

The
military budget
A military budget (or military expenditure), also known as a defense budget, is the amount of financial resources dedicated by a state to raising and maintaining an armed forces or other methods essential for defense purposes.
Financing militar ...
is the largest portion of the discretionary
United States federal budget
The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. Th ...
allocated to the
Department of Defense Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philipp ...
, or more broadly, the portion of the budget that goes to any military-related expenditures. The military budget pays the salaries, training, and health care of uniformed and civilian personnel, maintains arms, equipment and facilities, funds operations, and develops and buys new items. The budget funds five branches of the U.S. military: the
Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
,
Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
,
Marine Corps
Marines, or naval infantry, are typically a military force trained to operate in littoral zones in support of naval operations. Historically, tasks undertaken by marines have included helping maintain discipline and order aboard the ship (refl ...
,
Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ...
, and
Space Force
A space force is a military branch of a nation's armed forces that conducts military operations in outer space and space warfare. The world's first space force was the Russian Space Forces, established in 1992 as an independent military service. ...
.
Budget for FY2023
As of 2 March 2022, the defense department was still operating under a
continuing resolution
In the United States, a continuing resolution (often abbreviated to CR) is a type of appropriations legislation. An appropriations bill is a bill that appropriates (gives to, sets aside for) money to specific federal government departments, ag ...
,
which constrains spending even though DoD has to respond to world events, such as the
2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. A ...
;
[Li Zho]
(17 Feb 2022) Congress’s short-term funding bills are a terrible way to govern
/ref>[John Ferrari and Elaine McCuske]
(2 Mar 2022) The Ukraine invasion shows why America needs to get its defense budget in order
/ref> the FY2023 defense budget request will exceed $773 billion, according to the chairman of the House Armed Services Committee.[Jacqueline Feldscher and Marcus Weisgerbe]
(3 Mar 2022) Russia’s Invasion Will Boost 2023 Defense Budget, Top Democrat Says; Rep. Adam Smith: Putin’s war "fundamentally altered what our national security posture" needs to be.
The president's FY2023 budget request will be in excess of $773 billion By 9 March 2022
a bipartisan agreement on a $782 billion defense budget had been reached (as part of an overall $1.5 trillion budget for FY2022 —thus avoiding a government shutdown).[Alan Fra]
(9 March 2022) Top lawmakers reach deal on Ukraine aid, $1.5T spending
including bipartisan agreement on a $782 billion defense budget
As of 4 April 2022 the FY2023 presidential budget request of $773 billion included $177.5 billion for the Army,[ U.S. Army Public Affair]
(28 Mar 2022) Army releases fiscal year 2023 presidential budget request
/ref>[Andrew Eversde]
(28 Mar 2022) Army’s $177.5B budget request will ‘maintain’ momentum on modernization, but cuts vehicle buys
$194 billion for the Air Force and Space Force,[Dr Charles Pop]
(28 Mar 2022) Department of the Air Force budget proposal focuses on transformation, modernization
/ref> and $230.8 billion for the Navy and Marine Corps (up 4.1% from FY2022 request).[Meredith A. Berger, Performing The Duties Of Under Secretary Of The Navy; Rear Admiral John Gumbleton, Deputy Assistant Secretary Of The Navy For Budge]
(28 Mar 2022) Navy Officials Hold a Press Briefing on FY23 Navy Budget, March 28, 2022
/ref> As of 12 December 2022 the House and Senate versions of the Fiscal Year 2023 National Defense Authorization bill (FY2023 NDAA) were to be $839 billion, and $847 billion, for the HASC, and SASC respectively, for a compromise $857.9 billion topline.[Aaron Meht]
(6 Dec 2022) Compromise NDAA released with $857.9 billion topline
$816.7 billion DoD, $30.3 billion DoE nuclear. By 16 December 2022 the current budget extension resolution will have expired.[Leo Shane III]
(28 Nov 2022) SecDef tells Congress to get a military budget done already
The presidential budget request was "$800 billion for fiscal 2023, which would be around 2.5% above the fiscal 2022 level"; Congress has proposed a budget higher than the requested amount. The delay is affecting training schedules and PCS moves.
The United States' military spending in 2021 reached $801bn a year according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute.
Budget for FY2022
In May 2021, the President's defense budget request for fiscal year 2022 (FY2022) was $715 billion, up $10 billion, from FY2021's $705 billion.[Scott Maucione (May 28, 2021) DoD budget largely flat, cuts legacy systems for modernization]
Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) account ($69 billion in FY2021) is now deleted after the withdrawal from Afghanistan; 'direct and enduring' contingency costs ($43 billion) are now an official part of the budget request. The total FY2022 defense budget request, including the Department of Energy, was $753 billion, up $12 billion from FY2021's budget request.[ ][Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller) comptroller.defense.gov NATIONAL DEFENSE BUDGET ESTIMATES FOR FY 2021]
Green book, 308 pp., cf. TABLE 1-1 NATIONAL DEFENSE BUDGET - LONG RANGE FORECAST On 22 July 2021 the Senate Armed Services Committee approved a budget $25 billion greater than the President's defense budget request for FY2022.[Bill Greenwalt]
(13 Dec 2021) New defense budget commission could be last hope for fixing DoD spending
A 14-member commission for reforming the PPBE process -- Bill Greenwalt's critique of the Planning, Programming, Budgeting, and Execution system (PPBE) which was instituted by McNamara in 1961. The National Defense Authorization Act, budgeting $740 billion for defense, was signed 27 December 2021.[Stephen Lose]
(27 December 2021) Biden signs $740B defense policy bill to overhaul sexual assault prosecutions, review Afghan war
/ref>
By military department,[Paul McLeary ((May 28, 2021) Biden’s Budget Cuts Ships, Planes, But Huge Boost in R&D]
/ref>[Joe Gould (29 May 2021) Eyeing China, Biden defense budget boosts research and cuts procurement]
/ref>[Andrew Eversden (29 May 2021) Pentagon wants to spend big on joint war-fighting systems]
/ref> the Army's portion of the budget request, $173 billion, dropped $3.6 billion from the enacted FY2021 budget;[Sydney Freedberg (28 May 2021) Army Modernization Budget Drops $4.2B; Budget Drops $3.6B Overall]
/ref>[Jen Judson (23 Jul 2021) Senate authorizers want to fund the Army’s entire wish list ]
/ref>[MG Paul A Chamberlain (10 Feb 2020) Army FY2021 Budget Overview]
/ref> the Department of the Navy's portion of the budget request, $211.7 billion, rose 1.8% from the enacted FY2021 budget, largely due to the 6% increase for the Marine Corps' restructuring to a littoral combat force (Navy request: $163.9 billion, or just 0.6% over FY2021, Marine Corps request: $47.9 billion, a 6.2% increase over FY2021);[Megan Eckstein (29 May 2021) US Navy FY22 budget request prioritizes readiness over procurement]
/ref> the Air Force's $156.3 billion request for FY2022 is a 2.3% increase over FY21 enacted budget; the Space Force budget of $17.4 billion is a 13.1% increase over FY21 enacted budget.[AF President's Budget FY22]
/ref>
Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) is now replaced by 'direct war and enduring costs', which are now migrated into the budget.
/ref>[[https://www.defensenews.com/naval/2021/06/01/if-congress-can-find-the-money-the-us-navy-would-like-another-new-destroyer-this-year/ Megan Eckstein (1 Jun 2021) If Congress can find the money, the US Navy would like another new destroyer this year]][Megan Eckstein (2 Jun 2021) US Marines request more missiles, radars in FY22 wish list]
/ref>[Valerie Insinna (2 Jun 2021) US Air Force wish list includes more F-15EX jets but no F-35s]
/ref>[Nathan Strout (11 Jun 2021) Space Command asks Congress for $67 million to achieve full operational capability]
/ref>
Budget for FY2021
For Fiscal Year 2021 (FY2021), the Department of Defense's discretionary budget authority is approximately $705.39 billion ($705,390,000,000). Mandatory spending of $10.77 billion, the Department of Energy and defense-related spending of $37.335 billion added up to the total FY2021 Defense budget of $753.5 billion.[(June 27, 2014) FY 2015 DoD Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) Budget Amendment(Mar 2015)]
OCO 2016
(Feb 2016)
OCO 2017
(May 2017)
OCO 2018
Budget Summary for FY 2021 with Projections for FY 2022-2025
(Expenditures listed in million $)
Budget for FY2020
For Fiscal Year 2020 (FY2020), the Department of Defense's budget authority is approximately $721.5 billion ($721,531,000,000). Approximately $712.6 billion is discretionary spending with approximately $8.9 billion in mandatory spending. The Department of Defense estimates that $689.6 billion ($689,585,000,000) will actually be spent (outlays). Both left-wing and right-wing commentators have advocated for the cutting of military spending.[Seamus Daniels (22 Sep 2021) ACCOUNTING FOR THE COSTS OF MILITARY PERSONNEL]
FY1952 to FY2020 diffs when adjusted for inflation
Budget for FY2019
For FY2019, the Department of Defense's budget authority was $693,058,000,000 (Including Discretionary and Mandatory Budget Authority).
Total overview
For personnel payment and benefits
Personnel payment and benefits take up approximately 39.14% of the total budget of $686,074,048,000[https://comptroller.defense.gov/Portals/45/Documents/defbudget/fy2020/FY20_Green_Book.pdf ]
By Overseas Contingency Operation
Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) funds are sometimes called War funds
By Military Department
Military Health Care Funding
The MHS offers, but does not always provide, a health care benefit to 9.5 million eligible beneficiaries, which includes active military members and their families, military retirees and their families, dependent survivors, and certain eligible Reserve Component members and their families. The Unified Medical Budget (UMB), which comprise the funding and personnel needed to support the MHS’ mission, consumes nearly 9% of the Department’s topline budget authority. Thus, it is a significant line item in the Department’s financial portfolio.
Budgeting Terms
Budget Authority: the authority to legally incur binding obligations (like signing contracts and placing orders), that will result in current and future outlays. When "military budget" is mentioned, people generally are referring to discretionary budget authority.
Outlays: Also known as expenditures or disbursements, it is the liquidation of obligations and general represent cash payments.
Total Obligational Authority: DoD financial term expressing the value of the direct Defense program for a given fiscal year, exclusive of the obligation authority from other sources (such as reimbursable orders accepted)
Discretionary: Annually appropriated by the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...
, subject to budget caps.
Mandatory: Budget Authority authorized by permanent law.
Previous budgets
As of 2013, the Department of Defense was the third largest executive branch department and utilized 20% of the federal budget.
For the 2011 fiscal year, the president's base budget for the Department of Defense and spending on "overseas contingency operations" combine to bring the sum to US$664.84 billion.[Updated Summary Tables, Budget of the United States Government Fiscal Year 2010 (Table S.12)](_blank)
Emergency and supplemental spending
The recent military operations in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
were largely funded through supplementary spending bills that supplemented the annual military budget requests for each fiscal year. However, the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan were categorized as "overseas contingency operations" in the starting of the fiscal year 2010, and the budget is included in the federal budget.
By the end of 2008, the U.S. had spent approximately $900 billion in direct costs on the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan. The government also incurred indirect costs, which include interests on additional debt and incremental costs, financed by the Veterans Administration
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is a Cabinet-level executive branch department of the federal government charged with providing life-long healthcare services to eligible military veterans at the 170 VA medical centers an ...
, of caring for more than 33,000 wounded. Some experts estimate the indirect costs will eventually exceed the direct costs. As of June 2011, the total cost of the wars was approximately $1.3 trillion.
By title
 The federally budgeted (see below) military expenditure of the United States Department of Defense for fiscal year 2013 are as follows. While data is provided from the 2015 budget, data for 2014 and 2015 is estimated, and thus data is shown for the last year for which definite data exists (2013).
The federally budgeted (see below) military expenditure of the United States Department of Defense for fiscal year 2013 are as follows. While data is provided from the 2015 budget, data for 2014 and 2015 is estimated, and thus data is shown for the last year for which definite data exists (2013).
By entity
Programs spending more than $1.5 billion
The Department of Defense's FY 2011 $137.5 billion procurement and $77.2 billion RDT&E budget requests included several programs worth more than $1.5 billion.
Other military-related expenditures
This does not include many military-related items that are outside of the Defense Department budget, such as nuclear weapons research, maintenance, cleanup, and production, which are in the Atomic Energy Defense Activities section, Veterans Affairs
Veterans' affairs is an area of public policy concerned with relations between a government and its communities of military veterans. Some jurisdictions have a designated government agency or department, a Department of Veterans' Affairs, Minist ...
, the Treasury Department's payments in pensions to military retirees and widows and their families, interest on debt incurred in past wars, or State Department financing of foreign arms sales and militarily-related development assistance. Neither does it include defense spending that is domestic rather than international in nature, such as the Department of Homeland Security
The United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is the U.S. federal executive department responsible for public security, roughly comparable to the interior or home ministries of other countries. Its stated missions involve anti-ter ...
, counter-terrorism spending by the Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice ...
, and intelligence-gathering spending by NSA
The National Security Agency (NSA) is a national-level intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the Director of National Intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collec ...
, although these programs contain certain weapons, military and security components.
Audit of 2011 budget
Again in 2011, the GAO could not "render an opinion on the 2011 consolidated financial statements of the federal government", with a major obstacle again being "serious financial management problems at the Department of Defense (DOD) that made its financial statements unauditable".
Audit of implementation of budget for 2010
The US Government Accountability Office
The U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) is a legislative branch government agency that provides auditing, evaluative, and investigative services for the United States Congress. It is the supreme audit institution of the federal gover ...
(GAO) was unable to provide an audit opinion
An auditor's report is a formal opinion, or disclaimer thereof, issued by either an internal auditor or an independent external auditor as a result of an internal or external audit, as an assurance service in order for the user to make decisions ...
on the 2010 financial statements of the US Government because of 'widespread material
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geolo ...
internal control weaknesses, significant uncertainties, and other limitations'.Inspector General
An inspector general is an investigative official in a civil or military organization. The plural of the term is "inspectors general".
Australia
The Inspector-General of Intelligence and Security (Australia) (IGIS) is an independent statutory of ...
reported 'material
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geolo ...
internal control weaknesses ... that affect the safeguarding of assets, proper use of funds, and impair the prevention and identification of fraud, waste, and abuse'. Further management discussion in the FY 2010 DoD Financial Report states 'it is not feasible to deploy a vast number of accountants to manually reconcile our books' and concludes that 'although the financial statements are not auditable for FY 2010, the Department's financial managers are meeting warfighter needs'.
Budget for 2016
On 9 February 2016, the US Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national sec ...
under President Obama released a statement outlining the proposed 2016 and 2017 defense spending budgets that " eflectthe priorities necessary for our force today and in the future to best serve and protect our nation in a rapidly changing security environment."
Budget request for FY2019
In February 2018, the Pentagon requested $686 billion for FY 2019.
The John S. McCain National Defense Authorization Act authorized Department of Defense appropriations for 2019 and established policies, but it did not contain the budget itself. On 26 July, this bill passed in the House of Representatives by 359-54. On 1 August, the US Senate passed it by 87-10. The bill was presented to President Trump two days later. He signed it on 13 August.
On 28 September 2018, Trump signed the Department of Defense appropriations bill. The approved 2019 Department of Defense discretionary budget was $686.1 billion. It has also been described as "$617 billion for the base budget and another $69 billion for war funding."
Budget request for FY2018
On 16 March 2017 President Trump submitted his request to Congress for $639 billion in military spending (an increase of $54 billion, 10% for FY 2018
File:2018 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2018 Winter Olympics opening ceremony in PyeongChang, South Korea; Protests erupt following the Assassination of Jamal Khashoggi; March for Our Lives protests take place across the United ...
, as well as $30 billion for FY2017, which ends in September). With a total federal budget of $3.9 trillion for FY2018, the increase in military spending would result in deep cuts to many other federal agencies and domestic programs, as well as the State Department.Scot J. Paltrow
Scot J. Paltrow is an American journalist. A financial journalist, Paltrow currently works for Reuters.
Paltrow is from New York. He received his bachelor's degree from the Cornell University College of Arts and Sciences and a master's degree fro ...
raised concerns about the increase in spending with the Pentagon's history of "faulty accounting".
H.R. 2810
the National Defense Authorization Act 2018 was passed by the U.S. House of Representatives 344 - 81, with 8 not voting. 60% of Democrats voted for this bill, which represented an 18% increase in defense spending. The Congress increased the budget to total 696 billion dollars.
Budget request for FY2017
 The currently available budget request for 2017 was filed on 9 February 2016,
The currently available budget request for 2017 was filed on 9 February 2016,The FY 2017 budget reflects recent strategic threats and changes that have taken place in Asia, the Middle East and Europe. Russian aggression, terrorism by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and others, and China's island building and claims of sovereignty in international waters all necessitate changes in our strategic outlook and in our operational commitments. Threats and actions originating in Iran and North Korea negatively affect our interests and our allies. These challenges have sharpened the focus of our planning and budgeting.
The proposal also includes a comparison of the 2016 and the proposed 2017 request amounts, a summary of acquisitions requested for 2017 and enacted in 2016, and provides in detail a breakdown of specific programs to be funded.
Investments
Amounts are in $ billions.
Major acquisition programs
These are the top 25 DoD weapon programs described in detail:
$ in billions, Qty being the number of items requested.
Science and Technology Program
This program's purpose is to "invest in and develop capabilities that advance the technical superiority of the U.S. Military to counter new and emerging threats."
= Total budget by department
=
Amounts in thousands of $US
= Total budget of military
=
*Research, Development, Test and Evaluation
Amounts in thousands of $US
= Funding of payments and benefits
=
This portion of the military budget comprises roughly one third to one half of the total defense budget, considering only military personnel or additionally including civilian personnel, respectively. These expenditures will typically be, the single largest expense category for the Department. Since 2001, military pay and benefits have increased by 85%, but remained roughly one third of the total budget due to an overall increased budget. Military pay remains at about the 70th percentile compared to the private sector to attract sufficient amounts of qualified personnel.
= Funding the military health system
=
The request for 2017 amounts to $48.8 billion. The system has 9.4 million beneficiaries, including active, retired, and eligible Reserve Component military personnel and their families, and dependent survivors.
Budget by year
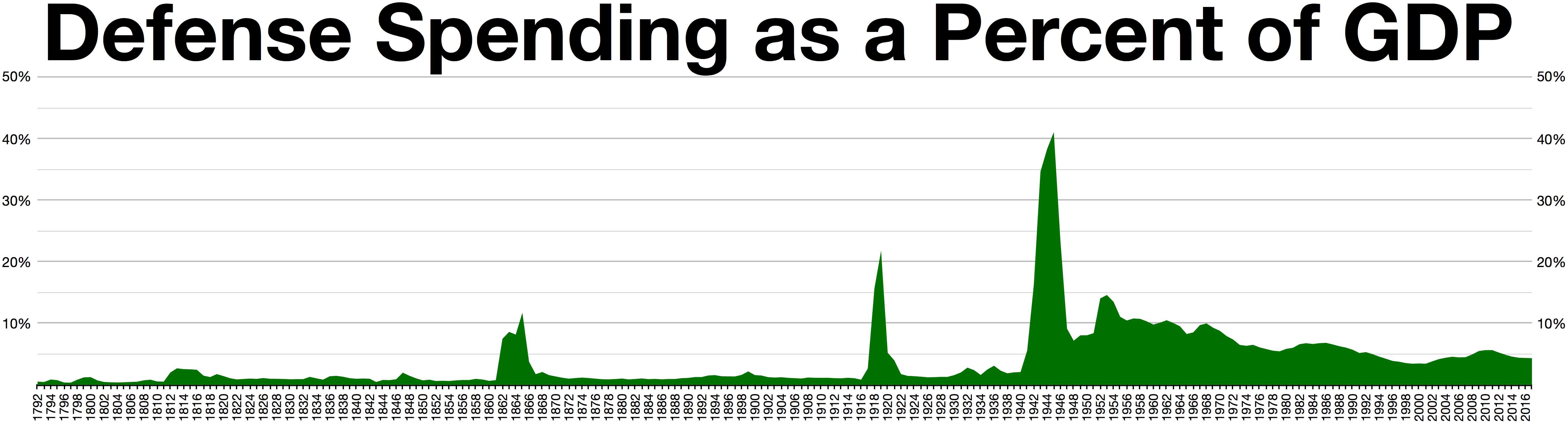
 The accompanying graphs show that U.S. military spending as a percent of GDP peaked during World War II.
The table shows historical spending on defense from 1996–2015, spending for 2014–15 is estimated.
The accompanying graphs show that U.S. military spending as a percent of GDP peaked during World War II.
The table shows historical spending on defense from 1996–2015, spending for 2014–15 is estimated.
Support service contractors
The role of support service contractors has increased since 2001 and in 2007 payments for contractor services exceeded investments in equipment for the armed forces for the first time. In the 2010 budget, the support service contractors will be reduced from the current 39 percent of the workforce down to the pre-2001 level of 26 percent. In a Pentagon review of January 2011, service contractors were found to be "increasingly unaffordable."
Military budget and total US federal spending
 The U.S. Department of Defense budget accounted in fiscal year 2017 for about 14.8% of the United States federal budgeted expenditures. According to the
The U.S. Department of Defense budget accounted in fiscal year 2017 for about 14.8% of the United States federal budgeted expenditures. According to the Congressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency within the United States Congress, legislative branch of the United States government that provides budget and economic information to Congress.
Ins ...
, defense spending grew 9% annually on average in fiscal years 2000–2009.
Because of constitutional
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these prin ...
limitations, military funding is appropriated in a discretionary spending
In American public finance, discretionary spending is government spending implemented through an appropriations bill. This spending is an optional part of fiscal policy, in contrast to social programs for which funding is mandatory and determine ...
account. (Such accounts permit government planners to have more flexibility to change spending each year, as opposed to mandatory spending
The United States federal budget is divided into three categories: mandatory spending, discretionary spending, and interest on debt. Also known as entitlement spending, in US fiscal policy, mandatory spending is government spending on certain p ...
accounts that mandate spending on programs in accordance with the law, outside of the budgetary process.) In recent years, discretionary spending as a whole has amounted to about one-third of total federal outlays. Department of Defense spending's share of discretionary spending was 50.5% in 2003, and has risen to between 53% and 54% in recent years.
For FY 2017, Department of Defense spending amounts to 3.42% of GDP. Because the U.S. GDP has grown over time, the military budget can rise in absolute terms while shrinking as a percentage of the GDP. For example, the Department of Defense budget was slated to be $664 billion in 2010 (including the cost of operations in Iraq and Afghanistan previously funded through supplementary budget legislation), higher than at any other point in American history, but still 1.1–1.4% lower as a percentage of GDP than the amount spent on military during the peak of Cold-War military spending in the late 1980s.[The President's FY 2010 Budget](_blank)
Admiral Mike Mullen, former Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (CJCS) is the presiding officer of the United States Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS). The chairman is the highest-ranking and most senior military officer in the United States Armed Forces Chairman: app ...
, has called four percent an "absolute floor". This calculation does not take into account some other military-related non-DOD spending, such as Veterans Affairs, Homeland Security, and interest paid on debt incurred in past wars, which has increased even as a percentage of the national GDP.
In 2015, Pentagon and related spending totaled $598 billion.
In addition, the United States will spend at least $179 billion over the fiscal years of 2010-2018 on its nuclear arsenal, averaging $20 billion per year. Despite President Barack Obama's attempts in the media to reduce the scope of the current nuclear arms race, the U.S. intends to spend an additional $1 trillion over the next 30 years modernizing its nuclear arsenal.
In September 2017 the United States Senate followed President Donald Trump's plan to expand military spending, which will boost spending to $700 billion, about 91.4% of which will be spent on maintaining the armed forces and primary Pentagon costs. Military spending is increasing regularly and more money is being spent every year on employee pay, operation and maintenance, and benefits including as health benefits. Methods to counteract rapidly increasing spending include shutting down bases, but that was banned by the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2013
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2013 (; ) is a federal statute concerning spending and the budget in the United States, that was signed into law by President Barack Obama on December 26, 2013. On December 10, 2013, pursuant to the provisions of t ...
.
Federal waste
As of September 2014, the Department of Defense was estimated to have "$857 million in excess parts and supplies". This figure has risen over the past years, and of the Pentagon waste that has been calculated, two figures are especially worth mentioning: the expenditure of "$150 million on private villas for a handful of Pentagon employees in Afghanistan and the procurement of the JLENS
The Joint Land Attack Cruise Missile Defense Elevated Netted Sensor System, or JLENS (colloquially, Spy Balloon), was a tethered aerial detection system designed to track boats, ground vehicles, cruise missiles, manned and unmanned aircraft (air ...
air-defense balloon" which, throughout the program's development over the past two decades, is estimated to have cost $2.7 billion.
Critics have also noted that an increase in military spending does not always yield greater safety from foreign military attacks. Critics note that the United States is expected to spend $770 billion on national defense in 2023, more than the next 10 countries spend combined with little measurable difference in safety. Russia, for instance, spends close to $62 billion, France and Germany spend almost $53 billion each and China spends $252 billion. Anti-War activists such as Scott Horton (radio host)
Scott Horton is an American radio host and author.
Career
Horton hosts ''Antiwar Radio'' for Pacifica Radio's KPFK 90.7 FM in Los Angeles, as well as the podcast ''The Scott Horton Show.'' Horton has conducted over 5,000 interviews since 2003 ...
argue that a hawkish foreign policy can lead to negative externalities, such as the United States involvement in Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and ...
contributing to the Famine in Yemen (2016–present)
Since 2016, a food insecurity crisis has been ongoing in Yemen which began during the Yemeni Civil War.
The UN estimates that the war has caused an estimated 130,000 deaths from indirect causes which include lack of food, health services, and ...
. Proponents for reduced military spending also sometimes assert the safety in remaining neutral in most international affairs and the utility of having an armed populace as a deterrent for foreign invasion. For example, Jo Jorgensen
Jo Jorgensen (born May 1, 1957) is an American libertarian political activist and academic. Jorgensen was the Libertarian Party's nominee for president of the United States in the 2020 election, in which she finished third in the popular vot ...
, Libertarian Party (United States)
The Libertarian Party (LP) is a political party in the United States that promotes civil liberties, non-interventionism, ''laissez-faire'' capitalism, and limiting the size and scope of government. The party was conceived in August 1971 at m ...
presidential candidate in 2020, asserted that her preferred policy would be if the United States had a similar system to Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, to remain neutral and have an armed populace.
Comparison with other countries

 The United States spends more on national defense than China, India, Russia, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, United Kingdom, Japan, South Korea, and Brazil combined. The 2018 U.S. military budget accounts for approximately 36% of global arms spending (for comparison, U.S. GDP is only 24% of global GDP). The 2018 budget is approximately 2.5 times larger than the $250 billion
The United States spends more on national defense than China, India, Russia, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, United Kingdom, Japan, South Korea, and Brazil combined. The 2018 U.S. military budget accounts for approximately 36% of global arms spending (for comparison, U.S. GDP is only 24% of global GDP). The 2018 budget is approximately 2.5 times larger than the $250 billion military budget of China
The military budget of China is the portion of the overall budget of China that is allocated for the funding of the military of China. This military budget finances employee salaries and training costs, the maintenance of equipment and facilitie ...
. The United States and its close allies are responsible for two-thirds to three-quarters of the world's military spending
A military budget (or military expenditure), also known as a defense budget, is the amount of financial resources dedicated by a state to raising and maintaining an armed forces or other methods essential for defense purposes.
Financing militar ...
(of which, in turn, the U.S. is responsible for the majority).Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
's 9.85%. This is historically low for the United States since it peaked in 1944 at 37.8% of GDP (it reached the lowest point of 3.0% in 1999–2001). Even during the peak of the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
the percentage reached a high of 9.4% in 1968.Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
spent 8.8%, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
spent 4.3%, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
spent 4.0%, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
spent 3.9%, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
spent 2.6%, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
spent 1.9%, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
spent 1.8%, and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
spent 1.2% of its GDP on defense.
The US Military's budget has plateaued in 2009, but is still considerably larger than any other military power.
Past commentary on military budget
In 2009, Secretary of Defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in so ...
Robert Gates
Robert Michael Gates (born September 25, 1943) is an American intelligence analyst and university president who served as the 22nd United States secretary of defense from 2006 to 2011. He was originally appointed by president George W. Bush a ...
wrote that the U.S. should adjust its priorities and spending to address the changing nature of threats in the world: "What all these potential adversaries—from terrorist cells to rogue nations to rising powers—have in common is that they have learned that it is unwise to confront the United States directly on conventional military terms. The United States cannot take its current dominance for granted and needs to invest in the programs, platforms, and personnel that will ensure that dominance's persistence. But it is also important to keep some perspective. As much as the U.S. Navy has shrunk since the end of the Cold War, for example, in terms of tonnage, its battle fleet is still larger than the next 13 navies combined—and 11 of those 13 navies are U.S. allies or partners." Secretary Gates announced some of his budget recommendations in April 2009.
According to a 2009 Congressional Research Service
The Congressional Research Service (CRS) is a public policy research institute of the United States Congress. Operating within the Library of Congress, it works primarily and directly for members of Congress and their committees and staff on a ...
there was a discrepancy between a budget that is declining as a percentage of GDP while the responsibilities of the DoD have not decreased and additional pressures on the military budget have arisen due to broader missions in the post-9/11 world, dramatic increases in personnel and operating costs, and new requirements resulting from wartime lessons in the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003–present), I ...
and Operation Enduring Freedom
Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) was the official name used synonymously by the U.S. government for both the War in Afghanistan (2001–2014) and the larger-scale Global War on Terrorism. On 7 October 2001, in response to the September 11 a ...
.
Expenses for fiscal years 2001 through 2010 were analyzed by Russell Rumbaugh, a retired Army officer and ex-CIA military analyst, in a report for the Stimson Center. Rumbaugh wrote: "Between 1981 and 1990, the Air Force bought 2,063 fighters. In contrast, between 2001 and 2010, it bought only 220. Yet between 2001 and 2010 the Air Force spent $38B of procurement funding just on fighter aircraft in inflation-adjusted dollars, compared with the $68B it spent between 1981 and 1990. In other words, the Air Force spent 55 percent as much money to get 10 percent as many fighters." As Adam Weinstein explained one of the report's findings: "Of the roughly $1 trillion spent on gadgetry since 9/11, 22 percent of it came from 'supplemental' war funding — annual outlays that are voted on separately from the regular defense budget."
Most of the $5 billion in budget "cuts" for 2013 that were mandated by Congress in 2012 really only shifted expenses from the general military budget to the Afghanistan war budget. Declaring that nearly 65,000 troops were temporary rather than part of the permanent forces resulted in the reallocation of $4 billion in existing expenses to this different budget.
 In May 2012, as part of Obama's East Asia "pivot", his 2013 national military request moved funding from the Army and Marines to favor the Navy, but the Congress has resisted this.
Reports emerged in February 2014 that
In May 2012, as part of Obama's East Asia "pivot", his 2013 national military request moved funding from the Army and Marines to favor the Navy, but the Congress has resisted this.
Reports emerged in February 2014 that Secretary of Defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in so ...
Chuck Hagel
Charles Timothy Hagel ( born October 4, 1946)[American Enterprise Institute
The American Enterprise Institute for Public Policy Research, known simply as the American Enterprise Institute (AEI), is a center-right Washington, D.C.–based think tank that researches government, politics, economics, and social welfare. A ...]
scholar Michael Auslin opined in the National Review that the Air Force needs to be fully funded as a priority, due to the air superiority, global airlift, and long-range strike capabilities it provides.
In January 2015 Defense Department published its internal study on how to save $125 billion on its military budget from 2016 to 2020 by renegotiating vendor contracts and pushing for stronger deals, and by offering workers early retirement and retraining.
2012 fiscal cliff
On 5 December 2012, the Department of Defense Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philipp ...
announced it was planning for automatic spending cuts, which include $500 billion and an additional $487 billion due to the 2011 Budget Control Act, due to the fiscal cliff.Politico
''Politico'' (stylized in all caps), known originally as ''The Politico'', is an American, German-owned political journalism newspaper company based in Arlington County, Virginia, that covers politics and policy in the United States and intern ...
'', the Department of Defense declined to explain to the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
Appropriations Committee, which controls federal spending, what its plans were regarding the fiscal cliff planning.Joe Lieberman
Joseph Isadore Lieberman (; born February 24, 1942) is an American politician, lobbyist, and attorney who served as a United States senator from Connecticut from 1989 to 2013. A former member of the Democratic Party, he was its nominee for ...
(I-CT).
Lawrence Korb has noted that given recent trends military entitlements and personnel costs will take up the entire defense budget by 2039.
GAO audits
The Government Accountability Office
The U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) is a legislative branch government agency that provides auditing, evaluative, and investigative services for the United States Congress. It is the supreme audit institution of the federal gover ...
was unable to provide an audit opinion
An auditor's report is a formal opinion, or disclaimer thereof, issued by either an internal auditor or an independent external auditor as a result of an internal or external audit, as an assurance service in order for the user to make decisions ...
on the 2010 financial statements of the U.S. government due to "widespread material
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geolo ...
internal control weaknesses, significant uncertainties, and other limitations."Fiscal Year
A fiscal year (or financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many ...
(FY) 2011, seven out of 33 DoD reporting entities received unqualified audit opinions.Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
has established a deadline of FY 2017 for the DoD to achieve audit readiness.
For FYs 1998-2010 the Department of Defense's financial statements were either unauditable or such that no audit opinion could be expressed.
Reform and Controversy
In a statement of 6 January 2011, Defense Secretary Robert M. Gates stated: "This department simply cannot risk continuing down the same path – where our investment priorities, bureaucratic
The term bureaucracy () refers to a body of non-elected governing officials as well as to an administrative policy-making group. Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments staffed with non-elected offi ...
habits and lax attitude towards costs are increasingly divorced from the real threats of today, the growing perils of tomorrow and the nation's grim financial outlook." Gates has proposed a budget that, if approved by Congress, would reduce the costs of many DOD programs and policies, including reports, the IT infrastructure, fuel, weapon programs, DOD bureaucracies, and personnel.
The 2015 expenditure for Army research, development and acquisition changed from $32 billion projected in 2012 for FY15, to $21 billion for FY15 expected in 2014.
In 2018, it was announced that the Department of Defense was indeed the subject of a comprehensive budgetary audit. This review was conducted by private, third-party accounting consultants. The audit ended and was deemed incomplete due to deficient accounting practices in the department.
Controversy
On January 17th, 1961, then President Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
in a farewell address to the United States warned the people and government of the United States about the creation of a “military-industrial complex”. As defined by the Encyclopedia Britannica, a military-industrial complex is “A network of individuals and institutions involved in the production of weapons and military technologies. The military-industrial complex in a country typically attempts to marshal political support for continued or increased military spending by the national government”. Many critics have argued that since the start of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, the United States has become a military-industrial complex.
The conclusion of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and the start of the Cold War prompted the rapid expansion of a military arms race. Subsequently, the reallocation of budgets, prompted by several wars and proxy wars forced the Department of Defense to increase research and development of new military systems and equipment to proliferate on a mass scale to compete with, at the time, the Soviet Union. As prompted by President Eisenhower, the war had arguably become an industry. It was also speculated (by Eisenhower) that the war industry
The arms industry, also known as the arms trade, is a global industry which manufactures and sells weapons and military technology. It consists of a commercial industry involved in the research and development, engineering, production, and s ...
would bring war-like industrial influence into the various sectors of government. In a section of President Eisenhower’s speech, he stated: “In the councils of government, we must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military-industrial complex. The potential for the disastrous rise of misplaced power exists and will persist”.
Following the departure of President Eisenhower, the expenditures and budgets of the United States military grew exponentially. The Cold War (1947-1991) developed the largest proliferation of a nuclear arsenal to date. New defense contractors stood up to supply the demand for the military and its various conflicts across the globe. In addition, the war in Indochina was the largest expenditure during the Cold War at approximately $168 billion or about $1 trillion in today’s inflated costs.
In 2022, the United States had the largest defense budget and expenditures of any other country in the world totaling around 777.1 billion dollars (FY22). It is speculated that these drastic rises in the budget were a product of the Global War on Terrorism and the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan. The rise in the military budget over the last decade can be traced to the production of new technologies such as 5th generation fighter aircraft to meet the increase of demand for new combat capabilities. Also to note, much of these costs were the result of “R&D”, or research and development. Research and Development is one of the United States’ primary focuses in the defense budget .
Modern Day Controversies
Through recent audits and reports, many in the federal government have investigated “price gouging” and sourcing from military contractors. One of these notable incidents occurred on May 15th, 2019, when Representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez of New York (D) reprimanded the military contractor TransDigm in a hearing about the gap in the pricing of a “non-vehicular clutch disc”. It was reported that the contractor TransDigm had charged taxpayers approximately $1,443 (totaling $215,007 million) for a clutch disc that cost $32 to produce. About 150 discs were purchased and TransDigm earned a 4,436% profit. TransDigm ultimately was ordered to pay back approximately $16 million in excess profit.
Defense Budget Focus
Opponents of growing military spending budgets have long argued that the United States should refocus and reallocate the military budgets to promote social welfare
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifical ...
and benefits among its citizens. However, the projections for the near future are that the defense budget and its expenditures are only going to continue to grow exponentially. In the published FY22 budget report, the authority has been given to increase the defense budget by about 17 billion dollars ($535 billion of which is a part of contract obligations) from FY21. In addition, the Biden Administration
Joe Biden's tenure as the 46th president of the United States began with his inauguration on January 20, 2021. Biden, a Democrat from Delaware who previously served as vice president under Barack Obama, took office following his victory ...
has proposed another increase of the FY23 budget to $737 billion. On the contrary, proponents of increasing the U.S. Defense budgets have long argued that factors such as China and other adversaries of the U.S. must be kept in check (from a military standpoint).
References
Further reading
*
External links
US Government Defense Spending History with Charts - a www.usgovernmentspending.com briefingarchived
{{DEFAULTSORT:Military Budget Of The United States
United States Department of Defense
United States federal budgets
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
 The
The  The federally budgeted (see below) military expenditure of the United States Department of Defense for fiscal year 2013 are as follows. While data is provided from the 2015 budget, data for 2014 and 2015 is estimated, and thus data is shown for the last year for which definite data exists (2013).
The federally budgeted (see below) military expenditure of the United States Department of Defense for fiscal year 2013 are as follows. While data is provided from the 2015 budget, data for 2014 and 2015 is estimated, and thus data is shown for the last year for which definite data exists (2013).
 The currently available budget request for 2017 was filed on 9 February 2016, under then-President Barack Obama.
The press release of the proposal specifies the structure and goals for the Fiscal Year (FY) 2017 budget:
The currently available budget request for 2017 was filed on 9 February 2016, under then-President Barack Obama.
The press release of the proposal specifies the structure and goals for the Fiscal Year (FY) 2017 budget:

 The accompanying graphs show that U.S. military spending as a percent of GDP peaked during World War II.
The table shows historical spending on defense from 1996–2015, spending for 2014–15 is estimated. The defense budget is shown in billions of dollars and total budget in trillions of dollars. The percentage of the total U.S. federal budget spent on defense is indicated in the third row, and change in defense spending from the previous year in the final row.
The accompanying graphs show that U.S. military spending as a percent of GDP peaked during World War II.
The table shows historical spending on defense from 1996–2015, spending for 2014–15 is estimated. The defense budget is shown in billions of dollars and total budget in trillions of dollars. The percentage of the total U.S. federal budget spent on defense is indicated in the third row, and change in defense spending from the previous year in the final row.
 The U.S. Department of Defense budget accounted in fiscal year 2017 for about 14.8% of the United States federal budgeted expenditures. According to the
The U.S. Department of Defense budget accounted in fiscal year 2017 for about 14.8% of the United States federal budgeted expenditures. According to the  The United States spends more on national defense than China, India, Russia, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, United Kingdom, Japan, South Korea, and Brazil combined. The 2018 U.S. military budget accounts for approximately 36% of global arms spending (for comparison, U.S. GDP is only 24% of global GDP). The 2018 budget is approximately 2.5 times larger than the $250 billion
The United States spends more on national defense than China, India, Russia, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, United Kingdom, Japan, South Korea, and Brazil combined. The 2018 U.S. military budget accounts for approximately 36% of global arms spending (for comparison, U.S. GDP is only 24% of global GDP). The 2018 budget is approximately 2.5 times larger than the $250 billion