
World War III (WWIII or WW3), also known as the Third World War, is a hypothetical future
global conflict
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003
* ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007
* ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989
* ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015
* Bruno ...
subsequent to
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1914–1918) and
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
(1939–1945). It is widely assumed that such a war would involve all of the
great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power inf ...
s, like its predecessors, as well as the use of
nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s or other
weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to numerous individuals or cause great damage to artificial structures (e.g., buildings), natura ...
, thus surpassing prior conflicts in geographic scope, devastation, and loss of life.
Since the
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
's development of nuclear weapons in 1945 and their use by the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
in the
atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August 1945, respectively. The two bombings killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians, and remain the onl ...
at the end of World War II, the risk of a
nuclear apocalypse
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
causing widespread destruction and the potential
collapse of civilization or
extinction of humanity
Human extinction, also known as omnicide, is the hypothetical end of the human species due to either natural causes such as population decline from sub-replacement fertility, an asteroid impact, or large-scale volcanism, or to anthropogenic ( ...
has become a common theme in speculation and fiction about World War III. With the advent of the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
(1947–1991) and spread of nuclear weapons to the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, which was followed by their acquisition by
several other countries, the risk of a third world war rose. During the Cold War, the possibility was anticipated and planned for by military and civil personnel around the world, with scenarios ranging from
conventional warfare to limited or total
nuclear warfare
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a theoretical military conflict or prepared political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conventional warfare, nuclear ...
. The strategic doctrine of
mutually assured destruction, which posited that a full-scale nuclear confrontation would completely annihilate all parties to the conflict, was developed. US and Soviet leaders worked to avoid such an outcome, though
several close calls, caused by faulty technology, human error or miscommunication, still occurred, underscoring the need for restraint by both sides.
Various military conflicts which have occurred since the beginning of the 21st century, most notably the
Russian invasion of Ukraine that has been ongoing since 2022, as well as rising geopolitical tensions between the US and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, have been perceived as potential flashpoints or triggers for a third world war.
Etymology
''Time'' magazine
''
Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to ...
'' magazine was an early adopter, if not originator, of the term "World WarIII". The first usage appears in its 3 November 1941 issue (preceding the Japanese
attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, j ...
on 7 December 1941) under its "National Affairs" section and entitled "World WarIII?" about
Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
refugee
Hermann Rauschning, who had just arrived in the United States.
In its 22 March 1943, issue under its "Foreign News" section, ''Time'' reused the same title "World WarIII?" about statements by then-
US Vice President Henry A. Wallace
Henry Agard Wallace (October 7, 1888 – November 18, 1965) was an American politician, journalist, farmer, and businessman who served as the 33rd vice president of the United States, the 11th U.S. Secretary of Agriculture, and the 10th U.S. S ...
: "We shall decide sometime in 1943 or 1944... whether to plant the seeds of World War III." ''Time'' continued to entitle with or mention in stories the term "World WarIII" for the rest of the decade and onwards: 1944, 1945, 1946 ("bacterial warfare"), 1947, and 1948. ''Time'' persists in using this term, for example, in a 2015 book review entitled "This Is What World War III Will Look Like".
Military plans
Military strategists have used war games to prepare for various war scenarios and to determine the most appropriate strategies. War games were utilized for World War I and World War II.
Operation Unthinkable
British Prime Minister Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
was concerned that, with the enormous size of Soviet
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
forces deployed in
Central and Eastern Europe
Central and Eastern Europe is a term encompassing the countries in the Baltics, Central Europe, Eastern Europe and Southeast Europe (mostly the Balkans), usually meaning former communist states from the Eastern Bloc and Warsaw Pact in Europe. ...
at the
end of World War II and the unreliability of the Soviet leader
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
, there was a serious threat to
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
. In April–May 1945, the
British Armed Forces
The British Armed Forces, also known as His Majesty's Armed Forces, are the military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests, s ...
developed
Operation Unthinkable
Operation Unthinkable was the name given to two related possible future war plans by the British Chiefs of Staff Committee against the Soviet Union in 1945. The plans were never implemented. The creation of the plans was ordered by British Prime ...
, thought to be the first scenario of the Third World War. Its primary goal was "to impose upon Russia the will of the United States and the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
". The plan was rejected by the British
Chiefs of Staff Committee
The Chiefs of Staff Committee (CSC) is composed of the most senior military personnel in the British Armed Forces who advise on operational military matters and the preparation and conduct of military operations. The committee consists of the Ch ...
as militarily unfeasible.
Operation Dropshot
Operation Dropshot was the 1950s United States contingency plan for a possible
nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
and conventional war with the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
in the Western European and Asian theaters. Although the scenario made use of nuclear weapons, they were not expected to play a decisive role.
At the time the
US nuclear arsenal was limited in size, based mostly in the United States, and depended on
bombers for delivery. Dropshot included mission profiles that would have used 300
nuclear bombs and 29,000 high-explosive bombs on 200 targets in 100 cities and towns to wipe out 85% of the Soviet Union's industrial potential in a single stroke. Between 75 and 100 of the 300 nuclear weapons were targeted to destroy Soviet combat aircraft on the ground.
The scenario was devised before the development of
intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
s. It was also devised before
US President
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination i ...
and his
Secretary of Defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
Robert McNamara changed the US Nuclear War plan from the 'city killing'
countervalue
In military doctrine, countervalue is the targeting of an opponent's assets that are of value but not actually a military threat, such as cities and civilian populations. Counterforce is the targeting of an opponent's military forces and faciliti ...
strike plan to a "
counterforce
In nuclear strategy, a counterforce target is one that has a military value, such as a launch silo for intercontinental ballistic missiles, an airbase at which nuclear-armed bombers are stationed, a homeport for ballistic missile submarines, or ...
" plan (targeted more at military forces). Nuclear weapons at this time were not accurate enough to hit a naval base without destroying the city adjacent to it, so the aim of using them was to destroy the enemy's industrial capacity to cripple their war economy.
British-Irish cooperation
The Republic of Ireland started planning for a possible nuclear war in the late 1940s. Co-operation between the United Kingdom and Ireland would be formed in the event of WWIII, where they would share weather data, control aids to navigation, and coordinate the Wartime Broadcasting Service that would occur after a nuclear attack.
in Ireland was a top-secret British-Irish military operation.
The armed forces from both states began a coastal survey of Britain and Ireland cooperating from 1948 to 1955. This was a request from the United States to identify suitable landing grounds for the US in the event of a successful Soviet invasion.
By 1953, the co-operation agreed upon sharing information on wartime weather and the evacuation of civilian refugees from Britain to Ireland.
Ireland's Operation Sandstone ended in 1966.
Exercises Grand Slam, Longstep, and Mainbrace
In January 1950, the
North Atlantic Council approved
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
's military strategy of
containment
Containment was a geopolitical strategic foreign policy pursued by the United States during the Cold War to prevent the spread of communism after the end of World War II. The name was loosely related to the term ''cordon sanitaire'', which was ...
. NATO military planning took on a renewed urgency following the outbreak of the
Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
in the early 1950s, prompting NATO to establish a "force under a centralized command, adequate to deter aggression and to ensure the defense of Western Europe".
Allied Command Europe
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
was established under
General of the Army Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
,
US Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
, on 2 April 1951. The
Western Union Defence Organization
From April 1948, the member states of the Western Union (WU), decided to create a military agency under the name of the Western Union Defence Organisation (WUDO). WUDO was formally established on September 27–28, 1948.
Objective
The objective o ...
had previously carried out
Exercise Verity
Exercise Verity was the only major training exercise of the Western Union (WU). Undertaken in July 1949, it involved 60 warships from the British, French, Belgian and Dutch navies. A contemporary newsreel described this exercise as involving "th ...
, a 1949 multilateral exercise involving naval air strikes and submarine attacks.
Exercise Mainbrace brought together 200 ships and over 50,000 personnel to practice the defense of
Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
and
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
from the Soviet attack in 1952. It was the first major NATO exercise. The exercise was jointly commanded by
Supreme Allied Commander Atlantic
The Supreme Allied Commander Atlantic (SACLANT) was one of two supreme commanders of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO), the other being the Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR). The SACLANT led Allied Command Atlantic was based at ...
Admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet, ...
Lynde D. McCormick
Lynde Dupuy McCormick (August 12, 1895 – August 16, 1956) was a List of United States Navy four-star admirals, four-star admiral in the United States Navy who served as Vice Chief of Naval Operations, vice chief of naval operations from 195 ...
,
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
, and
Supreme Allied Commander Europe
The Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR) is the commander of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's (NATO) Allied Command Operations (ACO) and head of ACO's headquarters, Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE). The commander is ...
General
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of highest military ranks, high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers t ...
Matthew B. Ridgeway,
US Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
, during the autumn of 1952.
The United States, the United Kingdom,
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Denmark, Norway,
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
,
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, and
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
participated.
Exercises Grand Slam and Longstep were naval exercises held in the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
during 1952 to practice dislodging an enemy occupying force and amphibious assault. It involved over 170 warships and 700 aircraft under the overall command of Admiral
Robert B. Carney
Robert Bostwick Carney (March 26, 1895 – June 25, 1990) was an admiral in the United States Navy who served as commander-in-chief of the NATO forces in Southern Europe (1951–1953) and then as Chief of Naval Operations (1953–1954) du ...
. The overall exercise commander, Carney summarized the accomplishments of Exercise Grand Slam by stating: "We have demonstrated that the senior commanders of all four powers can successfully take charge of a mixed task force and handle it effectively as a working unit."
The Soviet Union called the exercises "war-like acts" by NATO, with particular reference to the participation of
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and Denmark and prepared for its military maneuvers in the
Soviet Zone.
[''Time'', 29 September 1952]["NATO Ships Enter Baltic Sea" – ''Sydney Morning Herald'', p. 2]
Exercise Strikeback
Exercise Strikeback was a major NATO naval exercise held in 1957, simulating a response to an all-out Soviet attack on NATO. The exercise involved over 200 warships, 650 aircraft, and 75,000 personnel from the
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
, the United Kingdom's
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
, the
Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the Navy, naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack s ...
, the
French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in t ...
, the
Royal Netherlands Navy
The Royal Netherlands Navy ( nl, Koninklijke Marine, links=no) is the naval force of the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
During the 17th century, the navy of the Dutch Republic (1581–1795) was one of the most powerful naval forces in the world an ...
, and the
Royal Norwegian Navy
The Royal Norwegian Navy ( no, Sjøforsvaret, , Sea defence) is the branch of the Norwegian Armed Forces responsible for naval operations of Norway. , the Royal Norwegian Navy consists of approximately 3,700 personnel (9,450 in mobilized state, 3 ...
. As the largest peacetime naval operation up to that time, Exercise Strikeback was characterized by military analyst
Hanson W. Baldwin
Hanson Weightman Baldwin (March 22, 1903 – November 13, 1991) was an American journalist who was the long-time military editor of ''The New York Times''. He won a Pulitzer Prize "for his coverage of the early days of World War II". He wrote ...
of ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' as "constituting the strongest striking fleet assembled since World WarII".
Exercise Reforger
Exercise Reforger (from the REturn of FORces to GERmany) was an annual exercise conducted during the Cold War by
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
. While US troops could be easily flown across the Atlantic, the heavy equipment and armor reinforcements would have to come by sea and be delivered to POMCUS (Pre-positioned Overseas Material Configured to Unit Sets) sites.
These exercises tested the United States and allied abilities to carry out transcontinental reinforcement.
Timely reinforcement was a critical part of the NATO reinforcement exercises. The United States needed to be able to send active-duty army divisions to Europe within ten days as part of a wartime NATO general deployment.
In addition to assessing the capabilities of the United States, Reforger also monitored the personnel, facilities, and equipment of the European countries playing a significant role in the reinforcement effort.
The exercise was intended to ensure that NATO could quickly deploy forces to West Germany in the event of a conflict with the
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
. The Warsaw Pact outnumbered NATO throughout the Cold War in conventional forces, and especially in tanks and armoured vehicles. Therefore, in the event of a Soviet invasion, in order not to resort to
tactical nuclear strikes, NATO forces defending against a
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
armored spearhead
An armoured spearhead (American English: armored spearhead) is a formation of armoured fighting vehicles, mostly tanks, that form the front of an offensive thrust during a battle. The idea is to concentrate as much firepower into a small front as ...
would have to be quickly resupplied and replaced.
Reforger was not merely a show of force. In the event of a conflict, it would be the actual plan to strengthen the NATO presence in Europe. In that instance, it would have been referred to as Operation Reforger. The political goals of Reforger were to promote extended deterrence and foster NATO cohesion.
Important components in Reforger included the
Military Airlift Command, the
Military Sealift Command
Military Sealift Command (MSC) is an organization that controls the replenishment and military transport ships of the United States Navy. Military Sealift Command has the responsibility for providing sealift and ocean transportation for all US m ...
, and the
Civil Reserve Air Fleet.
Seven Days to the River Rhine
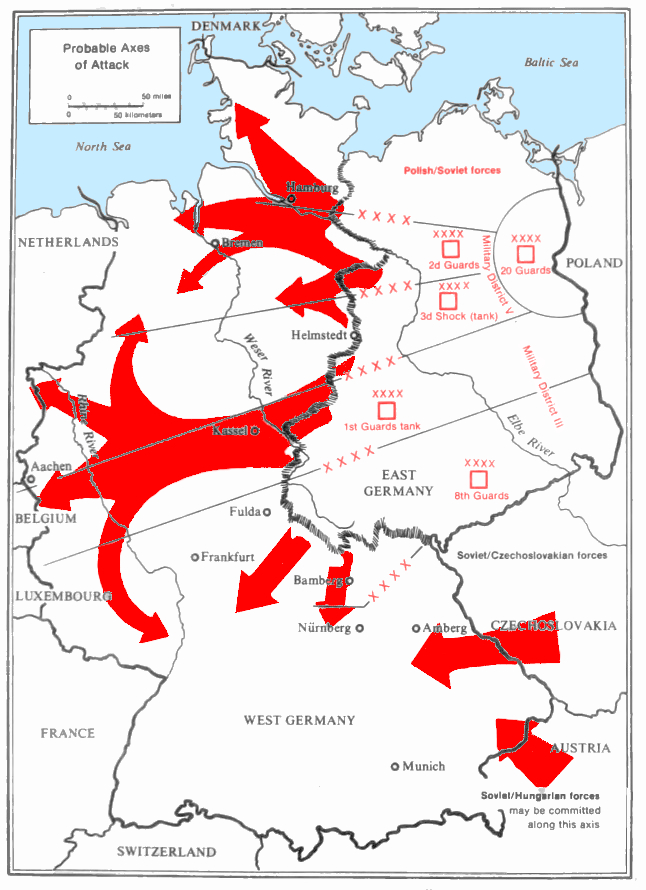
Seven Days to the River Rhine was a top-secret military simulation exercise developed in 1979 by the Warsaw Pact. It started with the assumption that NATO would launch a nuclear attack on the
Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river valley in a first-strike scenario, which would result in as many as two million Polish civilian casualties. In response, a Soviet counter-strike would be carried out against
West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
,
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and
Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
, with Warsaw Pact forces invading West Germany and aiming to stop at the
River Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, sourc ...
by the seventh day. Other USSR plans stopped only upon reaching the
French border on day nine. Individual Warsaw Pact states were only assigned their subpart of the strategic picture; in this case, the Polish forces were only expected to go as far as Germany. The Seven Days to the Rhine plan envisioned that Poland and Germany would be largely destroyed by nuclear exchanges and that large numbers of troops would die of
radiation sickness. It was estimated that NATO would fire nuclear weapons behind the advancing Soviet lines to cut off their supply lines and thus blunt their advance. While this plan assumed that NATO would use nuclear weapons to push back any Warsaw Pact invasion, it did not include nuclear strikes on France or the United Kingdom. Newspapers speculated when this plan was declassified, that France and the UK were not to be hit to get them to withhold the use of their nuclear weapons.
Exercise Able Archer

Exercise Able Archer was an annual exercise by the
US European Command that practiced command and control procedures, with emphasis on the transition from solely conventional operations to chemical, nuclear, and conventional operations during a time of war.
"Able Archer 83" was a five-day
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
command post exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic ...
starting on 7 November 1983, that spanned
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, centered on the
Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) Headquarters in
Casteau, north of the city of
Mons
Mons (; German and nl, Bergen, ; Walloon and pcd, Mont) is a city and municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the province of Hainaut, Belgium.
Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV of Hainaut in the 12th century. T ...
. Able Archer's exercises simulated a period of
conflict escalation
Conflict escalation is the process by which conflicts grow in severity or scale over time. That may refer to conflicts between individuals or groups in interpersonal relationships, or it may refer to the escalation of hostilities in a political or ...
, culminating in a coordinated
nuclear attack
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a theoretical military conflict or prepared political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conventional warfare, nuclear wa ...
.
The realistic nature of the 1983 exercise, coupled with
deteriorating relations between the United States and the Soviet Union and the anticipated arrival of
strategic
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "art of troop leader; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the "art ...
Pershing II
The Pershing II Weapon System was a solid-fuel rocket, solid-fueled multistage rocket, two-stage medium-range ballistic missile designed and built by Martin Marietta to replace the Pershing 1a Field Artillery Missile System as the United States ...
nuclear missiles in Europe, led some members of the
Soviet Politburo and military to believe that Able Archer 83 was a
ruse of war, obscuring preparations for a genuine nuclear first strike.
[Beth Fischer, ''Reagan Reversal'', 123, 131.][Pry, ''War Scare'', 37–9.] In response, the Soviets readied their nuclear forces and placed air units in
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
and
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
on alert.
[''SNIE 11–10–84'' "Implications of Recent Soviet Military-Political Activities" Central Intelligence Agency, 18 May 1984.]
This "1983 war scare" is considered by many historians to be the closest the world has come to nuclear war since the
Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis (of 1962) ( es, Crisis de Octubre) in Cuba, the Caribbean Crisis () in Russia, or the Missile Scare, was a 35-day (16 October – 20 November 1962) confrontation between the United S ...
of 1962. The threat of nuclear war ended with the conclusion of the exercise on 11 November.
[Pry, ''War Scare'', 43–4.]
Strategic Defense Initiative
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) was proposed by US President
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
on 23 March 1983.
Federation of American Scientists
The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) is an American nonprofit global policy think tank with the stated intent of using science and scientific analysis to attempt to make the world more secure. FAS was founded in 1946 by scientists who wo ...
Missile Defense Milestones
. Accessed 10 March 2006. In the latter part of his
presidency
A presidency is an administration or the executive, the collective administrative and governmental entity that exists around an office of president of a state or nation. Although often the executive branch of government, and often personified by a ...
, numerous factors (which included watching the 1983 movie ''
The Day After'' and hearing through a Soviet defector that
Able Archer 83 almost triggered a Russian first strike) had turned Reagan against the concept of winnable nuclear war, and he began to see nuclear weapons as more of a "
wild card" than a strategic deterrent. Although he later believed in
disarmament treaties slowly blunting the danger of nuclear weaponry by reducing their number and alert status, he also believed a technological solution might allow incoming ICBMs to be shot down, thus making the US invulnerable to a first strike. However, the USSR saw the SDI concept as a major threat, since a unilateral deployment of the system would allow the US to launch a massive first strike on the Soviet Union without any fear of retaliation.
The SDI concept was to use ground-based and space-based systems to protect the United States from attack by strategic
nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
ballistic missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within the ...
s. The initiative focused on strategic defense rather than the prior strategic offense doctrine of
mutually assured destruction (MAD). The Strategic Defense Initiative Organization (SDIO) was set up in 1984 within the
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national secu ...
to oversee the Strategic Defense Initiative.
NATO nuclear sharing
NATO operational plans for a Third World War have involved NATO allies who do not have their nuclear weapons, using nuclear weapons supplied by the United States as part of a general NATO war plan, under the direction of NATO's
Supreme Allied Commander
Supreme Allied Commander is the title held by the most senior commander within certain multinational military alliances. It originated as a term used by the Allies during World War I, and is currently used only within NATO for Supreme Allied Comm ...
.
Of the three nuclear powers in NATO (France, the United Kingdom, and the United States) only the United States has provided weapons for nuclear sharing. ,
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
,
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
are still hosting US nuclear weapons as part of NATO's nuclear sharing policy.
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
hosted weapons until 1984,
and
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
until 2001.
The
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
also received US tactical nuclear weapons such as
nuclear artillery
Nuclear artillery is a subset of limited- yield tactical nuclear weapons, in particular those weapons that are launched from the ground at battlefield targets. Nuclear artillery is commonly associated with shells delivered by a cannon, but in ...
and
Lance missile
The MGM-52 Lance was a mobile field artillery tactical surface-to-surface missile (tactical ballistic missile) system used to provide both W70, nuclear and conventional fire support to the United States Army. The missile's warhead was developed ...
s until 1992, despite the UK being a
nuclear weapons state
Eight sovereign states have publicly announced successful detonation of nuclear weapons. Five are considered to be nuclear-weapon states (NWS) under the terms of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT). In order of acquisit ...
in its own right; these were mainly deployed in
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
.
In
peace
Peace is a concept of societal friendship and harmony in the absence of hostility and violence. In a social sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict (such as war) and freedom from fear of violence between individuals or groups. ...
time, the nuclear weapons stored in non-nuclear countries are guarded by
US airmen though previously some artillery and missile systems were guarded by US Army soldiers; the codes required for detonating them are under American control. In case of war, the weapons are to be mounted on the participating countries' warplanes. The weapons are under custody and control of
USAF Munitions Support Squadrons co-located on NATO main operating bases that work together with the host nation forces.
180 tactical
B61 nuclear bombs of the 480 US nuclear weapons believed to be deployed in Europe fall under the nuclear sharing arrangement. The weapons are stored within a vault in
hardened aircraft shelters, using the
USAF WS3 Weapon Storage and Security System
Weapons Storage and Security System (WS3) is a system including electronic controls and vaults built into the floors of Protective Aircraft Shelters (PAS) on several NATO military airfields all over the world. These vaults are used for safe spe ...
. The delivery warplanes used are
F-16 Fighting Falcons and
Panavia Tornado
The Panavia Tornado is a family of twin-engine, variable-sweep wing multirole combat aircraft, jointly developed and manufactured by Italy, the United Kingdom and West Germany. There are three primary Tornado variants: the Tornado IDS (inter ...
s.
Historical close calls
With the initiation of the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
arms race
An arms race occurs when two or more groups compete in military superiority. It consists of a competition between two or more states to have superior armed forces; a competition concerning production of weapons, the growth of a military, and t ...
in the 1950s, an
apocalyptic war between the United States and the Soviet Union became a real possibility. During the Cold War era (1947–1991), several military events have been described as having come close to potentially triggering World WarIII. Even after the end of the Cold War and the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, some incidents afterward have been described as close calls as well.
Korean War: 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953
The
Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
was a war between two coalitions fighting for control over the
Korean Peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
: a communist coalition including
North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Y ...
, the People's Republic of China, and the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, and a capitalist coalition including
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, the United States and the
United Nations Command
United Nations Command (UNC or UN Command) is the multinational military force established to support the South Korea, Republic of Korea (South Korea) during and after the Korean War. It was the first international unified command in history, an ...
. Many then believed that the conflict was likely to soon escalate into a full-scale war between the three countries, the US, the USSR, and China.
CBS News
CBS News is the news division of the American television and radio service CBS. CBS News television programs include the ''CBS Evening News'', ''CBS Mornings'', news magazine programs '' CBS News Sunday Morning'', '' 60 Minutes'', and '' 48 H ...
war correspondent
Bill Downs wrote in 1951, "To my mind, the answer is: Yes, Korea is the beginning of World WarIII. The brilliant
landings at Inchon and the cooperative efforts of the
American armed forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
with the
United Nations Allies have won us a victory in Korea. But this is only the first battle in a major international struggle which now is engulfing the Far East and the entire world." Downs afterwards repeated this belief on ''
ABC Evening News
''ABC World News Tonight'' (titled ''ABC World News Tonight with David Muir'' for its weeknight broadcasts since September 2014) is the flagship daily evening television news program of ABC News, the news division of the American Broadcasting ...
'' while reporting on the
USS ''Pueblo'' incident in 1968. Secretary of State
Dean Acheson
Dean Gooderham Acheson (pronounced ; April 11, 1893October 12, 1971) was an American statesman and lawyer. As the 51st U.S. Secretary of State, he set the foreign policy of the Harry S. Truman administration from 1949 to 1953. He was also Truman ...
later acknowledged that the
Truman administration was concerned about the escalation of the conflict and that General
Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was C ...
warned him that a US-led intervention risked a Soviet response.
Berlin Crisis: 4 June – 9 November 1961
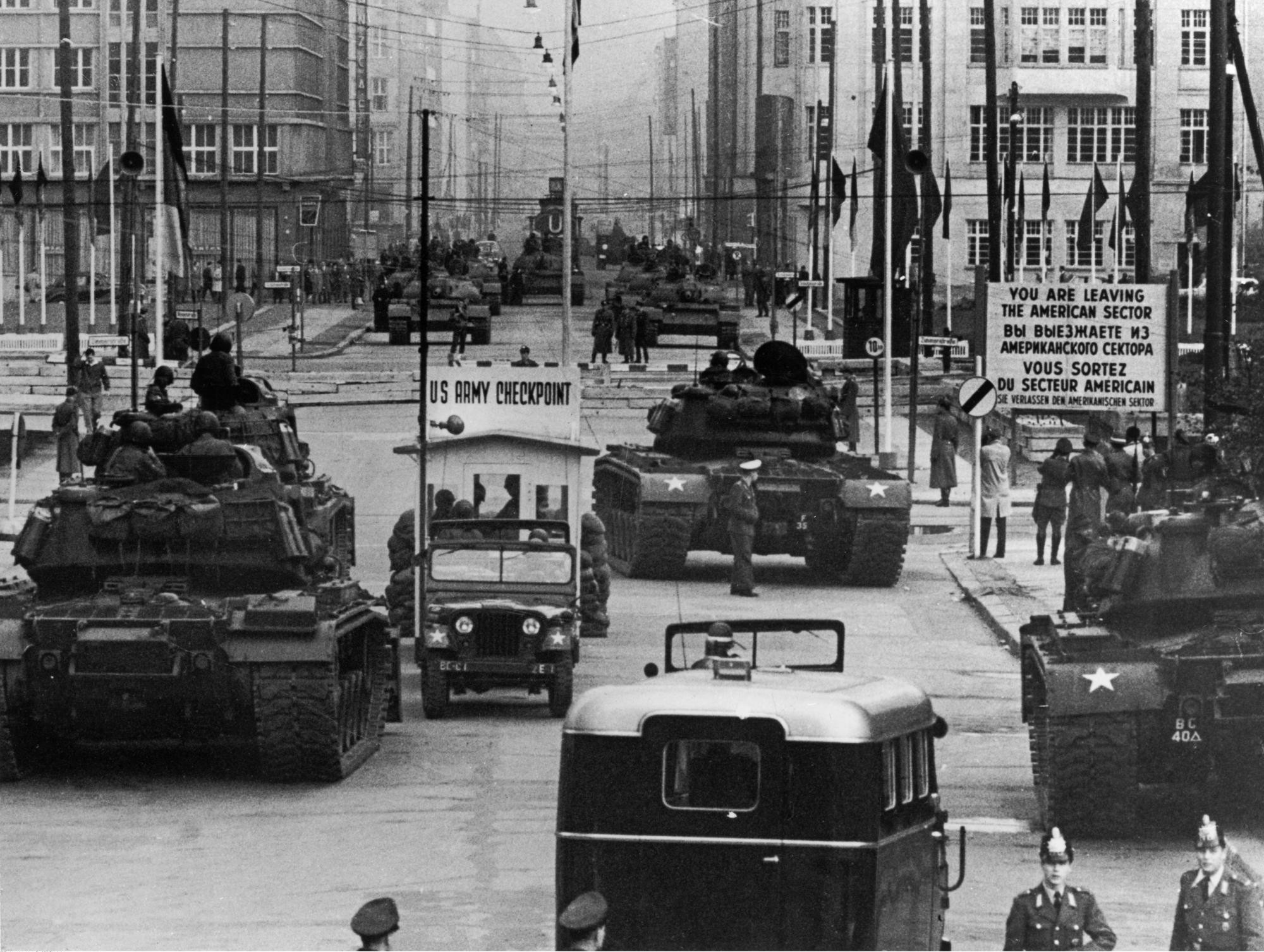

The
Berlin Crisis of 1961
The Berlin Crisis of 1961 (german: Berlin-Krise) occurred between 4 June – 9 November 1961, and was the last major European politico-military incident of the Cold War about the occupational status of the German capital city, Berlin, and of po ...
was a political-military confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union at
Checkpoint Charlie with both several American and Soviet/East German tanks and troops at the stand-off at each other only 100 yards on either side of the checkpoint. The reason behind the confrontation was the occupational status of the German capital city,
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
, and of
post–World War II Germany. The Berlin Crisis started when the USSR launched an ultimatum demanding the withdrawal of all armed forces from Berlin, including the Western armed forces in
West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under mi ...
. The crisis culminated in the city's de facto partition with the
East German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
erection of the
Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (german: Berliner Mauer, ) was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and East Germany (GDR). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the government ...
. This stand-off ended peacefully on 28 October following a US–Soviet understanding to withdraw tanks and reduce tensions.
Cuban Missile Crisis: 15–29 October 1962

The
Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis (of 1962) ( es, Crisis de Octubre) in Cuba, the Caribbean Crisis () in Russia, or the Missile Scare, was a 35-day (16 October – 20 November 1962) confrontation between the United S ...
, a confrontation on the stationing of Soviet nuclear missiles in Cuba in response to the failed
Bay of Pigs Invasion
The Bay of Pigs Invasion (, sometimes called ''Invasión de Playa Girón'' or ''Batalla de Playa Girón'' after the Playa Girón) was a failed military landing operation on the southwestern coast of Cuba in 1961 by Cuban exiles, covertly fina ...
, is considered as having been the closest to a nuclear exchange, which could have precipitated a third World War. The crisis peaked on 27 October, with three separate major incidents occurring on the same day:
* The most critical incident occurred when a Soviet submarine nearly launched a
nuclear-tipped torpedo in response to having been targeted by American naval
depth charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon. It is intended to destroy a submarine by being dropped into the water nearby and detonating, subjecting the target to a powerful and destructive Shock factor, hydraulic shock. Most depth ...
s in international waters, with the Soviet nuclear launch response only having been prevented by
Soviet Navy executive officer
An executive officer is a person who is principally responsible for leading all or part of an organization, although the exact nature of the role varies depending on the organization. In many militaries and police forces, an executive officer, o ...
Vasily Arkhipov.
* The shooting down of a
Lockheed U-2
The Lockheed U-2, nicknamed "''Dragon Lady''", is an American single-jet engine, high altitude reconnaissance aircraft operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) and previously flown by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). It provides day ...
spy plane piloted by
Rudolf Anderson
Rudolf Anderson Jr. (September 15, 1927 – October 27, 1962) was an American and United States Air Force major and pilot. He was the first recipient of the Air Force Cross, the U.S. military's and Air Force's second-highest award and decoratio ...
while violating Cuban airspace.
* The near interception of another U-2 that had strayed into Soviet airspace over
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
, which airspace violation nearly caused the Soviets to believe that this might be the vanguard of a US aerial bombardment.
Despite what many believe to be the closest the world has come to a nuclear conflict, throughout the entire standoff, the
Doomsday Clock
The Doomsday Clock is a symbol that represents the likelihood of a man-made global catastrophe, in the opinion of the members of the ''Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists''. Maintained since 1947, the clock is a metaphor for threats to humanity ...
, which is run by the ''
Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists'' to estimate how close the end of the world, or doomsday, is, with midnight being the apocalypse, stayed at a relatively stable seven minutes to midnight. This has been explained as being due to the brevity of the crisis since the clock monitored more long-term factors such as the leadership of countries, conflicts, wars, and political upheavals, as well as societies' reactions to said factors.
The ''Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists'' now credits the political developments resulting from the Cuban Missile Crisis with having enhanced global stability. The ''Bulletin'' posits that future crises and occasions that might otherwise escalate, were rendered more stable due to two major factors:
# A
Washington to Moscow direct telephone line, resulted from the communication trouble between the
White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. ...
and the
Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, Московский Кремль, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=ˈmɐˈskofskʲɪj krʲemlʲ, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty, Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of th ...
during the crisis, giving the leaders of the two largest nuclear powers the ability to contact each other in real-time, rather than sending written messages that needed to be translated and wired, which had dragged out conversations in which seconds could have potentially prevented a nuclear exchange.
# The second factor was caused in part due to the worldwide reaction to how close the US and USSR had come to the brink of World WarIII during the standoff. As the public began to more closely monitor topics involving nuclear weapons, and therefore to rally support for the cause of non-proliferation, the
1963 test ban treaty was signed. To date this treaty has been signed by 126 total nations, with the most notable exceptions being
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Both of these countries were still in the relative beginning stages of their nuclear programs at the time of the original treaty signing, and both sought nuclear capabilities independent of their allies. This Test Ban Treaty prevented the testing of nuclear ordnance that detonated in the
atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
, limiting
nuclear weapons testing to below ground and underwater, decreasing
fallout
Nuclear fallout is the residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast, so called because it "falls out" of the sky after the explosion and the shock wave has passed. It commonly refers to the radioac ...
and effects on the environment, and subsequently caused the Doomsday Clock to decrease by five minutes, to arrive at a total of twelve minutes to midnight. Up until this point, over 1000 nuclear bombs had been detonated, and concerns over both long and short term effects to the planet became increasingly more worrisome to scientists.
Sino-Soviet border conflicts: 2 March – 11 September 1969
The
Sino-Soviet border conflict
The Sino-Soviet border conflict was a seven-month undeclared military conflict between the Soviet Union and China in 1969, following the Sino-Soviet split. The most serious border clash, which brought the world's two largest communist states to ...
was a seven-month undeclared military border war between the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
at the height of the
Sino-Soviet split in 1969. The most serious of these border clashes, which brought the world's two largest
communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state that is administered and governed by a communist party guided by Marxism–Leninism. Marxism–Leninism was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, the Comint ...
s to the brink of war, occurred in March 1969 in the vicinity of
Zhenbao (Damansky) Island on the
Ussuri (Wusuli) River, near
Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer Manc ...
.
The conflict resulted in a ceasefire, with a return to the status quo. Critics point out that the Chinese attack on Zhenbao was to deter any potential future Soviet invasions; that by killing some Soviets, China demonstrated that it could not be 'bullied'; and that Mao wanted to teach them 'a bitter lesson'.
China's relations with the USSR remained sour after the conflict, despite the border talks, which began in 1969 and continued inconclusively for a decade. Domestically, the threat of war caused by the border clashes inaugurated a new stage in the
Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goal ...
; that of China's thorough militarization. The
9th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, held in the aftermath of the
Zhenbao Island incident
The Sino-Soviet border conflict was a seven-month undeclared military conflict between the Soviet Union and China in 1969, following the Sino-Soviet split. The most serious border clash, which brought the world's two largest communist states t ...
, confirmed Defense Minister
Lin Biao as
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
's heir apparent.
Following the events of 1969, the Soviet Union further increased its
forces along the
Sino-Soviet border, and in the
Mongolian People's Republic.
Yom Kippur War superpower tensions: 6–25 October 1973
The
Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was an armed conflict fought from October 6 to 25, 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egy ...
, also known as the Ramadan War, or October War, began with a surprise invasion of
Israeli-occupied territories
Israeli-occupied territories are the lands that were captured and occupied by Israel during the Six-Day War of 1967. While the term is currently applied to the Palestinian territories and the Golan Heights, it has also been used to refer to a ...
by a coalition of Arab states, aided by the Soviet Union. Israel successfully counterattacked with the aid of the US. Tensions grew between the two superpowers: American and Soviet naval forces came close to firing upon each other in the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. Admiral
Daniel J. Murphy
Daniel Joseph Murphy Sr. (March 24, 1922 – September 21, 2001) was a four-star Admiral (United States), admiral in the United States Navy and an official in the Jimmy Carter, Carter and Ronald Reagan, Reagan administrations.
Murphy grew up in ...
of the
US Sixth Fleet reckoned the chances of the Soviet squadron attempting a first strike against his fleet at 40 percent. The Pentagon moved Defcon status from 4to3. The superpowers had been pushed to the brink of war, but tensions eased with the ceasefire brought in under
UNSC 339.
NORAD computer error of 1979: 9 November 1979
The United States made emergency retaliation preparations after
NORAD
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection ...
systems indicated that a full-scale Soviet attack had been launched. No attempt was made to use the
Moscow–Washington hotline
The Moscow–Washington hotline (formally known in the United States as the Washington–Moscow Direct Communications Link; rus, Горячая линия Вашингтон — Москва, r=Goryachaya liniya Vashington–Moskva) is a system t ...
to clarify the situation with the USSR and it was not until early-warning radar systems confirmed no such launch had taken place that NORAD realized that a computer system test had caused the display errors. A senator inside the NORAD facility at the time described an atmosphere of absolute panic. A GAO investigation led to the construction of an off-site test facility to prevent similar mistakes.
Soviet radar malfunction: 26 September 1983
A false alarm occurred on the
Soviet nuclear early warning system, showing the launch of American
LGM-30 Minuteman
The LGM-30 Minuteman is an American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) in service with the Air Force Global Strike Command. , the LGM-30G Minuteman III version is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States and r ...
intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
s from bases in the United States. A retaliatory attack was prevented by
Stanislav Petrov, a
Soviet Air Defence Forces
The Soviet Air Defence Forces (russian: войска ПВО, ''voyska protivovozdushnoy oborony'', ''voyska PVO'', ''V-PVO'', lit. ''Anti-Air Defence Troops''; and formerly ''protivovozdushnaya oborona strany'', ''PVO strany'', lit. ''Anti-Air De ...
officer, who realised the system had simply malfunctioned (which was borne out by later investigations).
Able Archer 83 escalations: 2–11 November 1983
During
Able Archer 83, a ten-day
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
exercise simulating a period of
conflict escalation
Conflict escalation is the process by which conflicts grow in severity or scale over time. That may refer to conflicts between individuals or groups in interpersonal relationships, or it may refer to the escalation of hostilities in a political or ...
that culminated in a
DEFCON 1
The defense readiness condition (DEFCON) is an alert state used by the United States Armed Forces. (DEFCON is not mentioned in the 2010 and newer document)
The DEFCON system was developed by the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) and unified and spec ...
nuclear strike, some members of the
Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
Politburo
A politburo () or political bureau is the executive committee for communist parties. It is present in most former and existing communist states.
Names
The term "politburo" in English comes from the Russian ''Politbyuro'' (), itself a contraction ...
and
armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
treated the events as a
ruse of war concealing a genuine first strike. In response, the military prepared for a coordinated counter-attack by readying nuclear forces and placing air units stationed in the
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
states of
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
and
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
under high alert. However, the state of Soviet preparation for retaliation ceased upon completion of the Able Archer exercises.
Norwegian rocket incident: 25 January 1995
The
Norwegian rocket incident was the first World WarIII close call to occur outside the Cold War. This incident occurred when Russia's
Olenegorsk early warning station accidentally mistook the radar signature from a
Black Brant XII
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were firs ...
research rocket
A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are used to ...
(being jointly launched by Norwegian and US scientists from
Andøya Rocket Range), as appearing to be the radar signature of the launch of a
Trident
A trident is a three- pronged spear. It is used for spear fishing and historically as a polearm.
The trident is the weapon of Poseidon, or Neptune, the God of the Sea in classical mythology. The trident may occasionally be held by other marine ...
SLBM
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from Ballistic missile submarine, submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of whic ...
missile. In response,
Russian President Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
was summoned and the ''
Cheget''
nuclear briefcase was activated for the first and only time. However, the high command was soon able to determine that the rocket was not entering Russian airspace, and promptly aborted plans for combat readiness and retaliation. It was retrospectively determined that, while the rocket scientists had informed thirty states including Russia about the test launch, the information had not reached Russian radar technicians.
Incident at Pristina airport: 12 June 1999
On 12 June 1999, the day following the end of the
Kosovo War
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the war ...
, some 250 Russian peacekeepers occupied the
Pristina International Airport
Prishtina International Airport Adem Jashari ( sq, Aeroporti Ndërkombëtar i Prishtinës Adem Jashari, ), also referred to as Pristina International Airport ( sq, Aeroporti Ndërkombëtar i Prishtinës), is an international airport in Prishtina ...
ahead of the arrival of
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
troops and were to secure the arrival of reinforcements by air. American NATO Supreme Allied Commander Europe General
Wesley Clark ordered the use of force against the Russians.
, a
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
general who contacted the Russians during the incident, refused to enforce Clark's orders, famously telling him "I'm not going to start the Third World War for you".
Captain
James Blunt
James Blunt (born James Hillier Blount; 22 February 1974) is an English singer, songwriter and musician. A former reconnaissance officer in the Life Guards regiment of the British Army, he served under NATO during the 1999 Kosovo War. After l ...
, the lead officer at the front of the NATO column in the direct armed stand-off against the Russians, received the "Destroy!" orders from Clark over the radio, but he followed Jackson's orders to encircle the airfield instead and later said in an interview that even without Jackson's intervention he would have refused to follow Clark's order.
Shootdown of Sukhoi bomber: 24 November 2015
On 24 November 2015, at the border between Turkey and Syria, the
Turkish Air Force shot down a Russian
Sukhoi attack aircraft. The Turks claimed that the aircraft violated Turkish
airspace
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as aerospace, which is the ...
, a claim denied by the Russians; the plane was in the region as part of the
, in which Turkey supported opposing forces. The incident was the first destruction of a
Russian or
Soviet Air Forces
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
warplane by a
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
member state since the
attack on the Sui-ho Dam
The attack on the Sui-ho Dam was the collective name for a series of mass air attacks during the Korean War on thirteen hydroelectric generating facilities by United Nations Command air forces as part of the North Korean bombing campaign on Ju ...
during the Korean War in 1953.
The incident led to numerous media and individuals commenting that it could have sparked and escalated into a world war.
Current conflicts deemed a risk
Russian invasion of Ukraine: 24 February 2022 – present
On 24 February 2022, Russia's president
Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime min ...
ordered a full-scale invasion of
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, marking a major escalation of the
Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatist forces in Donbas, Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since Feb ...
, which began in 2014. The invasion has been described as the largest military conflict in Europe since World War II. The invasion received widespread
international condemnation, including new
sanctions imposed on Russia, which notably included Russia's ban from
SWIFT and the closing of most Western airspace to Russian planes. Moreover, both prior to and during the invasion, some of the 32
member states of NATO
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) is an international military alliance that consists of 30 member states from Europe and North America. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article 5 of the ...
have been providing Ukraine with arms and other
materiel
Materiel (; ) refers to supplies, equipment, and weapons in military supply-chain management, and typically supplies and equipment in a commercial supply chain context.
In a military context, the term ''materiel'' refers either to the specifi ...
support. Throughout the invasion, several senior Russian politicians, including president Putin, foreign minister
Sergey Lavrov and
United Russia
United Russia ( rus, Единая Россия, Yedinaya Rossiya, (j)ɪˈdʲinəjə rɐˈsʲijə) is a Conservatism in Russia, Russian conservative List of political parties in Russia, political party. As the largest party in Russia, it hold ...
party leader
Dmitry Medvedev
Dmitry Anatolyevich Medvedev ( rus, links=no, Дмитрий Анатольевич Медведев, p=ˈdmʲitrʲɪj ɐnɐˈtolʲjɪvʲɪtɕ mʲɪdˈvʲedʲɪf; born 14 September 1965) is a Russian politician who has been serving as the dep ...
, have made a number of statements widely seen as threatening the use of nuclear weapons, while several officials from the United States and NATO, including US president
Joe Biden and NATO secretary general
Jens Stoltenberg
Jens Stoltenberg (born 16 March 1959) is a Norwegian politician who has been serving as the 13th secretary general of NATO since 2014. A member of the Norwegian Labour Party, he previously served as the 34th prime minister of Norway from 2000 to ...
, have made statements reaffirming NATO's response in the event that Russia attacks any NATO member state or uses nuclear weapons, while also reiterating the need to prevent the crisis from escalating into a potential third world war. A number of incidents seen as a close call to an open conflict between Russia and NATO have since occurred, most notably
a missile strike on the Polish village of
Przewodów
Przewodów () is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Dołhobyczów, within Hrubieszów County, Lublin Voivodeship, in southeastern Poland, close to the border with Ukraine. It lies approximately southwest of Dołhobyczów, south o ...
near the border with Ukraine in November 2022.
In early 2023, Putin suspended Russia's participation in
New START
New START (Russian abbrev.: СНВ-III, ''SNV-III'' from ''сокращение стратегических наступательных вооружений'' "reduction of strategic offensive arms") is a nuclear arms reduction treaty between ...
, the last remaining nuclear treaty between Russia and the US, and later announced plans to install Russian tactical nuclear weapons in
Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
.
Various experts, analysts, and others have described the crisis as a close call to a third world war, while others have suggested the contrary.
Extended usage of the term
Cold War

As Soviet-American relations grew tense in the post-World WarII period, the fear that the tension could escalate into World WarIII was ever-present. A
Gallup poll in December 1950 found that more than half of Americans considered World WarIII to have already started.
In 2004, commentator
Norman Podhoretz
Norman Podhoretz (; born January 16, 1930) is an American magazine editor, writer, and conservative political commentator, who identifies his views as " paleo-neoconservative". proposed that the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, lasting from the surrender of the
Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
until the
fall of the Berlin Wall, might rightly be called World WarIII. By Podhoretz's reckoning, "World WarIV" would be the global campaign against
Islamofascism
"Islamofascism", first described as "Islamic fascism" in 1933, is a term popularized in the 1990s drawing an analogical comparison between the ideological characteristics of specific Islamist or Islamic fundamentalist movements and short-lived E ...
.
Still, the majority of historians would seem to hold that World WarIII would necessarily have to be a worldwide "war in which large forces from many countries fought" and a war that "involves most of the principal nations of the world". The Cold War received its name from the lack of action taken from both sides. The lack of action was out of fear that a nuclear war would possibly destroy humanity. In his book ''Secret Weapons of the Cold War'', Bill Yenne explains that the military standoff that occurred between the two 'Superpowers', namely the United States and the Soviet Union, from the 1940s through to 1991, was only the Cold War, which ultimately helped to enable mankind to avert the possibility of an all-out nuclear confrontation, and that it certainly was not World WarIII.
War on terror

The "
war on terror
The war on terror, officially the Global War on Terrorism (GWOT), is an ongoing international Counterterrorism, counterterrorism military campaign initiated by the United States following the September 11 attacks. The main targets of the campa ...
" that began with the
September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercia ...
has been claimed by some to be World War III or sometimes as World War IV
(assuming the Cold War was World War III). Others have disparaged such claims as "distorting
American history
The history of the lands that became the United States began with the arrival of the first people in the Americas around 15,000 BC. Numerous indigenous cultures formed, and many saw transformations in the 16th century away from more densely ...
". While there is general agreement amongst historians regarding the definitions and extent of the first two world wars, namely due to the unmistakable global scale of aggression and self-destruction of these two wars, a few have claimed that a "World War" might now no longer require such worldwide and large-scale aggression and carnage. Still, such claims of a new "lower threshold of aggression", that might now be sufficient to qualify a war as a "World War" have not gained such widespread acceptance and support as the definitions of the first two world wars have received amongst historians.
War on the Islamic State
On 1 February 2015,
Iraqi Foreign Minister Ibrahim al-Jaafari declared that the
war against the Islamic State
In response to rapid territorial gains made by the so-called Islamic State during the first half of 2014, and its universally condemned executions, reported human rights abuses and the fear of further spillovers of the Syrian Civil War, many st ...
was effectively "World WarIII", due to the Islamic State's aims for a worldwide caliphate, and its success in spreading the conflict to multiple countries outside of the
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
region. In response to the
November 2015 Paris attacks
The November 2015 Paris attacks () were a series of coordinated Islamist terrorist attacks that took place on Friday, 13 November 2015 in Paris, France, and the city's northern suburb, Saint-Denis. Beginning at 9:15p.m., three suicide bombers ...
,
King of Jordan Abdullah II stated "We are facing a Third World War
ithin Islam">Islam.html" ;"title="ithin Islam">ithin Islam.
In his 2016 State of the Union Address">State of the Union Address on 12 January 2016, US President Barack Obama warned that news reports granting ISIL the supposed ability to foment a third World War might be excessive and irresponsible, stating that "as we focus on destroying ISIL, over-the-top claims that this is World WarIII just play into their hands. Masses of fighters on the back of pickup trucks and twisted souls plotting in apartments or garages pose an enormous danger to civilians and must be stopped. But they do not threaten our national existence."
Multiple small wars as a "third war"
In multiple recorded interviews under somewhat casual circumstances, comparing the conflagrations of World WarI andII to the ongoing lower-intensity wars of the 21st century,
Pope Francis
Pope Francis ( la, Franciscus; it, Francesco; es, link=, Francisco; born Jorge Mario Bergoglio, 17 December 1936) is the head of the Catholic Church. He has been the bishop of Rome and sovereign of the Vatican City State since 13 March 2013. ...
has said, "The world is at war because it has lost the peace", and "perhaps one can speak of a third war, one fought piecemeal".
Hypothetical scenarios

In 1949, after the unleashing of nuclear weaponry at the end of World War II, physicist
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
suggested that any outcome of a possible World War III would be so dire as to revert mankind to the
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
. When asked by journalist Alfred Werner what types of weapons Einstein believed World WarIII might be fought with, Einstein warned, "I know not with what weapons World WarIII will be fought, but World WarIV will be fought with sticks and stones".
[''The New Quotable Einstein''. Alice Calaprice (2005), p. 173.]
As for the extermination of the human race as a consequence of atomic war,
Leslie A. White challenged Einstein, "this too may be admitted as possibility, and all we can say is that if it is to come, it will come. Extravagant expressions of horror will not alter the course of events."
Crane Brinton also doubted the psychological pacification of Einstein: "Teachers, preachers, educators, even politicians are telling the growing generation that there must be no war and, therefore, there will be no war. I have doubts as to whether this is wise teaching…" In spite of the atomic bomb, there will be another general war and humanity will survive it.
James Burnham of the
Office of Strategic Services
The Office of Strategic Services (OSS) was the intelligence agency of the United States during World War II. The OSS was formed as an agency of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) to coordinate espionage activities behind enemy lines for all branc ...
(the precursor to the
CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian intelligence agency, foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gat ...
), also believed in survival: The uniqueness of the atomic weapons is commonly found in that they can totally annihilate human life, including through climatic and geological chain reaction, but such is not the case. The great principles of military strategy stand unaltered. An atomic war will look different from older wars but it will be decided by the same combination of resources, morale and strategy.
A 1998 ''
New England Journal of Medicine'' overview found that "Although many people believe that the threat of a nuclear attack largely disappeared with the end of the Cold War, there is considerable evidence to the contrary".
In particular, the
United States–Russia mutual detargeting agreement in 1994 was largely symbolic and did not change the amount of time required to launch an attack. The most likely "accidental-attack" scenario was believed to be a
retaliatory launch due to a false warning, similar to the 1983 incident.
Historically, World War I happened through an escalating crisis; World War II happened through deliberate action. Hypothesized flashpoints in the 2010s and the 2020s include the
Russian invasion of Ukraine,
Chinese expansion into adjacent islands and seas,
Sino-Indian border dispute
The Sino-Indian border dispute is an ongoing territorial dispute over the sovereignty of two relatively large, and several smaller, separated pieces of territory between China and India. The first of the territories, Aksai Chin, is administe ...
,
Chinese threats of military operation against Taiwan,
Indo-Pakistani wars border conflicts, and
foreign involvement in the Syrian civil war. Other hypothesized risks are that a war involving or between
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
and
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
,
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and Iran,
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and Iran,
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
,
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
,
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
and
Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
,
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
and
North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Y ...
, or
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
could escalate via alliances or intervention into a war between "great powers" such as the United States, United Kingdom, France, Germany, Russia, China, India, Japan or an all out war between military alliances
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
and
CSTO
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The Collective Security Treaty has ...
, or even the possibility of a "rogue commander" under any nuclear power might launch an unauthorized strike that escalates into a full-blown war.
According to a peer-reviewed study published in the journal ''
Nature Food
''Nature Food'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Nature Portfolio. It was established in 2020. The editor-in-chief is Anne Mullen.
Abstracting and indexing
The journal is abstracted and indexed in:
* Science Citation Inde ...
'' in August 2022, a full-scale nuclear war between the United States and Russia, releasing over 150 Tg of stratospheric soot, could indirectly kill more than five billion people by
starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, dea ...
during a
nuclear winter
Nuclear winter is a severe and prolonged global climatic cooling effect that is hypothesized to occur after widespread firestorms following a large-scale nuclear war. The hypothesis is based on the fact that such fires can inject soot into th ...
. More than two billion people could die of starvation from a smaller-scale (5–47 Tg) nuclear war between India and Pakistan. In the event of a nuclear war between Russia and the United States, 99% of the population in the belligerent countries, as well as Europe and China, would die.
Some scenarios involve risks due to upcoming changes from the known status quo. In the 1980s the
Strategic Defense Initiative
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons (intercontinental ballistic ...
made an effort at nullifying the USSR's nuclear arsenal; some analysts believe the initiative was "destabilizing". In his book ''Destined for War'',
Graham Allison
Graham Tillett Allison Jr. (born March 23, 1940) is an American political scientist and the Douglas Dillon Professor of Government at the John F. Kennedy School of Government at Harvard University. He is renowned for his contribution in the late ...
views the global rivalry between the established power, the US, and the rising power, China, as an example of the
Thucydides Trap. Allison states that historically, "12 of 16 past cases where a rising power has confronted a ruling power" have led to fighting. In 2020 and 2023, the ''Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists'' advanced its Doomsday Clock, citing among other factors a predicted destabilizing effect from upcoming
hypersonic weapons
Hypersonic weapons are weapons travelling at hypersonic speed – at between 5 and 25 times the speed of sound, about .
Below such speeds, weapons would be characterized as subsonic or supersonic, while above such speeds, the molecules of the ...
.
Emerging technologies, such as
artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech re ...
, could hypothetically generate risk in the decades ahead. A 2018
RAND Corporation
The RAND Corporation (from the phrase "research and development") is an American nonprofit global policy think tank created in 1948 by Douglas Aircraft Company to offer research and analysis to the United States Armed Forces. It is financed ...
report has argued that AI and associated information technology "will have a large effect on nuclear-security issues in the next quarter century". A hypothetical future AI could provide a destabilizing ability to track "second-launch" launchers. Incorporating AI into decision support systems used to decide whether to launch, could also generate new risks, including the risk of an
adversarial exploitation of such an AI's algorithms by a third party to trigger a launch recommendation. A perception that some sort of emerging technology would lead to "world domination" might also be destabilizing, for example by leading to fear of a pre-emptive strike.
Cyber warfare is the exploitation of technology by a nation-state or international organization to attack and destroy the opposing nation's information networks and computers. The damage can be caused by computer viruses or denial-of-service attacks (DoS). Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly common, threatening cybersecurity and making it a global priority.
There has been a proliferation of state-sponsored attacks. The trends of these attacks suggest the potential of a cyber World War III.
The world's leading militaries are developing cyber strategies, including ways to alter the enemy's command and control systems, early warning systems, logistics, and transportation.
The 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine has sparked concerns about a large-scale cyberattack, with Russia having previously launched cyberattacks to compromise organizations across Ukraine. Nearly 40 discrete attacks were launched by Russia which permanently destroyed files in hundreds of systems across dozens of organizations, with 40% aimed at critical infrastructure sectors in Ukraine.
Russia's use of cyberwarfare has turned the war into a large-scale "hybrid" war in Ukraine.
[
]
See also
* Anti-nuclear movement
The anti-nuclear movement is a social movement that opposes various nuclear technologies. Some direct action groups, environmental movements, and professional organisations have identified themselves with the movement at the local, nationa ...
* Artificial intelligence arms race A military artificial intelligence arms race is a competition or arms race between two or more states to have their military forces equipped with the best artificial intelligence (AI). Since the mid-2010s many analysts have noted the emergence of su ...
* Artificial Intelligence Cold War
The Artificial Intelligence Cold War (AI Cold War) is a narrative in which tensions between the United States and the People's Republic of China lead to a second Cold War waged in the area of artificial intelligence technology rather than in t ...
* Nuclear arms race
* Nuclear holocaust
* Nuclear terrorism
* Second Cold War
The Second Cold War,
Cold War II,
or the New Cold War
are terms that refer to heightened political, social, ideological, informational, and military tensions in the 21st century. The term is used in the context of the tensions between th ...
* World War III in popular culture
* War
* World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
* World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
References
Further reading
* Huntington, Samuel (1996). '' The Clash of Civilizations and the Remaking of World Order'' Simon & Schuster, New York. .
*
* Mearsheimer, John (2001). ''The Tragedy of Great Power Politics
''The Tragedy of Great Power Politics'' is a book by the American scholar John Mearsheimer on the subject of international relations theory published by W.W. Norton & Company in 2001. Mearsheimer explains and argues for his theory of "offensive ...
''. W. W. Norton, New York. .
*
* Piepers, Ingo (2016).
2020: WARning
'. Conijn Advies. .
{{Authority control
Articles containing video clips
Political terminology
Global conflicts
Doomsday scenarios
Nuclear warfare
1940s neologisms
Theories of history
War
War scare
World Wars
 World War III (WWIII or WW3), also known as the Third World War, is a hypothetical future
World War III (WWIII or WW3), also known as the Third World War, is a hypothetical future  Seven Days to the River Rhine was a top-secret military simulation exercise developed in 1979 by the Warsaw Pact. It started with the assumption that NATO would launch a nuclear attack on the
Seven Days to the River Rhine was a top-secret military simulation exercise developed in 1979 by the Warsaw Pact. It started with the assumption that NATO would launch a nuclear attack on the  Exercise Able Archer was an annual exercise by the US European Command that practiced command and control procedures, with emphasis on the transition from solely conventional operations to chemical, nuclear, and conventional operations during a time of war.
"Able Archer 83" was a five-day North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) command post
Exercise Able Archer was an annual exercise by the US European Command that practiced command and control procedures, with emphasis on the transition from solely conventional operations to chemical, nuclear, and conventional operations during a time of war.
"Able Archer 83" was a five-day North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) command post  The
The  The
The  As Soviet-American relations grew tense in the post-World WarII period, the fear that the tension could escalate into World WarIII was ever-present. A Gallup poll in December 1950 found that more than half of Americans considered World WarIII to have already started.
In 2004, commentator
As Soviet-American relations grew tense in the post-World WarII period, the fear that the tension could escalate into World WarIII was ever-present. A Gallup poll in December 1950 found that more than half of Americans considered World WarIII to have already started.
In 2004, commentator  The "
The " In 1949, after the unleashing of nuclear weaponry at the end of World War II, physicist
In 1949, after the unleashing of nuclear weaponry at the end of World War II, physicist