seagrass on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Seagrasses are the only
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 International License
The seagrass species have specialized leaves with a reduced cuticle, an epidermis which lacks stomata and is the main photosynthetic tissue. The rhizome or underground stem is important in anchoring. The roots can live in an anoxic environment and depend on oxygen transport from the leaves and rhizomes but are also important in the nutrient transfer processes. Seagrasses profoundly influence the physical, chemical, and biological environments of coastal waters. Though seagrasses provide invaluable
 Around 140 million years ago, seagrasses evolved from early monocots which succeeded in conquering the marine environment.
Around 140 million years ago, seagrasses evolved from early monocots which succeeded in conquering the marine environment.
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License

 Seagrass populations are currently threatened by a variety of anthropogenic
Seagrass populations are currently threatened by a variety of anthropogenic  Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Seagrasses have contrasting
 Seagrasses occurring in the intertidal and subtidal zones are exposed to highly variable environmental conditions due to tidal changes. Subtidal seagrasses are more frequently exposed to lower light conditions, driven by plethora of natural and human-caused influences that reduce light penetration by increasing the density of suspended opaque materials. Subtidal light conditions can be estimated, with high accuracy, using artificial intelligence, enabling more rapid mitigation than was available using ''in situ'' techniques. Seagrasses in the intertidal zone are regularly exposed to air and consequently experience extreme high and low temperatures, high photoinhibitory irradiance, and
Seagrasses occurring in the intertidal and subtidal zones are exposed to highly variable environmental conditions due to tidal changes. Subtidal seagrasses are more frequently exposed to lower light conditions, driven by plethora of natural and human-caused influences that reduce light penetration by increasing the density of suspended opaque materials. Subtidal light conditions can be estimated, with high accuracy, using artificial intelligence, enabling more rapid mitigation than was available using ''in situ'' techniques. Seagrasses in the intertidal zone are regularly exposed to air and consequently experience extreme high and low temperatures, high photoinhibitory irradiance, and  In contrast, seagrasses in the subtidal zone adapt to reduced light conditions caused by light attenuation and scattering due to the overlaying water column and suspended particles. Seagrasses in the deep subtidal zone generally have longer leaves and wider leaf blades than those in the shallow subtidal or intertidal zone, which allows more photosynthesis, in turn resulting in greater growth. Seagrasses also respond to reduced light conditions by increasing chlorophyll content and decreasing the chlorophyll a/b ratio to enhance
In contrast, seagrasses in the subtidal zone adapt to reduced light conditions caused by light attenuation and scattering due to the overlaying water column and suspended particles. Seagrasses in the deep subtidal zone generally have longer leaves and wider leaf blades than those in the shallow subtidal or intertidal zone, which allows more photosynthesis, in turn resulting in greater growth. Seagrasses also respond to reduced light conditions by increasing chlorophyll content and decreasing the chlorophyll a/b ratio to enhance


File:Floridian seagrass bed.jpg, ''

 Seagrass cell walls contain the same polysaccharides found in
Seagrass cell walls contain the same polysaccharides found in
* Waycott, M, McMahon, K, & Lavery, P 2014, A guide to southern temperate seagrasses, CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne
Project Seagrass - Charity advancing the conservation of seagrass through community, research and actionSeagrasses
Project Regeneration.
SeagrassSpotter - Citizen Science project raising awaress for seagrass meadows and mapping their locationsSeagrass and Seagrass Beds
overview from the Smithsonian Ocean Portal
* ttp://www.seagrasswatch.org/ Seagrass-Watch - the largest scientific, non-destructive, seagrass assessment and monitoring program in the worldbr>Restore-A-Scar - a non-profit campaign to restore seagrass meadows damaged by boat propsSeagrassNet - global seagrass monitoring programThe Seagrass Fund at The Ocean FoundationWorld Seagrass AssociationSeagrassLISeagrass Science and Management in the South China Sea and Gulf of Thailand''Marine Ecology'' (December 2006)
- special issue on seagrasses
Seagrass Productivity - COST Action ES0906 Fisheries Western Australia - Seagrass Fact Sheet
{{Authority control Blue carbon Plant common names Roofing materials de:Seegras
flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
(Posidoniaceae
''Posidonia'' is a genus of flowering plants. It contains nine species of marine plants ("seagrass"), found in the seas of the Mediterranean and around the south coast of Australia.
The APG system (1998) and APG II system (2003) accept this gen ...
, Zosteraceae
Zosteraceae (one of the four seagrasses families, Kubitzki ed. 1998) is a family of marine perennial flowering plants found in temperate and subtropical coastal waters, with the highest diversity located around Korea and Japan. Most seagrasses ...
, Hydrocharitaceae
Hydrocharitaceae is a flowering plant family including 16 known genera with a total of ca 135 known species (Christenhusz & Byng 2016), that including a number of species of aquatic plant, for instance the tape-grasses, the well known Canadia ...
and Cymodoceaceae
Cymodoceaceae is a family of flowering plants, sometimes known as the "manatee-grass family", which includes only marine species.
The 2016 APG IV does recognize Cymodoceaceae and places it in the order Alismatales, in the clade monocots. The fam ...
), all in the order Alismatales
The Alismatales (alismatids) are an order of flowering plants including about 4,500 species. Plants assigned to this order are mostly Tropical vegetation, tropical or Aquatic plant, aquatic. Some grow in fresh water, some in marine habitats.
...
(in the clade of monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of ...
s). Seagrasses evolved from terrestrial plant
A terrestrial plant is a plant that grows on, in, or from land. Other types of plants are aquatic (living in water), epiphytic (living on trees) and lithophytic (living in or on rocks).
The distinction between aquatic and terrestrial plants i ...
s which recolonised the ocean 70 to 100 million years ago.
The name ''seagrass'' stems from the many species with long and narrow leaves
A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", wh ...
, which grow by rhizome extension and often spread across large "meadows
A meadow ( ) is an open habitat, or field, vegetated by grasses, herbs, and other non-woody plants. Trees or shrubs may sparsely populate meadows, as long as these areas maintain an open character. Meadows may be naturally occurring or artificia ...
" resembling grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
; many species superficially resemble terrestrial grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns an ...
es of the family Poaceae
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns an ...
.
Like all autotrophic
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Works", ...
plants, seagrasses photosynthesize
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Most species undergo submarine pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by wind. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, birds ...
and complete their life cycle underwater. While it was previously believed this pollination was carried out without pollinators and purely by sea current drift, this has been shown to be false for at least one species, ''Thalassia testudinum
''Thalassia testudinum'', commonly known as turtlegrass, is a species of marine seagrass. It forms meadows in shallow sandy or muddy locations in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. Turtle grass and other seagrasses form meadows which are i ...
'', which carries out a mixed biotic-abiotic strategy. Crustaceans (such as crabs, ''Majidae
Majidae is a family of crabs, comprising around 200 marine species inside 52 genera, with a carapace that is longer than it is broad, and which forms a point at the front. The legs can be very long in some species, leading to the name "spider c ...
zoae'', ''Thalassinidea
Thalassinidea is a former infraorder of decapod crustaceans that live in burrows in muddy bottoms of the world's oceans. In Australian English, the littoral thalassinidean ''Trypaea australiensis'' is referred to as the ''yabby'' (a term whic ...
zoea'') and syllid
Syllidae is a family of small to medium-sized polychaete worms. Syllids are distinguished from other polychaetes by the presence of a muscular region of the anterior digestive tract known as the ''proventricle''.
Syllid worms range in size from ...
polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made ...
worm larvae have both been found with pollen grains, the plant producing nutritious mucigenous clumps of pollen to attract and stick to them instead of nectar as terrestrial flowers do.
Seagrasses form dense underwater seagrass meadow
A seagrass meadow or seagrass bed is an underwater ecosystem formed by seagrasses. Seagrasses are marine (saltwater) plants found in shallow coastal waters and in the brackish waters of estuaries. Seagrasses are flowering plants with stems and ...
s which are among the most productive ecosystems in the world. They function as important carbon sink
A carbon sink is anything, natural or otherwise, that accumulates and stores some carbon-containing chemical compound for an indefinite period and thereby removes carbon dioxide () from the atmosphere.
Globally, the two most important carbon si ...
s and provide habitats and food for a diversity of marine life comparable to that of coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
s.
Overview
Seagrasses are a paraphyletic group of marineangiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s which evolved in parallel three to four times from land plants back to the sea. The following characteristics can be used to define a seagrass species. It lives in an estuarine or in the marine environment
Marine habitats are habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term ''marine'' comes from the Latin ''mare'', meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental ...
, and nowhere else. The pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by wind. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, birds ...
takes place underwater with specialized pollen. The seeds which are dispersed by both biotic and abiotic agents are produced underwater. Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 International License
The seagrass species have specialized leaves with a reduced cuticle, an epidermis which lacks stomata and is the main photosynthetic tissue. The rhizome or underground stem is important in anchoring. The roots can live in an anoxic environment and depend on oxygen transport from the leaves and rhizomes but are also important in the nutrient transfer processes. Seagrasses profoundly influence the physical, chemical, and biological environments of coastal waters. Though seagrasses provide invaluable
ecosystem service
Ecosystem services are the many and varied benefits to humans provided by the natural environment and healthy ecosystems. Such ecosystems include, for example, agroecosystems, forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystems, and aquatic ecosystems. ...
s by acting as breeding and nursery ground for a variety of organisms and promote commercial fisheries
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often p ...
, many aspects of their physiology are not well investigated. Several studies have indicated that seagrass habitat is declining worldwide. Ten seagrass species are at elevated risk of extinction (14% of all seagrass species) with three species qualifying as endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inva ...
. Seagrass loss and degradation of seagrass biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
will have serious repercussions for marine biodiversity and the human population that depends upon the resources and ecosystem services that seagrasses provide.
Seagrasses form important coastal ecosystems. The worldwide endangering of these sea meadows, which provide food and habitat for many marine species, prompts the need for protection and understanding of these valuable resources.
Evolution
 Around 140 million years ago, seagrasses evolved from early monocots which succeeded in conquering the marine environment.
Around 140 million years ago, seagrasses evolved from early monocots which succeeded in conquering the marine environment. Monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one Embryo#Plant embryos, embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. Th ...
s are grass and grass-like flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf or cotyledon
A cotyledon (; ; ; , gen. (), ) is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant, and is defined as "the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or more of which are the first to appear from a germinating seed." The num ...
.
Terrestrial plant
A terrestrial plant is a plant that grows on, in, or from land. Other types of plants are aquatic (living in water), epiphytic (living on trees) and lithophytic (living in or on rocks).
The distinction between aquatic and terrestrial plants i ...
s evolved perhaps as early as 450 million years ago from a group of green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
. Seagrasses then evolved from terrestrial plants which migrated back into the ocean. Between about 70 million and 100 million years ago, three independent seagrass lineages (Hydrocharitaceae
Hydrocharitaceae is a flowering plant family including 16 known genera with a total of ca 135 known species (Christenhusz & Byng 2016), that including a number of species of aquatic plant, for instance the tape-grasses, the well known Canadia ...
, Cymodoceaceae
Cymodoceaceae is a family of flowering plants, sometimes known as the "manatee-grass family", which includes only marine species.
The 2016 APG IV does recognize Cymodoceaceae and places it in the order Alismatales, in the clade monocots. The fam ...
complex, and Zosteraceae
Zosteraceae (one of the four seagrasses families, Kubitzki ed. 1998) is a family of marine perennial flowering plants found in temperate and subtropical coastal waters, with the highest diversity located around Korea and Japan. Most seagrasses ...
) evolved from a single lineage of the monocotyledonous
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, ( Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of ...
flowering plants.
Other plants that colonised the sea, such as salt marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is domin ...
plants, mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evoluti ...
s, and marine algae
Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of organic compounds from atmospheric or dissolved carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it al ...
, have more diverse evolutionary lineages. In spite of their low species diversity, seagrasses have succeeded in colonising the continental shelves of all continents except Antarctica.
Recent sequencing of the genomes of ''Zostera marina
''Zostera marina'' is a flowering vascular plant species as one of many kinds of seagrass, with this species known primarily by the English name of eelgrass with seawrack much less used, and refers to the plant after breaking loose from the submer ...
'' and ''Zostera muelleri
''Zostera muelleri '' is a southern hemisphere temperate species of seagrass native to the seacoasts of South Australia, Victoria and Tasmania.Paul Friedrich August Ascherson. 1867. Sitzungsberichte der Gesellschaft Naturforschender Freunde zu ...
'' has given a better understanding of angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
adaption
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the ...
to the sea. During the evolutionary step back to the ocean, different genes have been lost (e.g., stomatal genes) or have been reduced (e.g., genes involved in the synthesis of terpenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes" ...
s) and others have been regained, such as in genes involved in sulfation
Sulfation is the chemical reaction that entails the addition of SO3 group. In principle, many sulfations would involve reactions of sulfur trioxide (SO3). In practice, most sulfations are effected less directly. Regardless of the mechanism, the ...
.
Genome information has shown further that adaption to the marine habitat was accomplished by radical changes in cell wall composition. However the cell walls of seagrasses are not well understood. In addition to the ancestral traits of land plant
The Embryophyta (), or land plants, are the most familiar group of green plants that comprise vegetation on Earth. Embryophytes () have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of green algae as sist ...
s one would expect habitat-driven adaption process to the new environment characterized by multiple abiotic
In biology and ecology, abiotic components or abiotic factors are non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment that affect living organisms and the functioning of ecosystems. Abiotic factors and the phenomena associated with them under ...
(high amounts of salt) and biotic (different seagrass grazers and bacterial colonization) stressors. The cell walls of seagrasses seem intricate combinations of features known from both angiosperm land plants and marine macroalgae with new structural elements.
Taxonomy
Today, seagrasses are a polyphyletic group of marine angiosperms with around 60 species in five families (Zosteraceae
Zosteraceae (one of the four seagrasses families, Kubitzki ed. 1998) is a family of marine perennial flowering plants found in temperate and subtropical coastal waters, with the highest diversity located around Korea and Japan. Most seagrasses ...
, Hydrocharitaceae
Hydrocharitaceae is a flowering plant family including 16 known genera with a total of ca 135 known species (Christenhusz & Byng 2016), that including a number of species of aquatic plant, for instance the tape-grasses, the well known Canadia ...
, Posidoniaceae
''Posidonia'' is a genus of flowering plants. It contains nine species of marine plants ("seagrass"), found in the seas of the Mediterranean and around the south coast of Australia.
The APG system (1998) and APG II system (2003) accept this gen ...
, Cymodoceaceae
Cymodoceaceae is a family of flowering plants, sometimes known as the "manatee-grass family", which includes only marine species.
The 2016 APG IV does recognize Cymodoceaceae and places it in the order Alismatales, in the clade monocots. The fam ...
, and Ruppiaceae
''Ruppia'', also known as the widgeonweeds, ditch grasses or widgeon grass, is the only extant genus in the family Ruppiaceae, with eight known species. These are aquatic plants widespread over much of the world. The genus name honours Heinrich ...
), which belong to the order Alismatales according to the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group
The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) is an informal international group of systematic botanists who collaborate to establish a consensus on the taxonomy of flowering plants (angiosperms) that reflects new knowledge about plant relationships disc ...
IV System. The genus ''Ruppia
''Ruppia'', also known as the widgeonweeds, ditch grasses or widgeon grass, is the only extant genus in the family Ruppiaceae, with eight known species. These are aquatic plants widespread over much of the world. The genus name honours Heinrich ...
'', which occurs in brackish water, is not regarded as a "real" seagrass by all authors and has been shifted to the Cymodoceaceae by some authors. The APG IV system
The APG IV system of flowering plant classification is the fourth version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy for flowering plants (angiosperms) being developed by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG). It was published ...
and The Plant List Webpage do not share this family assignment. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Sexual recruitment

 Seagrass populations are currently threatened by a variety of anthropogenic
Seagrass populations are currently threatened by a variety of anthropogenic stressor
A stressor is a chemical or biological agent, environmental condition, external stimulus or an event seen as causing stress to an organism. Psychologically speaking, a stressor can be events or environments that individuals might consider demandin ...
s. The ability of seagrasses to cope with environmental perturbations depends, to some extent, on genetic variability
Genetic variability is either the presence of, or the generation of, genetic differences.
It is defined as "the formation of individuals differing in genotype, or the presence of genotypically different individuals, in contrast to environmentally i ...
, which is obtained through sexual recruitment. By forming new individuals, seagrasses increase their genetic diversity and thus their ability to colonise
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
new areas and to adapt to environmental changes. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Seagrasses have contrasting
colonisation
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
strategies. Some seagrasses form seed bank
A seed bank (also seed banks or seeds bank) stores seeds to preserve genetic diversity; hence it is a type of gene bank. There are many reasons to store seeds. One is to preserve the genes that plant breeders need to increase yield, disease res ...
s of small seeds with hard pericarp
Fruit anatomy is the plant anatomy of the internal structure of fruit. Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. They are found in three main anatomical categories: aggregate fruits, multiple fruits, and simple fruits. Aggr ...
s that can remain in the dormancy stage for several months. These seagrasses are generally short-lived and can recover quickly from disturbances by not germinating far away from parent meadows (e.g., ''Halophila
''Halophila'' is a genus of seagrasses in the family ''Hydrocharitaceae'', the tape-grasses. It was described as a genus in 1806. The number of its contained species, and its own placement in the order Alismatales, has evolved.
Description
Th ...
'' sp., ''Halodule
''Halodule'' is a genus of plants in the family Cymodoceaceae described as a genus in 1841. It is widespread on tropical and semi-tropical ocean shores of all continents except Europe and Antarctica.
Species
Hybridization has been reported in ...
'' sp., ''Cymodocea
''Cymodocea'' is a genus in the family Cymodoceaceae described as a genus in 1805. It includes four species of sea grass distributed in warm oceans.
Habitat
''Cymodocea'' can be found in clear water and in the high intertidal areas. It is a har ...
'' sp., ''Zostera
''Zostera'' is a small genus of widely distributed seagrasses, commonly called marine eelgrass, or simply seagrass or eelgrass, and also known as seaweed by some fishermen and recreational boaters including yachtsmen. The genus ''Zostera'' co ...
'' sp. and '' Heterozostera'' sp. In contrast, other seagrasses form dispersal propagule
In biology, a propagule is any material that functions in propagating an organism to the next stage in its life cycle, such as by dispersal. The propagule is usually distinct in form from the parent organism. Propagules are produced by organisms ...
s. This strategy is typical of long-lived seagrasses that can form buoyant fruits with inner large non-dormant seeds, such as the genera ''Posidonia
''Posidonia'' is a genus of flowering plants. It contains nine species of marine plants ("seagrass"), found in the seas of the Mediterranean and around the south coast of Australia.
The APG system (1998) and APG II system (2003) accept this ge ...
