Inflammatory Bowel Disease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and
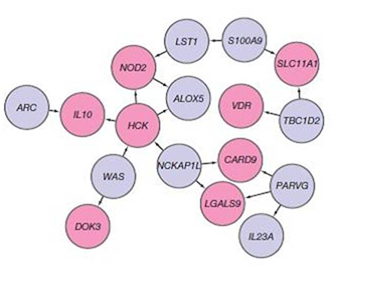 A genetic component to IBD has been recognized for over a century. Research that has contributed to understanding of the genetics include studies of ethnic groups (e.g.,
A genetic component to IBD has been recognized for over a century. Research that has contributed to understanding of the genetics include studies of ethnic groups (e.g.,
small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
, Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distensi ...
and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and the rectum.
IBD also occurs in dogs and is thought to arise from a combination of host genetics, intestinal microenvironment, environmental components and the immune system. There is an ongoing discussion, however, that the term "chronic enteropathy" might be better to use than "inflammatory bowel disease" in dogs because it differs from IBD in humans in how the dogs respond to treatment. For example, many dogs respond to only dietary changes compared to humans with IBD, who often need immunosuppressive treatment. Some dogs may also need immunosuppressant or antibiotic treatment when dietary changes are not enough. After having excluded other diseases that can lead to vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain in dogs, intestinal biopsies are often performed to investigate what kind of inflammation is occurring (lymphoplasmacytic, eosinophilic, or granulomatous). In dogs, low levels of cobalamin in the blood have been shown to be a risk factor for negative outcome.
Signs and symptoms
In spite of Crohn's and UC being very different diseases, both may present with any of the following symptoms: abdominal pain,diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
, rectal bleeding, severe internal cramps/muscle spasms in the region of the pelvis and weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat ( adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other co ...
. Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
is the most prevalent extraintestinal complication of inflammatory bowel disease. Associated complaints or diseases include arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and non-thyroidal illness syndrome (NTIS). Associations with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) have also been reported. Diagnosis is generally by assessment of inflammatory markers in stool followed by colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis ('' ...
with biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
of pathological lesions.
Causes
IBD is a complex disease which arises as a result of the interaction of environmental and genetic factors leading to immunological responses and inflammation in the intestine.Diet
People living with IBD are very interested in diet, but little is known about the impact of diet on these patients. Recent reviews underlined the important role of nutritional counselling in IBD patients. Patients should be encouraged to adopt diets that are best supported by evidence and involve monitoring for the objective resolution of inflammation. A 2022 study found that diets with increased intake of fruits and vegetables, reduction of processed meats and refined carbohydrates, and preference of water for hydration were associated with lower risk of active symptoms with IBD, although increased intake of fruits and vegetables alone did not reduce risk of symptoms with Crohn's disease. Dietary patterns are associated with a risk for ulcerative colitis. In particular, subjects who were in the highest tertile of the healthy dietary pattern had a 79% lower risk of ulcerative colitis. Gluten sensitivity is common in IBD and associated with having flareups. Gluten sensitivity was reported in 23.6 and 27.3% of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis patients, respectively. A diet high inprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
, particularly animal protein, and/or high in sugar may be associated with increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease and relapses.
Microbiota
As a result of microbial symbiosis and immunity, alterations in thegut microbiome
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the ...
may contribute to inflammatory gut diseases. IBD-affected individuals have been found to have 30–50 percent reduced biodiversity of commensal bacteria, such as decreases in Bacillota (namely Lachnospiraceae) and Bacteroidota
The phylum Bacteroidota (synonym Bacteroidetes) is composed of three large classes of Gram-negative, nonsporeforming, anaerobic or aerobic, and rod-shaped bacteria that are widely distributed in the environment, including in soil, sediments, and ...
. Further evidence of the role of gut flora in the cause of inflammatory bowel disease is that IBD-affected individuals are more likely to have been prescribed antibiotics in the 2–5 year period before their diagnosis than unaffected individuals. The enteral bacteria can be altered by environmental factors, such as concentrated milk fats (a common ingredient of processed foods and confectionery) or oral medications such as antibiotics and oral iron preparations. The mucosal microbiota in the large intestine of IBD patients with active inflammation was found to be associated with pro-inflammatory changes to the host epigenome. However, large international studies have failed to identify a single microbial biomarker of IBD indicating it's not driven by any single micro-organism.
Breach of intestinal barrier
Loss of integrity of theintestinal epithelium
The intestinal epithelium is the single cell layer that form the luminal surface (lining) of both the small and large intestine (colon) of the gastrointestinal tract. Composed of simple columnar epithelial cells, it serves two main functi ...
plays a key pathogenic role in IBD. Dysfunction of the innate immune system
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
as a result of abnormal signaling through immune receptors called toll-like receptors
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane-spanning receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recogniz ...
(TLRs)—which activates an immune response to molecules that are broadly shared by multiple pathogens—contributes to acute and chronic inflammatory processes in IBD colitis and associated cancer. Changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut m ...
are an important environmental factor in the development of IBD. Detrimental changes in the intestinal microbiota induce an inappropriate (uncontrolled) immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which coul ...
that results in damage to the intestinal epithelium. Breaches in this critical barrier (the intestinal epithelium) allow further infiltration of microbiota that, in turn, elicit further immune responses. IBD is a multifactorial disease that is nonetheless driven in part by an exaggerated immune response to gut microbiota that causes defects in epithelial barrier function.
Oxidative stress and DNA damage
Pereira et al. reviewed evidence from numerous studies indicating thatoxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal ...
and DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
likely have a role in the pathophysiology of IBD. Oxidative DNA damage as measured by 8-OHdG levels was found to be significantly increased in patients with IBD compared to control patients, and in inflamed mucosa compared with non-inflamed mucosa.
Genetics
 A genetic component to IBD has been recognized for over a century. Research that has contributed to understanding of the genetics include studies of ethnic groups (e.g.,
A genetic component to IBD has been recognized for over a century. Research that has contributed to understanding of the genetics include studies of ethnic groups (e.g., Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
, Irish), familial clustering, epidemiological studies, and twin studies. With the advent of molecular genetics, understanding of the genetic basis has expanded considerably, particularly in the past decade. The first gene linked to IBD was NOD2
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2 (NOD2), also known as caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 15 (CARD15) or inflammatory bowel disease protein 1 (IBD1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NOD2'' ...
in 2001. Genome-wide association studies have since added to understanding of the genomics and pathogenesis of the disease. More than 200 single nucleotide polymorphisms
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently lar ...
(SNPs or "snips") are now known to be associated with susceptibility to IBD. One of the largest genetic studies of IBD was published in 2012 . The analysis explained more of the variance in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis than previously reported. The results suggested that commensal microbiota are altered in such a way that they act as pathogens in inflammatory bowel diseases. Other studies show that mutations in IBD-associated genes might interfere with the cellular activity and interactions with the microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably wel ...
that promote normal immune responses. Many studies identified that microRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. mi ...
s dysregulation involved in IBD and to promote colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
. By 2020, single-cell RNA sequencing analysis was launched by a small consortium using IBD patient biopsy material in a search for therapeutic targets.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is usually confirmed bybiopsies
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disea ...
on colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis ('' ...
. Fecal calprotectin
Faecal calprotectin ( or fecal calprotectin) is a biochemical measurement of the protein calprotectin in the stool. Elevated faecal calprotectin indicates the migration of neutrophils to the intestinal mucosa, which occurs during intestinal inf ...
is useful as an initial investigation, which may suggest the possibility of IBD, as this test is sensitive but not specific for IBD.
Differential diagnosis
Other diseases may cause an increased excretion of fecal calprotectin, such asinfectious diarrhea
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea and gastro, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and de ...
, untreated coeliac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
, necrotizing enterocolitis
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating intestinal disease that affects premature or very low birth weight infants.Gephart S.M., Quinn M. A call to action to fight for equity and end necrotizing enterocolitis disparities. ''Adv. Neonata ...
, intestinal cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Ot ...
and neoplastic pediatric tumor cells.
Conditions with similar symptoms as Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distensi ...
includes intestinal tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
, Behçet's disease
Behçet's disease (BD) is a type of inflammatory disorder which affects multiple parts of the body. The most common symptoms include painful sores on the mucous membranes of the mouth and other parts of the body, inflammation of parts of the ey ...
, ulcerative colitis, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration o ...
enteropathy, irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
and coeliac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
.
Conditions with similar symptoms as ulcerative colitis includes acute self-limiting colitis
Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine ( colon). Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. It broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases.
In a medical context, the label ''colitis'' (without qualification ...
, amebic colitis, schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. The urinary tract or the intestines may be infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, blo ...
, Crohn's disease, colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowe ...
, irritable bowel syndrome, intestinal tuberculosis and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug enteropathy.
Liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
are often elevated in inflammatory bowel disease, and are often mild and generally return spontaneously to normal levels. The most relevant mechanisms of elevated liver functions tests in IBD are drug-induced hepatotoxicity and fatty liver.
Classification
The chief types of inflammatory bowel disease areCrohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distensi ...
and ulcerative colitis (UC). Inflammatory bowel diseases fall into the class of autoimmune diseases
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
, in which the body's own immune system attacks elements of the digestive system.
Accounting for fewer cases are other forms of IBD, which are not always classified as typical IBD:
* Microscopic colitis
Microscopic colitis refers to two related medical conditions which cause diarrhea: collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis. Both conditions are characterized by the presence of chronic non-bloody watery diarrhea, normal appearances on colonos ...
subdivided into collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis
* Diversion colitis
* Behçet's disease
Behçet's disease (BD) is a type of inflammatory disorder which affects multiple parts of the body. The most common symptoms include painful sores on the mucous membranes of the mouth and other parts of the body, inflammation of parts of the ey ...
* Early Onset IBD
* Indeterminate colitis
No disease specific markers are currently known in the blood, enabling the reliable separation of Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distensi ...
and ulcerative colitis patients. The way doctors can tell the difference between Crohn's disease and UC is the ''location'' and ''nature'' of the inflammatory changes. Crohn's can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
, from mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
to anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, ...
('' skip lesions''), although a majority of the cases start in the terminal ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine m ...
. Ulcerative colitis, in contrast, is restricted to the colon and the rectum. Microscopically
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of micr ...
, ulcerative colitis is restricted to the mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
( epithelial lining of the gut), while Crohn's disease affects the full thickness of the bowel wall ("transmural lesions"). Lastly, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis present with extra-intestinal manifestations (such as liver problems, arthritis, skin manifestations and eye problems) in different proportions.
In 10–15% of cases, a definitive diagnosis neither of Crohn's disease nor of ulcerative colitis can be made because of idiosyncrasies in the presentation. In this case, a diagnosis of indeterminate colitis may be made. Although a recognised definition, not all centres refer to this.
Treatment
Surgery
CD and UC are chronic inflammatory diseases, and are not medically curable. However, ulcerative colitis can in most cases be cured byproctocolectomy
Proctocolectomy is the surgical removal of the rectum and all or part of the colon. It is the most widely accepted surgical method for ulcerative colitis and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP).
A proctocolectomy is considered a cure for ulcerat ...
, although this may not eliminate extra-intestinal symptoms. An ileostomy
Ileostomy is a stoma (surgical opening) constructed by bringing the end or loop of small intestine (the ileum) out onto the surface of the skin, or the surgical procedure which creates this opening. Intestinal waste passes out of the ileostomy an ...
will collect feces in a bag. Alternatively, a pouch can be created from the small intestine; this serves as the rectum and prevents the need for a permanent ileostomy. Between one-quarter and one-half of patients with ileo-anal pouches do have to manage occasional or chronic pouchitis.
Surgery cannot cure Crohn's disease but may be needed to treat complications such as abscesses, strictures or fistulae. Severe cases may require surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pa ...
, such as bowel resection
A bowel resection or enterectomy ('' enter-'' + '' -ectomy'') is a surgical procedure in which a part of an intestine (bowel) is removed, from either the small intestine or large intestine. Often the word ''enterectomy'' is reserved for the sense ...
, strictureplasty or a temporary or permanent colostomy
A colostomy is an opening (stoma) in the large intestine (colon), or the surgical procedure that creates one. The opening is formed by drawing the healthy end of the colon through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and suturing it into ...
or ileostomy
Ileostomy is a stoma (surgical opening) constructed by bringing the end or loop of small intestine (the ileum) out onto the surface of the skin, or the surgical procedure which creates this opening. Intestinal waste passes out of the ileostomy an ...
. In Crohn's disease, surgery involves removing the worst inflamed segments of the intestine and connecting the healthy regions, but unfortunately, it does not cure Crohn's or eliminate the disease. At some point after the first surgery, Crohn's disease can recur in the healthy parts of the intestine, usually at the resection site. (For example, if a patient with Crohn's disease has an ileocecal anastomosis, in which the caecum and terminal ileum are removed and the ileum is joined to the ascending colon, their Crohn's will nearly always flare-up near the anastomosis or in the rest of the ascending colon).
Medical therapies
Medical treatment of IBD is individualised to each patient. The choice of which drugs to use and by which route to administer them (oral, rectal, injection, infusion) depends on factors including the type, distribution, and severity of the patient's disease, as well as other historical and biochemical prognostic factors, and patient preferences. For example, mesalazine is more useful in ulcerative colitis than inCrohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distensi ...
. Generally, depending on the level of severity, IBD may require immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
to control the symptoms, with drugs such as prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and ad ...
, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF inhibitors), azathioprine
Azathioprine (AZA), sold under the brand name Imuran, among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used in rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus erythematosus, ...
, methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
, or 6-mercaptopurine
Mercaptopurine (6-MP), sold under the brand name Purinethol among others, is a medication used for cancer and autoimmune diseases. Specifically it is used to treat acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), Crohn's dis ...
.
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
s, such as the glucocorticoid prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and ad ...
, are frequently used to control disease flares and were once acceptable as a maintenance drug. Biological therapy for inflammatory bowel disease
Biological therapy, the use of medications called biopharmaceuticals or biologics that are tailored to specifically target an immune or genetic mediator of disease, plays a major role in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Even for dis ...
, especially the TNF inhibitors, are used in people with more severe or resistant Crohn's disease and sometimes in ulcerative colitis.
Treatment is usually started by administering drugs with high anti-inflammatory effects, such as prednisone. Once the inflammation is successfully controlled, another drug to keep the disease in remission, such as mesalazine in UC, is the main treatment. If further treatment is required, a combination of an immunosuppressive drug (such as azathioprine) with mesalazine (which may also have an anti-inflammatory effect) may be needed, depending on the patient. Controlled release budesonide
Budesonide, sold under the brand name Pulmicort among others, is a medication of the corticosteroid type. It is available as an inhaler, nebulization solution, pill, nasal spray, and rectal forms. The inhaled form is used in the long-term mana ...
is used for mild ileal Crohn's disease.
Nutritional and dietetic therapies
Exclusive enteral nutrition is a first-line therapy in pediatric Crohn's disease with weaker data in adults. Evidence supporting exclusive enteral nutrition in ulcerative colitis is lacking. Nutritional deficiencies play a prominent role in IBD. Malabsorption, diarrhea, and GI blood loss are common features of IBD. Deficiencies of B vitamins, fat-soluble vitamins, essential fatty acids, and key minerals such as magnesium, zinc, andselenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
are extremely common and benefit from replacement therapy. Dietary interventions, including certain exclusion diets like the specific carbohydrate diet
The specific carbohydrate diet (SCD) is a restrictive diet originally created to manage celiac disease; it limits the use of complex carbohydrates ( disaccharides and polysaccharides). Monosaccharides are allowed, and various foods including fish, ...
(SCD) can be beneficial for symptom management. Dietary fiber interventions, such as psyillium supplementation (a mixture of soluble and insoluble fibers), may relieve symptoms as well as induce/maintain remission by altering the microbiome composition of the GI tract, thereby improving regulation of immune function, reducing inflammation, and helping to restore the intestinal mucosal lining.
Anaemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, th ...
is commonly present in both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Due to raised levels of inflammatory cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
s which lead to the increased expression of hepcidin
Hepcidin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HAMP'' gene. Hepcidin is a key regulator of the entry of iron into the circulation in mammals.
During conditions in which the hepcidin level is abnormally high, such as inflammation, s ...
, parenteral iron is the preferred treatment option as it bypasses the gastrointestinal system, has lower incidence of adverse events and enables quicker treatment. Hepcidin itself is also an anti-inflammatory agent. In the murine model very low levels of iron restrict hepcidin synthesis, worsening the inflammation that is present. Enteral nutrition has been found to be efficient to improve hemoglobin level in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, especially combined with erythropoietin.
Microbiome
There is preliminary evidence of an infectious contribution to inflammatory bowel disease in some patients that may benefit from antibiotic therapy, such as with rifaximin. The evidence for a benefit of rifaximin is mostly limited to Crohn's disease with less convincing evidence supporting use in ulcerative colitis.Fecal microbiota transplant
Fecal microbiota transplant (FMT), also known as a stool transplant, is the process of transferring fecal bacteria and other microbes from a healthy individual into another individual. FMT is an effective treatment for ''Clostridioides diffici ...
is a relatively new treatment option for IBD which has attracted attention since 2010. Some preliminary studies have suggested benefits similar to those in Clostridium difficile infection
''Clostridioides difficile'' infection
(CDI or C-diff), also known as ''Clostridium difficile'' infection, is a symptomatic infection due to the spore-forming bacterium ''Clostridioides difficile''. Symptoms include watery diarrhea, fever, na ...
but a review of use in IBD shows that FMT is safe, but of variable efficacy. A 2014 review stated that more randomized controlled trials were needed.
Alternative medicine
Complementary and alternative medicine approaches have been used in inflammatory bowel disorders. Evidence from controlled studies of these therapies has been reviewed; risk of bias was quite heterogeneous. The best supportive evidence was found for herbal therapy, withPlantago ovata
''Plantago ovata'', known by many common names including blond plantain, desert Indianwheat, blond psyllium, and ispagol, is native to the Mediterranean region and naturalized in central, eastern, and south Asia and North America.
It is a commo ...
and curcumin in UC maintenance therapy, wormwood in CD, mind/body therapy and self-intervention in UC, and acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientif ...
in UC and CD.
Novel approaches
Stem cell therapy
Stem-cell therapy is the use of stem cells to treat or prevent a disease or condition. , the only established therapy using stem cells is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. This usually takes the form of a bone-marrow transplantation, bu ...
is undergoing research as a possible treatment for IBD. A review of studies suggests a promising role, although there are substantial challenges, including cost and characterization of effects, which limit the current use in clinical practice.
Psychological interventions
Currently, there is no evidence to recommend psychological treatment, such aspsychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome pro ...
, stress management
Stress management is a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies aimed at controlling a person's level of stress, especially chronic stress, usually for the purpose of and for the motive of improving everyday functioning. Stress produces ...
and patient's education, to all adults with IBD in general. These treatments had no effect on quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
, emotional well-being
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or displeasure. There is currently no scientific consensus on a definition. ...
and disease activity. The need for these approaches should be individually assessed and further researched to identify subgroups and determine type of therapy that may benefit individuals with IBD. In adolescents population such treatments may be beneficial on quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
and depression, although only short-term effects have been found, which also imposes the need for further research.
Treatment standards
Crohn's and Colitis Australia, the peak body for IBD in Australia, where prevalence is one of the highest in the world, reviewed the quality of care for patients admitted to Australian hospitals. They found that only one hospital met accepted standards for multidisciplinary care, but that care was improved with the availability of even minimal specialised services.Prognosis
While IBD can limit quality of life because of pain, vomiting, and diarrhea, it is rarely fatal on its own. Fatalities due to complications such as toxic megacolon, bowel perforation and surgical complications are also rare. Fatigue is a common symptom of IBD and can be a burden. Around one-third of individuals with IBD experience persistent gastrointestinal symptoms similar toirritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
(IBS) in the absence of objective evidence of disease activity. Despite enduring the side-effects of long-term therapies, this cohort has a quality of life that is not significantly different to that of individuals with uncontrolled, objectively active disease, and escalation of therapy to biological agents is typically ineffective in resolving their symptoms. The cause of these IBS-like symptoms is unclear, but it has been suggested that changes in the gut-brain axis, epithelial barrier dysfunction, and the gut flora
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut m ...
may be partially responsible.
While patients of IBD do have an increased risk of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
, this is usually caught much earlier than the general population in routine surveillance of the colon by colonoscopy, and therefore patients are much more likely to survive.
New evidence suggests that patients with IBD may have an elevated risk of endothelial dysfunction and coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pl ...
.
The goal of treatment is toward achieving remission, after which the patient is usually switched to a lighter drug with fewer potential side effects. Every so often, an acute resurgence of the original symptoms may appear; this is known as a "flare-up". Depending on the circumstances, it may go away on its own or require medication. The time between flare-ups may be anywhere from weeks to years, and varies wildly between patients – a few have never experienced a flare-up.
Life with IBD can be challenging; however, many with the condition lead relatively normal lives. IBD carries a psychological burden due to stigmatization of being diagnosed, leading to high levels of anxiety, depression, and a general reduction in the quality of life. Although living with IBD can be difficult, there are numerous resources available to help families navigate the ins and out of IBD, such as the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America
The Crohn's & Colitis Foundation (CCF) is a volunteer-driven non-profit organization dedicated to finding cures for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis and improving the quality of life of children and adults affected by these digestive disease ...
(CCFA).
Epidemiology
IBD resulted in a global total of 51,000 deaths in 2013 and 55,000 deaths in 1990. The increased incidence of IBD since World War 2 has been correlated to the increase in meat consumption worldwide, supporting the claim that animal protein intake is associated with IBD. However, there are many environmental risk factors that have been linked to the increased and decreased risk of IBD, such as smoking, air pollution and greenspace, urbanization and Westernization. Inflammatory bowel diseases are increasing in Europe. Incidence and prevalence of IBD has risen steadily for the last decades in Asia, which could be related changes in diet and other environmental factors. Around 0.8% of people in the UK have IBD. Similarly, around 270,000 (0.7%) of people in Canada have IBD, with that number expected to rise to 400,000 (1%) by 2030.Research
The following treatment strategies are not used routinely, but appear promising in some forms of inflammatory bowel disease. Initial reports suggest that " helminthic therapy" may not only prevent but even control IBD: a drink with roughly 2,500 ova of the ''Trichuris suis
''Trichuris suis'' is a whipworm; the variations in thickness of the anterior and posterior segments give the parasite the characteristic "whip-like" appearance. Adult females measure 6 to 8 cm and adult males 3 to 4 cm. ''T. suis'' egg ...
'' helminth taken twice monthly decreased symptoms markedly in many patients. It is even speculated that an effective "immunization" procedure could be developed—by ingesting the cocktail at an early age.
Prebiotics and probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host i ...
s are focusing increasing interest as treatments for IBD. Currently, there is evidence to support the use of certain probiotics in addition to standard treatments in people with ulcerative colitis but there is no sufficient data to recommend probiotics in people with Crohn's disease. Both single strain and multi-strain probiotics have been researched for mild to moderate cases of ulcerative colitis. The most clinically researched multi-strain probiotic with over 70 human trials is the De Simone Formulation. Further research is required to identify specific probiotic strains or their combinations and prebiotic substances for therapies of intestinal inflammation.
Currently, the probiotic strain, frequency, dose and duration of the probiotic therapy are not established. In severely ill people with IBD there is a risk of the passage of viable bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the internal organs (bacterial translocation) and subsequent bacteremia
Bloodstream infections (BSIs), which include bacteremias when the infections are bacterial and fungemias when the infections are fungal, are infections present in the blood. Blood is normally a sterile environment, so the detection of microbe ...
, which can cause serious adverse health consequences. Live bacteria might not be essential because of beneficial effects of probiotics seems to be mediated by their DNA and by secreted soluble factors, and their therapeutic effects may be obtained by systemic administration rather than oral administration.
In 2005 New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publish ...
published a joint study by Bristol University
, mottoeng = earningpromotes one's innate power (from Horace, ''Ode 4.4'')
, established = 1595 – Merchant Venturers School1876 – University College, Bristol1909 – received royal charter
, type ...
and the University of Bath
(Virgil, Georgics II)
, mottoeng = Learn the culture proper to each after its kind
, established = 1886 (Merchant Venturers Technical College) 1960 (Bristol College of Science and Technology) 1966 (Bath University of Technology) 1971 (univ ...
on the apparent healing power of cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternative ...
on IBD. Reports that cannabis eased IBD symptoms indicated the possible existence of cannabinoid receptors in the intestinal lining, which respond to molecules in the plant-derived chemicals. CB1 cannabinoid receptors – which are known to be present in the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
– exist in the endothelial cells
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
which line the gut, it is thought that they are involved in repairing the lining of the gut when damaged.
The team deliberately damaged the cells to cause inflammation of the gut lining and then added synthetically produced cannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tet ...
s; the result was that gut started to heal: the broken cells were repaired and brought back closer together to mend the tears. It is believed that in a healthy gut, natural endogenous cannabinoids are released from endothelial cells when they are injured, which then bind to the CB1 receptors. The process appears to set off a wound-healing reaction, and when people use cannabis, the cannabinoids bind to these receptors in the same way.
Previous studies have shown that CB1 receptors located on the nerve cells in the gut respond to cannabinoids by slowing gut motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
, therefore reducing the painful muscle contractions associated with diarrhea. CB2, another cannabinoid receptor predominantly expressed by immune cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mul ...
, was detected in the gut of people with IBD at a higher concentration. These receptors, which also respond to chemicals in cannabis, appear to be associated with apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
– programmed cell death – and may have a role in suppressing the overactive immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
and reducing inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
by mopping up excess cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
.
Activation of the endocannabinoid system
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system composed of endocannabinoids, which are endogenous lipid-based retrograde neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors (CBRs), and cannabinoid receptor proteins that are expressed ...
was found efficient in ameliorating colitis
Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine ( colon). Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. It broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases.
In a medical context, the label ''colitis'' (without qualification ...
and increasing the survival rate of mice, and reducing remote organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
changes induced by colitis, further suggest that modulation of this system is a potential therapeutic approach for IBDs and the associated remote organ lesions.
Alicaforsen is a first generation antisense oligodeoxynucleotide designed to bind specifically to the human ICAM-1 messenger RNA through Watson-Crick base pair interactions in order to subdue expression of ICAM-1. ICAM-1 propagates an inflammatory response promoting the extravasation and activation of leukocytes
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mu ...
(white blood cells) into inflamed tissue. Increased expression of ICAM-1 has been observed within the inflamed intestinal mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
of people with ulcerative colitis, pouchitis and Crohn's, where ICAM-1 over production correlated with disease activity. This suggests that ICAM-1 is a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of these diseases.
Cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
s are found to decrease the induction of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 surface expression in human brain tissues and primary human brain endothelial cells (BMVEC) exposed to various pro-inflammatory mediators.
In 2014, an alliance among the Broad Institute
The Eli and Edythe L. Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard (IPA: , pronunciation respelling: ), often referred to as the Broad Institute, is a biomedical and genomic research center located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. The insti ...
, Amgen
Amgen Inc. (formerly Applied Molecular Genetics Inc.) is an American multinational biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Thousand Oaks, California. One of the world's largest independent biotechnology companies, Amgen was established in T ...
and Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General or MGH) is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the third oldest general hospital in the United Stat ...
formed with the intention to "collect and analyze patient DNA samples to identify and further validate genetic targets."
In 2015, a meta-analysis on 938 IBD patients and 953 controls, IBD was significantly associated with having higher odds of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
deficiency.
Gram-positive bacteria present in the lumen could be associated with extending the time of relapse for ulcerative colitis.
Bidirectional pathways between depression and IBD have been suggested and psychological processes have been demonstrated to influence self-perceived physical and psychological health over time. IBD-disease activity may impact quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
and over time may significantly affect individual's mental well-being, which may be related to the increased risk to develop anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
and/or depression. On the other hand, psychological distress may also influence IBD activity.
Higher rates of anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
and depression are observed among those with IBD compared to healthy individuals, which correlated with disease severity. Moreover, anxiety and depression rates increase during active disease compared with inactive phases.
See also
* Inflammatory bowel disease-22 * World Inflammatory Bowel Disease DayReferences
External links
* {{Authority control Autoimmune diseases Gastrointestinal tract disorders Steroid-responsive inflammatory conditions