|
Ancylostoma Tubaeforme
''Ancylostoma tubaeforme'' is a hookworm that infects cats worldwide. Infection can occur through penetration of the skin, ingestion of infected hosts, such as birds, or by directly consuming the organism. ''Ancylostoma tubaeforme'' along with ''Ancylostoma braziliense'' are the two most common hookworms to infect cats, causing anemia and compromising the immune system. Morphology The body of an adult A. tubaeforme is between 7 to 12 millimeters long. Youssefi, M. R., Hoseini, S. H., Hoseini, S. M., Zaheri, B. A., & Tabari, M. A. (2010). First report of Ancylostoma tubaeforme in Persian Leopard (Panthera pardus saxicolor). Iranian Journal of Parasitology, 5(1), 61–63. Signs ''Ancylostoma tubaeforme'' infection may lead to dermatitis, anemia, weight loss, and pulmonary lesions. Life cycle ''Ancylostoma tubaeforme'' larvae may infect a host through oral ingestion or through skin lesions. Larvae ingested by the host pass through the esophagus into the stomach. From there, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hookworm
Hookworms are intestinal, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, and hygiene. In humans, infections are caused by two main species of roundworm, belonging to the genera ''Ancylostoma'' and '' Necator''. In other animals the main parasites are species of ''Ancylostoma''. Species The two most common types of hookworm that infect humans are ''Ancylostoma duodenale'' and '' Necator americanus''. Hookworm species that are known to infect domestic cats are '' Ancylostoma braziliense'' and '' Ancylostoma tubaeforme''. Wild cats are infected by '' Ancylostoma pluridentatum''. Dogs are commonly infected by '' Ancylostoma caninum'', but may also be infected by '' Uncinaria stenocephala'' and ''Ancylostoma braziliense''. In Asia, '' Ancylostoma ceylanicum'' is endemic among dogs and cats and infects humans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancylostoma Braziliense
''Ancylostoma braziliense'' is a species of hookworm belonging to the genus ''Ancylostoma''. It is an intestinal parasite of domestic cats and dogs. Severe infection is often fatal to these pets, especially in puppies and kittens. The infection is particularly endemic in the southern United States. It is most often confused with the zoonotic hookworm species '' Ancylostoma ceylanicum'' because of their uncanny resemblance. ''Ancyclostoma braziliense'' larvae can cause accidental infection in humans called cutaneous larval migration or creeping eruption, which produces severe itching in the skin. It is the most common skin infection in tropical region, particularly along the beaches of the Caribbean. Discovery and history When ''A. braziliense'' was described by Gomes de Faria in 1910, and ''A. ceylanicum'' by Arthur Looss in 1911, the two species were regarded as synonymous because of their apparent similarities in almost all respect. Especially in 1913, comparison of specimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
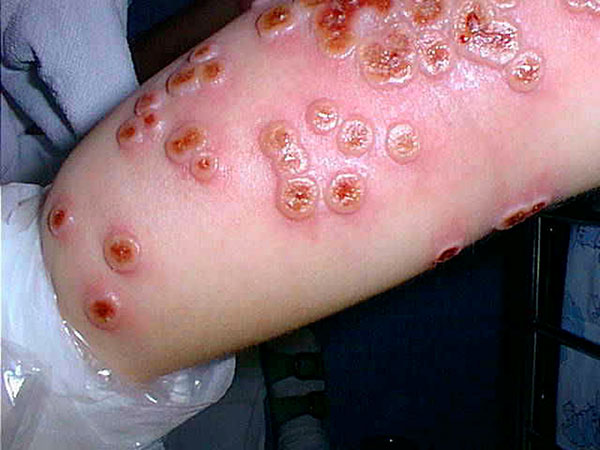
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is often called eczema, and the difference between those terms is not standardized. The exact cause of the condition is often unclear. Cases may involve a combination of allergy and poor venous return. The type of dermatitis is generally determined by the person's history and the location of the rash. For example, irritant dermatitis often occurs on the hands of those who frequently get them wet. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs upon exposure to an allergen, causing a hypersensitivity reaction in the skin. Prevention of atopic dermatitis is typically with essential fatty acids, and may be treated with moisturizers and steroid creams. The steroid creams should generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cell production, and increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Since lesions can occur anywhere in the body and the definition of a lesion is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, their sizes, their locations, or their causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called '' chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries. Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, a "skin lesion" or a " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthelmintic
Anthelmintics or antihelminthics are a group of antiparasitic drugs that expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them and without causing significant damage to the host. They may also be called vermifuges (those that stun) or vermicides (those that kill). Anthelmintics are used to treat people who are infected by helminths, a condition called helminthiasis. These drugs are also used to treat infected animals. Pills containing anthelmintics are used in mass deworming campaigns of school-aged children in many developing countries. The drugs of choice for soil-transmitted helminths are mebendazole and albendazole; for schistosomiasis and tapeworms it is praziquantel. Types Antiparasitics that specifically target worms of the genus ''Ascaris'' are called ascaricides. * Benzimidazoles: ** Albendazole – effective against threadworms, roundworms, whipworms, tapeworms, hookworms ** Mebendazole – effective ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenbendazole
Fenbendazole is a broad spectrum benzimidazole anthelmintic used against gastrointestinal parasites including: giardia, roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, the tapeworm genus '' Taenia'' (but not effective against '' Dipylidium caninum'', a common dog tapeworm), pinworms, aelurostrongylus, paragonimiasis, strongyles, and strongyloides that can be administered to sheep, cattle, horses, fish, dogs, cats, rabbits, most reptiles, freshwater shrimp tanks as planaria and hydra treatments, as well as seals. Drug interactions Drug interactions may occur if salicylanilides such as dibromsalan and niclosamide are co-administered. Abortions in cattle and death in sheep have been reported after using these medications together. Abortions in domestic ruminants have been associated with concurrent use of anti-trematode therapeutic agents. Toxicity Fenbendazole is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract in most species. The in laboratory animals exceeds 10 g/kg when admi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selamectin
Selamectin (trade names Revolution and Stronghold manufactured by Zoetis, and Revolt manufactured by Aurora Pharmaceuticals, among others) is a topical parasiticide and anthelminthic used on dogs and cats. It treats and prevents infections of heartworms, fleas, ear mites, sarcoptic mange (scabies), and certain types of ticks in dogs, and prevents heartworms, fleas, ear mites, hookworms, and roundworms in cats. It is structurally related to ivermectin and milbemycin. Selamectin is not approved for human use. Usage The drug is applied topically. It is isopropyl alcohol based, packaged according to its varying dosage sizes and applied once monthly. It is not miscible in water. Mode of action Selamectin disables parasites by activating glutamate-gated chloride channels at muscle synapses. Selamectin activates the chloride channel without desensitization, allowing chloride ions to enter the nerve cells and causing neuromuscular paralysis, impaired muscular contraction, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feline Zoonosis
A feline zoonosis is a viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoan, nematode or arthropod infection that can be transmitted to humans from the domesticated cat, ''Felis catus''. Some of these diseases are reemerging and newly emerging infections or infestations caused by zoonotic pathogens transmitted by cats. In some instances, the cat can display symptoms of infection (these may differ from the symptoms in humans) and sometimes the cat remains asymptomatic. There can be serious illnesses and clinical manifestations in people who become infected. This is dependent on the immune status and age of the person. Those who live in close association with cats are more prone to these infections. But those that do not keep cats as pets are also able to acquire these infections because of the transmission can be from cat feces and the parasites that leave their bodies. People can acquire cat-associated infections through bites, scratches or other direct contact of the skin or mucous membranes with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasites Of Cats
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's body; an ect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Nematodes Of Mammals
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's body; an ect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |