history of Bosnia and Herzegovina on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
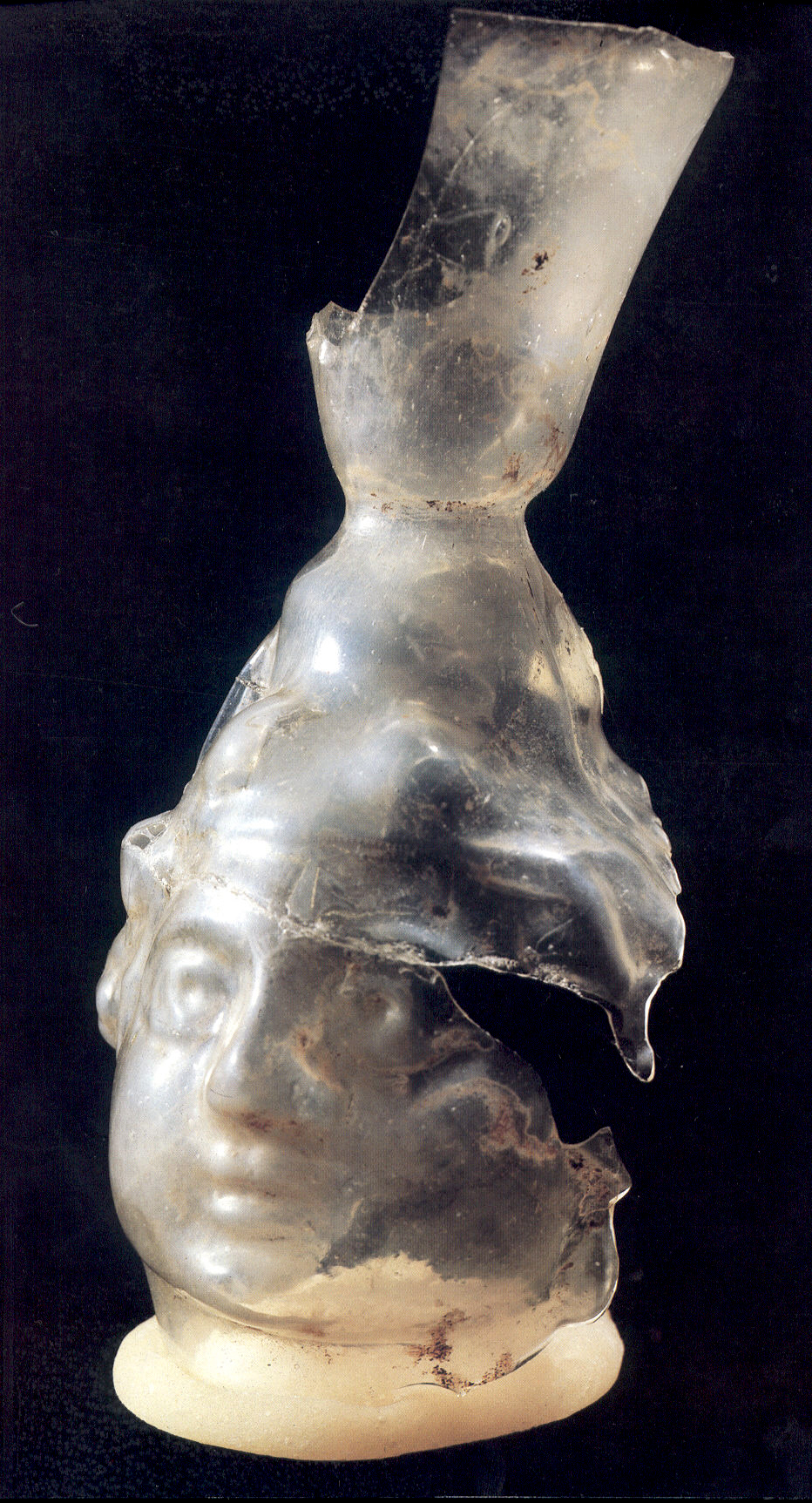 Bosnia has been inhabited since
Bosnia has been inhabited since
 By the 6th century, Emperor
By the 6th century, Emperor

 It is only from the 9th century that Frankish and Byzantine sources begin to mention early Slavic polities in the region. In this regard, the earliest widely acknowledged reference to Bosnia dates from the 10th century '' De Administrando Imperio'' written by Byzantine emperor
It is only from the 9th century that Frankish and Byzantine sources begin to mention early Slavic polities in the region. In this regard, the earliest widely acknowledged reference to Bosnia dates from the 10th century '' De Administrando Imperio'' written by Byzantine emperor

 Bosnian history from then until the early 14th century was marked by the power struggle between the Šubić and Kotromanić families. This conflict came to an end in 1322, when Stjepan II Kotromanić became ban. By the time of his death in 1353, he had succeeded in annexing territories to the north and west, as well as Zahumlje and parts of Dalmatia. He was succeeded by his nephew Tvrtko who, following a prolonged struggle with nobility and inter-family strife, gained full control of the country in 1367. Under Tvrtko, Bosnia grew in both size and power, finally becoming an independent kingdom in 1377. Following his death in 1391 however, Bosnia fell into a long period of decline. The
Bosnian history from then until the early 14th century was marked by the power struggle between the Šubić and Kotromanić families. This conflict came to an end in 1322, when Stjepan II Kotromanić became ban. By the time of his death in 1353, he had succeeded in annexing territories to the north and west, as well as Zahumlje and parts of Dalmatia. He was succeeded by his nephew Tvrtko who, following a prolonged struggle with nobility and inter-family strife, gained full control of the country in 1367. Under Tvrtko, Bosnia grew in both size and power, finally becoming an independent kingdom in 1377. Following his death in 1391 however, Bosnia fell into a long period of decline. The


 The Ottoman conquest of Bosnia marked a new era in the country's history and introduced tremendous changes in the political and cultural landscape of the region. Although the kingdom had been crushed and its high nobility executed, the Ottomans nonetheless allowed for the preservation of Bosnia's identity by incorporating it as an integral province of the Ottoman Empire with its historical name and territorial integrity - a unique case among subjugated states in the Balkans.Riedlmayer, Andras (1993)
The Ottoman conquest of Bosnia marked a new era in the country's history and introduced tremendous changes in the political and cultural landscape of the region. Although the kingdom had been crushed and its high nobility executed, the Ottomans nonetheless allowed for the preservation of Bosnia's identity by incorporating it as an integral province of the Ottoman Empire with its historical name and territorial integrity - a unique case among subjugated states in the Balkans.Riedlmayer, Andras (1993)
A Brief History of Bosnia-Herzegovina
. The Bosnian Manuscript Ingathering Project. Within this

 Though an
Though an
 Following World War I, Bosnia was incorporated into the South Slav
Following World War I, Bosnia was incorporated into the South Slav
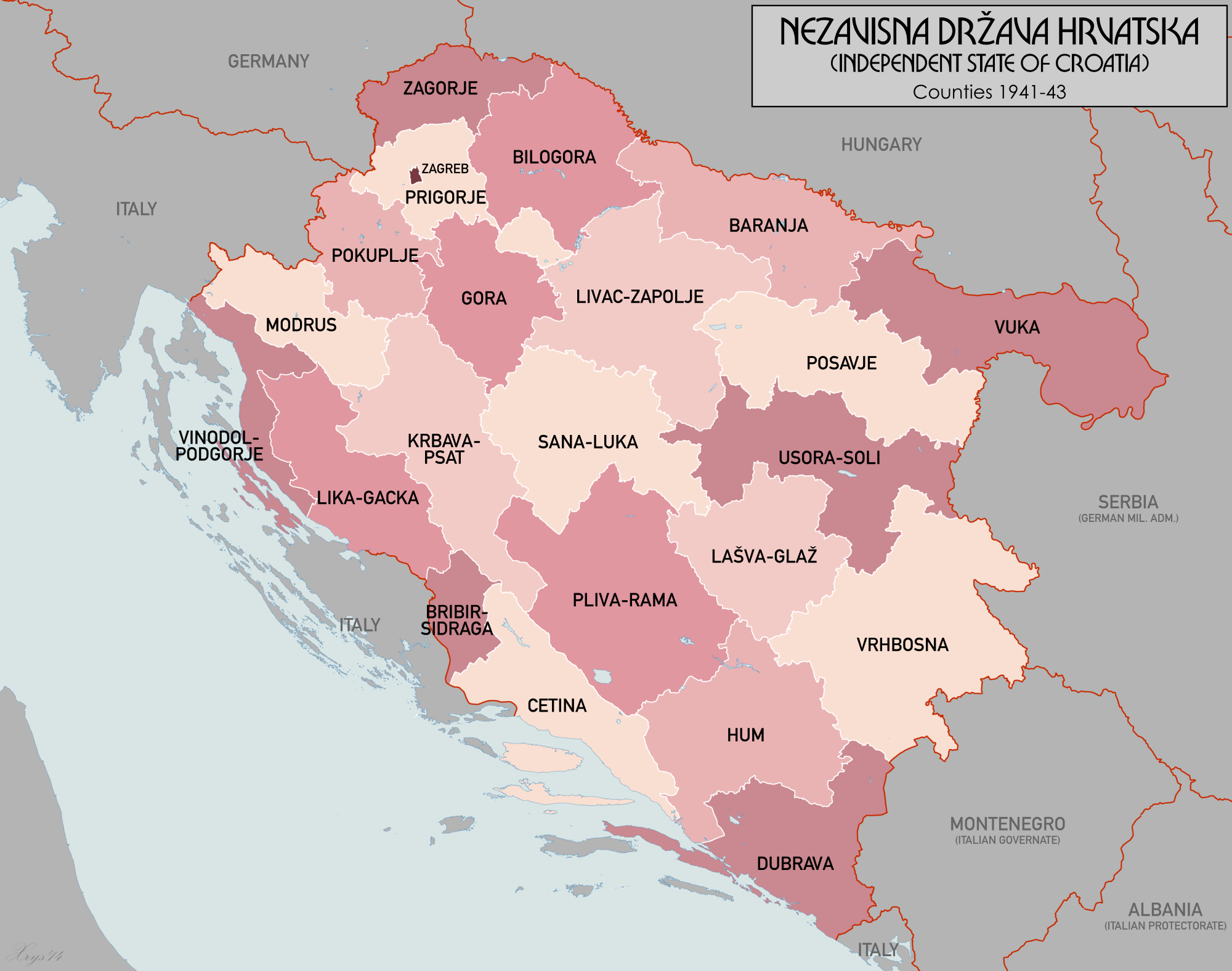
 Once the kingdom of Yugoslavia was conquered by
Once the kingdom of Yugoslavia was conquered by
 Because of its central geographic position within the for much of the 1950s and 1960s, the 1970s saw the ascension of a strong Bosnian political elite. While working within the Communism, communist system, politicians such as Džemal Bijedić, Branko Mikulić and Hamdija Pozderac reinforced and protected the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina Stojic, Mile (2005)
Because of its central geographic position within the for much of the 1950s and 1960s, the 1970s saw the ascension of a strong Bosnian political elite. While working within the Communism, communist system, politicians such as Džemal Bijedić, Branko Mikulić and Hamdija Pozderac reinforced and protected the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina Stojic, Mile (2005)
Branko Mikulic - socialist emperor manqué
. BH Dani Their efforts proved key during the turbulent period following Tito's death in 1980, and are today considered some of the early steps towards Bosnian independence. However, the republic could not escape the increasingly nationalistic climate of the time unscathed.
 The first multi-party parliamentary elections held on 18 and 25 November 1990 led to a national assembly dominated by three ethnically-based parties, which had formed a loose coalition to oust the communists from power. Croatia and Slovenia's subsequent declarations of independence and the warfare that ensued placed Bosnia and Herzegovina and its three constituent peoples in an awkward position. A significant split soon developed on the issue of whether to stay with the Yugoslav federation (overwhelmingly favored among Serbs) or seek independence (overwhelmingly favored among Bosniaks and Croats). A declaration of sovereignty on 15 October 1991 was followed by a referendum for independence from Yugoslavia on 29 February and 1 March 1992. The referendum was boycotted by the great majority of Bosnian Serbs, so with a voter turnout of 64%, 98% of which voted in favor of the proposal. Bosnia and Herzegovina became an independent state on 3 March 1992.
While the first casualty of the war is debated, significant Serbian offensives began in March 1992 in Eastern and Northern Bosnia. Following a tense period of escalating tensions the opening shots in the incipient Bosnian conflict were fired when Serb paramilitary forces attacked Bosniak villages around Čapljina on 7 March 1992 and around Bosanski Brod and Goražde on 15 March. These minor attacks were followed by much more serious Serb artillery attacks on Neum on 19 March and on Bosanski Brod on 24 March. The killing of Suada Dilberović, a Bosniak civilian woman on 5 April 1992 by a sniper, while she was demonstrating in Sarajevo against the raising of barricades by Bosnian Serbs, is widely regarded as marking the start of warfare between the three major communities. Open warfare began in Sarajevo on 6 April.
International recognition of Bosnia and Herzegovina meant that the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) officially withdrew from the republic's territory, although their Bosnian Serb members merely joined the Army of Republika Srpska. Armed and equipped from JNA stockpiles in Bosnia, supported by volunteers, Republika Srpska's offensives in 1992 managed to place much of the country under its control. By 1993, when an armed conflict erupted between the Sarajevo government and the Croat statelet of Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, Herzeg-Bosnia, about 70% of the country was controlled by the Serbs.
In March 1994, the signing of the Washington Agreement, Washington accords between the Bosniak and ethnic-Croatian leaders led to the creation of a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. This, along with international outrage at Bosnian Genocide, Serb war crimes and atrocities (most notably the Srebrenica massacre of as many as 8,000 Bosniak males in July 1995) helped turn the tide of war. The signing of the Dayton Agreement in Paris by the presidents of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Alija Izetbegović), Croatia (Franjo Tuđman), and Yugoslavia (Slobodan Milošević) brought a halt to the fighting, roughly establishing the basic structure of the present-day state. The three years of war and bloodshed had left between 90,000 and 110,000 people killed and more than 2 million displaced.November. 21, 2005. Bosnian war "claimed 100,000 lives". Deutsche Presse-Agentur.
The first multi-party parliamentary elections held on 18 and 25 November 1990 led to a national assembly dominated by three ethnically-based parties, which had formed a loose coalition to oust the communists from power. Croatia and Slovenia's subsequent declarations of independence and the warfare that ensued placed Bosnia and Herzegovina and its three constituent peoples in an awkward position. A significant split soon developed on the issue of whether to stay with the Yugoslav federation (overwhelmingly favored among Serbs) or seek independence (overwhelmingly favored among Bosniaks and Croats). A declaration of sovereignty on 15 October 1991 was followed by a referendum for independence from Yugoslavia on 29 February and 1 March 1992. The referendum was boycotted by the great majority of Bosnian Serbs, so with a voter turnout of 64%, 98% of which voted in favor of the proposal. Bosnia and Herzegovina became an independent state on 3 March 1992.
While the first casualty of the war is debated, significant Serbian offensives began in March 1992 in Eastern and Northern Bosnia. Following a tense period of escalating tensions the opening shots in the incipient Bosnian conflict were fired when Serb paramilitary forces attacked Bosniak villages around Čapljina on 7 March 1992 and around Bosanski Brod and Goražde on 15 March. These minor attacks were followed by much more serious Serb artillery attacks on Neum on 19 March and on Bosanski Brod on 24 March. The killing of Suada Dilberović, a Bosniak civilian woman on 5 April 1992 by a sniper, while she was demonstrating in Sarajevo against the raising of barricades by Bosnian Serbs, is widely regarded as marking the start of warfare between the three major communities. Open warfare began in Sarajevo on 6 April.
International recognition of Bosnia and Herzegovina meant that the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) officially withdrew from the republic's territory, although their Bosnian Serb members merely joined the Army of Republika Srpska. Armed and equipped from JNA stockpiles in Bosnia, supported by volunteers, Republika Srpska's offensives in 1992 managed to place much of the country under its control. By 1993, when an armed conflict erupted between the Sarajevo government and the Croat statelet of Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, Herzeg-Bosnia, about 70% of the country was controlled by the Serbs.
