hookworm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
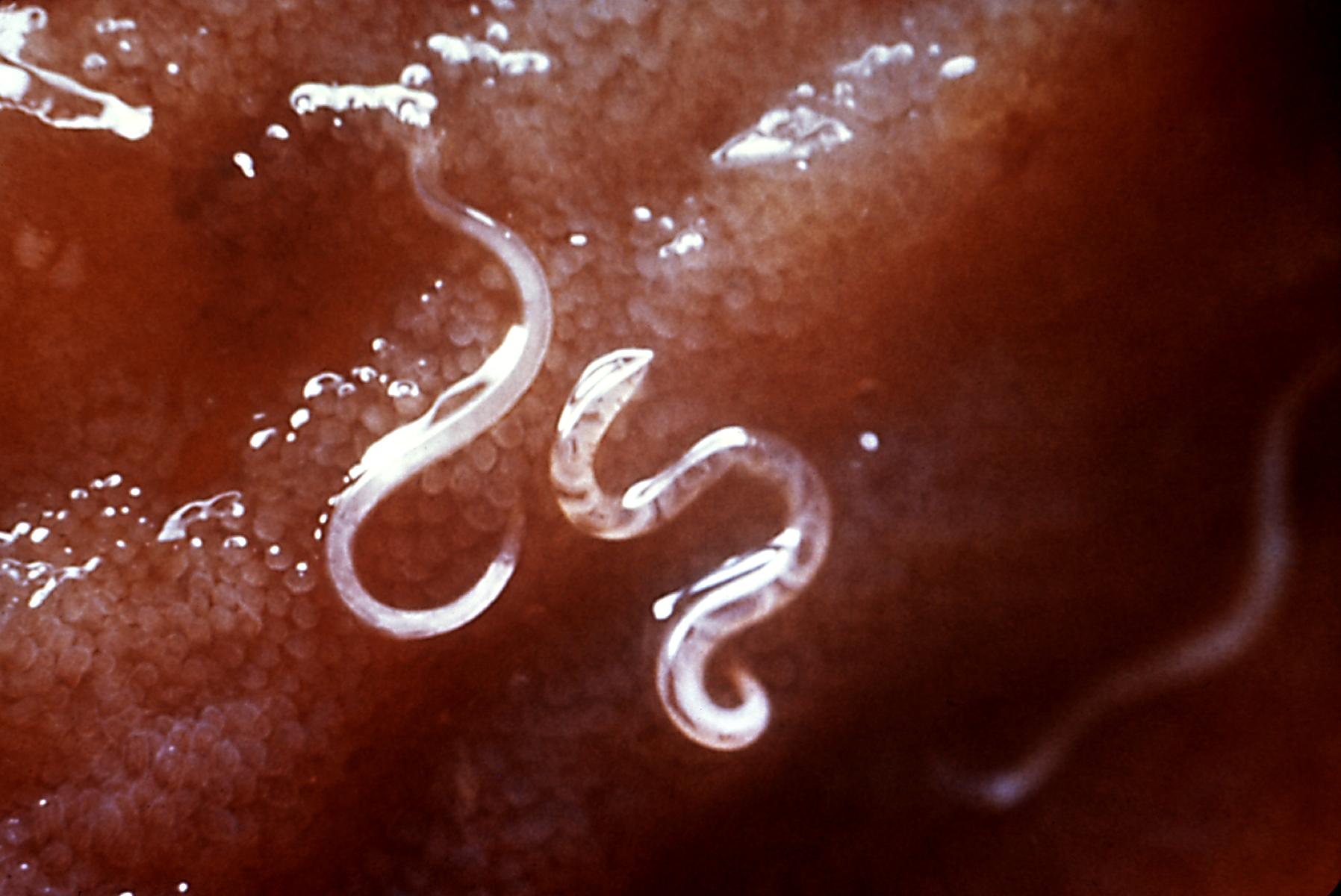 Hookworms are
Hookworms are
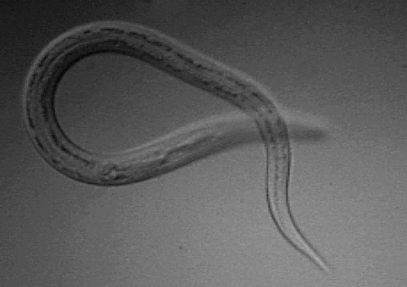 The two most common types of hookworm that infect humans are ''
The two most common types of hookworm that infect humans are ''
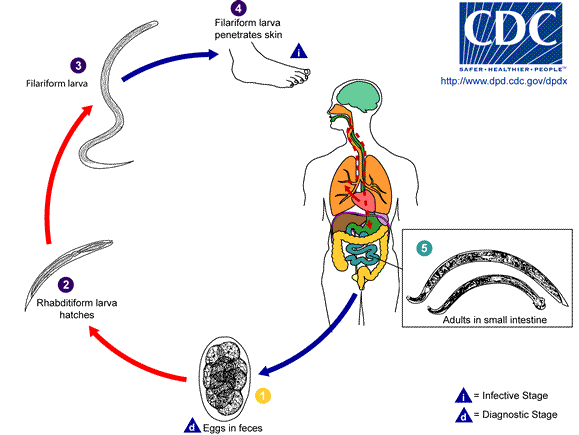 The host is infected by the larvae, not by the eggs, and the usual route is through the skin. Hookworm larvae need warm, moist soil, above 18 °C, in order to hatch. They will die if exposed to direct sunlight or if they become dried out. ''Necator'' larvae can survive at higher temperatures than ''Ancylostoma'' larvae.
First-stage larvae (L1) are non-infective, and once hatched in the deposited feces, they feed on that, and then feed on soil microorganisms until they moult into second stage larvae (L2). First- and second-stage larvae are in the rhabditiform stage. After feeding for seven days or so they will moult into third-stage larvae (L3) known as the filariform stage, which is the non-feeding, infective stage. Filariform larvae can survive for up to two weeks. They are extremely motile and will move onto higher ground to improve their chances of finding a host.
''N. americanus'' larvae can only infect through penetrating skin, but ''A. duodenale'' can also infect orally. A common route of passage for the larvae is the skin of
The host is infected by the larvae, not by the eggs, and the usual route is through the skin. Hookworm larvae need warm, moist soil, above 18 °C, in order to hatch. They will die if exposed to direct sunlight or if they become dried out. ''Necator'' larvae can survive at higher temperatures than ''Ancylostoma'' larvae.
First-stage larvae (L1) are non-infective, and once hatched in the deposited feces, they feed on that, and then feed on soil microorganisms until they moult into second stage larvae (L2). First- and second-stage larvae are in the rhabditiform stage. After feeding for seven days or so they will moult into third-stage larvae (L3) known as the filariform stage, which is the non-feeding, infective stage. Filariform larvae can survive for up to two weeks. They are extremely motile and will move onto higher ground to improve their chances of finding a host.
''N. americanus'' larvae can only infect through penetrating skin, but ''A. duodenale'' can also infect orally. A common route of passage for the larvae is the skin of
intestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broa ...
that cause types of infection known as helminthiases
Helminthiasis, also known as worm infection, is any macroparasitic disease of humans and other animals in which a part of the body is infected with parasitic worms, known as helminths. There are numerous species of these parasites, which are br ...
. Hookworm infection
Hookworm infection is an infection by a type of intestinal parasite known as a hookworm. Initially, itching and a rash may occur at the site of infection. Those only affected by a few worms may show no symptoms. Those infected by many worms may e ...
is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, and hygiene. In humans, infections are caused by two main species of roundworm, belonging to the genera ''Ancylostoma
''Ancylostoma'' is a genus of nematodes that includes some species of hookworms.
Species include:
: ''Ancylostoma braziliense'', commonly infects cats, popularly known in Brazil as ''bicho-geográfico''
: ''Ancylostoma caninum'', commonly infec ...
'' and '' Necator''. In other animals the main parasites are species of ''Ancylostoma''.
Species
 The two most common types of hookworm that infect humans are ''
The two most common types of hookworm that infect humans are ''Ancylostoma duodenale
''Ancylostoma'' is a genus of nematodes that includes some species of hookworms.
Species include:
: ''Ancylostoma braziliense'', commonly infects cats, popularly known in Brazil as ''bicho-geográfico''
: ''Ancylostoma caninum'', commonly infec ...
'' and ''Necator americanus
''Necator americanus'' is a species of hookworm (a type of helminth) commonly known as the New World hookworm. Like other hookworms, it is a member of the phylum Nematoda. It is an obligatory parasitic nematode that lives in the small intestine ...
''.
Hookworm species that are known to infect domestic cats are ''Ancylostoma braziliense
''Ancylostoma braziliense'' is a species of hookworm belonging to the genus ''Ancylostoma''. It is an intestinal parasite of domestic cats and dogs. Severe infection is often fatal to these pets, especially in puppies and kittens. The infection ...
'' and ''Ancylostoma tubaeforme
''Ancylostoma tubaeforme'' is a hookworm that infects cats worldwide. Infection can occur through penetration of the skin, ingestion of infected hosts, such as birds, or by directly consuming the organism. ''Ancylostoma tubaeforme'' along with ' ...
''. Wild cats are infected by ''Ancylostoma pluridentatum
''Ancylostoma pluridentatum'' is a species of parasitic hookworm
Hookworms are intestinal, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, an ...
''.
Dogs are commonly infected by ''Ancylostoma caninum
''Ancylostoma caninum'' is a species of nematode known as a hookworm, which principally infects the small intestine of dogs. The result of ''A. caninum'' infection ranges from asymptomatic cases to death of the dog; better nourishment, increasi ...
'', but may also be infected by ''Uncinaria stenocephala
''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is a nematode that parasitizes dogs, cats, and foxes as well as humans. It is rare to find in cats in the United States. ''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is the most common canine hookworm in cooler regions, such as Canada ...
'' and ''Ancylostoma braziliense''.
In Asia, ''Ancylostoma ceylanicum
''Ancylostoma ceylanicum'' is a parasitic roundworm belonging to the genus ''Ancylostoma''. It is a hookworm both of humans and of other mammals such as dogs, cats, and golden hamsters. It is the only zoonotic hookworm species that is able to ...
'' is endemic among dogs and cats and infects humans.
Cattle are infected by ''Bunostomum
''Bunostomum'' is a genus of nematodes of the small intestine of ruminants and camelids. Important species include: ''B. phlebotomum'' in calves and ''B. trigonocephalum'' in lambs. The worms are stout and measure in length. Young animals are mo ...
phlebotomum''.
At least 68 species have been described in wild mammals.
Characteristics
The two species that commonly infect humans have a similar morphology. ''A. duodenale'' worms are pale grey or slightly pink. The head is bent a little in relation to the rest of the body, forming a hook shape – hence the name. The hook is at the front end of the body. They have well-developed mouths with two pairs of teeth. Males measure approximately 10 by 0.5 mm, and females are often longer and stouter. Males also have a prominent copulatory bursa posteriorly. ''N. americanus'' is generally smaller than ''A. duodenale'', with males usually being 5 to 9 mm long and females about 10 mm long. Instead of the two pairs of teeth in ''A. duodenale'', ''N. americanus'' has a pair of cutting plates in the buccal capsule. Also, the hook is much more defined in ''Necator americanus''.Life cycle
 The host is infected by the larvae, not by the eggs, and the usual route is through the skin. Hookworm larvae need warm, moist soil, above 18 °C, in order to hatch. They will die if exposed to direct sunlight or if they become dried out. ''Necator'' larvae can survive at higher temperatures than ''Ancylostoma'' larvae.
First-stage larvae (L1) are non-infective, and once hatched in the deposited feces, they feed on that, and then feed on soil microorganisms until they moult into second stage larvae (L2). First- and second-stage larvae are in the rhabditiform stage. After feeding for seven days or so they will moult into third-stage larvae (L3) known as the filariform stage, which is the non-feeding, infective stage. Filariform larvae can survive for up to two weeks. They are extremely motile and will move onto higher ground to improve their chances of finding a host.
''N. americanus'' larvae can only infect through penetrating skin, but ''A. duodenale'' can also infect orally. A common route of passage for the larvae is the skin of
The host is infected by the larvae, not by the eggs, and the usual route is through the skin. Hookworm larvae need warm, moist soil, above 18 °C, in order to hatch. They will die if exposed to direct sunlight or if they become dried out. ''Necator'' larvae can survive at higher temperatures than ''Ancylostoma'' larvae.
First-stage larvae (L1) are non-infective, and once hatched in the deposited feces, they feed on that, and then feed on soil microorganisms until they moult into second stage larvae (L2). First- and second-stage larvae are in the rhabditiform stage. After feeding for seven days or so they will moult into third-stage larvae (L3) known as the filariform stage, which is the non-feeding, infective stage. Filariform larvae can survive for up to two weeks. They are extremely motile and will move onto higher ground to improve their chances of finding a host.
''N. americanus'' larvae can only infect through penetrating skin, but ''A. duodenale'' can also infect orally. A common route of passage for the larvae is the skin of barefoot
Barefoot is the state of not wearing any footwear.
There are health benefits and some risks associated with going barefoot. Shoes, while they offer protection, can limit the flexibility, strength, and mobility of the foot and can lead to h ...
walkers. Once the larvae have entered the host they travel in the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
to the lungs where they leave the venule
A venule is a very small blood vessel in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the larger blood vessels, the veins. Venules range from 7μm to 1mm in diameter. Veins contain approximately 70% of t ...
s and enter the alveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* ...
. They then travel up the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the ...
and are coughed up, swallowed and end up in the small intestine. In the small intestine, the larvae moult into stage four (L4) the adult worm. It takes from five to nine weeks from penetration to maturity in the intestine.
''Necator americanus'' can cause a prolonged infection lasting from one to five years with many worms dying in the first year or two. Some worms though have been recorded as living for fifteen years or more. In comparison, ''Ancyclostoma duodenale'' worms are short-lived lasting for around six months. However, larvae can remain dormant in tissue stores and be recruited over many years to replace the worms that die.
The worms mate inside the host, in which the females also lay their eggs, to be passed out in the host's feces into the environment to start the cycle again. ''N. americanus'' can lay between nine and ten thousand eggs per day, and ''A. duodenale'' between twenty-five and thirty thousand per day. The eggs of the two species are indistinguishable.
Worms need five to seven weeks to reach maturity and symptoms of infection can therefore appear before eggs are to be found in the feces, making the diagnosis of hookworm infection difficult.
Diagnosis
Signs and symptoms of hookworm infection vary by host and hookworm species. In humans, the first sign of infection is itching and skin rash. Humans with light infections may show no symptoms, but humans with heavy infections may have abdominal pain, diarrhea, loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue and anemia. Children's physical and cognitive growth may be affected. Dogs and cats may experience dermatitis, enteritis, and intestinal blood loss. Dogs may additionally experience anemia, hemorrhagic diarrhea, anorexia and dehydration. Cattle may experience skin lesions, anemia, and rapid weight loss. Diagnosis for many forms of hookworm infections is confirmed through fecal analysis to identify hookworm eggs. In animals, fecal floatation is used to detect hookworm eggs.Treatment
Treatment for hookworm infections depends on the species of hookworm and the species of the infected host. In humans, treatment is byanthelminthic
Anthelmintics or antihelminthics are a group of antiparasitic drugs that expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them and without causing significant damage to the host. They may ...
medications, such as albendazole
Albendazole (also known as albendazolum) is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic and antiprotozoal agent of the benzimidazole type. It is used for the treatment of a variety of intestinal parasite infections, including ascariasis, pinworm infection, ho ...
and mebendazole
Mebendazole (MBZ), sold under the brand name Vermox among others, is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infestations. This includes ascariasis, pinworm infection, hookworm infections, guinea worm infections, hydatid disea ...
. Treatment in animals can be done with a variety of anthelminthics. A high-protein diet, supplemental iron, or a blood transfusion may also be necessary.
Prevention
Humans can avoid hookworm infections by avoiding skin-to-soil contact, such as walking barefoot, in areas where hookworms are common. Additionally, infection can be controlled by defecating indoors and not using human feces as a plant fertilizer. Lawns and kennels may be sterilized bysodium borate Sodium borate is a generic name for any salt of sodium with an anion consisting of boron and oxygen, and possibly hydrogen, or any hydrate thereof. It can be seen as a hydrated sodium salt of the appropriate boroxy acid, although the latter may n ...
. Large education efforts funded by John D. Rockefeller
John Davison Rockefeller Sr. (July 8, 1839 – May 23, 1937) was an American business magnate and philanthropist. He has been widely considered the wealthiest American of all time and the richest person in modern history. Rockefeller was ...
helped reduce the rates of infection among children in the American South during the 1910s.
References
{{reflist Parasitic nematodes of mammals Ancylostomatidae