|
Rate Of Reaction
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit time. Reaction rates can vary dramatically. For example, the oxidative rusting of iron under Earth's atmosphere is a slow reaction that can take many years, but the combustion of cellulose in a fire is a reaction that takes place in fractions of a second. For most reactions, the rate decreases as the reaction proceeds. A reaction's rate can be determined by measuring the changes in concentration over time. Chemical kinetics is the part of physical chemistry that concerns how rates of chemical reactions are measured and predicted, and how reaction-rate data can be used to deduce probable reaction mechanisms. The concepts of chemical kinetics are applied in many disciplines, such as chemical engineering, enzymology and environmental engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rust03102006
Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air moisture. Rust consists of hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH), Fe(OH)3), and is typically associated with the corrosion of refined iron. Given sufficient time, any iron mass, in the presence of water and oxygen, could eventually convert entirely to rust. Surface rust is commonly flaky and friable, and provides no passivational protection to the underlying iron, unlike the formation of patina on copper surfaces. ''Rusting'' is the common term for corrosion of elemental iron and its alloys such as steel. Many other metals undergo similar corrosion, but the resulting oxides are not commonly called "rust". Several forms of rust are distinguishable both visually and by spectroscopy, and form under different circumstances. Other forms of rust include the result of reactions between iron and chl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (chemistry)
Products are the species formed from chemical reactions. During a chemical reaction, reactants are transformed into products after passing through a high energy transition state. This process results in the consumption of the reactants. It can be a spontaneous reaction or mediated by catalysts which lower the energy of the transition state, and by solvents which provide the chemical environment necessary for the reaction to take place. When represented in chemical equations, products are by convention drawn on the right-hand side, even in the case of reversible reactions. The properties of products such as their energies help determine several characteristics of a chemical reaction, such as whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic. Additionally, the properties of a product can make it easier to extract and purify following a chemical reaction, especially if the product has a different state of matter than the reactants. Spontaneous reaction : R \rightarrow P *Where R i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Concentration
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called ''numerals''; for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the number five. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any number using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels (as with telephone numbers), for ordering (as with serial numbers), and for codes (as with ISBNs). In common usage, a ''numeral'' is not clearly distinguished from the ''number'' that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Balance
In physics, a mass balance, also called a material balance, is an application of conservation of mass to the analysis of physical systems. By accounting for material entering and leaving a system, mass flows can be identified which might have been unknown, or difficult to measure without this technique. The exact conservation law used in the analysis of the system depends on the context of the problem, but all revolve around mass conservation, i.e., that matter cannot disappear or be created spontaneously. Therefore, mass balances are used widely in engineering and environmental analyses. For example, mass balance theory is used to design chemical reactors, to analyse alternative processes to produce chemicals, as well as to model pollution dispersion and other processes of physical systems. Closely related and complementary analysis techniques include the population balance, energy balance and the somewhat more complex entropy balance. These techniques are required for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Energy
In chemistry and physics, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be provided for compounds to result in a chemical reaction. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in joules per mole (J/mol), kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). Activation energy can be thought of as the magnitude of the potential barrier (sometimes called the energy barrier) separating minima of the potential energy surface pertaining to the initial and final thermodynamic state. For a chemical reaction to proceed at a reasonable rate, the temperature of the system should be high enough such that there exists an appreciable number of molecules with translational energy equal to or greater than the activation energy. The term "activation energy" was introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius. Other uses Although less commonly used, activation energy also applies to nuclear reactions and various other physical phenomena. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition State
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked with the double dagger ‡ symbol. As an example, the transition state shown below occurs during the SN2 reaction of bromoethane with a hydroxide anion: The activated complex of a reaction can refer to either the transition state or to other states along the reaction coordinate between reactants and products, especially those close to the transition state.Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, ''Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed., W.H. Freeman 2006), p.809 According to the transition state theory, once the reactants have passed through the transition state configuration, they always continue to form products. History of concept The concept of a transition state has been important in many theories of the rates at which chemical reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversible Reaction
