Browning (food process) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Browning is the process of food turning
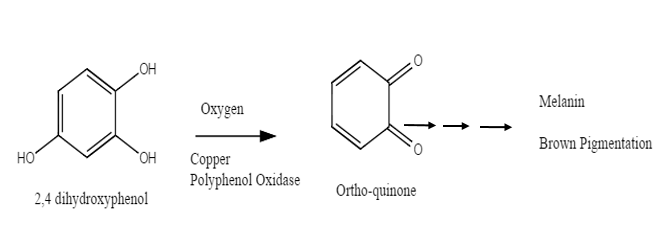 Enzymatic browning is one of the most important reactions that takes place in most fruits and vegetables as well as in seafood. These processes affect the taste, color, and value of such foods. Generally, it is a chemical reaction involving polyphenol oxidase (PPO),
Enzymatic browning is one of the most important reactions that takes place in most fruits and vegetables as well as in seafood. These processes affect the taste, color, and value of such foods. Generally, it is a chemical reaction involving polyphenol oxidase (PPO),
 The control of enzymatic browning has always been a challenge for the food industry. A variety of approaches are used to prevent or slow down enzymatic browning of foods, each method aimed at targeting specific steps of the chemical reaction. The different types of enzymatic browning control can be classified into two large groups: physical and chemical. Usually, multiple methods are used. The use of sulfites (powerful anti-browning chemicals) have been reconsidered due to the potential hazards that it causes along with its activity. Much research has been conducted regarding the exact types of control mechanisms that take place when confronted with the enzymatic process. Besides prevention, control over browning also includes measures intended to recover the food color after its browning. For instance,
The control of enzymatic browning has always been a challenge for the food industry. A variety of approaches are used to prevent or slow down enzymatic browning of foods, each method aimed at targeting specific steps of the chemical reaction. The different types of enzymatic browning control can be classified into two large groups: physical and chemical. Usually, multiple methods are used. The use of sulfites (powerful anti-browning chemicals) have been reconsidered due to the potential hazards that it causes along with its activity. Much research has been conducted regarding the exact types of control mechanisms that take place when confronted with the enzymatic process. Besides prevention, control over browning also includes measures intended to recover the food color after its browning. For instance,
 *Antioxidants − Many antioxidants are used in food industry as food additives. These compounds react with oxygen and suppress the initiation of the browning process. Also, they interfere with intermediate products of the following reactions and inhibit
*Antioxidants − Many antioxidants are used in food industry as food additives. These compounds react with oxygen and suppress the initiation of the browning process. Also, they interfere with intermediate products of the following reactions and inhibit
 The second type of browning, non-enzymatic browning, is a process that also produces the brown pigmentation in foods but without the activity of enzymes. The two main forms of non-enzymatic browning are
The second type of browning, non-enzymatic browning, is a process that also produces the brown pigmentation in foods but without the activity of enzymes. The two main forms of non-enzymatic browning are 
 The other non-enzymatic reaction is the
The other non-enzymatic reaction is the
brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
due to the chemical reactions that take place within. The process of browning is one of the chemical reactions that take place in food chemistry
Food chemistry is the study of chemical processes and interactions of all biological and non-biological components of foods. The biological substances include such items as meat, poultry, lettuce, beer, milk as examples. It is similar to biochemist ...
and represents an interesting research topic regarding health, nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain sufficient ...
, and food technology. Though there are many different ways food chemically changes over time, browning in particular falls into two main categories: enzymatic
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. ...
versus non-enzymatic browning processes.
Browning has many important implications on the food industry relating to nutrition, technology, and economic cost. Researchers are especially interested in studying the control (inhibition) of browning and the different methods that can be employed to maximize this inhibition and ultimately prolong the shelf life
Shelf life is the length of time that a commodity may be stored without becoming unfit for use, consumption, or sale. In other words, it might refer to whether a commodity should no longer be on a pantry shelf (unfit for use), or no longer on a ...
of food.
Enzymatic browning
 Enzymatic browning is one of the most important reactions that takes place in most fruits and vegetables as well as in seafood. These processes affect the taste, color, and value of such foods. Generally, it is a chemical reaction involving polyphenol oxidase (PPO),
Enzymatic browning is one of the most important reactions that takes place in most fruits and vegetables as well as in seafood. These processes affect the taste, color, and value of such foods. Generally, it is a chemical reaction involving polyphenol oxidase (PPO), catechol oxidase
Catechol oxidase is a copper oxidase that contains a type 3 di-copper cofactor and catalyzes the oxidation of ortho-diphenols into ortho-quinones coupled with the reducing agent, reduction of molecular oxygen to water. It is present in a variet ...
, and other enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s that create melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
s and benzoquinone Benzoquinone (C6H4O2) is a quinone with a single benzene ring. There are 2 (out of 3 hypothetical) benzoquinones:
* 1,4-Benzoquinone, most commonly, right image (also ''para''-benzoquinone, ''p''-benzoquinone, ''para''-quinone, or just quinone)
* 1 ...
from natural phenols. Enzymatic browning (also called oxidation of foods) requires exposure to oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
. It begins with the oxidation of phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are ...
by polyphenol oxidase into quinones, whose strong electrophilic state causes high susceptibility to a nucleophilic attack from other proteins. These quinones are then polymerized in a series of reactions, eventually resulting in the formation of brown pigments ( melanosis) on the surface of the food. The rate of enzymatic browning is reflected by the amount of active polyphenol oxidases present in the food. Hence, most research into methods of preventing enzymatic browning has been directed towards inhibiting polyphenol oxidase activity. However, not all browning of food produces negative effects.
Examples of beneficial enzymatic browning:
* Developing color and flavor in coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
, cocoa bean
The cocoa bean (technically cocoa seed) or simply cocoa (), also called the cacao bean (technically cacao seed) or cacao (), is the dried and fully fermented seed of ''Theobroma cacao'', from which cocoa solids (a mixture of nonfat substance ...
s, and tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and north ...
.
* Developing color and flavor in dried fruit
Dried fruit is fruit from which the majority of the original water content has been removed either naturally, through sun drying, or through the use of specialized dryers or dehydrators. Dried fruit has a long tradition of use dating back to th ...
such as figs and raisin
A raisin is a dried grape. Raisins are produced in many regions of the world and may be eaten raw or used in cooking, baking, and brewing. In the United Kingdom, Ireland, New Zealand, and Australia, the word ''raisin'' is reserved for the ...
s.
Examples of non-beneficial enzymatic browning:
* Fresh fruit and vegetables, including apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, ' ...
s, potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
es, bananas and avocado
The avocado (''Persea americana'') is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family ( Lauraceae). It is native to the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Then as now it was prized for ...
s.
* Oxidation of polyphenols is the major cause of melanosis in crustaceans such as shrimp.
Control of enzymatic browning
 The control of enzymatic browning has always been a challenge for the food industry. A variety of approaches are used to prevent or slow down enzymatic browning of foods, each method aimed at targeting specific steps of the chemical reaction. The different types of enzymatic browning control can be classified into two large groups: physical and chemical. Usually, multiple methods are used. The use of sulfites (powerful anti-browning chemicals) have been reconsidered due to the potential hazards that it causes along with its activity. Much research has been conducted regarding the exact types of control mechanisms that take place when confronted with the enzymatic process. Besides prevention, control over browning also includes measures intended to recover the food color after its browning. For instance,
The control of enzymatic browning has always been a challenge for the food industry. A variety of approaches are used to prevent or slow down enzymatic browning of foods, each method aimed at targeting specific steps of the chemical reaction. The different types of enzymatic browning control can be classified into two large groups: physical and chemical. Usually, multiple methods are used. The use of sulfites (powerful anti-browning chemicals) have been reconsidered due to the potential hazards that it causes along with its activity. Much research has been conducted regarding the exact types of control mechanisms that take place when confronted with the enzymatic process. Besides prevention, control over browning also includes measures intended to recover the food color after its browning. For instance, ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, ...
filtration or ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a variety of membrane filtration in which forces such as pressure or concentration gradients lead to a separation through a semipermeable membrane. Suspended solids and solutes of high molecular weight are retained in the ...
can be used in winemaking
Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. The science of wine and ...
to remove the brown color sediments in the solution.
Physical methods
*Heat treatment − Treating food with heat, such asblanching
Blanch or blanching may refer to:
People
* Andrea Blanch (born 1935), portrait, commercial, and fine art photographer
* Arnold Blanch (1896–1968), born and raised in Mantorville, Minnesota
* Stuart Blanch, Baron Blanch (1918–1994), Anglican bi ...
or roasting, de-naturates enzymes and destroys the reactants responsible for browning. Blanching is used, for example, in winemaking
Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. The science of wine and ...
, tea processing
Tea processing is the method in which the leaves from the tea plant ''Camellia sinensis'' are transformed into the dried leaves for brewing tea.
The categories of tea are distinguished by the processing they undergo. In its most general form, t ...
, storing nuts and bacon, and preparing vegetables for freezing preservation. Meat is often partially browned under high heat before being incorporated into a larger preparation to be cooked at a lower temperature which produces less browning.
*Cold treatment − Refrigeration
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, ht ...
and freezing
Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid ...
are the most common ways of storing food, preventing decay. The activity of browning enzymes, i.e., rate of reaction
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit ...
, drops in low temperatures. Thus, refrigeration helps to keep the initial look, color, and flavour of fresh vegetables and fruits. Refrigeration is also used during distribution and retailing of fruits and vegetables.
*Oxygen elimination − Presence of oxygen is crucial for enzymatic browning, therefore eliminating oxygen from the environment helps to slow down the browning reaction. Withdrawing air or replacing it with other gases (e.g., N2 or CO2) during preservation, such as in vacuum-packaging or modified atmosphere packaging, wine or juice bottling, using impermeable films or edible coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. Pow ...
s, dipping into salt or sugar solutions, keeps the food away from direct contact with oxygen. Impermeable films made of plastic or other materials prevent food being exposed to oxygen in the air and avoid moisture loss. There is an increasing activity in developing packaging materials impregnated with antioxidants, antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals ar ...
, and antifungal substances, such as butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) and butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), tocopherol
Tocopherols (; TCP) are a class of organic chemical compounds (more precisely, various methylated phenols), many of which have vitamin E activity. Because the vitamin activity was first identified in 1936 from a dietary fertility factor in rat ...
s, hinokitiol
Hinokitiol (β-thujaplicin) is a natural monoterpenoid found in the wood of trees in the family Cupressaceae. It is a tropolone derivative and one of the thujaplicins. Hinokitiol is used in oral and skin care products, and is a food additive us ...
, lysozyme
Lysozyme (EC 3.2.1.17, muramidase, ''N''-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase; systematic name peptidoglycan ''N''-acetylmuramoylhydrolase) is an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. It is a glycoside ...
, nisin
Nisin is a polycyclic antibacterial peptide produced by the bacterium ''Lactococcus lactis'' that is used as a food preservative. It has 34 amino acid residues, including the uncommon amino acids lanthionine (Lan), methyllanthionine (MeLan), di ...
, natamycin
Natamycin, also known as pimaricin, is an antifungal medication used to treat fungal infections around the eye. This includes infections of the eyelids, conjunctiva, and cornea. It is used as eyedrops. Natamycin is also used in the food indust ...
, chitosan
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed β-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine (deacetylated unit) and ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine (acetylated unit). It is made by treating the chitin shells of shrimp and other crustacean ...
, and ε-polylysine. Edible coatings can be made of polysaccharides, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s, lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids includ ...
s, vegetable skins, plants or other natural products.
*Irradiation − Food irradiation using UV-C
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
, gamma rays
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
, x-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s, and electron beams is another method to extend the food shelf life
Shelf life is the length of time that a commodity may be stored without becoming unfit for use, consumption, or sale. In other words, it might refer to whether a commodity should no longer be on a pantry shelf (unfit for use), or no longer on a ...
. Ionizing radiation inhibits the vitality of microorganisms responsible for food spoilage
Food spoilage is the process where a food product becomes unsuitable to ingest by the consumer. The cause of such a process is due to many outside factors as a side-effect of the type of product it is, as well as how the product is packaged and s ...
and delays the maturation and sprouting of preserving vegetables and fruits.
Chemical methods
*Acidification − Browning enzymes, as other enzymes, are active at a specific range of pH. For example, PPO shows optimal activity at pH 5-7 and is inhibited below pH 3. Acidifying agents and acidity regulators are widely used as food additives to maintain a desired pH in food products. Acidulants, such ascitric acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in ...
, ascorbic acid, and glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, pe ...
, are used as anti-browning agents. Many of these agents also show other anti-browning effects, such as chelating and antioxidant activities.
 *Antioxidants − Many antioxidants are used in food industry as food additives. These compounds react with oxygen and suppress the initiation of the browning process. Also, they interfere with intermediate products of the following reactions and inhibit
*Antioxidants − Many antioxidants are used in food industry as food additives. These compounds react with oxygen and suppress the initiation of the browning process. Also, they interfere with intermediate products of the following reactions and inhibit melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
formation. Ascorbic acid, N-acetylcysteine
Acetylcysteine, also known as ''N''-acetylcysteine (NAC), is a medication that is used to treat paracetamol overdose and to loosen thick mucus in individuals with chronic bronchopulmonary disorders like pneumonia and bronchitis. It has been used ...
, L-cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, somet ...
, 4-hexylresorcinol, erythorbic acid, cysteine hydrochloride, glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, pe ...
are examples of antioxidants that have been studied for their anti-browning properties.
*Chelating agents − Polyphenol oxidase requires copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
as a cofactor for its functionality, thus copper- chelating agents inhibit the activity of this enzyme. Many agents possessing chelating activity have been studied and used in different fields of food industry, such as citric acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in ...
, sorbic acid
Sorbic acid, or 2,4-hexadienoic acid, is a natural organic compound used as a food preservative. It has the chemical formula and the structure . It is a colourless solid that is slightly soluble in water and sublimes readily. It was first isol ...
, polyphosphate
Polyphosphates are salts or esters of polymeric oxyanions formed from tetrahedral PO4 (phosphate) structural units linked together by sharing oxygen atoms. Polyphosphates can adopt linear or a cyclic ring structures. In biology, the polyphosphate e ...
s, hinokitiol
Hinokitiol (β-thujaplicin) is a natural monoterpenoid found in the wood of trees in the family Cupressaceae. It is a tropolone derivative and one of the thujaplicins. Hinokitiol is used in oral and skin care products, and is a food additive us ...
, kojic acid
Kojic acid is a chelation agent produced by several species of fungi, especially ''Aspergillus oryzae'', which has the Japanese common name ''koji''. Kojic acid is a by-product in the fermentation process of malting rice, for use in the manufactur ...
, EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula H2N(CH2CO2H)2sub>2. This white, water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-soluble complexes ev ...
, porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are a group of heterocyclic macrocycle organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (=CH−). The parent of porphyrin is porphine, a rare chemical com ...
s, polycarboxylic acids, different proteins. Some of these compounds also have other anti-browning effects, such as acidifying or antioxidant. Hinokitiol is used in coating materials for food packaging.
Other methods
*Natural agents − Different natural products and their extracts, such asonion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onio ...
, pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae. The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been cultivated for many centuri ...
, lemon
The lemon (''Citrus limon'') is a species of small evergreen trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, primarily Northeast India (Assam), Northern Myanmar or China.
The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culin ...
, and white wine
White wine is a wine that is fermented without skin contact. The colour can be straw-yellow, yellow-green, or yellow-gold. It is produced by the alcoholic fermentation of the non-coloured pulp of grapes, which may have a skin of any colour. ...
, are known to inhibit or slow the browning of some products. Onion and its extract exhibit potent anti-browning properties by inhibiting the PPO activity. Pineapple juice have shown to possess anti-browning effect on apples and bananas. Lemon juice is used in making doughs to make the pastry
Pastry is baked food made with a dough of flour, water and shortening (solid fats, including butter or lard) that may be savoury or sweetened. Sweetened pastries are often described as '' bakers' confectionery''. The word "pastries" sugges ...
products look brighter. This effect is possibly explained by the anti-browning properties of citric and ascorbic acids in the lemon juice.
*Genetic modification − Arctic apples have been genetically modified to silence the expression
Expression may refer to:
Linguistics
* Expression (linguistics), a word, phrase, or sentence
* Fixed expression, a form of words with a specific meaning
* Idiom, a type of fixed expression
* Metaphorical expression, a particular word, phrase, o ...
of PPO, thereby delaying the browning effect, and improving apple eating quality.
Non-enzymatic browning
 The second type of browning, non-enzymatic browning, is a process that also produces the brown pigmentation in foods but without the activity of enzymes. The two main forms of non-enzymatic browning are
The second type of browning, non-enzymatic browning, is a process that also produces the brown pigmentation in foods but without the activity of enzymes. The two main forms of non-enzymatic browning are caramelization
Caramelization is a process of browning of sugar used extensively in cooking for the resulting sweet nutty flavor and brown color. The brown colors are produced by three groups of polymers: caramelans (C24H36O18), caramelens (C36H50O25), and ca ...
and the Maillard reaction
The Maillard reaction ( ; ) is a chemical reaction between Amino acid, amino acids and Reducing sugar, reducing sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor. Searing, Seared steaks, fried dumplings, cookies and other kinds of biscuits, b ...
. Both vary in the reaction rate as a function of water activity
Water activity (''aw'') is the partial vapor pressure of water in a solution divided by the standard state partial vapor pressure of water. In the field of food science, the standard state is most often defined as pure water at the same tempe ...
(in food chemistry, the standard state of water activity is most often defined as the partial vapor pressure of pure water at the same temperature).
Caramelization
Caramelization is a process of browning of sugar used extensively in cooking for the resulting sweet nutty flavor and brown color. The brown colors are produced by three groups of polymers: caramelans (C24H36O18), caramelens (C36H50O25), and ca ...
is a process involving the pyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''py ...
of sugar. It is used extensively in cooking for the desired nutty flavor and brown color. As the process occurs, volatile chemicals are released, producing the characteristic caramel flavor.

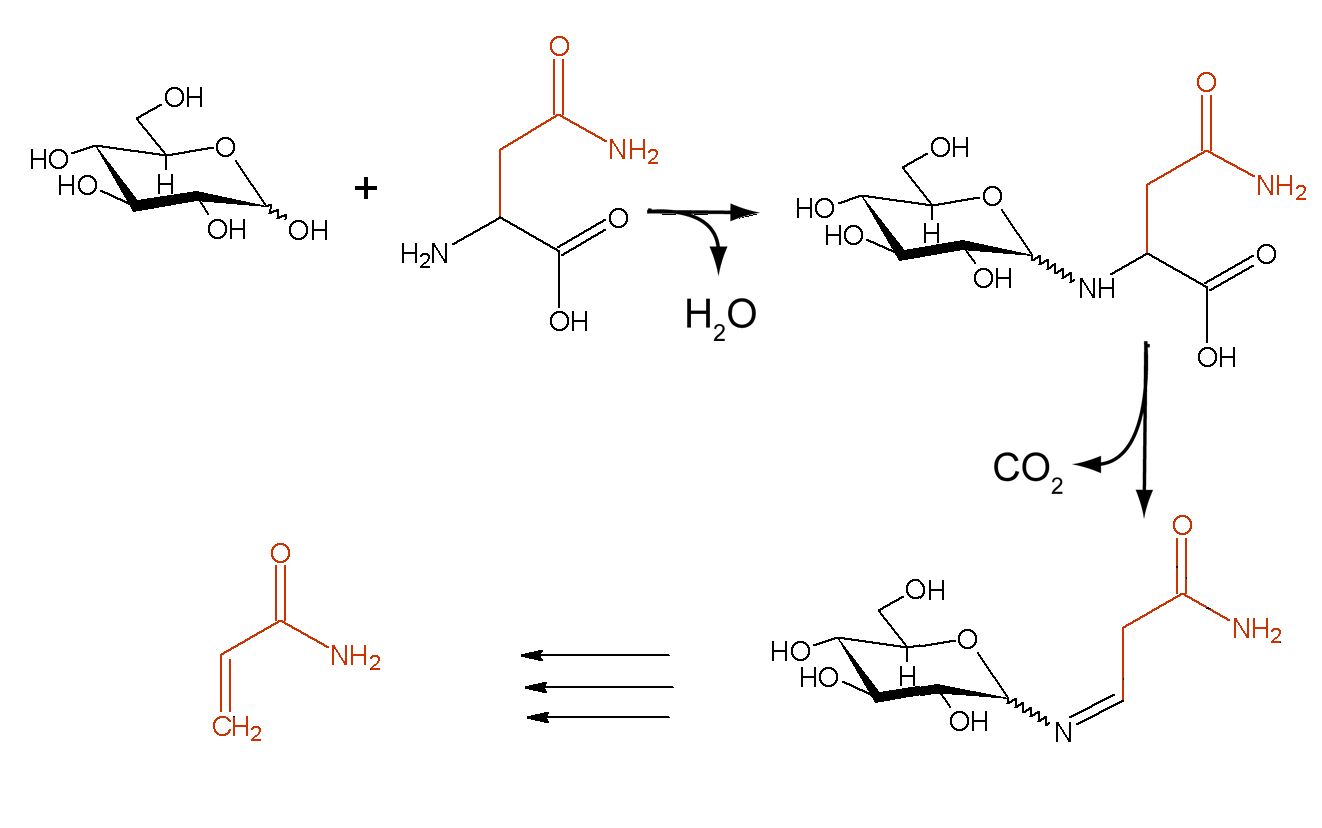
 The other non-enzymatic reaction is the
The other non-enzymatic reaction is the Maillard reaction
The Maillard reaction ( ; ) is a chemical reaction between Amino acid, amino acids and Reducing sugar, reducing sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor. Searing, Seared steaks, fried dumplings, cookies and other kinds of biscuits, b ...
. This reaction is responsible for the production of the flavor when foods are cooked. Examples of foods that undergo Maillard reaction include breads, steaks, and potatoes. It is a chemical reaction that takes place between the amine group
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent ...
of a free amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
and the carbonyl group
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containi ...
of a reducing sugar
A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent. In an alkaline solution, a reducing sugar forms some aldehyde or ketone, which allows it to act as a reducing agent, for example in Benedict's reagent. In such a reacti ...
, usually with the addition of heat. The sugar interacts with the amino acid, producing a variety of odors and flavors. The Maillard reaction is the basis for producing artificial flavors for processed foods in the flavoring industry since the type of amino acid involved determines the resulting flavor.
Melanoidin Melanoidins are brown, high molecular weight heterogeneous polymers that are formed when sugars and amino acids combine (through the Maillard Reaction) at high temperatures and low water activity. They were discovered by Schmiedeberg in 1897.
Melan ...
s are brown, high molecular weight heterogeneous polymers that are formed when sugars and amino acids combine through the Maillard reaction at high temperatures and low water activity. Melanoidins are commonly present in foods that have undergone some form of non-enzymatic browning, such as barley malts (Vienna and Munich), bread crust, bakery products and coffee. They are also present in the wastewater of sugar refineries, necessitating treatment in order to avoid contamination around the outflow of these refineries.
Browning of grapes during winemaking
Like most fruit, grapes vary in the number of phenolic compounds they have. This characteristic is used as a parameter in judging the quality of the wine. The general process of winemaking is initiated by the enzymatic oxidation of phenolic compounds by polyphenol oxidases. Contact between the phenolic compounds in thevacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic m ...
of the grape cell and the polyphenol oxidase enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
(located in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
) triggers the oxidation of the grape. Thus, the initial browning of grapes occurs as a result of "compartmentalization modification" in the cells of the grape.
Implications in food industry and technology
Enzymatic browning affects the color, flavor, and nutritional value of foods, causing huge economic loss when not sold to consumers on time. It is estimated that more than 50% of produce is lost as a result of enzymatic browning. The increase in human population and consequential depletion in natural resources has prompted many biochemists and food engineers alike to find new or improved techniques to preserve food and for longer by using methods to inhibit the browning reaction. This effectively increases the shelf life of foods, solving this part of the waste problem. A better understanding of the enzymatic browning mechanisms, specifically, understanding the properties of the enzymes and substrates that are involved in the reaction may help food technologists to control certain stages in the mechanism and ultimately apply that knowledge to inhibit browning. Apples are fruits commonly studied by researchers due to their high phenolic content, which make them highly susceptible to enzymatic browning. In accordance with other findings regarding apples and browning activity, a correlation has been found between higher phenolic quantities and increased enzymatic activity in apples. This provides a potential target and thus hope for food industries wishing to genetically modify foods to decrease polyphenol oxidase activity and thus decrease browning. An example of such accomplishments in food engineering is in the production of Arctic apples. These apples, engineered by ''Okanagan Specialty Fruits Inc,'' are a result of applying gene splicing, a laboratory technique that has allowed for the reduction in polyphenol oxidase. Another type of issue that is closely studied is the browning of seafood. Seafood, in particular shrimp, is a staple consumed by people all over the world. The browning of shrimp, which is actually referred to as melanosis, creates a great concern for food handlers and consumers. Melanosis mainly occurs during postmortem handling and refrigerated storage. Recent studies have found a plant extract that acts as an anti-melatonin polyphenol oxidase inhibitor serves the same function as sulfites but without the health risks.See also
*Browning (partial cooking)
Browning is the process of partially cooking the surface of meat to develop its flavor through various browning reactions and give it a more attractive color.
It is a common first step in cooking braised meats and stews.
Techniques
Browning ...
* Decomposition
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is e ...
* Gravy
Gravy is a sauce often made from the juices of meats that run naturally during cooking and often thickened with wheat flour or corn starch for added texture. The gravy may be further coloured and flavoured with gravy salt (a simple mix of salt ...
* Water activity
Water activity (''aw'') is the partial vapor pressure of water in a solution divided by the standard state partial vapor pressure of water. In the field of food science, the standard state is most often defined as pure water at the same tempe ...
References