carbonate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A carbonate is a
 This structure is incompatible with the observed symmetry of the ion, which implies that the three bonds are the same length and that the three oxygen atoms are equivalent. As in the case of the
This structure is incompatible with the observed symmetry of the ion, which implies that the three bonds are the same length and that the three oxygen atoms are equivalent. As in the case of the  This resonance can be summarized by a model with fractional bonds and
This resonance can be summarized by a model with fractional bonds and 
Carbonate/bicarbonate/carbonic acid equilibrium in water: pH of solutions, buffer capacity, titration and species distribution vs. pH computed with a free spreadsheet
* {{Authority control Oxyanions
salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zero. The term molecule may or may no ...
with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester
In organic chemistry, a carbonate ester (organic carbonate or organocarbonate) is an ester of carbonic acid. This functional group consists of a carbonyl group flanked by two alkoxy groups. The general structure of these carbonates is and they ...
, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C(=O)(O–)2.
The term is also used as a verb, to describe carbonation
Carbonation is the chemical reaction of carbon dioxide to give carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbonic acid. In chemistry, the term is sometimes used in place of carboxylation, which refers to the formation of carboxylic acids.
In inorganic ch ...
: the process of raising the concentrations of carbonate and bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochem ...
ions in water to produce carbonated water and other carbonated beverageseither by the addition of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
gas under pressure or by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts into the water.
In geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ear ...
and mineralogy, the term "carbonate" can refer both to carbonate minerals
Carbonate minerals are those minerals containing the carbonate ion, .
Carbonate divisions Anhydrous carbonates
*Calcite group: trigonal
**Calcite CaCO3
**Gaspéite (Ni,Mg,Fe2+)CO3
**Magnesite MgCO3
**Otavite CdCO3
**Rhodochrosite MnCO3
**Sider ...
and carbonate rock
Carbonate rocks are a class of sedimentary rocks composed primarily of carbonate minerals. The two major types are limestone, which is composed of calcite or aragonite (different crystal forms of CaCO3), and dolomite rock (also known as dolosto ...
(which is made of chiefly carbonate minerals), and both are dominated by the carbonate ion, . Carbonate minerals are extremely varied and ubiquitous in chemically precipitated sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
. The most common are calcite or calcium carbonate, CaCO3, the chief constituent of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
(as well as the main component of mollusc shells and coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and ...
skeletons); dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
, a calcium-magnesium carbonate CaMg(CO3)2; and siderite
Siderite is a mineral composed of iron(II) carbonate (FeCO3). It takes its name from the Greek word σίδηρος ''sideros,'' "iron". It is a valuable iron mineral, since it is 48% iron and contains no sulfur or phosphorus. Zinc, magnesium and ...
, or iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
(II) carbonate, FeCO3, an important iron ore. Sodium carbonate ("soda" or "natron") and potassium carbonate
Potassium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2 CO3. It is a white salt, which is soluble in water. It is deliquescent, often appearing as a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is mainly used in the production of soap and gl ...
("potash") have been used since antiquity for cleaning and preservation, as well as for the manufacture of glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling ( quenching ...
. Carbonates are widely used in industry, such as in iron smelting, as a raw material for Portland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19th ...
and lime
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a color between yellow and green
Lime may also refer to:
Botany ...
manufacture, in the composition of ceramic glaze
Ceramic glaze is an impervious layer or coating of a vitreous substance which has been fused to a pottery body through firing. Glaze can serve to color, decorate or waterproof an item. Glazing renders earthenware vessels suitable for holding ...
s, and more.
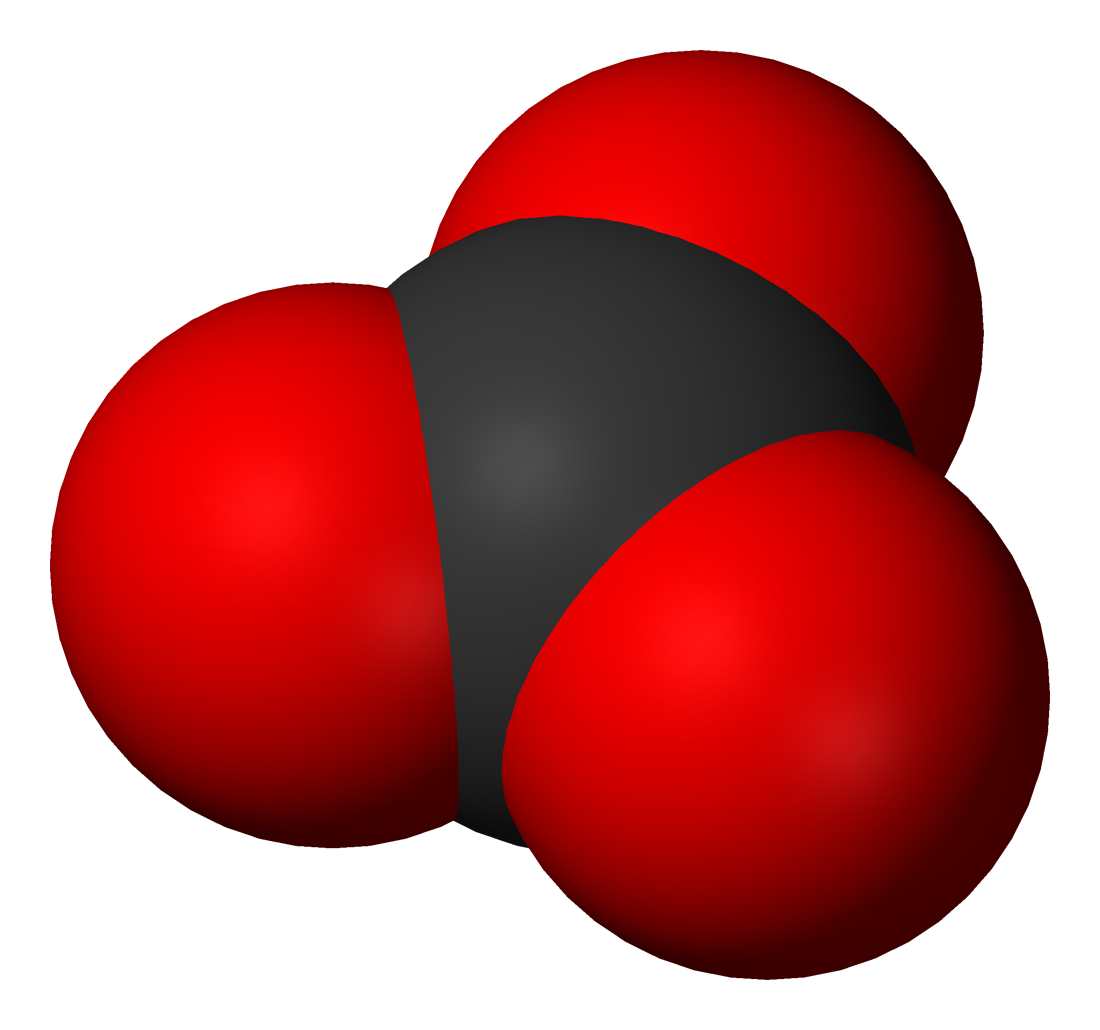
Structure and bonding
The carbonate ion is the simplestoxocarbon anion
In chemistry, an oxocarbon anion is a negative ion consisting solely of carbon and oxygen atoms, and therefore having the general formula for some integers ''x'', ''y'', and ''n''.
The most common oxocarbon anions are carbonate, , and oxalate, ...
. It consists of one carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
atom surrounded by three oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
atoms, in a trigonal planar arrangement, with ''D''3h molecular symmetry. It has a molecular mass of 60.01 g/mol and carries a total formal charge of −2. It is the conjugate base
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid donates a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as in the reverse reaction it loses a ...
of the hydrogencarbonate (bicarbonate) ion, , which is the conjugate base of , carbonic acid.
The Lewis structure
Lewis structures, also known as Lewis dot formulas, Lewis dot structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis electron dot structures (LEDS), are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, as well as the lone pairs of electrons t ...
of the carbonate ion has two (long) single bonds to negative oxygen atoms, and one short double bond to a neutral oxygen atom.
: This structure is incompatible with the observed symmetry of the ion, which implies that the three bonds are the same length and that the three oxygen atoms are equivalent. As in the case of the
This structure is incompatible with the observed symmetry of the ion, which implies that the three bonds are the same length and that the three oxygen atoms are equivalent. As in the case of the isoelectronic
Isoelectronicity is a phenomenon observed when two or more molecules have the same structure (positions and connectivities among atoms) and the same electronic configurations, but differ by what specific elements are at certain locations in th ...
nitrate ion, the symmetry can be achieved by a resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied Periodic function, periodic force (or a Fourier analysis, Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system ...
among three structures:
: This resonance can be summarized by a model with fractional bonds and
This resonance can be summarized by a model with fractional bonds and delocalized
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond.IUPAC Gold Boo''delocalization''/ref>
The term delocalization is general and can have slightly dif ...
charges:
:

Chemical properties
Metal carbonates generally decompose on heating, liberating carbon dioxide from the long termcarbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major componen ...
to the short term carbon cycle and leaving behind an oxide of the metal. This process is called calcination
Calcination refers to thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), gener ...
, after ''calx'', the Latin name of quicklime or calcium oxide
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ...
, CaO, which is obtained by roasting limestone in a lime kiln
A lime kiln is a kiln used for the calcination of limestone ( calcium carbonate) to produce the form of lime called quicklime (calcium oxide). The chemical equation for this reaction is
: CaCO3 + heat → CaO + CO2
This reaction can take p ...
.
A carbonate salt forms when a positively charged ion, , , or , associates with the negatively charged oxygen atoms of the ion by forming electrostatic attractions with them, forming an ionic compound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struc ...
:
:
:
:
Most carbonate salts are insoluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubil ...
in water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
at standard temperature and pressure, with solubility constant Solubility equilibrium is a type of dynamic equilibrium that exists when a chemical compound in the solid state is in chemical equilibrium with a solution of that compound. The solid may dissolve unchanged, with dissociation, or with chemical reacti ...
s of less than . Exceptions include lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
, potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosph ...
, rubidium, caesium, and ammonium carbonates, as well as many uranium carbonate
Uranyl carbonate refers to the inorganic compound with the formula UO2CO3. Also known by its mineral name rutherfordine, this material consists of uranyl (UO22+) and carbonate (CO32-). Like most uranyl salts, the compound is a polymeric, each uran ...
s.
In aqueous solution, carbonate, bicarbonate, carbon dioxide, and carbonic acid exist together in a dynamic equilibrium
In chemistry, a dynamic equilibrium exists once a reversible reaction occurs. Substances transition between the reactants and products at equal rates, meaning there is no net change. Reactants and products are formed at such a rate that the co ...
. In strongly basic conditions, the carbonate ion predominates, while in weakly basic conditions, the bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochem ...
ion is prevalent. In more acid conditions, aqueous carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
, CO2(aq), is the main form, which, with water, H2O, is in equilibrium with carbonic acidthe equilibrium lies strongly towards carbon dioxide. Thus sodium carbonate is basic, sodium bicarbonate is weakly basic, while carbon dioxide itself is a weak acid.
Carbonated water is formed by dissolving CO2 in water under pressure. When the partial pressure of CO2 is reduced, for example when a can of soda is opened, the equilibrium for each of the forms of carbonate (carbonate, bicarbonate, carbon dioxide, and carbonic acid) shifts until the concentration of CO2 in the solution is equal to the solubility of CO2 at that temperature and pressure. In living systems an enzyme, carbonic anhydrase, speeds the interconversion of CO2 and carbonic acid.
Although the carbonate salts of most metals are insoluble in water, the same is not true of the bicarbonate salts. In solution this equilibrium between carbonate, bicarbonate, carbon dioxide and carbonic acid changes constantly to the changing temperature and pressure conditions. In the case of metal ions with insoluble carbonates, such as CaCO3, formation of insoluble compounds results. This is an explanation for the buildup of scale inside pipes caused by hard water
Hard water is water that has high mineral content (in contrast with "soft water"). Hard water is formed when water percolates through deposits of limestone, chalk or gypsum, which are largely made up of calcium and magnesium carbonates, bicarbo ...
.
Carbonate in the inorganic nomenclature
Systematic additive IUPAC name for carbonate anion is trioxidocarbonate(2−). Similarly,cyanide
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms.
In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of ...
anion CN− is named nitridocarbonate(1−). However, following the same logic for carbonate(4−) (orthocarbonic acid
Orthocarbonic acid (methanetetrol) is the name given to a hypothetical compound with the chemical formula or . Its molecular structure consists of a single carbon atom bonded to four hydroxy groups. It would be therefore a fourfold alcohol. ...
), by similitude to silicate(4−) (orthosilicic acid
Orthosilicic acid () is an inorganic compound with the formula . Although rarely observed, it is the key compound of silica and silicates and the precursor to other silicic acids . Silicic acids play important roles in biomineralization and ...
), in the systematic additive nomenclature makes no sense as this species has never been identified under normal conditions of temperature and pressure. Orthocarbonic acid is energetically much less stable than orthosilicic acid and cannot exist under normal conditions because of the energetically unfavorable orbital configuration of a single central carbon atom bound to four oxygen atoms.
Organic carbonates
Inorganic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; ...
a carbonate can also refer to a functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the re ...
within a larger molecule that contains a carbon atom bound to three oxygen atoms, one of which is double bonded. These compounds are also known as organocarbonates or carbonate esters, and have the general formula ROCOOR′, or RR′CO3. Important organocarbonates include dimethyl carbonate
Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) is an organic compound with the formula OC(OCH3)2. It is a colourless, flammable liquid. It is classified as a carbonate ester. This compound has found use as a methylating agent and more recently as a solvent that is ...
, the cyclic compounds ethylene carbonate
Ethylene carbonate (sometimes abbreviated EC) is the organic compound with the formula (CH2O)2CO. It is classified as the cyclic carbonate ester of ethylene glycol and carbonic acid. At room temperature (25 °C) ethylene carbonate is a tran ...
and propylene carbonate
Propylene carbonate (often abbreviated PC) is an organic compound with the formula C4H6O3. It is a cyclic carbonate ester derived from propylene glycol. This colorless and odorless liquid is useful as a polar, aprotic solvent. Propylene carbo ...
, and the phosgene replacement, triphosgene
Triphosgene (bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate (BTC) is a chemical compound with the formula OC(OCCl3)2. It is used as a solid substitute for phosgene, which is a gas. Triphosgene is stable up to 200 °C. Triphosgene is used in a variety of halogena ...
.
Buffer
Three reversible reactions control the pH balance of blood and act as abuffer
Buffer may refer to:
Science
* Buffer gas, an inert or nonflammable gas
* Buffer solution, a solution used to prevent changes in pH
* Buffering agent, the weak acid or base in a buffer solution
* Lysis buffer, in cell biology
* Metal ion buffer
* ...
to stabilise it in the range 7.37–7.43:
#
#
#
Exhaled CO2(g) depletes CO2(aq), which in turn consumes H2CO3, causing the equilibrium of the first reaction to try to restore the level of carbonic acid by reacting bicarbonate with a hydrogen ion, an example of Le Châtelier's principle
Le Chatelier's principle (pronounced or ), also called Chatelier's principle (or the Equilibrium Law), is a principle of chemistry used to predict the effect of a change in conditions on chemical equilibria. The principle is named after French ...
. The result is to make the blood more alkaline (raise pH). By the same principle, when the pH is too high, the kidneys excrete bicarbonate () into urine as urea via the urea cycle
The urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle) is a cycle of Biochemistry, biochemical reactions that produces urea (NH2)2CO from ammonia (NH3). Animals that use this cycle, mainly amphibians and mammals, are called ureotelic.
The urea cycle ...
(or Krebs–Henseleit ornithine cycle). By removing the bicarbonate, more H+ is generated from carbonic acid (H2CO3), which comes from CO2(g) produced by cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
.
Crucially, a similar buffer operates in the oceans. It is a major factor in climate change and the long-term carbon cycle, due to the large number of marine organisms (especially coral) which are made of calcium carbonate. Increased solubility of carbonate through increased temperatures results in lower production of marine calcite and increased concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide. This, in turn, increases Earth temperature. The amount of available is on a geological scale and substantial quantities may eventually be redissolved into the sea and released to the atmosphere, increasing CO2 levels even more.
Carbonate salts
* Carbonate overview:Presence outside Earth
It is generally thought that the presence of carbonates inrock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
is strong evidence for the presence of liquid water. Recent observations of the planetary nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelate ...
NGC 6302
NGC 6302 (also known as the Bug Nebula, Butterfly Nebula, or Caldwell 69) is a bipolar planetary nebula in the constellation Scorpius. The structure in the nebula is among the most complex ever observed in planetary nebulae. The spectrum of N ...
show evidence for carbonates in space, where aqueous alteration similar to that on Earth is unlikely. Other minerals have been proposed which would fit the observations.
Until recently carbonate deposits have not been found on Mars via remote sensing or in situ missions, even though Martian meteorites contain small amounts. Groundwater may have existed at Gusev and Meridiani Planum
The Meridiani Planum (alternately Meridiani plain, Meridiani plains, Terra Meridiani, or Terra Meridiani plains) is either a large plain straddling the equator of Mars and covered with a vast number of spherules containing a lot of iron oxide or ...
.
See also
* Cap carbonates *Orthocarbonic acid
Orthocarbonic acid (methanetetrol) is the name given to a hypothetical compound with the chemical formula or . Its molecular structure consists of a single carbon atom bonded to four hydroxy groups. It would be therefore a fourfold alcohol. ...
, , or , a hypothetic unstable molecule
* Oxalate
Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate) is an anion with the formula C2O42−. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4), and several esters such as dimethyl ...
* Peroxocarbonate
* Sodium percarbonate
Sodium percarbonate is a chemical substance with formula . It is an adduct of sodium carbonate ("soda ash" or "washing soda") and hydrogen peroxide (that is, a perhydrate) whose formula is more properly written as 2 · 3 . ...
References
External links
Carbonate/bicarbonate/carbonic acid equilibrium in water: pH of solutions, buffer capacity, titration and species distribution vs. pH computed with a free spreadsheet
* {{Authority control Oxyanions