In March 1994, the signing of the Washington Agreement, Washington accords between the Bosniak and ethnic-Croatian leaders led to the creation of a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. This, along with international outrage at Bosnian Genocide, Serb war crimes and atrocities (most notably the Srebrenica massacre of as many as 8,000 Bosniak males in July 1995) helped turn the tide of war. The signing of the Dayton Agreement in Paris by the presidents of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Alija Izetbegović), Croatia (Franjo Tuđman), and Yugoslavia (Slobodan Milošević) brought a halt to the fighting, roughly establishing the basic structure of the present-day state. The three years of war and bloodshed had left between 90,000 and 110,000 people killed and more than 2 million displaced.November. 21, 2005. Bosnian war "claimed 100,000 lives". Deutsche Presse-Agentur.

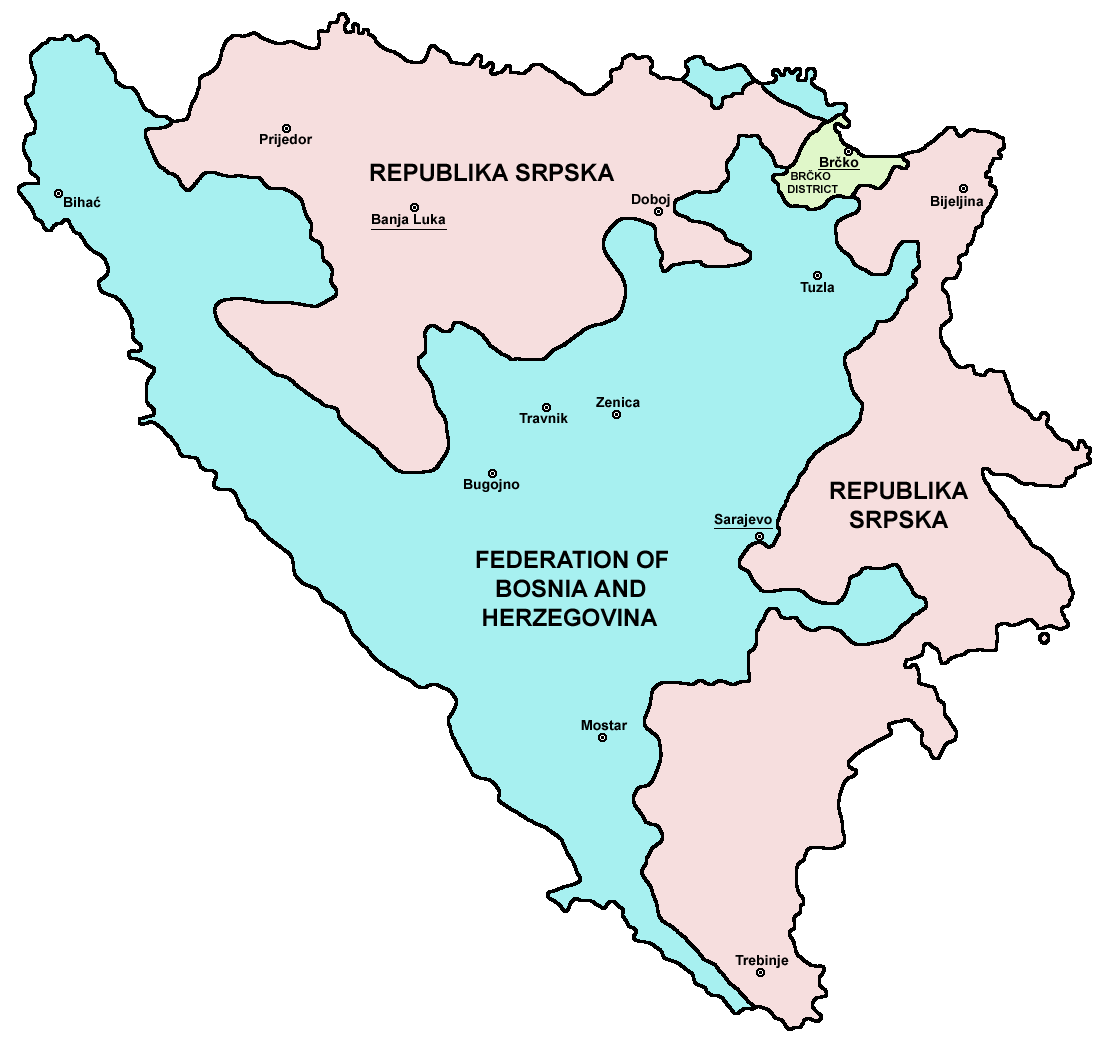 Since its 1992 independence and the 1995 Constitutional framework of the Dayton Agreement, Bosnia and Herzegovina has followed a path of state-building, while remaining under final international supervision through the figure of the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina. Bosnia and Herzegovina is a federation of two Entities - the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Republika Srpska, as well as the district of Brčko District, Brčko. Each of the Entities has its own Constitution and extensive legislative powers.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, potential candidate country for accession into the EU; the EU-BiH Stabilization and Association Agreement (SAA) was signed in 2008 and entered into force in June 2015. Bosnia and Herzegovina submitted its formal application for EU membership on 15 February 2016; the EU Council conditioned its consideration to further progress on the implementation of the Reform Agenda, as well as to the adaptation of the SAA to take into account the EU accession of Croatia, and to an agreement on a functioning Coordination Mechanism on EU matters. These conditions were fulfilled by the Summer 2016.
The accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to NATO is in the negotiation phase, and a Membership Action Plan was signed in April 2010. It requires Bosnia and Herzegovina to define the issue of property over defence assets before NATO may consider the next steps. Bosnian political parties have different attitudes towards NATO: while Bosniak and Bosnian Croat parties support it, Bosnian Serb parties are more cautious and, while not opposing it in principle, require it to be put to a referendum first.
Since its 1992 independence and the 1995 Constitutional framework of the Dayton Agreement, Bosnia and Herzegovina has followed a path of state-building, while remaining under final international supervision through the figure of the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina. Bosnia and Herzegovina is a federation of two Entities - the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Republika Srpska, as well as the district of Brčko District, Brčko. Each of the Entities has its own Constitution and extensive legislative powers.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, potential candidate country for accession into the EU; the EU-BiH Stabilization and Association Agreement (SAA) was signed in 2008 and entered into force in June 2015. Bosnia and Herzegovina submitted its formal application for EU membership on 15 February 2016; the EU Council conditioned its consideration to further progress on the implementation of the Reform Agenda, as well as to the adaptation of the SAA to take into account the EU accession of Croatia, and to an agreement on a functioning Coordination Mechanism on EU matters. These conditions were fulfilled by the Summer 2016.
The accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to NATO is in the negotiation phase, and a Membership Action Plan was signed in April 2010. It requires Bosnia and Herzegovina to define the issue of property over defence assets before NATO may consider the next steps. Bosnian political parties have different attitudes towards NATO: while Bosniak and Bosnian Croat parties support it, Bosnian Serb parties are more cautious and, while not opposing it in principle, require it to be put to a referendum first.
 On 4 February 2014, the protests against the government of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, one of the country's two entities, began in the northern town of Tuzla. Workers from several factories which were privatised and which have now gone bankrupt united to demand action over jobs, unpaid salaries and pensions. Soon protests spread to the rest of the Federation, with violent clashes reported in close to 20 towns, the biggest of which were Sarajevo, Zenica,
On 4 February 2014, the protests against the government of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, one of the country's two entities, began in the northern town of Tuzla. Workers from several factories which were privatised and which have now gone bankrupt united to demand action over jobs, unpaid salaries and pensions. Soon protests spread to the rest of the Federation, with violent clashes reported in close to 20 towns, the biggest of which were Sarajevo, Zenica,
excerpt
* * * * * * Matthew Parish, ''A Free City in the Balkans: Reconstructing a Divided Society in Bosnia'', London: I.B.Tauris, 2009. * * * * Ed Vulliamy, ''The War is Dead, Long Live the War: Bosnia: the Reckoning'' Bodley Head (London 19 April 2012)
Oriental Institute Sarajevo
Bosniak Institute Sarajevo
Bosnian Institute
About the Slavic, East European and Central Asian Collection at Yale University Library
''(Excellent web source)''
History of Bosnia and Herzegovina: Primary Documents
* [http://vlib.iue.it/history/europe/Bosnia/ WWW-VL: History: Bosnia & Herzegovina]
Timeline: Bosnia-Hercegovina at BBC News
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20000616071650/http://www.time.com/time/daily/bosnia/bosniatimeline.html TIME Daily short timeline of Bosnian conflict]
OHR ethnic maps of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia: a single country or an apple of discord?
Bosnian Institute, 12 May 2006 {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Bosnia And Herzegovina History of Bosnia and Herzegovina,
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
, sometimes referred to simply as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (al ...
on the Balkan Peninsula
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. It has had permanent settlement since the Neolithic Age
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
. By the early historical period it was inhabited by Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
and Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
. Christianity arrived in the 1st century, and by the 4th century the area became part of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
. Germanic tribes invaded soon after, followed by Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
in the 6th Century.
In 1136, Béla II of Hungary
Béla the Blind ( hu, Vak Béla; hr, Bela Slijepi; sk, Belo Slepý; 1109 – 13 February 1141) was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1131 to 1141. He was blinded along with his rebellious father Álmos on the order of Álmos's brother, ...
invaded Bosnia and created the title "Ban of Bosnia" as an honorary title for his son Ladislaus II of Hungary
Ladislaus II or Ladislas II ( hu, II. László, Croatian and Slovak: ''Ladislav II''; 113114 January 1163) was King of Hungary and Croatia between 1162 and 1163, having usurped the crown from his nephew, Stephen III.
Ladislaus received the ti ...
. During this time, Bosnia became virtually autonomous, and was eventually proclaimed a kingdom in 1377. The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
followed in 1463 and lasted over 400 years. They wrought great changes to the political and administrative system, introduced land reforms, and class and religious distinctions. A series of uprisings began in 1831, which culminated in the Herzegovinian rebellion, a widespread peasant uprising, in 1875. The conflict eventually forced the Ottomans to cede administration of the country to Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
through the Treaty of Berlin in 1878.
The establishment of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast Europe, Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 unt ...
in 1929 brought the redrawing of administrative regions into the Kingdom of Yugoslavia which purposely avoided all historical and ethnic lines, and removed any trace of Bosnian identity. The kingdom of Yugoslavia was conquered by Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
forces in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, and Bosnia was ceded to the Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia ( sh, Nezavisna Država Hrvatska, NDH; german: Unabhängiger Staat Kroatien; it, Stato indipendente di Croazia) was a World War II-era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. It was established in p ...
(NDH), which led to widespread persecution and genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
.
Following Axis defeat, Bosnia and Herzegovina achieved its current borders by becoming a federal unit within the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yu ...
, which was later renamed to the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in 1963. After the breakup of Yugoslavia
The breakup of Yugoslavia occurred as a result of a series of political upheavals and conflicts during the early 1990s. After a period of political and economic crisis in the 1980s, constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yu ...
, three years of war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
began in 1992 which caused around 100,000 deaths and 2 million refugees. It was then when the country became an independent state.
Prehistory and Roman Era
 Bosnia has been inhabited since
Bosnia has been inhabited since Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
times. In the late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, the Neolithic population was replaced by more warlike Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
tribes known as the Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
. Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
migrations in the 4th and 3rd century BCE displaced many Illyrian tribes from their former lands, but some Celtic and Illyrian tribes mixed.Malcolm, Noel (1994). Bosnia A Short History. New York University Press. . Concrete historical evidence for this period is scarce, but overall it appears that the region was populated by a number of different peoples speaking distinct languages.
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
had already arrived in the region by the end of the 2nd century, and numerous artefacts and objects from the time testify to this. Following events from the years 337 and 395 when the Empire split, Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
and Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
were included in the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
. The region was conquered by the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the larg ...
in 455, and further exchanged hands between the Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Al ...
and Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
in the years to follow.
Middle Ages
Early Bosnia
 By the 6th century, Emperor
By the 6th century, Emperor Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
had re-conquered the area and large parts of the former Western Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
for the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
with its capital in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
. The Slavs, a migratory people from southeastern Europe, were allied by the Eurasian Avars Eurasian Avars may refer to:
* Avars (Caucasus), a people from the North East Caucasus
** Avar Khanate, Caucasus
* Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples wer ...
in the 6th century, and together they invaded the Eastern Roman Empire in the 6th and 7th centuries, settling in what is now Bosnia and Herzegovina and the surrounding lands. More South Slavs came in a second wave, and according to some scholars were invited by Emperor Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was List of Byzantine emperors, Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exa ...
to drive the Avars from Dalmatia on the coast of the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
. Around this time the Eastern Romans speaking Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
were evolving into what was called in later centuries as the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, speaking the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(named for the ancient city of Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
, now the capital of Constantinople since the 330s, established by Emperor Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
).
Modern knowledge of Bosnia in the western Balkans during the Dark Ages is patchy. Upon the looter
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. ...
invasions
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
by the Avars and Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
from 6th-9th century, bringing Slavic languages, both probably gave way to feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
only with the might by the Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
penetrating into the region in the late 9th century (Bosnia probably originated as one such pre-feudal entity). It was also around this time that the Bosnians
Bosnians (Bosnian language: / ; / , / ) are people identified with the country of Bosnia and Herzegovina or with the region of Bosnia. As a common demonym, the term ''Bosnians'' refers to all inhabitants/citizens of the country, regardless ...
were Christianized. Bosnia, due to its geographic position and terrain, was probably one of the last areas to go through this process, which presumably originated from the urban centers along the Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
n coast.
In addition to the Slavic-speaking population, a good number of romanized people remained in south Bosnia by the year 1000. Speaking a Balkan Romance language (related to Romanian), and having retreated into mountainous areas and adopted a pastoralist way of life, they became known as ''Vlachs''. With time they assimilated, though maintaining specific customs, and the word Vlach came to indicate any shepherd. Being well-versed with horse breeding, Vlachs came to dominate trade and caravan from coastal merchant town towards the interior, growing prosperous and coming to dominate entire regions of Hum
Hum may refer to:
Science
* Hum (sound), a sound produced with closed lips, or by insects, or other periodic motion
* Mains hum, an electric or electromagnetic phenomenon
* The Hum, an acoustic phenomenon
* Venous hum, a physiological sensation
...
, thus merging in Bosnia's medieval feudal society.
Banate of Bosnia
 It is only from the 9th century that Frankish and Byzantine sources begin to mention early Slavic polities in the region. In this regard, the earliest widely acknowledged reference to Bosnia dates from the 10th century '' De Administrando Imperio'' written by Byzantine emperor
It is only from the 9th century that Frankish and Byzantine sources begin to mention early Slavic polities in the region. In this regard, the earliest widely acknowledged reference to Bosnia dates from the 10th century '' De Administrando Imperio'' written by Byzantine emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Ka ...
, during which period Bosnia is part of the Serbian state of Časlav, after whose death in battle in about 960, much of Bosnia finds itself briefly incorporated into the Croatian state of Krešimir II. Shortly thereafter, in 997, Samuel of Bulgaria
Samuel (also Samuil; bg, Самуил, ; mk, Самоил/Самуил, ; Old Church Slavonic: Самоилъ; died October 6, 1014) was the Tsar (''Emperor'') of the First Bulgarian Empire from 997 to 6 October 1014. From 977 to 997, he was a ...
marches through Bosnia and asserts his over-lordship in parts of it, however, only to be defeated by the Byzantine Empire in 1018 which annexes Bulgaria and asserts its suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
in Bosnia. This lasted until later in the century when some parts of Bosnia are briefly incorporated into Croatia and others into Duklja
Duklja ( sh-Cyrl, Дукља; el, Διόκλεια, Diokleia; la, Dioclea) was a medieval South Slavic state which roughly encompassed the territories of modern-day southeastern Montenegro, from the Bay of Kotor in the west to the Bojana Ri ...
from which the latter Bosnia appears to have seceded in about 1101, upon which Bosnia's bans tried to rule for themselves. However, they all too often found themselves in a tug-of-war between Hungary and the Byzantine Empire. In the year of 1137, Hungary annexes most of Bosnia, then briefly losing her in 1167 to the Byzantine Empire before regaining her in 1180. Thus, prior to 1180 and the reign of Ban Kulin parts of Bosnia were briefly found in Serbian or Croatian units, but neither neighbor had held the Bosnians long enough to acquire their loyalty or to impose any serious claim to Bosnia.
The first recorded Ban (viceroy) was Ban Borić }
References
Sources and further reading
;Books
*
*
*
*
*
*
;Journals
*
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ban Boric
Bans of Bosnia
12th-century rulers in Europe
12th-century Hungarian people
12th-century Bosnian people
Borićević dynast ...
, vassal to the Hungarian king. However, he was deposed when he backed the loser in a succession crisis over the Hungarian throne. In 1167, Byzantium reconquered Bosnia and eventually emplaced their own vassal as Ban – the native Ban Kulin ( r. 1180–1204). However, this vassalage was largely nominal, and Bosnia had for all practical purposes made itself into an independent state under Kulin. Ban Kulin presided over nearly three decades of peace and stability during which he strengthened the country's economy through treaties with Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik (), historically known as Ragusa (; see notes on naming), is a city on the Adriatic Sea in the region of Dalmatia, in the southeastern semi-exclave of Croatia. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterran ...
and Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
. His rule also marked the start of a controversy with the Bosnian Church
The Bosnian Church ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Crkva bosanska, Црква Босанска) was a Christian church in medieval Bosnia and Herzegovina that was independent of and considered heretical by both the Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox ...
, an indigenous Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
sect considered heretical by both the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
churches. In response to Hungarian attempts to use church politics regarding the issue as a way to reclaim sovereignty over Bosnia, Kulin held a council of local church leaders to renounce the heresy in 1203. Despite this, Hungarian ambitions remained unchanged long after Kulin's death in 1204, waning only after an unsuccessful invasion in 1254, which also fostered the schism of the Bosnian Church
The Bosnian Church ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Crkva bosanska, Црква Босанска) was a Christian church in medieval Bosnia and Herzegovina that was independent of and considered heretical by both the Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox ...
.
Kingdom of Bosnia
 Bosnian history from then until the early 14th century was marked by the power struggle between the Šubić and Kotromanić families. This conflict came to an end in 1322, when Stjepan II Kotromanić became ban. By the time of his death in 1353, he had succeeded in annexing territories to the north and west, as well as Zahumlje and parts of Dalmatia. He was succeeded by his nephew Tvrtko who, following a prolonged struggle with nobility and inter-family strife, gained full control of the country in 1367. Under Tvrtko, Bosnia grew in both size and power, finally becoming an independent kingdom in 1377. Following his death in 1391 however, Bosnia fell into a long period of decline. The
Bosnian history from then until the early 14th century was marked by the power struggle between the Šubić and Kotromanić families. This conflict came to an end in 1322, when Stjepan II Kotromanić became ban. By the time of his death in 1353, he had succeeded in annexing territories to the north and west, as well as Zahumlje and parts of Dalmatia. He was succeeded by his nephew Tvrtko who, following a prolonged struggle with nobility and inter-family strife, gained full control of the country in 1367. Under Tvrtko, Bosnia grew in both size and power, finally becoming an independent kingdom in 1377. Following his death in 1391 however, Bosnia fell into a long period of decline. The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
had already started its conquest of Europe and posed a major threat to the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
throughout the first half of the 15th century. Finally, after decades of political and social instability, Bosnia officially fell in 1463, while resistance was active and fierce for a few more centuries. Southern regions of Bosnia, nowadays known as "Herzegovina
Herzegovina ( or ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Hercegovina, separator=" / ", Херцеговина, ) is the southern and smaller of two main geographical region of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Bosnia. It has never had strictly defined geogra ...
" would follow in 1483, with a Hungarian-backed reinstated "Bosnian Kingdom" being the last to succumb in 1527.
Ottoman Era (1463–1878)

 The Ottoman conquest of Bosnia marked a new era in the country's history and introduced tremendous changes in the political and cultural landscape of the region. Although the kingdom had been crushed and its high nobility executed, the Ottomans nonetheless allowed for the preservation of Bosnia's identity by incorporating it as an integral province of the Ottoman Empire with its historical name and territorial integrity - a unique case among subjugated states in the Balkans.Riedlmayer, Andras (1993)
The Ottoman conquest of Bosnia marked a new era in the country's history and introduced tremendous changes in the political and cultural landscape of the region. Although the kingdom had been crushed and its high nobility executed, the Ottomans nonetheless allowed for the preservation of Bosnia's identity by incorporating it as an integral province of the Ottoman Empire with its historical name and territorial integrity - a unique case among subjugated states in the Balkans.Riedlmayer, Andras (1993)A Brief History of Bosnia-Herzegovina
. The Bosnian Manuscript Ingathering Project. Within this
sandžak
Sandžak (; sh, / , ; sq, Sanxhaku; ota, سنجاق, Sancak), also known as Sanjak, is a historical geo-political region in Serbia and Montenegro. The name Sandžak derives from the Sanjak of Novi Pazar, a former Ottoman administrative dis ...
(and eventual vilayet
A vilayet ( ota, , "province"), also known by various other names, was a first-order administrative division of the later Ottoman Empire. It was introduced in the Vilayet Law of 21 January 1867, part of the Tanzimat reform movement initiated ...
) of Bosnia, the Ottomans introduced a number of key changes in the territory's socio-political administration; including a new landholding system, a reorganization of administrative units, and a complex system of social differentiation by class and religious affiliation.
The four centuries of Ottoman rule also had a drastic impact on Bosnia's population make-up, which changed several times as a result of the empire's conquests, frequent wars with European powers, migrations, and epidemics. A native Slavic-speaking Muslim community emerged and eventually became the largest ethno-religious groupBy the early 1600s, approximately 450,000 Muslims (67%), 150,000 Catholics (22%) and 75,000 Orthodox Christians (11%) lived Bosnia (Malcolm, 1995) (mainly as a result of a gradually rising number of conversions to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
),Imamović, Mustafa (1996). Historija Bošnjaka. Sarajevo: BZK Preporod. while a significant number of Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefar ...
arrived following their expulsion
Expulsion or expelled may refer to:
General
* Deportation
* Ejection (sports)
* Eviction
* Exile
* Expeller pressing
* Expulsion (education)
* Expulsion from the United States Congress
* Extradition
* Forced migration
* Ostracism
* Persona non ...
from Spain in the late 15th century. The Bosnian Christian communities also experienced major changes. The Bosnian Franciscans
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
(and the Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
population as a whole) were protected by official imperial decree, although on the ground these guarantees were often disregarded and their numbers dwindled. The Orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pa ...
community in Bosnia, initially confined to Herzegovina and southeastern Bosnia, spread throughout the country during this period and went on to experience relative prosperity until the 19th century. Meanwhile, the native schismatic Bosnian Church
The Bosnian Church ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Crkva bosanska, Црква Босанска) was a Christian church in medieval Bosnia and Herzegovina that was independent of and considered heretical by both the Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox ...
disappeared altogether.
As the Ottoman Empire thrived and expanded into Central Europe, Bosnia was relieved of the pressures of being a frontier province and experienced a prolonged period of general welfare and prosperity. A number of cities, such as Sarajevo and Mostar
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline = Mostar (collage image).jpg
, image_caption = From top, left to right: A panoramic view of the heritage town site and the Neretva river from Lučki Bridge, Koski Mehmed Pasha ...
, were established and grew into major regional centers of trade and urban culture. Within these cities, various Sultans and governors financed the construction of many important works of Bosnian architecture
The architecture of Bosnia and Herzegovina is largely influenced by four major periods, when political and social changes determined the creation of distinct cultural and architectural habits of the region.
Medieval period
The medieval period in ...
(such as the Stari most
Stari Most ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Stari most, Стари мост, Old Bridge), also known as Mostar Bridge, is a rebuilt 16th-century Ottoman bridge in the city of Mostar in Bosnia and Herzegovina that crosses the river Neretva and connects the two ...
and Gazi Husrev-beg's Mosque
Gazi Husrev-beg Mosque (, ) is a mosque in the city of Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Built in the 16th century, it is the largest historical mosque in Bosnia and Herzegovina and one of the most representative Ottoman structures in the Balkan ...
). Furthermore, numerous Bosnians played influential roles in the Ottoman Empire's cultural and political history during this time. Bosnian soldiers formed a large component of the Ottoman ranks in the battles of Mohács
Mohács (; Croatian and Bunjevac: ''Mohač''; german: Mohatsch; sr, Мохач; tr, Mohaç) is a town in Baranya County, Hungary, on the right bank of the Danube.
Etymology
The name probably comes from the Slavic ''*Mъchačь'',''*Mocháč'': ...
and Krbava field, two decisive military victories, while numerous other Bosnians rose through the ranks of the Ottoman military bureaucracy to occupy the highest positions of power in the Empire, including admirals, generals, and grand viziers. Many Bosnians also made a lasting impression on Ottoman culture, emerging as mystics, scholars, and celebrated poets in the Turkish, Arabic, and Persian languages.
By the late 17th century, however, the Ottoman Empire's military misfortunes caught up with the country, and the conclusion of the Great Turkish War with the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the ...
in 1699 once again made Bosnia the empire's westernmost province. But they allowed some of the Bosnian tribes to immigrate into the Arabian countries ( Palestine, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
). The following hundred years were marked by further military failures, numerous revolts within Bosnia, and several outbursts of plague.
According to an Ottoman Muslim account of the Austro-Russian–Turkish War (1735–39) translated into English by C. Fraser, Bosnian Muslim women fought in battle since they "acquired the courage of heroes" against the Austrian Germans at the siege of Osterwitch-atyk (Östroviç-i âtık) fortress. Bosnian Muslim women and men were among the casualties during the Battle of Osterwitchatyk. Bosnian Muslim women fought in the defense of the fortress of Būzin (Büzin). Women and men resisted the Austrians at the Chetin (Çetin) Fortress. The women of the Bosnians were deemed to be militaristic according to non-Ottoman records of the war between the Ottomans and Austrians and they played a role in the Bosnian success in battle against the Austrian attackers. Yeni Pazar, Izvornik, Östroviç-i âtık, Çetin, Būzin, Gradişka, and Banaluka were struck by the Austrians. A French account described the bravery in battle of Bosnian Muslim women who fought in the war.
The Porte
Porte may refer to:
*Sublime Porte, the central government of the Ottoman empire
*Porte, Piedmont, a municipality in the Piedmont region of Italy
*John Cyril Porte, British/Irish aviator
*Richie Porte, Australian professional cyclist who competes ...
's efforts at modernizing the Ottoman state were met with great hostility in Bosnia, where local aristocrats stood to lose much through the proposed reforms. This, combined with frustrations over political concessions to nascent Christian states in the east, culminated in a famous (albeit ultimately unsuccessful) revolt by Husein Gradaščević
Husein Gradaščević (''Husein-kapetan'') (31 August 1802 – 17 August 1834) was a Bosnian military commander who later led a rebellion against the Ottoman government, seeking autonomy for Bosnia. Born into a Bosnian noble family, Gradaš� ...
in 1831. Related rebellions would be extinguished by 1850. A renewed effort at Ottoman reforms occurred in the 1860s under the leadership of the governor Topal Şerif Osman occurred, as he founded a provincial printing press in 1866 that published in both Ottoman Turkish and Bosnian. Later, agrarian unrest eventually sparked the Herzegovinian rebellion, a widespread peasant uprising, in 1875. The conflict rapidly spread and came to involve several Balkan states and Great Powers, which eventually forced the Ottomans to cede administration of the country to Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
through the Treaty of Berlin in 1878. While violent revolt prompted many to disparage Ottoman rule, it was in fact Ottoman reforms in the realm of cultural production and education that "created the conditions for greater intellectual production that continued during the Habsburg era."
Occupation by Austria-Hungary (1878–1918)
 Though an
Though an Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
military force quickly subjugated initial armed resistance upon take-over, tensions remained in certain parts of the country (particularly Herzegovina) and a mass emigration of predominantly Muslim dissidents occurred. However, a state of relative stability was reached soon enough and Austro-Hungarian authorities were able to embark on a number of social and administrative reforms which intended to make Bosnia and Herzegovina into a "model colony
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the ''metropole, metropolit ...
". With the aim of establishing the province as a stable political model that would help dissipate rising South Slav nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
, Habsburg rule did much to codify laws, to introduce new political practices, and generally to provide for modernization. The Habsburgs took special care to integrate local Muslims into the fabric of empire, continuing, for example, to publish a provincial yearbook—much like the Ottomans—in Turkish for over a decade after the end of Ottoman rule. Many local officials moreover stayed the same, with the Mehmed-Beg Kapetanović Ljubušak, for example, remaining the mayor of Sarajevo under both polities and, moreover, obtaining the very same level of honor from both the Ottomans and the Habsburgs, with a Third Class Order of Mecidiye and an Order of the Iron Crown Third Class, respectively. All of this amounted to what one historian has called an "almost seamless transition from one empire to another."
Although successful economically, Austro-Hungarian policy - which focused on advocating the ideal of a pluralist and multi-confessional Bosnian nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective identity of a group of people understood as defined by those ...
(largely favored by the Muslims) - failed to curb the rising tides of nationalism. The concept of Croat and Serb nationhood had already spread to Bosnia and Herzegovina's Catholics and Orthodox communities from neighboring Croatia and Serbia in the mid 19th century, and was too well-entrenched to allow for the widespread acceptance of a parallel idea of Bosnian nationhood. By the latter half of the 1910s, nationalism was an integral factor of Bosnian politics, with national political parties corresponding to the three groups dominating elections.
The idea of a unified South Slavic state (typically expected to be spearheaded by independent Serbia) became a popular political ideology in the region at this time, including in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The Austro-Hungarian government's decision to formally annex Bosnia-Herzegovina in 1908 (the Bosnian Crisis) added to a sense of urgency among these nationalists. The political tensions caused by all this culminated on 28 June 1914, when a Young Bosnia
Young Bosnia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Mlada Bosna, Млада Босна) was a separatist and revolutionary movement active in the Condominium of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Austria-Hungary before World War I. Its members were predominantly ...
revolutionary named Gavrilo Princip
Gavrilo Princip ( sr-Cyrl, Гаврило Принцип, ; 25 July 189428 April 1918) was a Bosnian Serb student who assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria and his wife Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, in Sarajevo on 28 June 1914.
Pr ...
assassinated the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand Carl Ludwig Joseph Maria of Austria, (18 December 1863 – 28 June 1914) was the heir presumptive to the throne of Austria-Hungary. His assassination in Sarajevo was the most immediate cause of World War I.
F ...
, in Sarajevo. The event set off a chain of events that led to the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. Although 10% of the Bosniak population died serving in the armies or being killed by the various warring states, Bosnia and Herzegovina itself managed to escape the conflict relatively unscathed.
Kingdom of Yugoslavia (1918–41)
 Following World War I, Bosnia was incorporated into the South Slav
Following World War I, Bosnia was incorporated into the South Slav kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
(soon renamed Yugoslavia).
Political life in Bosnia at this time was marked by two major trends: social and economic unrest over the Agrarian Reform of 1918–19 manifested through mass colonization and property confiscation; also formation of several political parties that frequently changed coalitions and alliances with parties in other Yugoslav regions. The dominant ideological conflict of the Yugoslav state, between Croatian regionalism and Serbian centralization, was approached differently by Bosnia's major ethnic groups and was dependent on the overall political atmosphere. Although the initial split of the country into 33 oblast
An oblast (; ; Cyrillic (in most languages, including Russian and Ukrainian): , Bulgarian: ) is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Ukraine, as well as the Soviet Union and the Kingdom of ...
s erased the presence of traditional geographic entities from the map, the efforts of Bosnian politicians such as Mehmed Spaho
Mehmed Spaho (13 March 1883 – 29 June 1939) was a Bosnian politician and leader of the Yugoslav Muslim Organization. He was the first Bosnian Muslim politician in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. Spaho was described as the "undispu ...
ensured that the six oblasts carved up from Bosnia and Herzegovina corresponded to the six sanjaks from Ottoman times and, thus, matched the country's traditional boundary as a whole.
The establishment of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929, however, brought the redrawing of administrative regions into banates that purposely avoided all historical and ethnic lines, removing any trace of a Bosnian entity. Serbo-Croat tensions over the structuring of the Yugoslav state continued, with the concept of a separate Bosnian division receiving little or no consideration. The famous Cvetković-Maček agreement that created the Croatian banate in 1939 encouraged what was essentially a partition of Bosnia between Croatia and Serbia. However, outside political circumstances forced Yugoslav politicians to shift their attention to the rising threat posed by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
's Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. Following a period that saw attempts at appeasement
Appeasement in an international context is a diplomatic policy of making political, material, or territorial concessions to an aggressive power in order to avoid conflict. The term is most often applied to the foreign policy of the UK governm ...
, the joining of the Tripartite Pact
The Tripartite Pact, also known as the Berlin Pact, was an agreement between Germany, Italy, and Japan signed in Berlin on 27 September 1940 by, respectively, Joachim von Ribbentrop, Galeazzo Ciano and Saburō Kurusu. It was a defensive milit ...
, and a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
, Yugoslavia was finally invaded by Germany on 6 April 1941.
World War II (1941–1945)

Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
forces in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, all of Bosnia was ceded to the Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia ( sh, Nezavisna Država Hrvatska, NDH; german: Unabhängiger Staat Kroatien; it, Stato indipendente di Croazia) was a World War II-era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. It was established in p ...
(NDH). The NDH rule over Bosnia led to widespread persecution and genocide. The Jewish population was nearly exterminated. Hundreds of thousands of Serbs died either in Ustaše concentration camps or in widespread mass killings by Ustaše
The Ustaše (), also known by anglicised versions Ustasha or Ustashe, was a Croats, Croatian Fascism, fascist and ultranationalism, ultranationalist organization active, as one organization, between 1929 and 1945, formally known as the Ustaš ...
militia. Many Serbs themselves took up arms and joined the Chetniks, a Serb nationalist movement with the aim of establishing an ethnically homogeneous 'Greater Serbia
The term Greater Serbia or Great Serbia ( sr, Велика Србија, Velika Srbija) describes the Serbian nationalist and irredentist ideology of the creation of a Serb state which would incorporate all regions of traditional significance to S ...
n' state.
The Chetniks were responsible for widespread persecution and murder of non-Serbs and communist sympathizers, with the Muslim population of Bosnia, Herzegovina and Sandžak
Sandžak (; sh, / , ; sq, Sanxhaku; ota, سنجاق, Sancak), also known as Sanjak, is a historical geo-political region in Serbia and Montenegro. The name Sandžak derives from the Sanjak of Novi Pazar, a former Ottoman administrative dis ...
being a primary target. Once captured, Muslim villages were systematically massacred by the Chetniks. The total estimate of Muslims killed by Chetniks is between 80,000 and 100,000, most likely about 86,000 or 6.7 percent of their population (8.1 percent in Bosnia and Herzegovina alone). Several Bosnian Muslim paramilitary units joined the NDH forces to counter their own persecution in the hands of the Serbs in Bosnia. On 12 October 1941 a group of 108 notable Muslim citizens of Sarajevo signed the Resolution of Sarajevo Muslims The Resolution of Sarajevo Muslims or Muslim Resolution of 1941 ( sh, Sarajevska rezolucija/Сарајевска резолуција) was one of the Resolutions of Muslims from Bosnia and Herzegovina (then parts of the Independent State of Croati ...
by which they condemned the persecution of Serbs
Anti-Serb sentiment or Serbophobia ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, србофобија, srbofobija, separator=" / ") is a generally negative view of Serbs as an ethnic group. Historically it has been a basis for the persecution of ethnic Serbs.
A distincti ...
organized by Ustaše, made distinction between Muslims who participated in such persecutions and the wider Muslim population, presented information about the persecutions of Muslims by Serbs and requested security for all citizens of the country, regardless of their identity. According to the US Holocaust Museum, 320,000-340,000 ethnic Serbs were murdered. According to the Yad Vashem Holocaust Museum and Research Center, "More than 500,000 Serbs were murdered in horribly sadistic ways, 250,000 were expelled, and another 200,000 were forced to convert" during WWII in the Independent State of Croatia (modern day Croatia and Bosnia).
Starting in 1941, Yugoslav communists under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito organized their own multi-ethnic resistance group, the Partisans, who fought against Axis, Ustaše, and Chetnik forces. They too, committed numerous atrocities, mainly against political opponents of all ethnicities. Some Bosnian Muslims
The Bosniaks ( bs, Bošnjaci, Cyrillic: Бошњаци, ; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia, which is today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, who share a common Bosnian ancestry, cu ...
joined the Waffen-SS and the 13th Waffen Mountain Division of the SS Handschar (1st Croatian), SS "Handschar" division, an SS division of the Nazis that pledged allegiance to both Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
and NDH leader, Ante Pavelić. The division was the first SS division which was constituted of non-Germans. On 25 November 1943 the Anti-Fascist Council of National Liberation of Yugoslavia with Tito at its helm held a founding conference in Jajce where Bosnia and Herzegovina was reestablished as a republic within the Yugoslavian federation in its Ottoman borders. Military success eventually prompted the Allies to support the Partisans. On 6 April 1945 Sarajevo was captured by the Partisans. The end of the war resulted in the establishment of the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia, with the constitution of 1946 officially making Bosnia and Herzegovina one of six constituent republics in the new state.
Socialist Yugoslavia (1945–1992)
Branko Mikulic - socialist emperor manqué
. BH Dani Their efforts proved key during the turbulent period following Tito's death in 1980, and are today considered some of the early steps towards Bosnian independence. However, the republic could not escape the increasingly nationalistic climate of the time unscathed.
Independence and Bosnian War (1992–1995)
 The first multi-party parliamentary elections held on 18 and 25 November 1990 led to a national assembly dominated by three ethnically-based parties, which had formed a loose coalition to oust the communists from power. Croatia and Slovenia's subsequent declarations of independence and the warfare that ensued placed Bosnia and Herzegovina and its three constituent peoples in an awkward position. A significant split soon developed on the issue of whether to stay with the Yugoslav federation (overwhelmingly favored among Serbs) or seek independence (overwhelmingly favored among Bosniaks and Croats). A declaration of sovereignty on 15 October 1991 was followed by a referendum for independence from Yugoslavia on 29 February and 1 March 1992. The referendum was boycotted by the great majority of Bosnian Serbs, so with a voter turnout of 64%, 98% of which voted in favor of the proposal. Bosnia and Herzegovina became an independent state on 3 March 1992.
While the first casualty of the war is debated, significant Serbian offensives began in March 1992 in Eastern and Northern Bosnia. Following a tense period of escalating tensions the opening shots in the incipient Bosnian conflict were fired when Serb paramilitary forces attacked Bosniak villages around Čapljina on 7 March 1992 and around Bosanski Brod and Goražde on 15 March. These minor attacks were followed by much more serious Serb artillery attacks on Neum on 19 March and on Bosanski Brod on 24 March. The killing of Suada Dilberović, a Bosniak civilian woman on 5 April 1992 by a sniper, while she was demonstrating in Sarajevo against the raising of barricades by Bosnian Serbs, is widely regarded as marking the start of warfare between the three major communities. Open warfare began in Sarajevo on 6 April.
International recognition of Bosnia and Herzegovina meant that the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) officially withdrew from the republic's territory, although their Bosnian Serb members merely joined the Army of Republika Srpska. Armed and equipped from JNA stockpiles in Bosnia, supported by volunteers, Republika Srpska's offensives in 1992 managed to place much of the country under its control. By 1993, when an armed conflict erupted between the Sarajevo government and the Croat statelet of Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, Herzeg-Bosnia, about 70% of the country was controlled by the Serbs.
In March 1994, the signing of the Washington Agreement, Washington accords between the Bosniak and ethnic-Croatian leaders led to the creation of a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. This, along with international outrage at Bosnian Genocide, Serb war crimes and atrocities (most notably the Srebrenica massacre of as many as 8,000 Bosniak males in July 1995) helped turn the tide of war. The signing of the Dayton Agreement in Paris by the presidents of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Alija Izetbegović), Croatia (Franjo Tuđman), and Yugoslavia (Slobodan Milošević) brought a halt to the fighting, roughly establishing the basic structure of the present-day state. The three years of war and bloodshed had left between 90,000 and 110,000 people killed and more than 2 million displaced.November. 21, 2005. Bosnian war "claimed 100,000 lives". Deutsche Presse-Agentur.
The first multi-party parliamentary elections held on 18 and 25 November 1990 led to a national assembly dominated by three ethnically-based parties, which had formed a loose coalition to oust the communists from power. Croatia and Slovenia's subsequent declarations of independence and the warfare that ensued placed Bosnia and Herzegovina and its three constituent peoples in an awkward position. A significant split soon developed on the issue of whether to stay with the Yugoslav federation (overwhelmingly favored among Serbs) or seek independence (overwhelmingly favored among Bosniaks and Croats). A declaration of sovereignty on 15 October 1991 was followed by a referendum for independence from Yugoslavia on 29 February and 1 March 1992. The referendum was boycotted by the great majority of Bosnian Serbs, so with a voter turnout of 64%, 98% of which voted in favor of the proposal. Bosnia and Herzegovina became an independent state on 3 March 1992.
While the first casualty of the war is debated, significant Serbian offensives began in March 1992 in Eastern and Northern Bosnia. Following a tense period of escalating tensions the opening shots in the incipient Bosnian conflict were fired when Serb paramilitary forces attacked Bosniak villages around Čapljina on 7 March 1992 and around Bosanski Brod and Goražde on 15 March. These minor attacks were followed by much more serious Serb artillery attacks on Neum on 19 March and on Bosanski Brod on 24 March. The killing of Suada Dilberović, a Bosniak civilian woman on 5 April 1992 by a sniper, while she was demonstrating in Sarajevo against the raising of barricades by Bosnian Serbs, is widely regarded as marking the start of warfare between the three major communities. Open warfare began in Sarajevo on 6 April.
International recognition of Bosnia and Herzegovina meant that the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) officially withdrew from the republic's territory, although their Bosnian Serb members merely joined the Army of Republika Srpska. Armed and equipped from JNA stockpiles in Bosnia, supported by volunteers, Republika Srpska's offensives in 1992 managed to place much of the country under its control. By 1993, when an armed conflict erupted between the Sarajevo government and the Croat statelet of Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, Herzeg-Bosnia, about 70% of the country was controlled by the Serbs.
In March 1994, the signing of the Washington Agreement, Washington accords between the Bosniak and ethnic-Croatian leaders led to the creation of a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. This, along with international outrage at Bosnian Genocide, Serb war crimes and atrocities (most notably the Srebrenica massacre of as many as 8,000 Bosniak males in July 1995) helped turn the tide of war. The signing of the Dayton Agreement in Paris by the presidents of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Alija Izetbegović), Croatia (Franjo Tuđman), and Yugoslavia (Slobodan Milošević) brought a halt to the fighting, roughly establishing the basic structure of the present-day state. The three years of war and bloodshed had left between 90,000 and 110,000 people killed and more than 2 million displaced.November. 21, 2005. Bosnian war "claimed 100,000 lives". Deutsche Presse-Agentur.
Post-war Bosnia and Herzegovina (1995–present)
 Since its 1992 independence and the 1995 Constitutional framework of the Dayton Agreement, Bosnia and Herzegovina has followed a path of state-building, while remaining under final international supervision through the figure of the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina. Bosnia and Herzegovina is a federation of two Entities - the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Republika Srpska, as well as the district of Brčko District, Brčko. Each of the Entities has its own Constitution and extensive legislative powers.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, potential candidate country for accession into the EU; the EU-BiH Stabilization and Association Agreement (SAA) was signed in 2008 and entered into force in June 2015. Bosnia and Herzegovina submitted its formal application for EU membership on 15 February 2016; the EU Council conditioned its consideration to further progress on the implementation of the Reform Agenda, as well as to the adaptation of the SAA to take into account the EU accession of Croatia, and to an agreement on a functioning Coordination Mechanism on EU matters. These conditions were fulfilled by the Summer 2016.
The accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to NATO is in the negotiation phase, and a Membership Action Plan was signed in April 2010. It requires Bosnia and Herzegovina to define the issue of property over defence assets before NATO may consider the next steps. Bosnian political parties have different attitudes towards NATO: while Bosniak and Bosnian Croat parties support it, Bosnian Serb parties are more cautious and, while not opposing it in principle, require it to be put to a referendum first.
Since its 1992 independence and the 1995 Constitutional framework of the Dayton Agreement, Bosnia and Herzegovina has followed a path of state-building, while remaining under final international supervision through the figure of the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina. Bosnia and Herzegovina is a federation of two Entities - the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Republika Srpska, as well as the district of Brčko District, Brčko. Each of the Entities has its own Constitution and extensive legislative powers.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, potential candidate country for accession into the EU; the EU-BiH Stabilization and Association Agreement (SAA) was signed in 2008 and entered into force in June 2015. Bosnia and Herzegovina submitted its formal application for EU membership on 15 February 2016; the EU Council conditioned its consideration to further progress on the implementation of the Reform Agenda, as well as to the adaptation of the SAA to take into account the EU accession of Croatia, and to an agreement on a functioning Coordination Mechanism on EU matters. These conditions were fulfilled by the Summer 2016.
The accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to NATO is in the negotiation phase, and a Membership Action Plan was signed in April 2010. It requires Bosnia and Herzegovina to define the issue of property over defence assets before NATO may consider the next steps. Bosnian political parties have different attitudes towards NATO: while Bosniak and Bosnian Croat parties support it, Bosnian Serb parties are more cautious and, while not opposing it in principle, require it to be put to a referendum first.
 On 4 February 2014, the protests against the government of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, one of the country's two entities, began in the northern town of Tuzla. Workers from several factories which were privatised and which have now gone bankrupt united to demand action over jobs, unpaid salaries and pensions. Soon protests spread to the rest of the Federation, with violent clashes reported in close to 20 towns, the biggest of which were Sarajevo, Zenica,
On 4 February 2014, the protests against the government of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, one of the country's two entities, began in the northern town of Tuzla. Workers from several factories which were privatised and which have now gone bankrupt united to demand action over jobs, unpaid salaries and pensions. Soon protests spread to the rest of the Federation, with violent clashes reported in close to 20 towns, the biggest of which were Sarajevo, Zenica, Mostar
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline = Mostar (collage image).jpg
, image_caption = From top, left to right: A panoramic view of the heritage town site and the Neretva river from Lučki Bridge, Koski Mehmed Pasha ...
, Bihać, Brčko and Tuzla. The Bosnian news media reported that hundreds of people had been injured during the protests, including dozens of police officers, with bursts of violence in Sarajevo, in the northern city of Tuzla, in Mostar in the south, and in Zenica in central Bosnia. The same level of unrest or activism did not occur in the Republika Srpska, but hundreds of people also gathered in support of protests in the town of Banja Luka against its separate government.
The protests marked the largest outbreak of public anger over high unemployment and two decades of political inertia in the country since the end of the Bosnian War in 1995.
See also
* League of Communists of Yugoslavia * President of Bosnia and Herzegovina * List of prime ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina * List of heads of state of Yugoslavia * List of prime ministers of Yugoslavia * Politics of Bosnia and Herzegovina * Republika Srpska * 2014 unrest in Bosnia and Herzegovina * 2014 Bosnia and Herzegovina floodsReferences
Notes
Further reading
* Allcock, John B., Marko Milivojevic, et al. ''Conflict in the Former Yugoslavia: An Encyclopedia'' (1998) * * Hall, Richard C. ''War in the Balkans: An Encyclopedic History from the Fall of the Ottoman Empire to the Breakup of Yugoslavia'' (2014excerpt
* * * * * * Matthew Parish, ''A Free City in the Balkans: Reconstructing a Divided Society in Bosnia'', London: I.B.Tauris, 2009. * * * * Ed Vulliamy, ''The War is Dead, Long Live the War: Bosnia: the Reckoning'' Bodley Head (London 19 April 2012)
External links
General history
Oriental Institute Sarajevo
Bosniak Institute Sarajevo
Bosnian Institute
About the Slavic, East European and Central Asian Collection at Yale University Library
''(Excellent web source)''
History of Bosnia and Herzegovina: Primary Documents
* [http://vlib.iue.it/history/europe/Bosnia/ WWW-VL: History: Bosnia & Herzegovina]
Timeline: Bosnia-Hercegovina at BBC News
Bosnian War and post-war history
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20000616071650/http://www.time.com/time/daily/bosnia/bosniatimeline.html TIME Daily short timeline of Bosnian conflict]
OHR ethnic maps of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia: a single country or an apple of discord?
Bosnian Institute, 12 May 2006 {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Bosnia And Herzegovina History of Bosnia and Herzegovina,