A reversible reaction is a reaction in which the conversion of reactants to products and the conversion of products to reactants occur simultaneously. : \mathit aA + \mathit bB \mathit cC + \mathit dD A and B can react to form C and D or, in the reverse reaction, C and D can react to form A and B. This is distinct from a reversible process in thermodynamics. Weak acids and bases undergo reversible reactions. For example, carbonic acid: : H2CO3 (l) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCO3−(aq) + H3O+(aq). The concentrations of reactants and products in an equilibrium mixture are determined by the analytical concentrations of the reagents (A and B or C and D) and the equilibrium constant, ''K''. The magnitude of the equilibrium constant depends on the Gibbs free energy change for the reaction. So, when the free energy change is large (more than about 30 kJ mol−1), the equilibrium constant is large (log K > 3) and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium are very small. Such a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
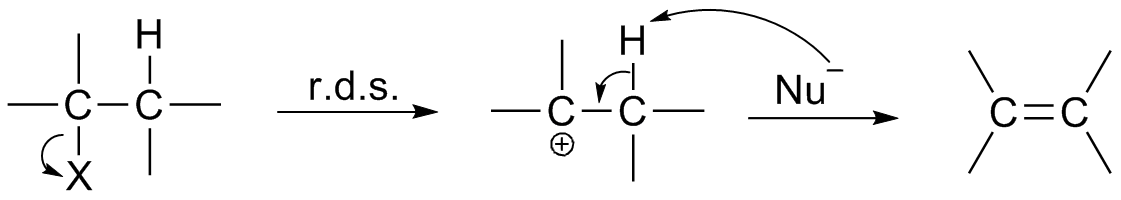
Elementary Reaction
An elementary reaction is a chemical reaction in which one or more chemical species react directly to form products in a single reaction step and with a single transition state. In practice, a reaction is assumed to be elementary if no reaction intermediates have been detected or need to be postulated to describe the reaction on a molecular scale. An apparently elementary reaction may be in fact a stepwise reaction, i.e. a complicated sequence of chemical reactions, with reaction intermediates of variable lifetimes. In a unimolecular elementary reaction, a molecule dissociates or isomerises to form the products(s) :\mbox \rightarrow \mbox At constant temperature, the rate of such a reaction is proportional to the concentration of the species :\frac=-k mbox In a bimolecular elementary reaction, two atoms, molecules, ions or radicals, and , react together to form the product(s) :\mbox \rightarrow \mbox The rate of such a reaction, at constant temperature, is proportional t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoichiometric Number
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products, leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated. This is illustrated in the image here, where the balanced equation is: : Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. This particular chemical equation is an example of complete combustion. Sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plus And Minus Signs
The plus and minus signs, and , are mathematical symbols used to represent the notions of positive and negative, respectively. In addition, represents the operation of addition, which results in a sum, while represents subtraction, resulting in a difference. Their use has been extended to many other meanings, more or less analogous. ''Plus'' and ''minus'' are Latin terms meaning "more" and "less", respectively. History Though the signs now seem as familiar as the alphabet or the Hindu-Arabic numerals, they are not of great antiquity. The Egyptian hieroglyphic sign for addition, for example, resembled a pair of legs walking in the direction in which the text was written ( Egyptian could be written either from right to left or left to right), with the reverse sign indicating subtraction: Nicole Oresme's manuscripts from the 14th century show what may be one of the earliest uses of as a sign for plus. In early 15th century Europe, the letters "P" and "M" were general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Intermediate
In chemistry, a reaction intermediate or an intermediate is a molecular entity that is formed from the reactants (or preceding intermediates) but is consumed in further reactions in stepwise chemical reactions that contain multiple elementary steps. Intermediates are the reaction product of one elementary step, but do not appear in the chemical equation for an overall chemical equation. For example, consider this hypothetical stepwise reaction: :A + B -> C + D The reaction includes two elementary steps: :A + B -> X :X -> C + D In this example, X is a reaction intermediate. IUPAC definition The IUPAC Gold Book defines an ''intermediate'' as a compound that has a lifetime greater than a molecular vibration that is formed (directly or indirectly) from the reactants and reacts further to give (either directly or indirectly) the products of a chemical reaction. The lifetime condition distinguishes true, chemically distinct intermediates from vibrational states or such transition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isochoric Process
In thermodynamics, an isochoric process, also called a constant-volume process, an isovolumetric process, or an isometric process, is a thermodynamic process during which the volume of the closed system undergoing such a process remains constant. An isochoric process is exemplified by the heating or the cooling of the contents of a sealed, inelastic container: The thermodynamic process is the addition or removal of heat; the isolation of the contents of the container establishes the closed system; and the inability of the container to deform imposes the constant-volume condition. The isochoric process here should be a quasi-static process. Formalism An isochoric thermodynamic quasi-static process is characterized by constant volume, i.e., . The process does no pressure-volume work, since such work is defined by W = P \Delta V , where is pressure. The sign convention is such that positive work is performed by the system on the environment. If the process is not quasi-static, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |