pleomorphic adenoma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pleomorphic adenoma is a common benign salivary gland neoplasm characterised by neoplastic proliferation of epithelial (ductal) cells along with myoepithelial components, having a malignant potentiality. It is the most common type of salivary gland tumor and the most common tumor of the

 Morphological diversity is the most characteristic feature of this neoplasm. Histologically, it is highly variable in appearance, even within individual tumors. Classically it is biphasic and is characterized by an admixture of polygonal
Morphological diversity is the most characteristic feature of this neoplasm. Histologically, it is highly variable in appearance, even within individual tumors. Classically it is biphasic and is characterized by an admixture of polygonal
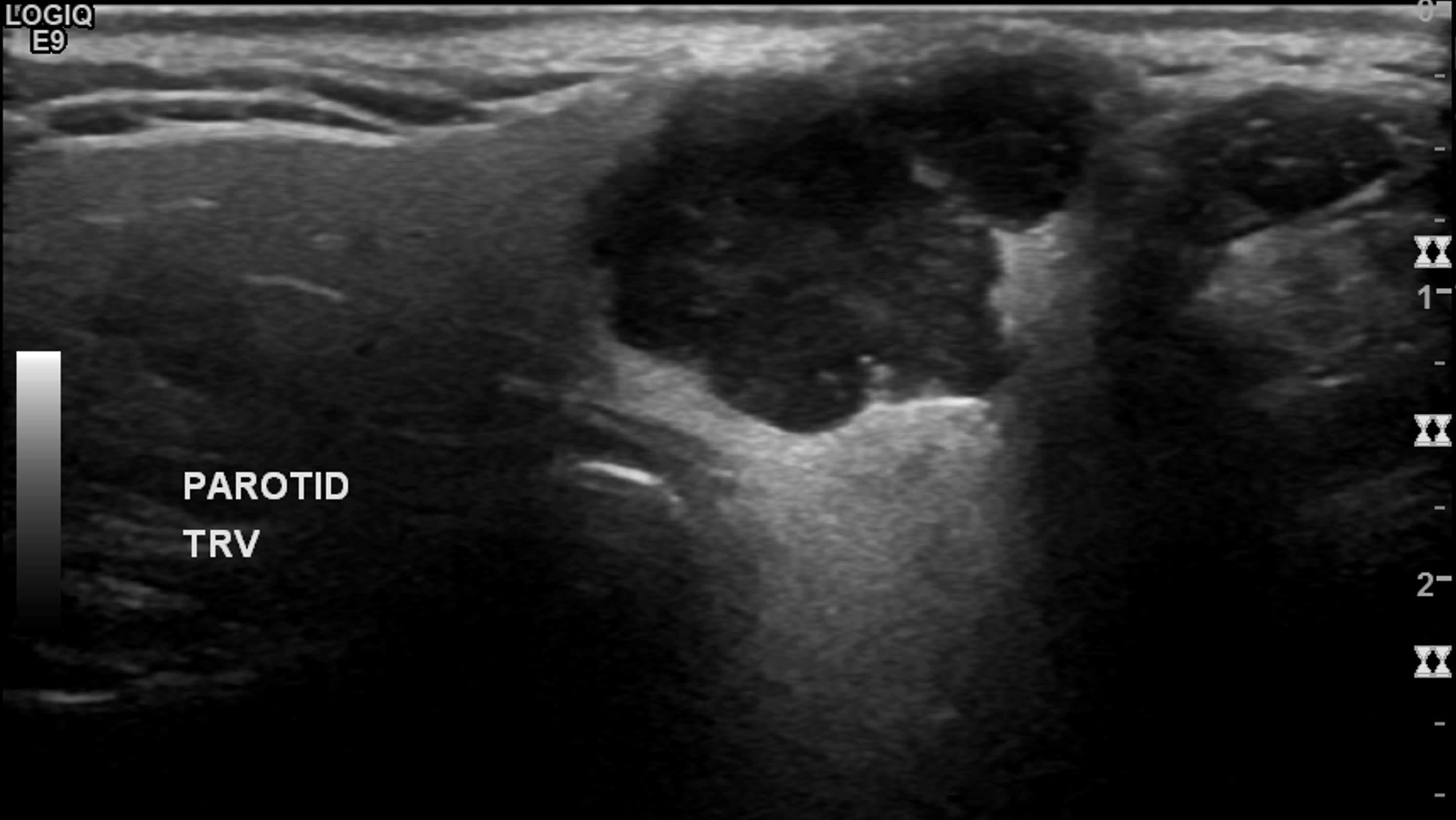 The diagnosis of salivary gland tumors utilize both tissue sampling and radiographic studies. Tissue sampling procedures include
The diagnosis of salivary gland tumors utilize both tissue sampling and radiographic studies. Tissue sampling procedures include
 Overall, the mainstay of the treatment for salivary gland tumor is surgical resection. Needle biopsy is highly recommended prior to surgery to confirm the diagnosis. More detailed surgical technique and the support for additional
Overall, the mainstay of the treatment for salivary gland tumor is surgical resection. Needle biopsy is highly recommended prior to surgery to confirm the diagnosis. More detailed surgical technique and the support for additional
parotid gland
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the ma ...
. It derives its name from the architectural Pleomorphism
Pleomorphism may refer to:
* Pleomorphism (cytology), variability in the size and shape of cells and/or their nuclei
* Pleomorphism (microbiology), the ability of some bacteria to alter their shape or size in response to environmental conditions
...
(variable appearance) seen by light microscopy. It is also known as "Mixed tumor, salivary gland
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary ...
type", which refers to its dual origin from epithelial and myoepithelial elements as opposed to its pleomorphic appearance.
Clinical presentation
The tumor is usually solitary and presents as a slow growing, painless, firm single nodular mass. Isolated nodules are generally outgrowths of the main nodule rather than a multinodular presentation. It is usually mobile unless found in the palate and can cause atrophy of the mandibular ramus when located in the parotid gland. When found in the parotid tail, it may present as an eversion of the ear lobe. Though it is classified as abenign tumor
A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that does not invade neighboring tissue or metastasize (spread throughout the body). Compared to malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate. Benign tumors have re ...
, pleomorphic adenomas have the capacity to grow to large proportions and may undergo malignant transformation, to form carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma, a risk that increases with time (9.5% chance to convert into malignancy in 15 years). Although it is "benign", the tumor is aneuploid
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any ...
, it can recur after resection, it invades normal adjacent tissue, and distant metastases have been reported after long (+10 years) time intervals. This tumour most often presents in the lower pole of the superficial lobe of the gland, about 10% of the tumours arise in the deeper portions of the gland. It occurs more frequently in females than in males, the ratio approximating 6:4. The majority of the lesion are found in patients in the fourth to sixth decades with an average age of occurrences of about 43 years, but these are relatively common in young adults and have been known to occur in children.
Histology

 Morphological diversity is the most characteristic feature of this neoplasm. Histologically, it is highly variable in appearance, even within individual tumors. Classically it is biphasic and is characterized by an admixture of polygonal
Morphological diversity is the most characteristic feature of this neoplasm. Histologically, it is highly variable in appearance, even within individual tumors. Classically it is biphasic and is characterized by an admixture of polygonal epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercell ...
and spindle-shaped myoepithelial elements in a variable background stroma that may be mucoid, myxoid, cartilaginous or hyaline. Epithelial elements may be arranged in duct-like structures, sheets, clumps and/or interlacing strands and consist of polygonal, spindle or stellate-shaped cells (hence pleiomorphism). Areas of squamous metaplasia and epithelial pearls may be present. The tumor is not enveloped, but it is surrounded by a fibrous pseudocapsule of varying thickness. The tumor extends through normal glandular parenchyma in the form of finger-like pseudopodia, but this is not a sign of malignant transformation.
The tumor often displays characteristic chromosomal translocations between chromosomes #3 and #8. This causes the PLAG gene to be juxtaposed to the gene for beta catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcripti ...
. This activates the catenin pathway and leads to inappropriate cell division.
Diagnosis
 The diagnosis of salivary gland tumors utilize both tissue sampling and radiographic studies. Tissue sampling procedures include
The diagnosis of salivary gland tumors utilize both tissue sampling and radiographic studies. Tissue sampling procedures include fine needle aspiration
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, aft ...
(FNA) and core needle biopsy (bigger needle comparing to FNA). Both of these procedures can be done in an outpatient setting. Diagnostic imaging techniques for salivary gland tumors include ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
, computer tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNA), operated in experienced hands, can determine whether the tumor is malignant in nature with sensitivity around 90%. FNA can also distinguish primary salivary tumor from metastatic disease.
Core needle biopsy can also be done in outpatient setting. It is more invasive but is more accurate compared to FNA with diagnostic accuracy
Accuracy and precision are two measures of ''observational error''.
''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements ( observations or readings) are to their ''true value'', while ''precision'' is how close the measurements are to each oth ...
greater than 97%. Furthermore, core needle biopsy allows more accurate histological typing of the tumor.
In terms of imaging studies, ultrasound can determine and characterize superficial parotid tumors. Certain types of salivary gland tumors have certain sonographic characteristics on ultrasound. Ultrasound is also frequently used to guide FNA or core needle biopsy.
CT allows direct, bilateral visualization of the salivary gland tumor and provides information about overall dimension and tissue invasion. CT is excellent for demonstrating bony invasion. MRI provides superior soft tissue delineation such as perineural invasion
In pathology, perineural invasion, abbreviated PNI, refers to the invasion of cancer to the space surrounding a nerve. It is common in head and neck cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal cancer.
Unlike perineurial spread (PNS), which is defined ...
when compared to CT only.
Treatment
 Overall, the mainstay of the treatment for salivary gland tumor is surgical resection. Needle biopsy is highly recommended prior to surgery to confirm the diagnosis. More detailed surgical technique and the support for additional
Overall, the mainstay of the treatment for salivary gland tumor is surgical resection. Needle biopsy is highly recommended prior to surgery to confirm the diagnosis. More detailed surgical technique and the support for additional adjuvant In pharmacology, an adjuvant is a drug or other substance, or a combination of substances, that is used to increase the efficacy or potency of certain drugs. Specifically, the term can refer to:
* Adjuvant therapy in cancer management
* Analgesi ...
radiotherapy depends on whether the tumor is malignant or benign.
Surgical treatment of parotid gland tumors is sometimes difficult, partly because of the anatomical relationship of the facial nerve and the parotid lodge, but also through the increased potential for postoperative relapse. Thus, detection of early stages of a tumor of the parotid gland is extremely important in terms of prognosis after surgery.(webpage has a translation button)
There have been several approaches for surgery of parotid pleomorphic adenoma in the course of time. Enucleation of the tumor (i.e. intracapsular dissection), a procedure that was common in the early 20th century, is nowadays obsolete due to very high incidence of recurrence. After the time of enucleations, pleomorphic adenomas of parotid gland were recommended to be routinely treated with superficial or total parotidectomy. These procedures combine complete tumor removal and identification of the main trunk of facial nerve during surgery to avoid any lesions to the nerve. However, extensive surgery may cause significant morbidity, such as Frey´s syndrome (excessive sweat while eating) and salivary fistula. Also, aesthetic outcome may be compromised. Therefore, less invasive procedures have been preferred in selected cases during the recent years, and introduction of perioperative neuromonitoring enabled the evolution of several different surgical techniques some twenty years ago.
Currently, the choice of surgical approach for parotid pleomorphic adenoma is mainly based on the size, location, and mobility of the tumor. The recommended main techniques include extracapsular dissection, partial superficial parotidectomy, and lateral or total parotidectomy. Nevertheless, the experience of surgeon plays a key role in the results of these distinct procedures. An important point of view is that recurrent pleomorphic adenomas may occur after a very long time from primary surgery, on average over 7–10 years but up to 24 years afterwards. Thus, it is of utmost importance to evaluate the ultimate results of these different surgical techniques in the future.
The benign tumors of the submandibular gland is treated by simple excision with preservation of mandibular branch of the facial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste ...
, the hypoglossal nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by ...
, and the lingual nerve
The lingual nerve carries sensory innervation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It contains fibres from both the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3
) and from the facial nerve (CN VII). The fibres from the trigeminal nerv ...
. Other benign tumors of minor salivary glands are treated similarly.
Malignant salivary tumors usually require wide local resection of the primary tumor. However, if complete resection cannot be achieved, adjuvant radiotherapy should be added to improve local control. This surgical treatment has many sequelae such as cranial nerve damage, Frey's syndrome, cosmetic problems, etc.
Usually about 44% of the patients have a complete histologic removal of the tumor and this refers to the most significant survival rate.
See also
*Warthin's tumor
Warthin's tumor, also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, is a benign cystic tumor of the salivary glands containing abundant lymphocytes and germinal centers (lymph node-like stroma). It is named for pathologist Aldred Scott Warthin, wh ...
- monomorphic adenoma
* Carcinoma
* Sialadenitis
Sialadenitis (sialoadenitis) is inflammation of salivary glands, usually the major ones, the most common being the parotid gland, followed by submandibular and sublingual glands. It should not be confused with sialadenosis (sialosis) which is a non ...
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pleomorphic Adenoma Benign neoplasms Salivary gland neoplasia