'' sp., ''Enhalus
''Enhalus'' is a monotypic genus of marine flowering plants. The sole species is ''Enhalus acoroides''. ''Enhalus'' is a large seagrass native to coastal waters of the tropical Indian and Western Pacific Oceans. It is the only species of seagr ...
'' sp. and '' Thalassia'' sp. Accordingly, the seeds of long-lived seagrasses have a large dispersal capacity compared to the seeds of the short-lived type, which permits the evolution of species beyond unfavourable light conditions by the seedling development of parent meadows.
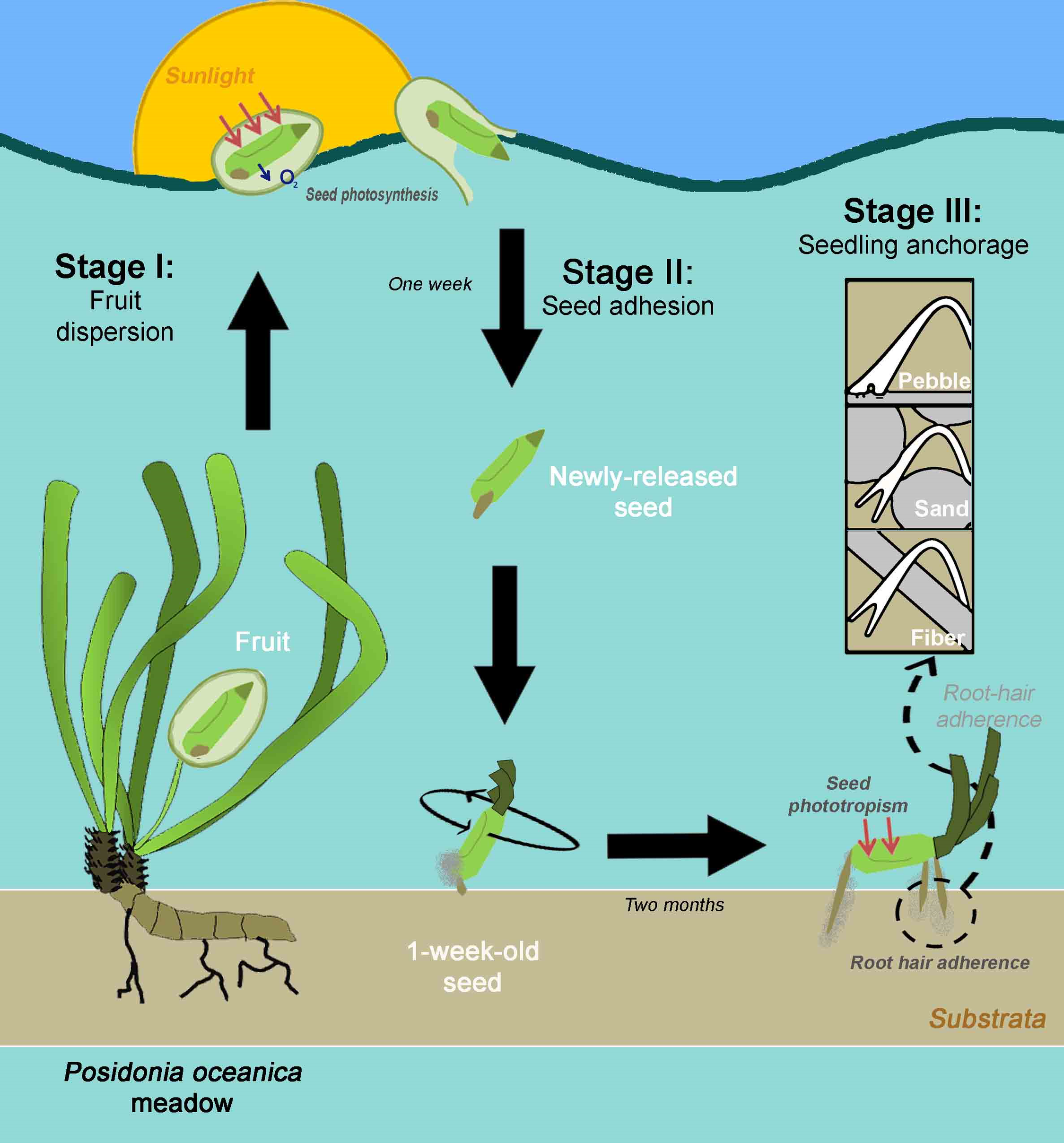
The seagrass ''Posidonia oceanica
''Posidonia oceanica'', commonly known as Neptune grass or Mediterranean tapeweed, is a seagrass species that is endemic to the Mediterranean Sea. It forms large underwater meadows that are an important part of the ecosystem. The fruit is free f ...
'' (L.) Delile is one of the oldest and largest species on Earth. An individual can form meadows
A meadow ( ) is an open habitat, or field, vegetated by grasses, herbs, and other non-woody plants. Trees or shrubs may sparsely populate meadows, as long as these areas maintain an open character. Meadows may be naturally occurring or artificia ...
measuring nearly 15 km wide and can be hundreds to thousands of years old. ''P. oceanica'' meadows
A meadow ( ) is an open habitat, or field, vegetated by grasses, herbs, and other non-woody plants. Trees or shrubs may sparsely populate meadows, as long as these areas maintain an open character. Meadows may be naturally occurring or artificia ...
play important roles in the maintenance of the geomorphology of Mediterranean coasts, which, among others, makes this seagrass a priority habitat of conservation. Currently, the flowering and recruitment of ''P. oceanica'' seems to be more frequent than that expected in the past. Further, this seagrass has singular adaptations to increase its survival during recruitment. The large amounts of nutrient reserves contained in the seeds of this seagrass support shoot and root growth, even up to the first year of seedling development. In the first months of germination, when leaf development is scarce, ''P. oceanica'' seeds perform photosynthetic activity, which increases their photosynthetic rates and thus maximises seedling establishment success. Seedlings also show high morphology plasticity during their root system
In mathematics, a root system is a configuration of vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, especially the classification and representati ...
development by forming adhesive root hair
Root hair, or absorbent hairs, are outgrowths of epidermal cells, specialized cells at the tip of a plant root. They are lateral extensions of a single cell and are only rarely branched. They are found in the region of maturation, of the root. Root ...
s to help anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal , used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ''ancora'', which itself comes from the Greek ἄγ ...
themselves to rocky sediments. However, many factors about ''P. oceanica'' sexual recruitment remain unknown, such as when photosynthesis in seeds is active or how seeds can remain anchored to and persist on substrate until their root systems have completely developed.
Intertidal and subtidal
 Seagrasses occurring in the intertidal and subtidal zones are exposed to highly variable environmental conditions due to tidal changes. Subtidal seagrasses are more frequently exposed to lower light conditions, driven by plethora of natural and human-caused influences that reduce light penetration by increasing the density of suspended opaque materials. Subtidal light conditions can be estimated, with high accuracy, using artificial intelligence, enabling more rapid mitigation than was available using ''in situ'' techniques. Seagrasses in the intertidal zone are regularly exposed to air and consequently experience extreme high and low temperatures, high photoinhibitory irradiance, and
Seagrasses occurring in the intertidal and subtidal zones are exposed to highly variable environmental conditions due to tidal changes. Subtidal seagrasses are more frequently exposed to lower light conditions, driven by plethora of natural and human-caused influences that reduce light penetration by increasing the density of suspended opaque materials. Subtidal light conditions can be estimated, with high accuracy, using artificial intelligence, enabling more rapid mitigation than was available using ''in situ'' techniques. Seagrasses in the intertidal zone are regularly exposed to air and consequently experience extreme high and low temperatures, high photoinhibitory irradiance, and desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container.
...
stress relative to subtidal seagrass. Such extreme temperatures can lead to significant seagrass dieback when seagrasses are exposed to air during low tide. Desiccation stress during low tide has been considered the primary factor limiting seagrass distribution at the upper intertidal zone. Seagrasses residing the intertidal zone are usually smaller than those in the subtidal zone to minimize the effects of emergence stress. Intertidal seagrasses also show light-dependent responses, such as decreased photosynthetic efficiency and increased photoprotection during periods of high irradiance and air exposure.
 In contrast, seagrasses in the subtidal zone adapt to reduced light conditions caused by light attenuation and scattering due to the overlaying water column and suspended particles. Seagrasses in the deep subtidal zone generally have longer leaves and wider leaf blades than those in the shallow subtidal or intertidal zone, which allows more photosynthesis, in turn resulting in greater growth. Seagrasses also respond to reduced light conditions by increasing chlorophyll content and decreasing the chlorophyll a/b ratio to enhance
In contrast, seagrasses in the subtidal zone adapt to reduced light conditions caused by light attenuation and scattering due to the overlaying water column and suspended particles. Seagrasses in the deep subtidal zone generally have longer leaves and wider leaf blades than those in the shallow subtidal or intertidal zone, which allows more photosynthesis, in turn resulting in greater growth. Seagrasses also respond to reduced light conditions by increasing chlorophyll content and decreasing the chlorophyll a/b ratio to enhance light absorption
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy — and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy). A ...
efficiency by using the abundant wavelengths efficiently. As seagrasses in the intertidal and subtidal zones are under highly different light conditions, they exhibit distinctly different photoacclimatory responses to maximize photosynthetic activity and photoprotection from excess irradiance.
Seagrasses assimilate large amounts of inorganic carbon
Total inorganic carbon (''C''T or TIC) is the sum of the inorganic carbon species.
Carbon compounds can be distinguished as either organic or inorganic, and dissolved or particulate, depending on their composition. Organic carbon forms the back ...
to achieve high level production. Marine macrophytes
Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments ( saltwater or freshwater). They are also referred to as hydrophytes or macrophytes to distinguish them from algae and other microphytes. A macrophyte is a plant that ...
, including seagrass, use both and (bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochem ...
) for photosynthetic carbon reduction. Despite air exposure during low tide, seagrasses in the intertidal zone can continue to photosynthesize utilizing CO2 in the air. Thus, the composition of inorganic carbon sources for seagrass photosynthesis probably varies between intertidal and subtidal plants. Because stable carbon isotope ratio
An isotopic signature (also isotopic fingerprint) is a ratio of non-radiogenic ' stable isotopes', stable radiogenic isotopes, or unstable radioactive isotopes of particular elements in an investigated material. The ratios of isotopes in a sample ...
s of plant tissues change based on the inorganic carbon sources for photosynthesis, seagrasses in the intertidal and subtidal zones may have different stable carbon isotope ratio ranges.
Seagrass meadows


Seagrass bed
A seagrass meadow or seagrass bed is an underwater ecosystem formed by seagrasses. Seagrasses are marine (saltwater) plants found in shallow coastal waters and in the brackish waters of estuaries. Seagrasses are flowering plants with stems and ...
s/meadows can be either monospecific (made up of a single species) or in mixed beds. In temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
areas, usually one or a few species dominate (like the eelgrass ''Zostera marina
''Zostera marina'' is a flowering vascular plant species as one of many kinds of seagrass, with this species known primarily by the English name of eelgrass with seawrack much less used, and refers to the plant after breaking loose from the submer ...
'' in the North Atlantic), whereas tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
beds usually are more diverse, with up to thirteen species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
recorded in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
.
Seagrass beds are diverse and productive ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
s, and can harbor hundreds of associated species from all phyla, for example juvenile and adult fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, epiphytic
An epiphyte is an organism that grows on the surface of a plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphytes grow are called phoroph ...
and free-living macroalgae
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
and microalgae, mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is e ...
s, bristle worm
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are ...
s, and nematodes. Few species were originally considered to feed directly on seagrass leaves
A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", wh ...
(partly because of their low nutritional content), but scientific reviews and improved working methods have shown that seagrass herbivory
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
is an important link in the food chain, feeding hundreds of species, including green turtle
The green sea turtle (''Chelonia mydas''), also known as the green turtle, black (sea) turtle or Pacific green turtle, is a species of large sea turtle of the family Cheloniidae. It is the only species in the genus ''Chelonia''. Its range exten ...
s, dugong
The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest m ...
s, manatee
Manatees (family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living speci ...
s, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, geese
A goose ( : geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera '' Anser'' (the grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (the black geese). Some other birds, mostly related to the she ...
, swans, sea urchins and crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
s. Some fish species that visit/feed on seagrasses raise their young in adjacent mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evoluti ...
s or coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
s.
Seagrasses trap sediment and slow down water movement, causing suspended sediment to settle out. Trapping sediment benefits coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...
by reducing sediment loads, improving photosynthesis for both coral and seagrass.
Although often overlooked, seagrasses provide a number of ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the many and varied benefits to humans provided by the natural environment and healthy ecosystems. Such ecosystems include, for example, agroecosystems, forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystems, and aquatic ecosystems. ...
. Seagrasses are considered ecosystem engineers. This means that the plants alter the ecosystem around them. This adjusting occurs in both physical and chemical forms. Many seagrass species produce an extensive underground network of roots and rhizome which stabilizes sediment and reduces coastal erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of waves, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts of storms. The landwa ...
. This system also assists in oxygenating the sediment, providing a hospitable environment for sediment-dwelling organisms. Seagrasses also enhance water quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through tr ...
by stabilizing heavy metals, pollutants, and excess nutrients. The long blades of seagrasses slow the movement of water which reduces wave energy and offers further protection against coastal erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
and storm surge. Furthermore, because seagrasses are underwater plants, they produce significant amounts of oxygen which oxygenate the water column. These meadows account for more than 10% of the ocean's total carbon storage. Per hectare, it holds twice as much carbon dioxide as rain forests and can sequester about 27.4 million tons of CO2 annually.
Seagrass meadows
A seagrass meadow or seagrass bed is an underwater ecosystem formed by seagrasses. Seagrasses are marine (saltwater) plants found in shallow coastal waters and in the brackish waters of estuaries. Seagrasses are flowering plants with stems and ...
provide food for many marine herbivores. Sea turtles, manatees, parrotfish, surgeonfish, sea urchins and pinfish feed on seagrasses. Many other smaller animals feed on the epiphytes and invertebrates that live on and among seagrass blades. Seagrass meadows also provide physical habitat in areas that would otherwise be bare of any vegetation. Due to this three dimensional structure in the water column, many species occupy seagrass habitats for shelter and foraging. It is estimated that 17 species of coral reef fish spend their entire juvenile life stage solely on seagrass flats. These habitats also act as a nursery grounds for commercially and recreationally valued fishery species, including the gag grouper (''Mycteroperca microlepis
''Mycteroperca microlepis'', the gag, gag grouper, velvet rockfish or charcoal belly, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and ...
''), red drum, common snook
The common snook (''Centropomus undecimalis'') is a species of marine fish in the family Centropomidae of the order Perciformes. The common snook is also known as the sergeant fish or robalo. It was originally assigned to the sciaenid genus ...
, and many others. Some fish species utilize seagrass meadows and various stages of the life cycle. In a recent publication, Dr. Ross Boucek and colleagues discovered that two highly sought after flats fish, the common snook and spotted sea trout provide essential foraging habitat during reproduction. Sexual reproduction is extremely energetically expensive to be completed with stored energy; therefore, they require seagrass meadows in close proximity to complete reproduction. Furthermore, many commercially important invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s also reside in seagrass habitats including bay scallops (''Argopecten irradians
''Argopecten irradians'', formerly classified as ''Aequipecten irradians'', common names Atlantic bay scallop or bay scallop, is a species of scallop in the family Pectinidae. An edible saltwater clam, it is native to the northwest Atlantic fro ...
''), horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or crustaceans: they are chelicerates, most closely related to ar ...
s, and shrimp. Charismatic fauna can also be seen visiting the seagrass habitats. These species include West Indian manatee
The West Indian manatee (''Trichechus manatus''), also known as the North American manatee, is a large, aquatic mammal native to warm coastal areas of the Caribbean, from the eastern US to northern Brazil. Living alone or in herds, it feeds on un ...
, green sea turtles, and various species of sharks. The high diversity of marine organisms that can be found on seagrass habitats promotes them as a tourist attraction and a significant source of income for many coastal economies along the Gulf of Mexico and in the Caribbean.
Thalassia testudinum
''Thalassia testudinum'', commonly known as turtlegrass, is a species of marine seagrass. It forms meadows in shallow sandy or muddy locations in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. Turtle grass and other seagrasses form meadows which are i ...
'' seagrass bed
A seagrass meadow or seagrass bed is an underwater ecosystem formed by seagrasses. Seagrasses are marine (saltwater) plants found in shallow coastal waters and in the brackish waters of estuaries. Seagrasses are flowering plants with stems and ...
File:White-spotted puffer.jpg, White-spotted puffer
The white-spotted puffer fish (''Arothron hispidus'') is a medium to large-sized puffer fish, it can reach 50 cm length. It is light grey in color, or greyish or yellowish, and clearly covered with more or less regular white points, that be ...
s, often found in seagrass areas
File:Seagrass Meadow - Porthdinllaen.webm, Underwater footage of seagrass meadow, bull huss and conger eel
''Conger'' ( ) is a genus of marine congrid eels. It includes some of the largest types of eels, ranging up to 2 m (6 ft) or more in length, in the case of the European conger. Large congers have often been observed by divers during ...
Seagrass microbiome

Seagrass holobiont
The concept of theholobiont
A holobiont is an assemblage of a host and the many other species living in or around it, which together form a discrete ecological unit through symbiosis, though there is controversy over this discreteness. The components of a holobiont are i ...
, which emphasizes the importance and interactions of a microbial host with associated microorganisms and viruses and describes their functioning as a single biological unit, has been investigated and discussed for many model systems, although there is substantial criticism of a concept that defines diverse host-microbe symbioses as a single biological unit. The holobiont and hologenome concepts have evolved since the original definition, and there is no doubt that symbiotic microorganisms are pivotal for the biology and ecology of the host by providing vitamins, energy and inorganic or organic nutrients, participating in defense mechanisms, or by driving the evolution of the host. Although most work on host-microbe interactions has been focused on animal systems such as corals, sponges, or humans, there is a substantial body of literature on plant holobiont
Since the colonization of land by ancestral plant lineages 450 million years ago, plants and their associated microbes have been interacting with each other, forming an assemblage of species that is often referred to as a holobiont. Selective p ...
s. Plant-associated microbial communities impact both key components of the fitness of plants, growth and survival, and are shaped by nutrient availability and plant defense mechanisms. Several habitats have been described to harbor plant-associated microbes, including the rhizoplane (surface of root tissue), the rhizosphere
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Soil pores in the rhizosphere can contain many bacteria and other microo ...
(periphery of the roots), the endosphere (inside plant tissue), and the phyllosphere (total above-ground surface area). The microbial community in the ''P. oceanica'' rhizosphere shows similar complexity as terrestrial habitats that contain thousands of taxa per gram of soil. In contrast, the chemistry in the rhizosphere of ''P. oceanica'' was dominated by the presence of sugars like sucrose and phenolics.
Cell walls
 Seagrass cell walls contain the same polysaccharides found in
Seagrass cell walls contain the same polysaccharides found in angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
land plants, such as cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell w ...
However, the cell walls of some seagrasses are characterised by sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
d polysaccharides, which is a common attribute of macroalgae
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
from the groups of red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
and also green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
. It was proposed in 2005 that the ability to synthesise sulfated polysaccharides was regained by marine angiosperms. Another unique feature of cell walls of seagrasses is the occurrence of unusual pectic
Pectin ( grc, πηκτικός ': "congealed" and "curdled") is a heteropolysaccharide, a structural acid contained in the primary lamella, in the middle lamella, and in the cell walls of terrestrial plants. The principal, chemical component o ...
polysaccharides called apiogalacturonan Apiogalacturonans are a type of pectins known to be found in the walls of Lemna and Zostera marina
''Zostera marina'' is a flowering vascular plant species as one of many kinds of seagrass, with this species known primarily by the English name of ...
s.
In addition to polysaccharides, glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
s of the hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelati ...
-rich glycoprotein family, are important components of cell walls of land plants. The highly glycosylated arabinogalactan proteins are of interest because of their involvement in both wall architecture and cellular regulatory processes. Arabinogalactan proteins are ubiquitous in seed land plants and have also been found in fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes exce ...
s, lycophyte
The lycophytes, when broadly circumscribed, are a vascular plant (tracheophyte) subgroup of the kingdom Plantae. They are sometimes placed in a division Lycopodiophyta or Lycophyta or in a subdivision Lycopodiophytina. They are one of the oldes ...
s and mosses. They are structurally characterised by large polysaccharide moieties composed of arabinogalactan
Arabinogalactan, also known as galactoarabinan, larch arabinogalactan, and larch gum, is a biopolymer consisting of arabinose and galactose monosaccharides. Two classes of arabinogalactans are found in nature: plant arabinogalactan and microbial a ...
s (normally over 90% of the molecule) which are covalently linked via hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelati ...
to relatively small protein/peptide backbones (normally less than 10% of the molecule). Distinct glycan modifications have been identified in different species and tissues and it has been suggested these influence physical properties and function. In 2020, AGPs were isolated and structurally characterised for the first time from a seagrass. Although the common backbone structure of land plant arabinogalactan proteins is conserved, the glycan structures exhibit unique features suggesting a role of seagrass arabinogalactan proteins in osmoregulation
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration o ...
.
Further components of secondary walls of plants are cross-linked phenolic
Phenolic is an adjective and a substantive (noun) that may apply to :
* Phenol (or carbolic acid), a colorless crystalline solid and aromatic compound
* Phenols, a class of chemical compounds that include phenol
* Phenolic content in wine
* Phenol ...
polymers called lignin, which are responsible for mechanical strengthening of the wall. In seagrasses, this polymer has also been detected, but often in lower amounts compared to angiosperm land plants. Thus, the cell walls of seagrasses seem to contain combinations of features known from both angiosperm land plants and marine macroalgae together with new structural elements. Dried seagrass leaves might be useful for papermaking or as insulating materials, so knowledge of cell wall composition has some technological relevance.
Threats and conservation
Despite only covering 0.1 - 0.2% of the ocean’s surface, seagrasses form critically important ecosystems. Much like many other regions of the ocean, seagrasses have been faced with an accelerating global decline. Since the late 19th century, over 20% of the global seagrass area has been lost, with seagrass bed loss occurring at a rate of 1.5% each year. Of the 72 global seagrass species, approximately one quarter (15 species) could be considered at aThreatened
Threatened species are any species (including animals, plants and fungi) which are vulnerable to endangerment in the near future. Species that are threatened are sometimes characterised by the population dynamics measure of ''critical depensa ...
or Near Threatened
A near-threatened species is a species which has been categorized as "Near Threatened" (NT) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as that may be vulnerable to endangerment in the near future, but it does not currently qualify f ...
status on the IUCN’s Red List of Threatened Species. Threats include a combination of natural factors, such as storms and disease, and anthropogenic in origin, including habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change.
By far the most common threat to seagrass is human activity. Up to 67 species (93%) of seagrasses are affected by human activity along coastal regions. Activities such as coastal land development, motorboating, and fishing practices like trawling
Trawling is a method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch different spec ...
either physically destroy seagrass beds or increase turbidity
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Fluids ...
in the water, causing seagrass die-off. Since seagrasses have some of the highest light requirements of angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
plant species, they are highly affected by environmental conditions that change water clarity and block light.
Seagrasses are also negatively affected by changing global climatic conditions. Increased weather events, sea level rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cry ...
, and higher temperatures as a result of global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
all have the potential to induce widespread seagrass loss. An additional threat to seagrass beds is the introduction of non-native species. For seagrass beds worldwide, at least 28 non-native species have become established. Of these invasive species, the majority (64%) have been documented to infer negative effects on the ecosystem.
Another major cause of seagrass disappearance is coastal eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phytopla ...
. Rapidly developing human population density along coastlines has led to high nutrient loads in coastal waters from sewage and other impacts of development. Increased nutrient loads create an accelerating cascade of direct and indirect effects that lead to seagrass decline. While some exposure to high concentrations of nutrients, especially nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
and phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
, can result in increased seagrass productivity, high nutrient levels can also stimulate the rapid overgrowth of macroalgae
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
and epiphytes in shallow water, and phytoplankton in deeper water. In response to high nutrient levels, macroalgae form dense canopies on the surface of the water, limiting the light able to reach the benthic seagrasses. Algal bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompass ...
s caused by eutrophication also lead to hypoxic
Hypoxia means a lower than normal level of oxygen, and may refer to:
Reduced or insufficient oxygen
* Hypoxia (environmental), abnormally low oxygen content of the specific environment
* Hypoxia (medical), abnormally low level of oxygen in the t ...
conditions, which seagrasses are also highly susceptible to. Since coastal sediment is generally anoxic
The term anoxia means a total depletion in the level of oxygen, an extreme form of hypoxia or "low oxygen". The terms anoxia and hypoxia are used in various contexts:
* Anoxic waters, sea water, fresh water or groundwater that are depleted of diss ...
, seagrass must supply oxygen to their below-ground roots either through photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
or by the diffusion of oxygen in the water column. When the water surrounding seagrass becomes hypoxic, so too do seagrass tissues. Hypoxic conditions negatively affect seagrass growth and survival with seagrasses exposed to hypoxic conditions shown to have reduced rates of photosynthesis, increased respiration, and smaller growth. Hypoxic conditions can eventually lead to seagrass die-off which creates a positive feedback cycle, where the decomposition of organic matter further decreases the amount of oxygen present in the water column.
Possible seagrass population trajectories have been studied in the Mediterranean sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. These studies suggest that the presence of seagrass depends on physical factors such as temperature, salinity, depth and turbidity, along with natural phenomena like climate change and anthropogenic pressure. While there are exceptions, regression was a general trend in many areas of the Mediterranean Sea. There is an estimated 27.7% reduction along the southern coast of Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on whi ...
, 18%-38% reduction in the Northern Mediterranean basin, 19%-30% reduction on Ligurian coasts since the 1960s and 23% reduction in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
in the past 50 years. In Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
the main reason for regression was due to human activity such as illegal trawling
Trawling is a method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch different spec ...
and aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
farming. It was found that areas with medium to high human impact suffered more severe reduction. Overall, it was suggested that 29% of known areal seagrass populations have disappeared since 1879. The reduction in these areas suggests that should warming in the Mediterranean basin continue, it may lead to a functional extinction of ''Posidonia oceanica
''Posidonia oceanica'', commonly known as Neptune grass or Mediterranean tapeweed, is a seagrass species that is endemic to the Mediterranean Sea. It forms large underwater meadows that are an important part of the ecosystem. The fruit is free f ...
'' in the Mediterranean by 2050. Scientists suggested that the trends they identified appear to be part of a large-scale trend worldwide.
Conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws.
Conservation may also refer to:
Environment and natural resources
* Nature conservation, the protection and managem ...
efforts are imperative to the survival of seagrass species. While there are many challenges to overcome with respect to seagrass conservation there are some major ones that can be addressed. Societal awareness of what seagrasses are and their importance to human well-being is incredibly important. As the majority of people become more urbanized they are increasingly more disconnected from the natural world. This allows for misconceptions and a lack of understanding of seagrass ecology and its importance. Additionally, it is a challenge to obtain and maintain information on the status and condition of seagrass populations. With many populations across the globe, it is difficult to map the current populations. Another challenge faced in seagrass conservation is the ability to identify threatening activities on a local scale. Also, in an ever growing human population, there is a need to balance the needs of the people while also balancing the needs of the planet. Lastly, it is challenging to generate scientific research to support conservation of seagrass. Limited efforts and resources are dedicated to the study of seagrasses. This is seen in areas such as India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
where there is little to no plan in place to conserve seagrass populations. However, the conservation and restoration of seagrass may contribute to 16 of the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
.
In a study of seagrass conservation in China, several suggestions were made by scientists on how to better conserve seagrass. They suggested that seagrass beds should be included in the Chinese conservation agenda as done in other countries. They called for the Chinese government to forbid land reclamation in areas near or in seagrass beds, to reduce the number and size of culture ponds, to control raft aquaculture and improve sediment quality, to establish seagrass reserves, to increase awareness of seagrass beds to fishermen and policy makers and to carry out seagrass restoration. Similar suggestions were made in India where scientists suggested that public engagement was important. Also, scientists, the public, and government officials should work in tandem to integrate traditional ecological knowledge
Traditional ecological knowledge (TEK) describes indigenous and other traditional knowledge of local resources. As a field of study in Northern American anthropology, TEK refers to "a cumulative body of knowledge, belief, and practice, evolving by ...
and socio-cultural practices to evolve conservation policies.
World Seagrass Day is an annual event held on March 1 to raise awareness about seagrass and its important functions in the marine ecosystem.
See also
*Alismatales
The Alismatales (alismatids) are an order of flowering plants including about 4,500 species. Plants assigned to this order are mostly Tropical vegetation, tropical or Aquatic plant, aquatic. Some grow in fresh water, some in marine habitats.
...
* Blue carbon
*Salt marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is domin ...
*Mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evoluti ...
* Sea rewilding
*Nursery habitat
In marine environments, a nursery habitat is a subset of all habitats where juveniles of a species occur, having a greater level of productivity per unit area than other juvenile habitats (Beck et al. 2001). Mangroves, salt marshes and seagrass ar ...
*Ocean Data Viewer
The UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC) is a collaboration centre of UN Environment Programme, based in Cambridge in the United Kingdom. UNEP-WCMC has been part of UN Environment Programme since 2000, and has r ...
: contains the global distribution of seagrasses dataset
References
Further references
* den Hartog, C. 1970. ''The Sea-grasses of the World''. ''Verhandl. der Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, Afd. Natuurkunde'', No. 59(1). * Duarte, Carlos M. and Carina L. Chiscano “Seagrass biomass and production: a reassessment” Aquatic Botany Volume 65, Issues 1–4, November 1999, Pages 159–174. * Green, E.P. & Short, F.T.(eds). 2003. ''World Atlas of Seagrasses''. University of California Press, Berkeley, CA. 298 pp. * Hemminga, M.A. & Duarte, C. 2000. ''Seagrass Ecology''. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 298 pp. * Hogarth, Peter ''The Biology of Mangroves and Seagrasses'' (Oxford University Press, 2007) * Larkum, Anthony W.D., Robert J. Orth, and Carlos M. Duarte (Editors) ''Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation'' (Springer, 2006) * Orth, Robert J. et al. "A Global Crisis for Seagrass Ecosystems" ''BioScience'' December 2006 / Vol. 56 No. 12, Pages 987–996. * Short, F.T. & Coles, R.G.(eds). 2001. ''Global Seagrass Research Methods''. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam. 473 pp. * A.W.D. Larkum, R.J. Orth, and C.M. Duarte (eds). Seagrass Biology: A Treatise. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, in press. * A. Schwartz; M. Morrison; I. Hawes; J. Halliday. 2006. Physical and biological characteristics of a rare marine habitat: sub-tidal seagrass beds of offshore islands. ''Science for Conservation 269.'' 39 pp* Waycott, M, McMahon, K, & Lavery, P 2014, A guide to southern temperate seagrasses, CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne
External links
*Project Seagrass - Charity advancing the conservation of seagrass through community, research and action
Project Regeneration.
SeagrassSpotter - Citizen Science project raising awaress for seagrass meadows and mapping their locations
overview from the Smithsonian Ocean Portal
* ttp://www.seagrasswatch.org/ Seagrass-Watch - the largest scientific, non-destructive, seagrass assessment and monitoring program in the worldbr>Restore-A-Scar - a non-profit campaign to restore seagrass meadows damaged by boat props
- special issue on seagrasses
{{Authority control Blue carbon Plant common names Roofing materials de:Seegras