrine complex composed of many Shinto shrines centered on two main shrines, and .
The Inn ...
's ''honden
In Shinto shrine architecture, the , also called , or sometimes as in Ise Shrine's case, is the most sacred building at a Shinto shrine, intended purely for the use of the enshrined ''kami'', usually symbolized by a mirror or sometimes by a sta ...
'', the holiest of Shinto shrines
A is a structure whose main purpose is to house ("enshrine") one or more ''kami'', the deities of the Shinto religion.
Overview
Structurally, a Shinto shrine typically comprises several buildings.
The '' honden''Also called (本殿, meani ...
.Encyclopedia of Shinto It is most common in Mie Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kansai region of Honshu. Mie Prefecture has a population of 1,781,948 () and has a geographic area of . Mie Prefecture is bordered by Gifu Prefecture to the north, Shiga Prefecture and Kyoto Prefecture to ...
.JAANUS
History
Ancient shrines were constructed according to the style of dwellings (Izumo Taisha
, officially Izumo Ōyashiro, is one of the most ancient and important Shinto shrines in Japan. No record gives the date of establishment. Located in Izumo, Shimane Prefecture, it is home to two major festivals. It is dedicated to the god , ...
)Young & Young (2007:50)Kishida (2008:33) or storehouses (Ise Grand Shrine
The , located in Ise, Mie Prefecture of Japan, is a Shinto shrine dedicated to the sun goddess Amaterasu. Officially known simply as , Ise Jingū is a shrine complex composed of many Shinto shrines centered on two main shrines, and .
The Inn ...
).Fletcher and Cruickshank (1996:724) The buildings had gabled roof
A gable roof is a roof consisting of two sections whose upper horizontal edges meet to form its ridge. The most common roof shape in cold or temperate climates, it is constructed of rafters, roof trusses or purlins. The pitch of a gable roof ca ...
s, raised floors, plank walls, and were thatched
Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge (''Cladium mariscus''), rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of ...
with reed or covered with hinoki cypress
''Chamaecyparis obtusa'' (Japanese cypress, hinoki cypress or hinoki; ja, 檜 or , ) is a species of cypress native to central Japan in East Asia, and widely cultivated in the temperate northern hemisphere for its high-quality timber and orna ...
bark. Such early shrines did not include a space for worship. Three important forms of ancient shrine architectural styles exist: ''taisha-zukuri
Kamosu Jinja's ''honden'' and a granary at Toro
is an ancient Japanese architectural style and the oldest Shinto shrine architectural style. Named after Izumo Taisha's ''honden'' (sanctuary), like Ise Grand Shrine's ''shinmei-zukuri'' styl ...
'', ''shinmei-zukuri'', and ''sumiyoshi-zukuri
is an ancient Japanese Shinto shrine architectural style which takes its name from Sumiyoshi Taisha's ''honden'' in Ōsaka. As in the case of the '' taisha-zukuri'' and '' shinmei-zukuri'' styles, its birth predates the arrival of Buddhism in Jap ...
''Kishida (2008:34) They are exemplified by Izumo Taisha
, officially Izumo Ōyashiro, is one of the most ancient and important Shinto shrines in Japan. No record gives the date of establishment. Located in Izumo, Shimane Prefecture, it is home to two major festivals. It is dedicated to the god , ...
, Nishina Shinmei Shrine
is a Shinto shrine in Ōmachi, Nagano Prefecture, Japan. The shrine is the oldest extant example of ''shinmei-zukuri'', one of three architectural styles which were conceived before the arrival of Buddhism in Japan. It predates in fact the more f ...
and Sumiyoshi Taisha
, also known as Sumiyoshi Grand Shrine, is a Shinto shrine in Sumiyoshi-ku, Osaka, Osaka Prefecture, Japan. It is the main shrine of all the Sumiyoshi shrines in Japan. However, the oldest shrine that enshrines the Sumiyoshi sanjin, the thr ...
Kishida (2008:35) respectively and date to before 552.Kishida (2008:126) According to the tradition of '', the buildings or shrines were faithfully rebuilt at regular intervals adhering to the original design. In this manner, ancient styles have been replicated through the centuries to the present day.

Structure
This style is characterized by an extreme simplicity. Its basic features can be seen in Japanese architecture from theKofun period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is ...
(250–538 C.E.) onwards and it is considered the pinnacle of Japanese traditional architecture. Built in plane-unfinished wood, the ''honden'' is either 3x2 ''ken'' or 1x1''ken'' in size, has a raised floor, a gabled roofA gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall enclosed between the edges of a sloping roof. with an entry on one of the non-gabled sides (), no upward curve at the eaves, and purely decorative logs called ''chigi Chigi may refer to:
* Chigi (dog), a crossbreed between a Welsh Corgi and a chihuahua (dog)
* House of Chigi
The House of Chigi () is an Italian princely family of Sienese origin descended from the counts of Ardenghesca, which possessed castles ...
'' (vertical) and ''katsuogi
or are short, decorative logs found on Japanese and Shinto architecture. They are placed at right angles to the ridgeline of roofs, and are usually featured in religious or imperial architecture. ''Katsuogi'' predate Buddhist influence and ...
'' (horizontal) protruding from the roof's ridge.
Because shrines used to be rebuilt every 20 years, as Ise Shrine still is, shrines of this type are mostly of recent construction. The oldest extant example is Nishina Shinmei Shrine
is a Shinto shrine in Ōmachi, Nagano Prefecture, Japan. The shrine is the oldest extant example of ''shinmei-zukuri'', one of three architectural styles which were conceived before the arrival of Buddhism in Japan. It predates in fact the more f ...
,Jinja KenchikuShogakukan
is a Japanese publisher of dictionaries, literature, comics (manga), non-fiction, DVDs, and other media in Japan.
Shogakukan founded Shueisha, which also founded Hakusensha. These are three separate companies, but are together called the Hit ...
Nihon Daihyakka Zensho, accessed on November 29, 2009 which gives the name to the style.
See also
*Austronesian architecture
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrone ...
Notes
References
*JAANUSShinmei-zukuri
accessed on December 1, 2009
History and Typology of Shrine Architecture
Encyclopedia of Shinto accessed on November 29, 2009 *, * {{Shinto shrine Shinto architecture