|
Canada And Weapons Of Mass Destruction
Canada has not officially maintained and possessed weapons of mass destruction since 1984 and, as of 1998, has signed treaties repudiating possession of them. Canada ratified the Geneva Protocol in 1930 and the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty in 1970. Nuclear weapons Introduction The first US nuclear weapon entered Canada in 1950 when the United States Air Force Strategic Air Command (SAC) stationed 11 model 1561 Fat Man atomic bombs at CFB Goose Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador. Goose Bay was used as an aircraft staging location for both the SAC and the Royal Air Force's V Force. The bombs were landed; crews relieved; aircraft refueled, or repaired; without returning to bases in the continental US. Nuclear weapons designs of the time were easily damaged but precise devices, that required off-aircraft inspection (after landing), and environmental sheltering (at a secure warm/dry location) while their carrier aircraft was on the ground for routine maintenance or repair. Fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weapon Of Mass Destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to numerous individuals or cause great damage to artificial structures (e.g., buildings), natural structures (e.g., mountains), or the biosphere. The scope and usage of the term has evolved and been disputed, often signifying more politically than technically. Originally coined in reference to aerial bombing with chemical explosives during World War II, it has later come to refer to large-scale weaponry of warfare-related technologies, such as chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear warfare. Early uses of this term The first use of the term "weapon of mass destruction" on record is by Cosmo Gordon Lang, Archbishop of Canterbury, in 1937 in reference to the aerial bombing of Guernica, Spain: At the time, nuclear weapons had not been developed. Japan conducted research on biological weapons (see Unit 731), and chemical w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
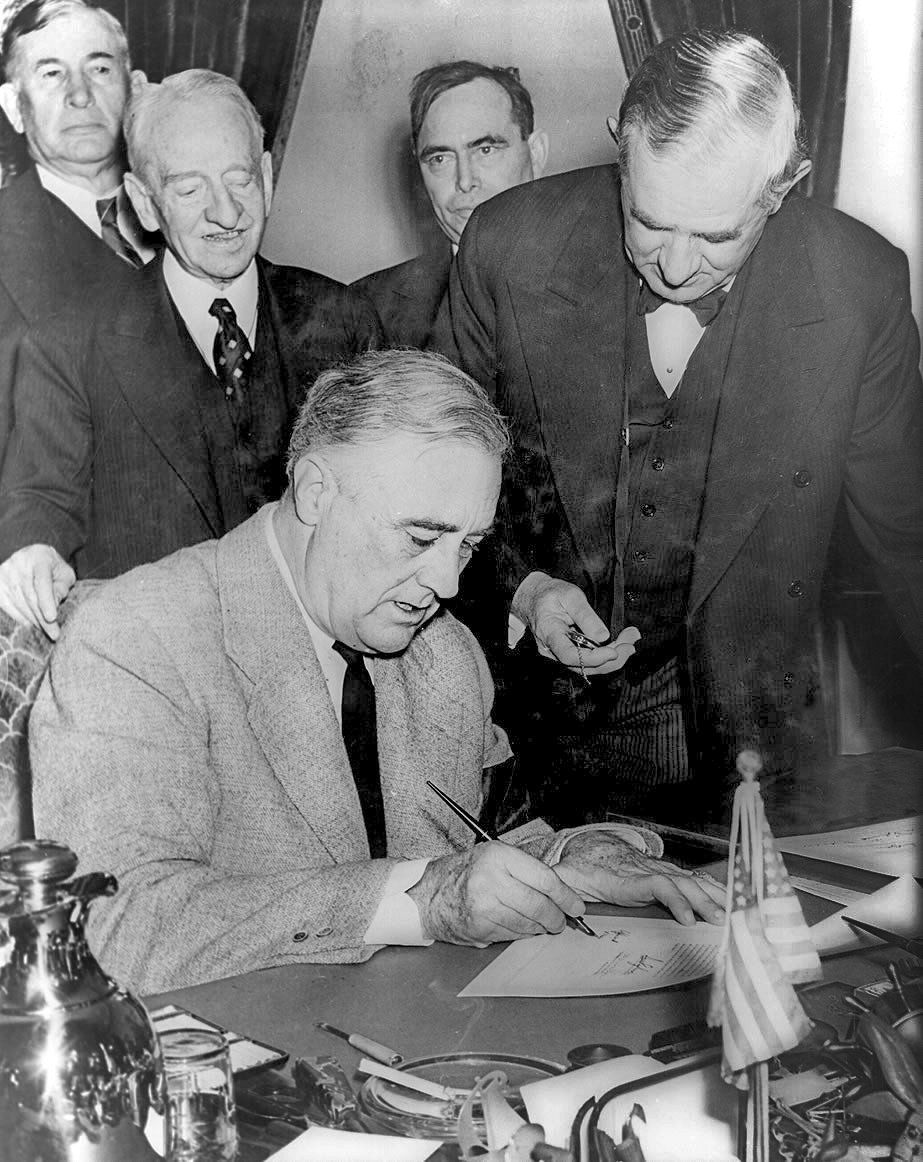
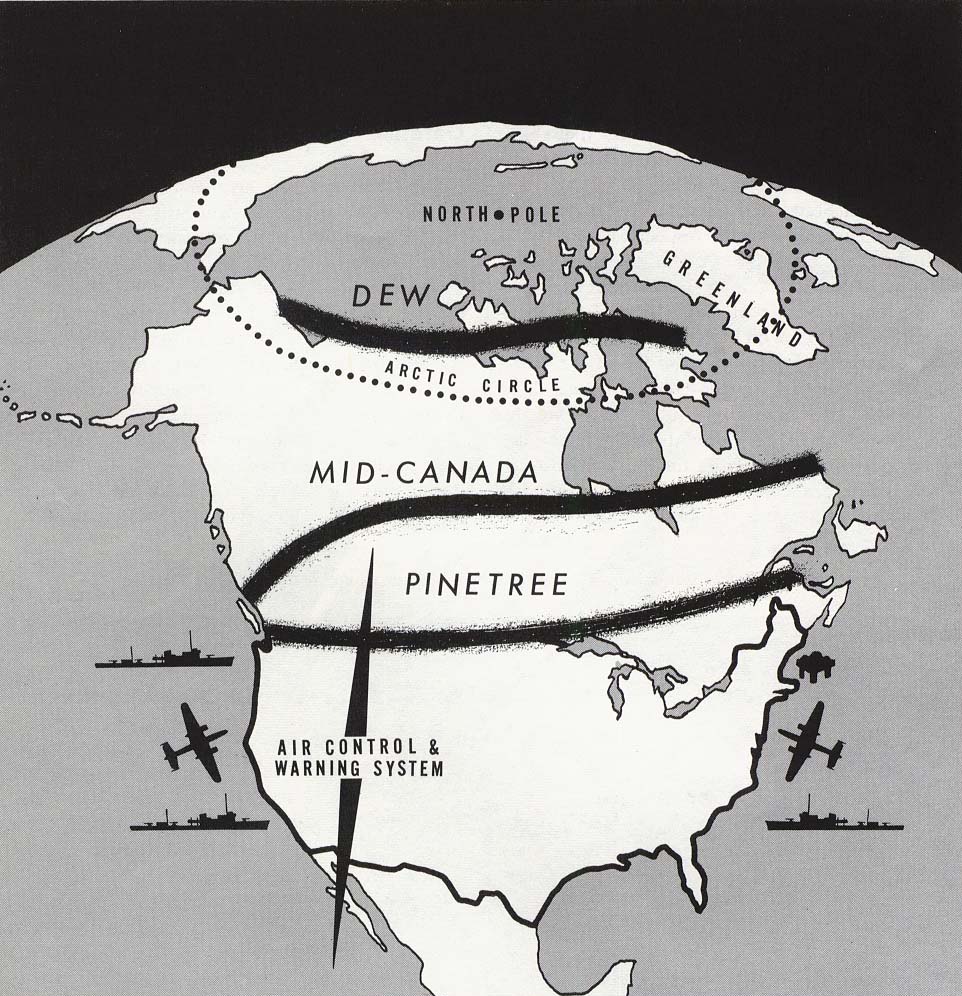
Ogdensburg Agreement
The Ogdensburg Agreement was an agreement concluded between Canadian Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King and U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt in Heuvelton near Ogdensburg, New York on August 17, 1940. It outlined a permanent plan for mutual defense overseas between the United States and Canada and established the Permanent Joint Board of Defense. History and Rationale Although Canada and the United States had long been economic partners, Canada had always considered Great Britain as its primary military partner. While Canada had been granted independence in its foreign policy from Britain in 1931, Canada's membership in the Commonwealth of Nations, the strength of the British Empire, and the historic and cultural ties between them made a military alliance with the United States seem unnecessary. Most Canadians believed that Britain could provide for all of Canada's defence needs. Canada had declared war on Nazi Germany shortly after the Second World War began in earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Declaration Of War On Japan
The government of the United Kingdom declared war on the Empire of Japan on 8 December 1941, following the Japanese attacks on British Malaya, Singapore and Hong Kong on the previous day as well as in response to the bombing of the US fleet at Pearl Harbor. Background The United Kingdom declared war on Nazi Germany on September 3, 1939 two days after the outbreak of war in Europe. The Empire of Japan and Nazi Germany had signed the Anti-Comintern Pact in 1936, to counter the perceived threat of the communism of the Soviet Union. During negotiations with the administration of U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill had promised to declare war "within the hour" of a Japanese attack on the United States. On 7/8 December 1941, Japan attacked British and American territories in Southeast Asia and the Central Pacific with near-simultaneous offensives including an attack on the US fleet at Pearl Harbor.. Decision and communication News o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Declaration Of War On Japan
A declaration of war by Canada is a formal declaration issued by the Government of Canada (the federal Crown- in-Council) indicating that a state of war exists between Canada and another nation. It is an exercise of the Royal Prerogative on the constitutional advice of the ministers of the Crown in Cabinet and does not require the direct approval of the Parliament of Canada, though such can be sought by the government. Since gaining the authority to declare war under the Statute of Westminster 1931, Canada has declared war only during the Second World War. Second World War Nazi Germany After Nazi Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, the United Kingdom and France declared war on September 3. To assert Canada's independence from the UK, as already established by the Statute of Westminster 1931, Canada's political leaders decided to seek the approval of the federal parliament to declare war. Parliament was not scheduled to return until October 2, but returned to session early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, just before 8:00a.m. (local time) on Sunday, December 7, 1941. The United States was a neutral country at the time; the attack led to its formal entry into World War II the next day. The Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning. Japan intended the attack as a preventive action. Its aim was to prevent the United States Pacific Fleet from interfering with its planned military actions in Southeast Asia against overseas territories of the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and those of the United States. Over the course of seven hours there were coordinated Japanese attacks on the US-held Philippines, Guam, and Wake Island and on the British Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Declaration Of War On Japan
On December 8, 1941, the United States Congress declared war () on the Empire of Japan in response to that country's Attack on Pearl Harbor, surprise attack on Pearl Harbor and Japanese declaration of war on the United States and the British Empire, declaration of war the prior day. The Joint Resolution Declaring that a state of war exists between the Imperial Government of Japan and the Government and the people of the United States and making provisions to prosecute the same was formulated an hour after the ''Infamy Speech'' of President of the United States, President Franklin D. Roosevelt. Following the U.S. declaration, Japan's allies, Nazi Germany, Germany and Kingdom of Italy, Italy, Axis Powers#Germany's and Italy's declaration of war against the United States, declared war on the United States, bringing the United States fully into World War II. Background The attack on Pearl Harbor took place before a declaration of war by Japan had been delivered to the United States. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Declaration Of War On Germany (1941)
__notoc__ On December 11, 1941, the United States Congress declared war on Germany (, Sess. 1, ch. 564, ), hours after Germany declared war on the United States after the attack on Pearl Harbor by the Empire of Japan. The vote was 88–0 in the Senate and 393–0 in the House. Text See also * Arcadia Conference * Declarations of war during World War II * Diplomatic history of World War II *German declaration of war against the United States (1941) *Kellogg–Briand Pact *United Kingdom declaration of war on Germany (1939) * United States declaration of war upon Germany (1917) *United States declaration of war upon Italy *United States declaration of war upon Japan References External links * 1941 in Germany 1941 in international relations 1941 in military history 1941 in the United States Declarations of war during World War II Germany–United States military relations Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Declaration Of War On Germany
A recommendation for a declaration of war by Canada on Nazi Germany was announced in a speech made by Canadian Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King on 3 September 1939. Though Mackenzie King was in Ottawa at the time of his speech, it was broadcast over the radio. There was also a Canadian announcement in the Canadian newspaper, the ''Canada Gazette''. The declaration of war was made on 10 September 1939, just 7 days after the United Kingdom and France declared war. Canada did not declare war on Germany in 1914 at the outset of World War I, as it had no authority to do so at the time; as part of the British Empire, it entered the war with the United Kingdom in consequence of its own declaration of war. Canada gained this authority with the Statute of Westminster 1931. Background and procedure After Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939, the United Kingdom and France declared war on September 3. To assert Canada's independence from the UK, as already established by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statute Of Westminster 1931
The Statute of Westminster 1931 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that sets the basis for the relationship between the Commonwealth realms and the Crown. Passed on 11 December 1931, the statute increased the sovereignty of the self-governing Dominions of the British Empire from the United Kingdom. It also bound them all to seek each other's approval for changes to monarchical titles and the common line of succession. The statute was effective either immediately or upon ratification. It thus became a statutory embodiment of the principles of equality and common allegiance to the Crown set out in the Balfour Declaration of 1926. As the statute removed nearly all of the British parliament's authority to legislate for the Dominions, it had the effect of making the Dominions largely sovereign nations in their own right. It was a crucial step in the development of the Dominions as separate states. Its modified versions are now domestic law within Australia and Canada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after its defeat in the First World War. Austria-Hungary was ruled by the House of Habsburg and constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy. It was a multinational state and one of Europe's major powers at the time. Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe after the Russian Empire, at and the third-most populous (after Russia and the German Empire). The Empire built up the fourth-largest machine building industry in the world, after the United States, Germany and the United Kingdom. Austria-Hungary also became the world's third-largest manufacturer and exporter of electric home appliances, el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |