The heart is a muscular
organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
found in most
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s. This organ pumps
blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in th ...
through the
blood vessel
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from ...
s of the
circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
.
The pumped blood carries
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
and
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excr ...
s to the body, while carrying
metabolic waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds, ...
such as
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
to the
lungs. In
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
s, the heart is approximately the size of a closed
fist
A fist is the shape of a hand when the fingers are bent inward against the palm and held there tightly. To make or clench a fist is to fold the fingers tightly into the center of the palm and then to clamp the thumb over the middle phalanges; in ...
and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the
chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
, called the
mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
.
In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right
atria and lower left and right
ventricles.
Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the
right heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
and their left counterparts as the
left heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers.
[ In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to ]heart valve
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart ...
s, which prevent backflow
Backflow is a term in plumbing for an unwanted flow of water in the reverse direction. It can be a serious health risk for the contamination of potable water supplies with foul water. In the most obvious case, a toilet flush cistern and its wate ...
.pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of ...
, which also contains a small amount of fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that continuously deforms (''flows'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shea ...
. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers: epicardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of ...
, myocardium
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle tha ...
, and endocardium
The endocardium is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. The endocardium also provides protection to the v ...
.vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, wi ...
, the heart has an asymmetric orientation, almost always on the left side. According to one theory, this is caused by a developmental axial twist in the early embryo.rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed ...
determined by a group of pacemaker cells
350px, Image showing the cardiac pacemaker or SA node, the primary pacemaker within the electrical conduction system of the heart.
The muscle contraction, contraction of cardiac muscle (heart muscle) in all animals is initiated by electrical ...
in the sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node or sinus node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approxi ...
. These generate an electric current that causes the heart to contract, traveling through the atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node or AV node electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of t ...
and along the conduction system of the heart
The cardiac conduction system (CCS) (also called the electrical conduction system of the heart) transmits the signals generated by the sinoatrial node – the heart's pacemaker, to cause the heart muscle to contract, and pump blood through ...
. In humans, deoxygenated blood enters the heart through the right atrium from the superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
* Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lak ...
and inferior venae cavae and passes to the right ventricle. From here, it is pumped into pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lung ...
to the lungs, where it receives oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
into systemic circulation
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, traveling through arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pul ...
, arteriole
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries.
Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the pri ...
s, and capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
—where nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excr ...
s and other substances are exchanged between blood vessels and cells, losing oxygen and gaining carbon dioxide—before being returned to the heart through venule
A venule is a very small blood vessel in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the larger blood vessels, the veins. Venules range from 7μm to 1mm in diameter. Veins contain approximately 70% of ...
s and vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenate ...
s. The heart beats at a resting rate close to 72 beats per minute. Exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic s ...
temporarily increases the rate, but lowers it in the long term, and is good for heart health.
Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
s are the most common cause of death globally as of 2008, accounting for 30% of all human deaths.coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the myocardium, heart muscle due to build-up o ...
and stroke.smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
, being overweight
Being overweight or fat is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.
, excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with m ...
, little exercise, high cholesterol
Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of hyperlipidemia (high levels of lipids in the blood), hyperlipoproteinemia (high levels of lipoproteins in the blood), ...
, high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high b ...
, and poorly controlled diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, among others. Cardiovascular diseases do not frequently have symptoms but may cause chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with ...
or shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
. Diagnosis of heart disease is often done by the taking of a medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either to the patient or to other pe ...
, listening
Listening is giving attention to a sound or action. When listening, a person hears what others are saying and tries to understand what it means. The act of listening involves complex affective, cognitive and behavioral processes. Affective p ...
to the heart-sound
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a stet ...
s with a stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. ...
, as well as with ECG
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the hear ...
, and echocardiogram
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart.
It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in ...
which uses ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
.cardiologists
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart d ...
, although many specialties of medicine may be involved in treatment.
Structure

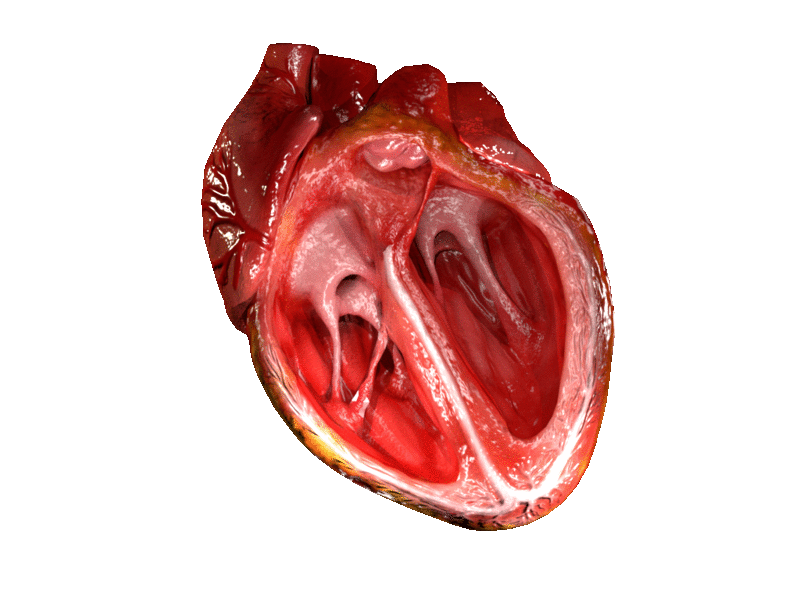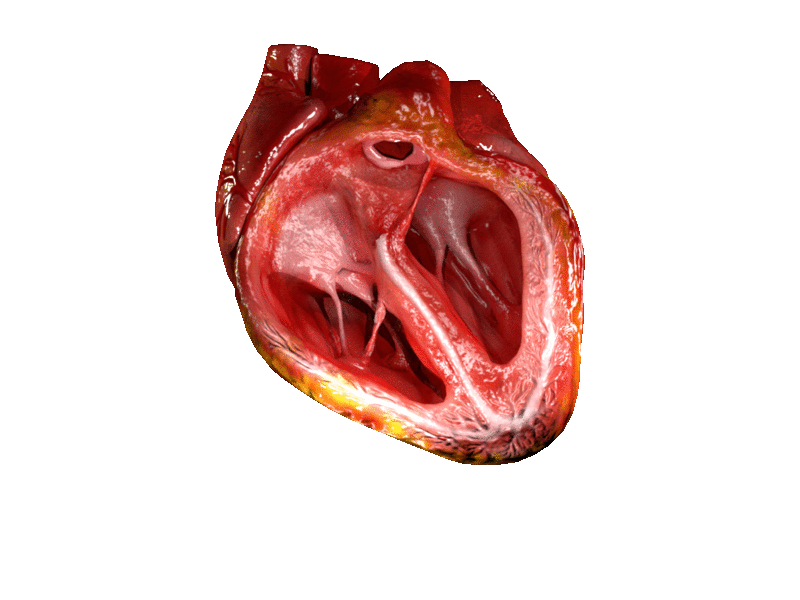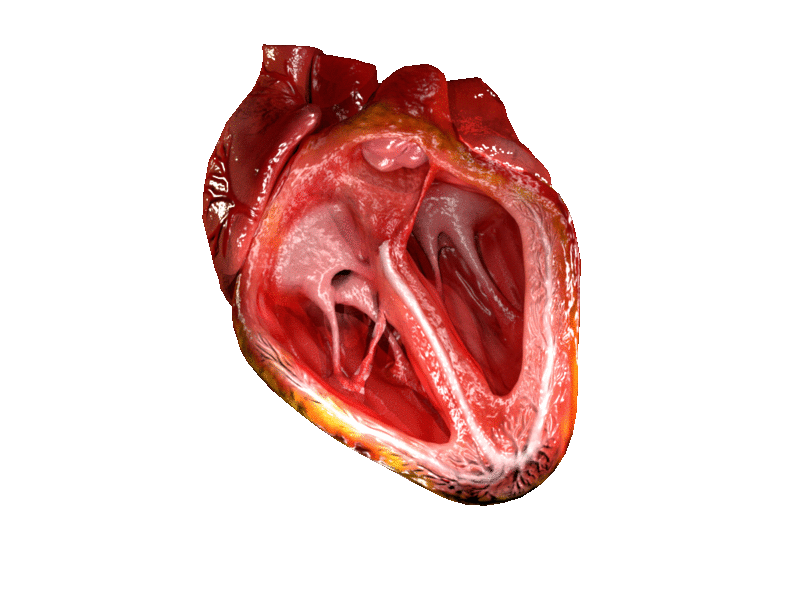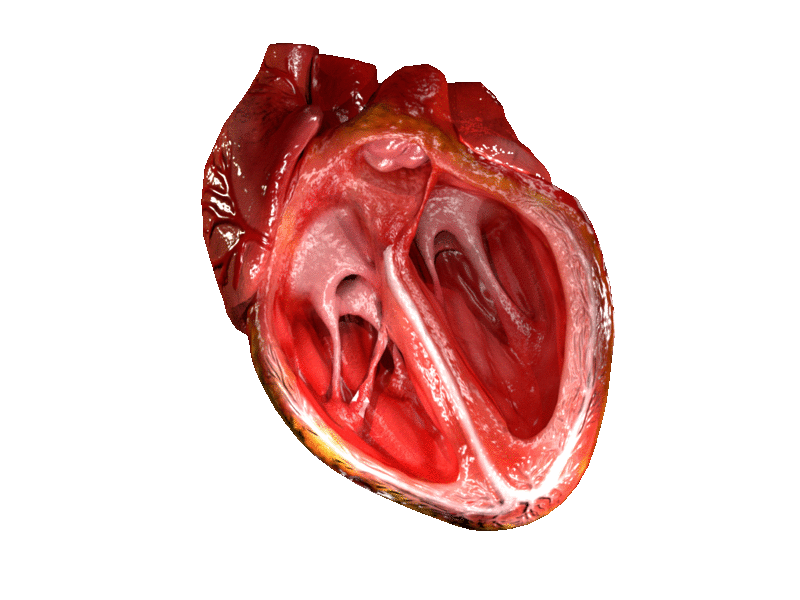
Location and shape
 The human heart is situated in the
The human heart is situated in the mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
, at the level of thoracic vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical ...
T5- T8. A double-membraned sac called the pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of ...
surrounds the heart and attaches to the mediastinum. The back surface of the heart lies near the vertebral column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordate ...
, and the front surface known as the sternocostal surface sits behind the sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. ...
and rib cartilages.venae cavae
In anatomy, the venae cavae (; singular: vena cava ; ) are two large veins (great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the ...
, aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
and pulmonary trunk
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
. The upper part of the heart is located at the level of the third costal cartilage.midsternal line
The Midsternal line is used to describe a part of the surface anatomy of the anterior thorax. The midsternal line runs vertical down the middle of the sternum.
It can be interpreted as a component of the median plane
The median plane also cal ...
) between the junction of the fourth and fifth ribs near their articulation with the costal cartilages.left heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
is stronger and larger, since it pumps to all body parts. Because the heart is between the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of ...
, the left lung is smaller than the right lung and has a cardiac notch in its border to accommodate the heart.athlete
An athlete (also sportsman or sportswoman) is a person who competes in one or more sports that involve physical strength, speed, or endurance.
Athletes may be professionals or amateurs. Most professional athletes have particularly well-dev ...
s can have much larger hearts due to the effects of exercise on the heart muscle, similar to the response of skeletal muscle.
Chambers
 The heart has four chambers, two upper atria, the receiving chambers, and two lower ventricles, the discharging chambers. The atria open into the ventricles via the
The heart has four chambers, two upper atria, the receiving chambers, and two lower ventricles, the discharging chambers. The atria open into the ventricles via the atrioventricular valve
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart v ...
s, present in the atrioventricular septum
The atrioventricular septum is a septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as sept ...
. This distinction is visible also on the surface of the heart as the coronary sulcus
The coronary sulcus (also called coronary groove, auriculoventricular groove, atrioventricular groove, AV groove) is a groove on the surface of the heart at the base of right auricle that separates the atria from the ventricles. The structure c ...
. There is an ear-shaped structure in the upper right atrium called the right atrial appendage
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two atr ...
, or auricle, and another in the upper left atrium, the left atrial appendage
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two atr ...
. The right atrium and the right ventricle together are sometimes referred to as the right heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
. Similarly, the left atrium and the left ventricle together are sometimes referred to as the left heart. The ventricles are separated from each other by the interventricular septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backwar ...
, visible on the surface of the heart as the anterior longitudinal sulcus
The anterior interventricular sulcus (or anterior longitudinal sulcus) is one of two grooves separating the ventricles of the heart (the other being the posterior interventricular sulcus). It is situated on the sternocostal surface of the heart ...
and the posterior interventricular sulcus
The posterior interventricular sulcus or posterior longitudinal sulcus is one of the two grooves that separates the ventricles of the heart and is on the diaphragmatic surface of the heart near the right margin. The other groove is the anterior ...
.
The fibrous
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorpora ...
cardiac skeleton
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through ...
gives structure to the heart. It forms the atrioventricular septum, which separates the atria from the ventricles, and the fibrous rings, which serve as bases for the four heart valve
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart ...
s. The cardiac skeleton also provides an important boundary in the heart's electrical conduction system since collagen cannot conduct electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
. The interatrial septum separates the atria, and the interventricular septum separates the ventricles.
Valves
 The heart has four valves, which separate its chambers. One valve lies between each atrium and ventricle, and one valve rests at the exit of each ventricle.
The heart has four valves, which separate its chambers. One valve lies between each atrium and ventricle, and one valve rests at the exit of each ventricle.[
The valves between the atria and ventricles are called the atrioventricular valves. Between the right atrium and the right ventricle is the ]tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
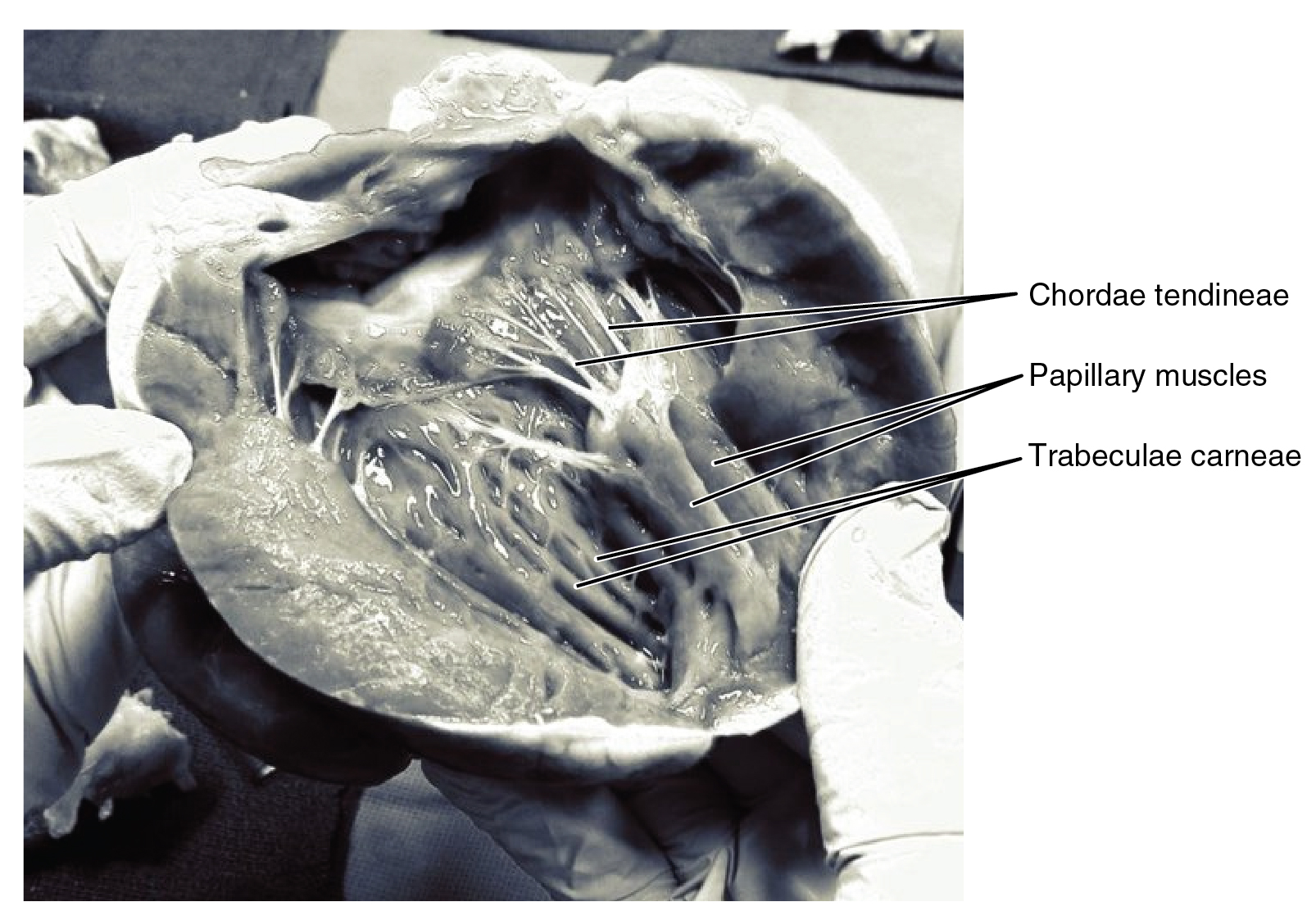
. The tricuspid valve has three cusps, which connect to chordae tendinae
The chordae tendineae (tendinous cords), colloquially known as the heart strings, are inelastic cords of fibrous connective tissue that connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid valve and the mitral valve in the heart.
Structure
The chordae ...
and three papillary muscle
The papillary muscles are muscles located in the ventricles of the heart. They attach to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves (also known as the mitral and tricuspid valves) via the chordae tendineae and contract to prevent inversion or p ...
s named the anterior, posterior, and septal muscles, after their relative positions. The mitral valve
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one- ...
lies between the left atrium and left ventricle. It is also known as the bicuspid valve due to its having two cusps, an anterior and a posterior cusp. These cusps are also attached via chordae tendinae to two papillary muscles projecting from the ventricular wall.
The papillary muscles extend from the walls of the heart to valves by cartilaginous connections called chordae tendinae. These muscles prevent the valves from falling too far back when they close. During the relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle, the papillary muscles are also relaxed and the tension on the chordae tendineae is slight. As the heart chambers contract, so do the papillary muscles. This creates tension on the chordae tendineae, helping to hold the cusps of the atrioventricular valves in place and preventing them from being blown back into the atria.pulmonary valve
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) is a valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar ...
is located at the base of the pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
. This has three cusps which are not attached to any papillary muscles. When the ventricle relaxes blood flows back into the ventricle from the artery and this flow of blood fills the pocket-like valve, pressing against the cusps which close to seal the valve. The semilunar aortic valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. Th ...
is at the base of the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
and also is not attached to papillary muscles. This too has three cusps which close with the pressure of the blood flowing back from the aorta.
Right heart
The right heart consists of two chambers, the right atrium and the right ventricle, separated by a valve, the tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
.vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenate ...
s, the superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
* Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lak ...
and inferior
Inferior may refer to:
* Inferiority complex
* An Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, anatomical term of location
* Inferior angle of the scapula, in the human skeleton
*Inferior (book), ''Inferior'' (book), by Angela Saini
* ''The ...
venae cavae
In anatomy, the venae cavae (; singular: vena cava ; ) are two large veins (great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the ...
. A small amount of blood from the coronary circulation also drains into the right atrium via the coronary sinus
In anatomy, the coronary sinus () is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle ( myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior ven ...
, which is immediately above and to the middle of the opening of the inferior vena cava.foramen ovale There are multiple structures in the human body with the name foramen ovale (plural: ''foramina ovalia''; Latin for "oval hole"):
* Foramen ovale (heart), in the fetal heart, a shunt from the right atrium to left atrium
* Foramen ovale (skull), at ...
.pectinate muscle
The pectinate muscles (musculi pectinati) are parallel muscular ridges in the walls of the atria of the heart.
Structure
Behind the crest (crista terminalis) of the right atrium the internal surface is smooth. Pectinate muscles make up the par ...
s, which are also present in the right atrial appendage
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two atr ...
.trabeculae carneae
The trabeculae carneae (columnae carneae, or meaty ridges) are rounded or irregular muscular columns which project from the inner surface of the right and left ventricle of the heart.Moore, K.L., & Agur, A.M. (2007). ''Essential Clinical Anatomy: ...
, ridges of cardiac muscle covered by endocardium. In addition to these muscular ridges, a band of cardiac muscle, also covered by endocardium, known as the moderator band
The moderator band (also known as septomarginal trabecula) is a band of cardiac muscle found in the right ventricle of the heart. It is well-marked in sheep and some other animals. It extends from the base of the anterior papillary muscle to the v ...
reinforces the thin walls of the right ventricle and plays a crucial role in cardiac conduction. It arises from the lower part of the interventricular septum and crosses the interior space of the right ventricle to connect with the inferior papillary muscle.pulmonary trunk
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
, into which it ejects blood when contracting. The pulmonary trunk branches into the left and right pulmonary arteries that carry the blood to each lung. The pulmonary valve lies between the right heart and the pulmonary trunk.
Left heart
The left heart has two chambers: the left atrium and the left ventricle, separated by the mitral valve
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one- ...
.pulmonary vein
The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four ''main pulmonary veins'', two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary v ...
s. The left atrium has an outpouching called the left atrial appendage
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two atr ...
. Like the right atrium, the left atrium is lined by pectinate muscles
The pectinate muscles (musculi pectinati) are parallel muscular ridges in the walls of the atria of the heart.
Structure
Behind the crest (crista terminalis) of the right atrium the internal surface is smooth. Pectinate muscles make up the par ...
. The left atrium is connected to the left ventricle by the mitral valve.trabeculae carneae
The trabeculae carneae (columnae carneae, or meaty ridges) are rounded or irregular muscular columns which project from the inner surface of the right and left ventricle of the heart.Moore, K.L., & Agur, A.M. (2007). ''Essential Clinical Anatomy: ...
, but there is no moderator band
The moderator band (also known as septomarginal trabecula) is a band of cardiac muscle found in the right ventricle of the heart. It is well-marked in sheep and some other animals. It extends from the base of the anterior papillary muscle to the v ...
. The left ventricle pumps blood to the body through the aortic valve and into the aorta. Two small openings above the aortic valve carry blood to the heart muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate Muscle tissue, muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striat ...
; the left coronary artery
The left coronary artery (LCA) is a coronary artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve, and feeds blood to the left side of the heart muscle. It is also known as the left main coronary artery (LMCA) and the left m ...
is above the left cusp of the valve, and the right coronary artery
In the blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux of the he ...
is above the right cusp.
Wall
 The heart wall is made up of three layers: the inner
The heart wall is made up of three layers: the inner endocardium
The endocardium is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. The endocardium also provides protection to the v ...
, middle myocardium
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle tha ...
and outer epicardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of ...
. These are surrounded by a double-membraned sac called the pericardium.
The innermost layer of the heart is called the endocardium. It is made up of a lining of simple squamous epithelium
A simple squamous epithelium, also known as pavement epithelium, and tessellated epithelium is a single layer of flattened, polygonal cells in contact with the basal lamina (one of the two layers of the basement membrane) of the epithelium. Th ...
and covers heart chambers and valves. It is continuous with the endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the ve ...
of the veins and arteries of the heart, and is joined to the myocardium with a thin layer of connective tissue.endothelins
Endothelins are peptides with receptors and effects in many body organs. Endothelin constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. The endothelins are normally kept in balance by other mechanisms, but when overexpressed, they contribute ...
, may also play a role in regulating the contraction of the myocardium.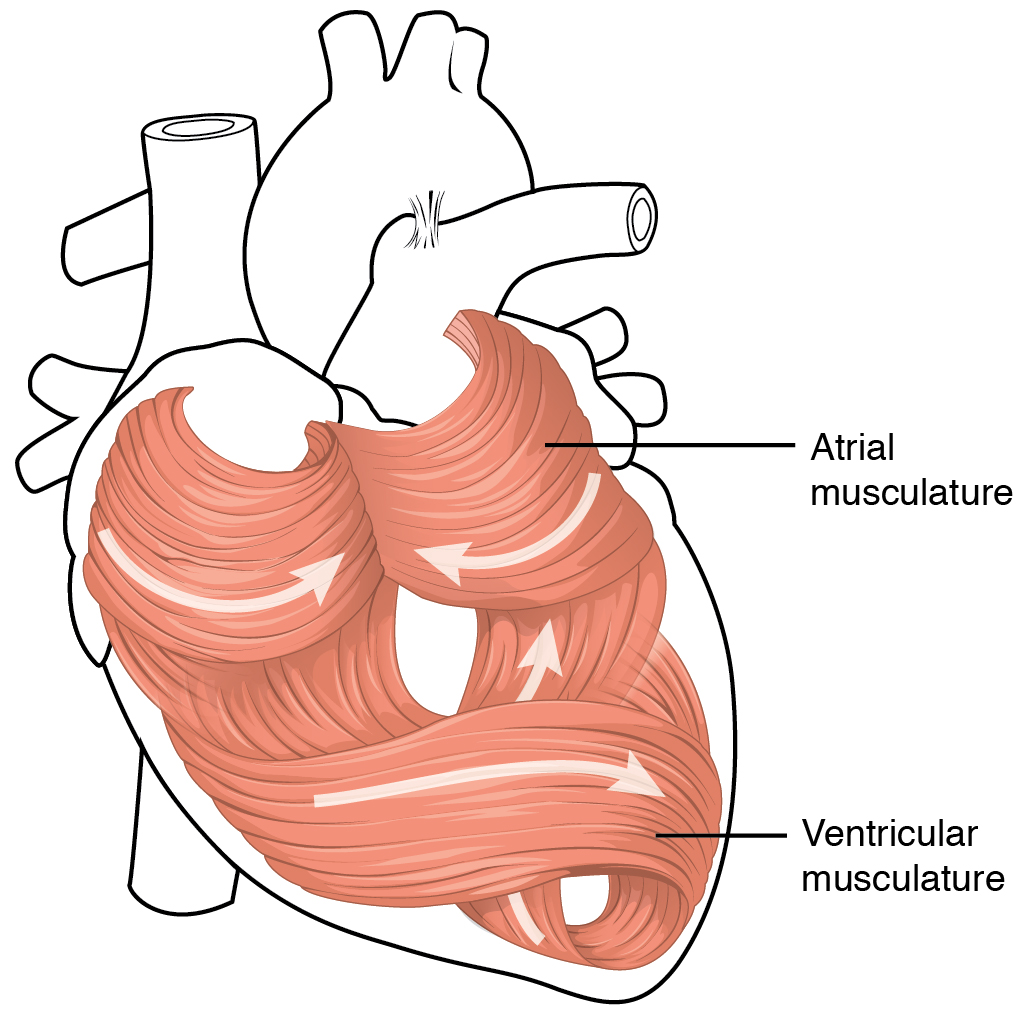 The middle layer of the heart wall is the myocardium, which is the
The middle layer of the heart wall is the myocardium, which is the cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle tha ...
—a layer of involuntary striated muscle tissue
Striations means a series of ridges, furrows or linear marks, and is used in several ways:
* Glacial striation
* Striation (fatigue), in material
* Striation (geology), a ''striation'' as a result of a geological fault
* Striation Valley, in Anta ...
surrounded by a framework of collagen. The cardiac muscle pattern is elegant and complex, as the muscle cells swirl and spiral around the chambers of the heart, with the outer muscles forming a figure 8 pattern around the atria and around the bases of the great vessels and the inner muscles, forming a figure 8 around the two ventricles and proceeding toward the apex. This complex swirling pattern allows the heart to pump blood more effectively.muscle cells
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscl ...
which have the ability to contract easily, and pacemaker cells
350px, Image showing the cardiac pacemaker or SA node, the primary pacemaker within the electrical conduction system of the heart.
The muscle contraction, contraction of cardiac muscle (heart muscle) in all animals is initiated by electrical ...
of the conducting system. The muscle cells make up the bulk (99%) of cells in the atria and ventricles. These contractile cells are connected by intercalated disc
Intercalated discs or lines of Eberth are microscopic identifying features of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) connected by intercalated discs to work as a single functional syncytium. By co ...
s which allow a rapid response to impulses of action potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, ...
from the pacemaker cells. The intercalated discs allow the cells to act as a syncytium
A syncytium (; plural syncytia; from Ancient Greek, Greek: σύν ''syn'' "together" and κύτος ''kytos'' "box, i.e. cell") or symplasm is a multinucleate cell (biology), cell which can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells (i.e ...
and enable the contractions that pump blood through the heart and into the major arteries.myofibril
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofib ...
s which gives them limited contractibility. Their function is similar in many respects to neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, electrically excitable cell (biology), cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous ...
s.
Pericardium
The pericardium is the sac that surrounds the heart. The tough outer surface of the pericardium is called the fibrous membrane. This is lined by a double inner membrane called the serous membrane that produces pericardial fluid to lubricate the surface of the heart. The part of the serous membrane attached to the fibrous membrane is called the parietal pericardium, while the part of the serous membrane attached to the heart is known as the visceral pericardium. The pericardium is present in order to lubricate its movement against other structures within the chest, to keep the heart's position stabilised within the chest, and to protect the heart from infection.
Coronary circulation
 Heart tissue, like all cells in the body, needs to be supplied with
Heart tissue, like all cells in the body, needs to be supplied with oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
, nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excr ...
s and a way of removing metabolic waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds, ...
s. This is achieved by the coronary circulation, which includes artery, arteries, vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenate ...
s, and lymph vessel, lymphatic vessels. Blood flow through the coronary vessels occurs in peaks and troughs relating to the heart muscle's relaxation or contraction.right coronary artery
In the blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux of the he ...
. The left main coronary artery splits shortly after leaving the aorta into two vessels, the left anterior descending and the left circumflex artery. The left anterior descending artery supplies heart tissue and the front, outer side, and septum of the left ventricle. It does this by branching into smaller arteries—diagonal and septal branches. The left circumflex supplies the back and underneath of the left ventricle. The right coronary artery supplies the right atrium, right ventricle, and lower posterior sections of the left ventricle. The right coronary artery also supplies blood to the atrioventricular node (in about 90% of people) and the sinoatrial node (in about 60% of people). The right coronary artery runs in a groove at the back of the heart and the left anterior descending artery runs in a groove at the front. There is significant variation between people in the anatomy of the arteries that supply the heart The arteries divide at their furthest reaches into smaller branches that join at the edges of each arterial distribution.coronary sinus
In anatomy, the coronary sinus () is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle ( myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior ven ...
is a large vein that drains into the right atrium, and receives most of the venous drainage of the heart. It receives blood from the great cardiac vein (receiving the left atrium and both ventricles), the posterior cardiac vein (draining the back of the left ventricle), the middle cardiac vein (draining the bottom of the left and right ventricles), and small cardiac veins. The anterior cardiac veins drain the front of the right ventricle and drain directly into the right atrium.
Nerve supply
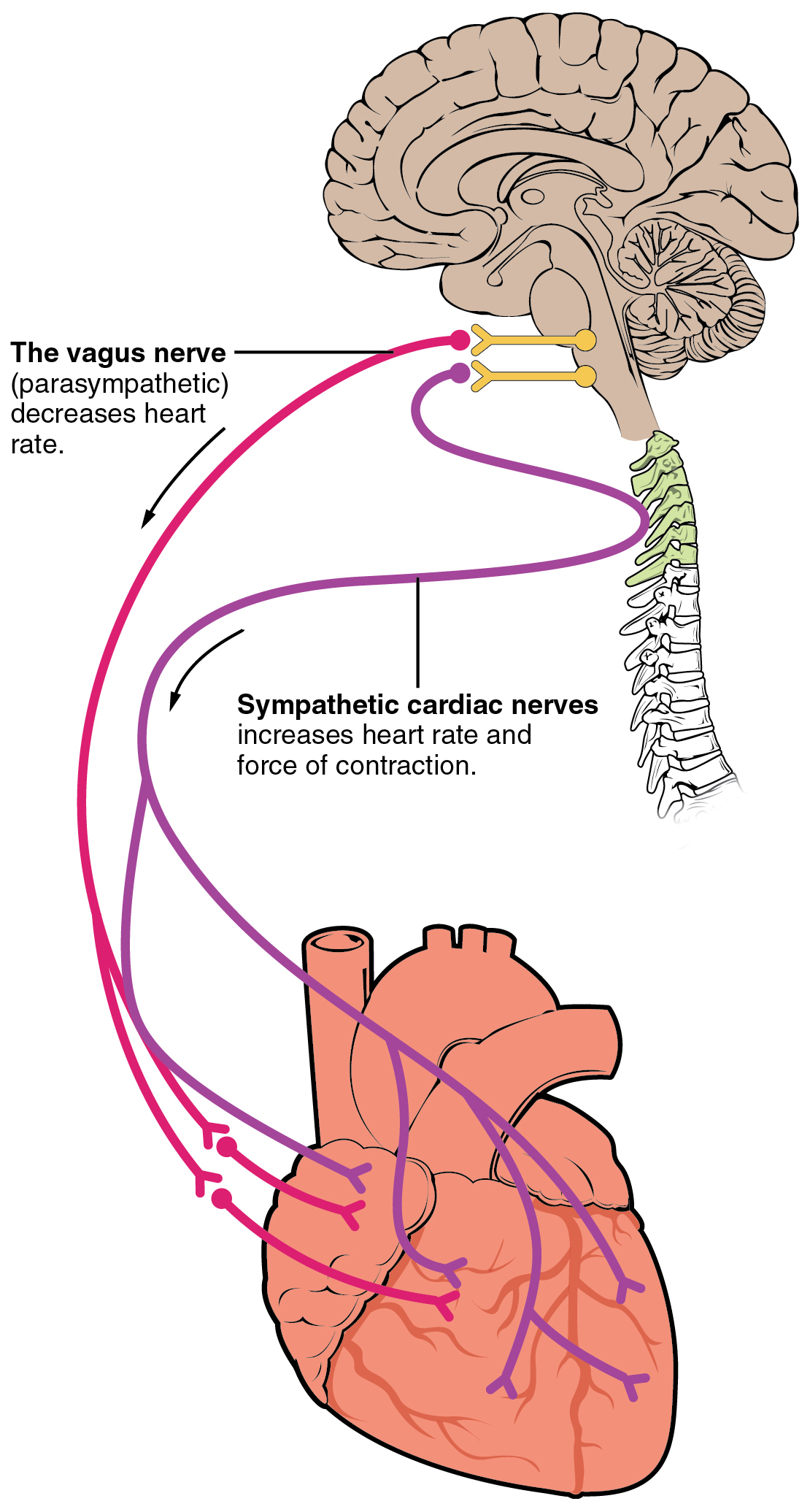 The heart receives nerve signals from the vagus nerve and from nerves arising from the sympathetic trunk. These nerves act to influence, but not control, the heart rate. Sympathetic nervous system, Sympathetic nerves also influence the force of heart contraction. Signals that travel along these nerves arise from two paired cardiovascular centres in the medulla oblongata. The vagus nerve of the parasympathetic nervous system acts to decrease the heart rate, and nerves from the sympathetic trunk act to increase the heart rate.
The heart receives nerve signals from the vagus nerve and from nerves arising from the sympathetic trunk. These nerves act to influence, but not control, the heart rate. Sympathetic nervous system, Sympathetic nerves also influence the force of heart contraction. Signals that travel along these nerves arise from two paired cardiovascular centres in the medulla oblongata. The vagus nerve of the parasympathetic nervous system acts to decrease the heart rate, and nerves from the sympathetic trunk act to increase the heart rate.
Development
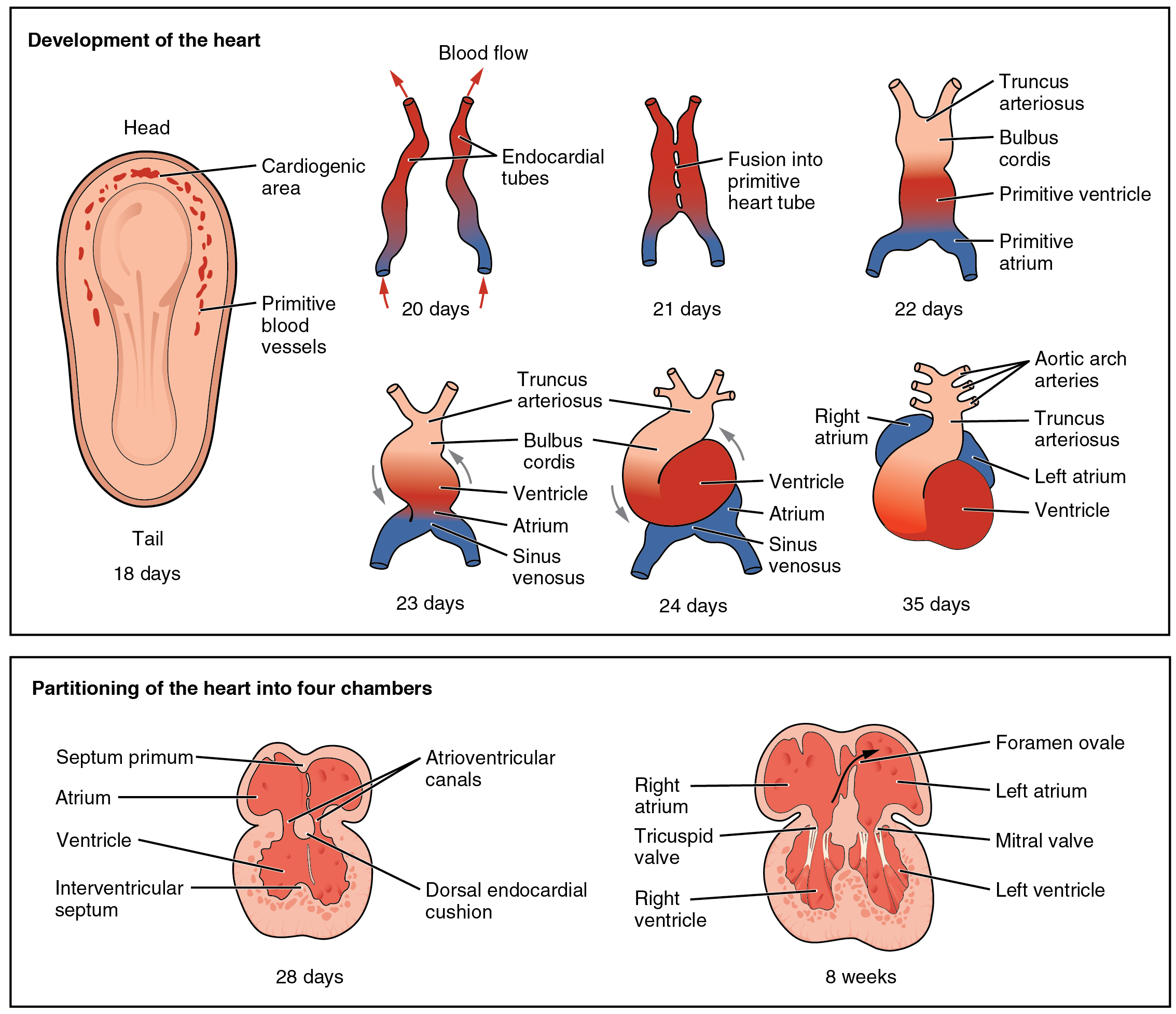 The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at about three weeks into human embryogenesis, embryogenesis. This early start is crucial for subsequent embryonic and prenatal development.
The heart derives from splanchnopleuric mesenchyme in the neural plate which forms the cardiogenic region. Two endocardial tubes form here that fuse to form a primitive heart tube known as the tubular heart. Between the third and fourth week, the heart tube lengthens, and begins to fold to form an S-shape within the pericardium. This places the chambers and major vessels into the correct alignment for the developed heart. Further development will include the formation of the septa and the valves and the remodeling of the heart chambers. By the end of the fifth week, the septa are complete, and by the ninth week, the heart valves are complete.
The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at about three weeks into human embryogenesis, embryogenesis. This early start is crucial for subsequent embryonic and prenatal development.
The heart derives from splanchnopleuric mesenchyme in the neural plate which forms the cardiogenic region. Two endocardial tubes form here that fuse to form a primitive heart tube known as the tubular heart. Between the third and fourth week, the heart tube lengthens, and begins to fold to form an S-shape within the pericardium. This places the chambers and major vessels into the correct alignment for the developed heart. Further development will include the formation of the septa and the valves and the remodeling of the heart chambers. By the end of the fifth week, the septa are complete, and by the ninth week, the heart valves are complete.foramen ovale There are multiple structures in the human body with the name foramen ovale (plural: ''foramina ovalia''; Latin for "oval hole"):
* Foramen ovale (heart), in the fetal heart, a shunt from the right atrium to left atrium
* Foramen ovale (skull), at ...
. The foramen ovale allowed blood in the fetal heart to pass directly from the right atrium to the left atrium, allowing some blood to bypass the lungs. Within seconds after birth, a flap of tissue known as the septum primum that previously acted as a valve closes the foramen ovale and establishes the typical cardiac circulation pattern. A depression in the surface of the right atrium remains where the foramen ovale was, called the fossa ovalis.[DuBose, TJ (1996) ''Fetal Sonography'', pp. 263–274; Philadelphia: WB Saunders ] After 9 weeks (start of the fetal stage) it starts to decelerate, slowing to around 145 (±25) bpm at birth. There is no difference in female and male heart rates before birth.
Physiology
Blood flow
 The heart functions as a pump in the
The heart functions as a pump in the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
to provide a continuous blood flow, flow of blood throughout the body. This circulation consists of the systemic circulation
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
to and from the body and the pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lung ...
to and from the lungs. Blood in the pulmonary circulation exchanges carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
for oxygen in the lungs through the process of breathing, respiration. The systemic circulation then transports oxygen to the body and returns carbon dioxide and relatively deoxygenated blood to the heart for transfer to the lungs.superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
* Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lak ...
and inferior vena cava, inferior venae cavae
In anatomy, the venae cavae (; singular: vena cava ; ) are two large veins (great vessels) that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the ...
. Blood collects in the right and left atrium continuously.coronary sinus
In anatomy, the coronary sinus () is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle ( myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior ven ...
returns deoxygenated blood from the myocardium to the right atrium. The blood collects in the right atrium. When the right atrium contracts, the blood is pumped through the tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
into the right ventricle. As the right ventricle contracts, the tricuspid valve closes and the blood is pumped into the pulmonary trunk through the pulmonary valve. The pulmonary trunk divides into pulmonary arteries and progressively smaller arteries throughout the lungs, until it reaches capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
. As these pass by Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli carbon dioxide is gas exchange, exchanged for oxygen. This happens through the passive process of diffusion.
In the #Left heart, left heart, oxygenated blood is returned to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins. It is then pumped into the left ventricle through the mitral valve
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one- ...
and into the aorta through the aortic valve for systemic circulation. The aorta is a large artery that branches into many smaller arteries, arteriole
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries.
Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the pri ...
s, and ultimately capillaries. In the capillaries, oxygen and nutrients from blood are supplied to body cells for metabolism, and exchanged for carbon dioxide and waste products.venule
A venule is a very small blood vessel in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the larger blood vessels, the veins. Venules range from 7μm to 1mm in diameter. Veins contain approximately 70% of ...
s and veins that ultimately collect in the superior and inferior vena cavae, and into the right heart.
Cardiac cycle
 The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in which the heart contracts and relaxes with every heartbeat. The period of time during which the ventricles contract, forcing blood out into the aorta and main pulmonary artery, is known as systole, while the period during which the ventricles relax and refill with blood is known as diastole. The atria and ventricles work in concert, so in systole when the ventricles are contracting, the atria are relaxed and collecting blood. When the ventricles are relaxed in diastole, the atria contract to pump blood to the ventricles. This coordination ensures blood is pumped efficiently to the body.
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in which the heart contracts and relaxes with every heartbeat. The period of time during which the ventricles contract, forcing blood out into the aorta and main pulmonary artery, is known as systole, while the period during which the ventricles relax and refill with blood is known as diastole. The atria and ventricles work in concert, so in systole when the ventricles are contracting, the atria are relaxed and collecting blood. When the ventricles are relaxed in diastole, the atria contract to pump blood to the ventricles. This coordination ensures blood is pumped efficiently to the body.
Cardiac output
 Cardiac output (CO) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle (stroke volume) in one minute. This is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (SV) by the beats per minute of the heart rate (HR). So that: CO = SV x HR.
Cardiac output (CO) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle (stroke volume) in one minute. This is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (SV) by the beats per minute of the heart rate (HR). So that: CO = SV x HR.echocardiogram
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart.
It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in ...
and can be influenced by the size of the heart, physical and mental condition of the individual, sex, Myocardial contractility, contractility, duration of contraction, preload (cardiology), preload and afterload.
Electrical conduction
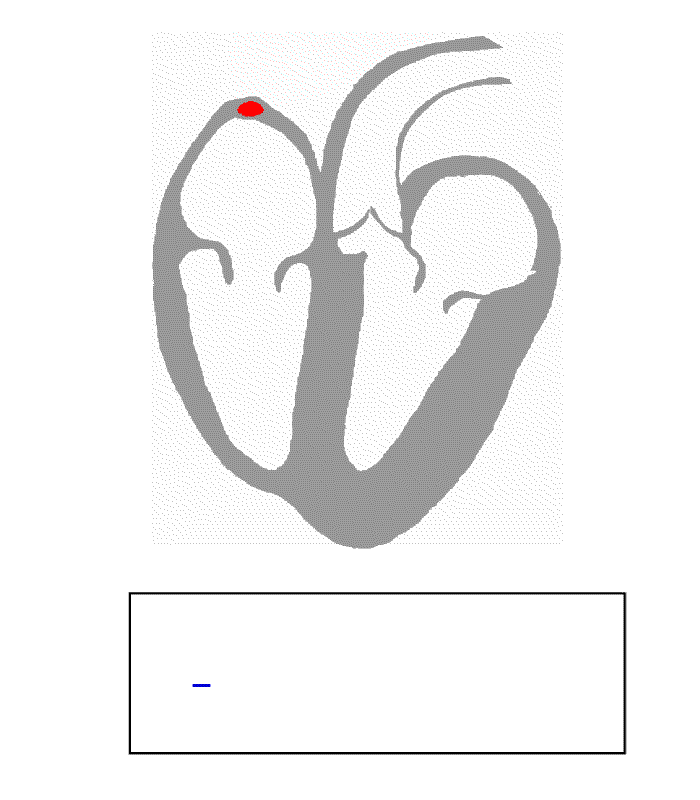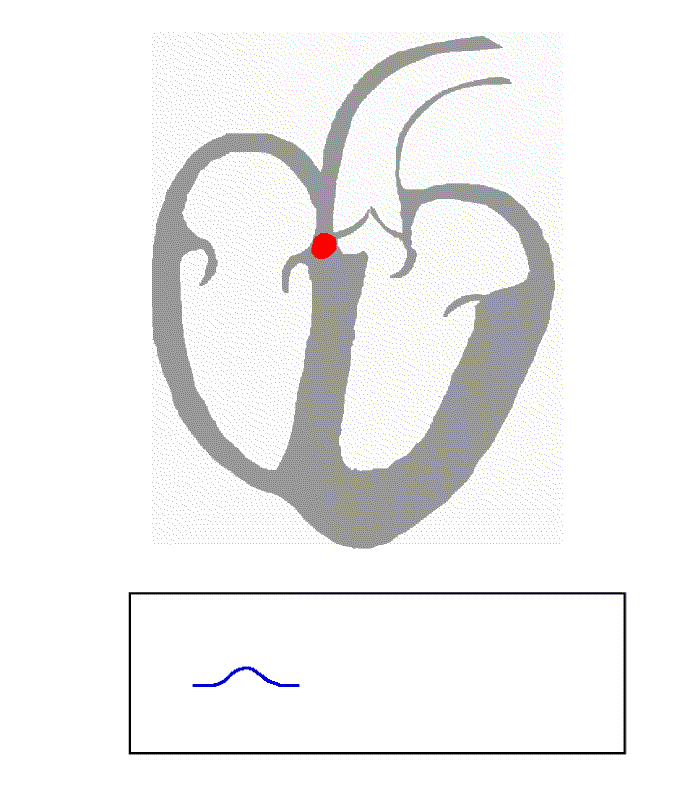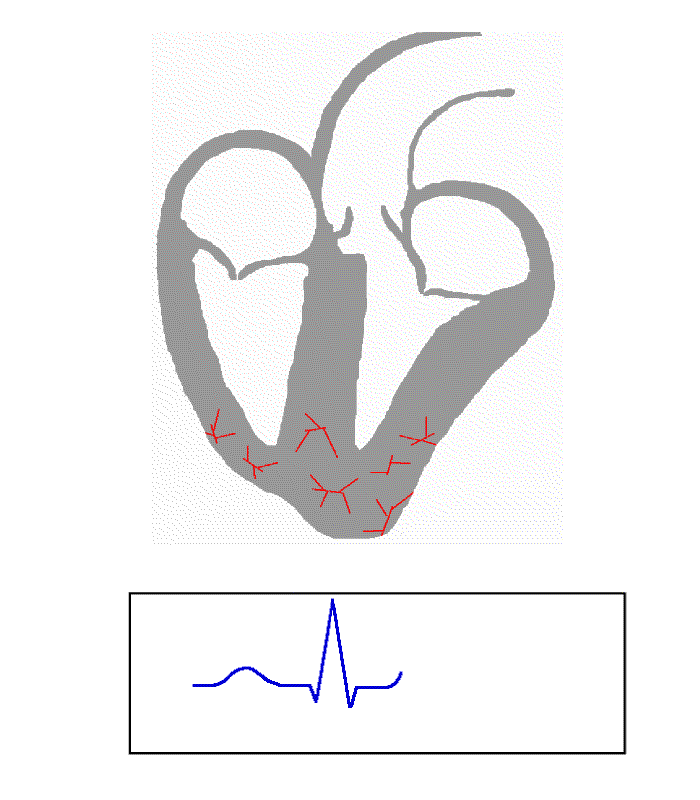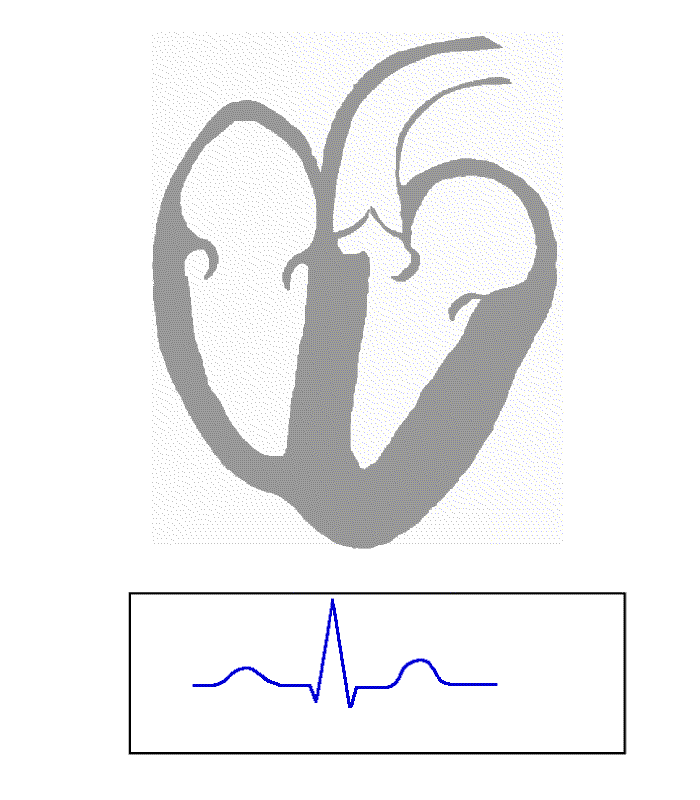 The normal rhythmical heart beat, called sinus rhythm, is established by the heart's own pacemaker, the
The normal rhythmical heart beat, called sinus rhythm, is established by the heart's own pacemaker, the sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node or sinus node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approxi ...
(also known as the sinus node or the SA node). Here an electrical signal is created that travels through the heart, causing the heart muscle to contract. The sinoatrial node is found in the upper part of the right atrium near to the junction with the superior vena cava. The electrical signal generated by the sinoatrial node travels through the right atrium in a radial way that is not completely understood. It travels to the left atrium via Bachmann's bundle, such that the muscles of the left and right atria contract together. The signal then travels to the atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node or AV node electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of t ...
. This is found at the bottom of the right atrium in the atrioventricular septum
The atrioventricular septum is a septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as sept ...
, the boundary between the right atrium and the left ventricle. The septum is part of the cardiac skeleton
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through ...
, tissue within the heart that the electrical signal cannot pass through, which forces the signal to pass through the atrioventricular node only.
Heart rate
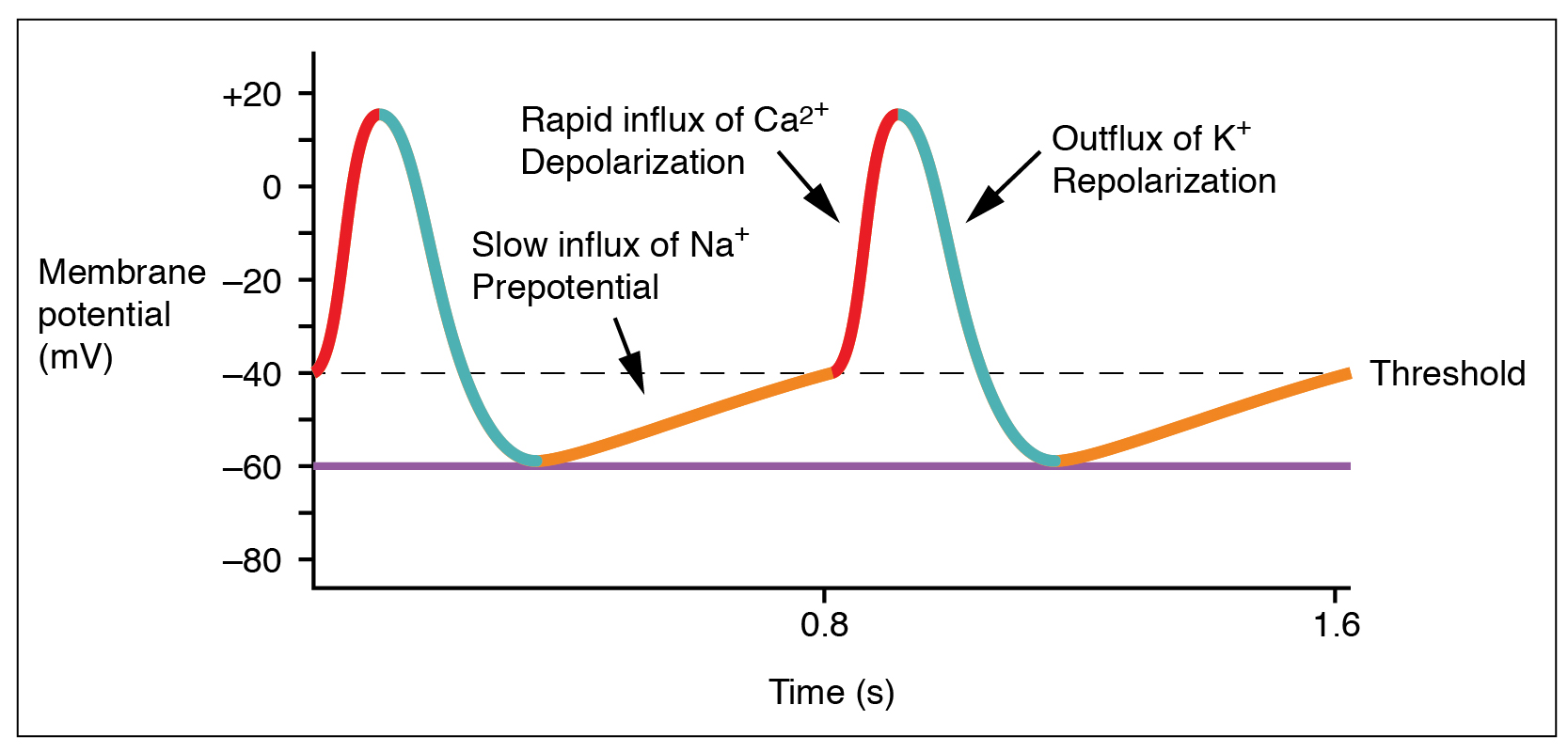 The normal resting heart rate is called the sinus rhythm, created and sustained by the
The normal resting heart rate is called the sinus rhythm, created and sustained by the sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node or sinus node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approxi ...
, a group of pacemaking cells found in the wall of the right atrium. Cells in the sinoatrial node do this by creating an action potential. The cardiac action potential is created by the movement of specific electrolytes into and out of the pacemaker cells. The action potential then spreads to nearby cells.
When the sinoatrial cells are resting, they have a negative charge on their membranes. A rapid influx of sodium ions causes the membrane's charge to become positive; this is called depolarisation and occurs spontaneously.
Influences
The normal sinus rhythm of the heart, giving the resting heart rate, is influenced by a number of factors. The cardiovascular centres in the brainstem control the sympathetic and parasympathetic influences to the heart through the vagus nerve and sympathetic trunk.
Clinical significance
Diseases
Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
s, which include diseases of the heart, are the leading cause of death worldwide.
Ischemic heart disease
Coronary artery disease, also known as ischemic heart disease, is caused by atherosclerosis—a build-up of fatty material along the inner walls of the arteries. These fatty deposits known as atherosclerotic plaques stenosis, narrow the coronary arteries, and if severe may reduce blood flow to the heart.high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high b ...
, uncontrolled diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, smoking and high cholesterol can all increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.
Heart failure
Heart failure is defined as a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the demands of the body.
Cardiomyopathies
Cardiomyopathies are diseases affecting the muscle of the heart. Some cause abnormal thickening of the heart muscle (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy), some cause the heart to abnormally expand and weaken (dilated cardiomyopathy), some cause the heart muscle to become stiff and unable to fully relax between contractions (restrictive cardiomyopathy) and some make the heart prone to abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy). These conditions are often genetic and can be Inherited disease, inherited, but some such as dilated cardiomyopathy may be caused by damage from toxins such as alcohol. Some cardiomyopathies such as hypertrophic cardiomopathy are linked to a higher risk of sudden cardiac death, particularly in athletes.
Valvular heart disease
Healthy heart valves allow blood to flow easily in one direction, and prevent it from flowing in the other direction. A diseased heart valve may have a narrow opening (stenosis), that restricts the flow of blood in the forward direction. A valve may otherwise be leaky, allowing blood to leak in the reverse direction ( Regurgitation (circulation), regurgitation). Valvular heart disease may cause breathlessness, blackouts, or chest pain, but may be asymptomatic and only detected on a routine examination by hearing abnormal heart sounds or a heart murmur. In the developed world, valvular heart disease is most commonly caused by degeneration secondary to old age, but may also be caused by infection of the heart valves (endocarditis). In some parts of the world Rheumatic Heart Disease, rheumatic heart disease is a major cause of valvular heart disease, typically leading to mitral or aortic stenosis and caused by the body's immune system reacting to a Group A streptococcal infection, streptococcal throat infection.
Cardiac arrhythmias
While in the healthy heart, waves of electrical impulses originate in the Sinoatrial node, sinus node before spreading to the rest of the atria, the atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node or AV node electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of t ...
, and finally the ventricles (referred to as a Sinus rhythm, normal sinus rhythm), this normal rhythm can be disrupted. Abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias may be asymptomatic or may cause palpitations, blackouts, or breathlessness. Some types of arrhythmia such as atrial fibrillation increase the long term risk of stroke.
Pericardial disease
The sac which surrounds the heart, called the pericardium, can become inflamed in a condition known as pericarditis. This condition typically causes chest pain that may spread to the back, and is often caused by a viral infection (Infectious mononucleosis, glandular fever, cytomegalovirus, or coxsackievirus). Fluid can build up within the pericardial sac, referred to as a pericardial effusion. Pericardial effusions often occur secondary to pericarditis, kidney failure, or tumours, and frequently do not cause any symptoms. However, large effusions or effusions which accumulate rapidly can compress the heart in a condition known as cardiac tamponade, causing breathlessness and potentially fatal low blood pressure. Fluid can be removed from the pericardial space for diagnosis or to relieve tamponade using a syringe in a procedure called pericardiocentesis.
Congenital heart disease
Some people are born with hearts that are abnormal and these abnormalities are known as congenital heart defects. They may range from the relatively minor (e.g. patent foramen ovale, arguably a variant of normal) to serious life-threatening abnormalities (e.g. hypoplastic left heart syndrome). Common abnormalities include those that affect the heart muscle that separates the two side of the heart (a "hole in the heart", e.g. ventricular septal defect). Other defects include those affecting the heart valves (e.g. Aortic stenosis, congenital aortic stenosis), or the main blood vessels that lead from the heart (e.g. coarctation of the aorta). More complex syndromes are seen that affect more than one part of the heart (e.g. Tetralogy of Fallot).
Some congenital heart defects allow blood that is low in oxygen that would normally be returned to the lungs to instead be pumped back to the rest of the body. These are known as Cyanotic heart defect, cyanotic congenital heart defects and are often more serious. Major congenital heart defects are often picked up in childhood, shortly after birth, or even before a child is born (e.g. Transposition of the great vessels, transposition of the great arteries), causing breathlessness and a lower rate of growth. More minor forms of congenital heart disease may remain undetected for many years and only reveal themselves in adult life (e.g., atrial septal defect).
Channelopathies
Channelopathies can be categorized based on the organ system they affect. In the cardiovascular system, the electrical impulse required for each heart beat is provided by the electrochemical gradient of each heart cell. Because the beating of the heart depends on the proper movement of ions across the surface membrane, cardiac ion channelopathies form a major group of heart diseases. Cardiac ion channelopathies may explain some of the cases of sudden death syndrome and sudden arrhythmic death syndrome.
Diagnosis
Heart disease is diagnosed by the taking of a medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either to the patient or to other pe ...
, a cardiac examination, and further investigations, including blood tests, echocardiogram
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart.
It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in ...
s, electrocardiograms, and cardiac imaging, imaging. Other invasive procedures such as cardiac catheterisation can also play a role.
Examination
The cardiac examination includes inspection, feeling the chest with the hands (palpation) and listening with a stethoscope (auscultation).
Heart sounds
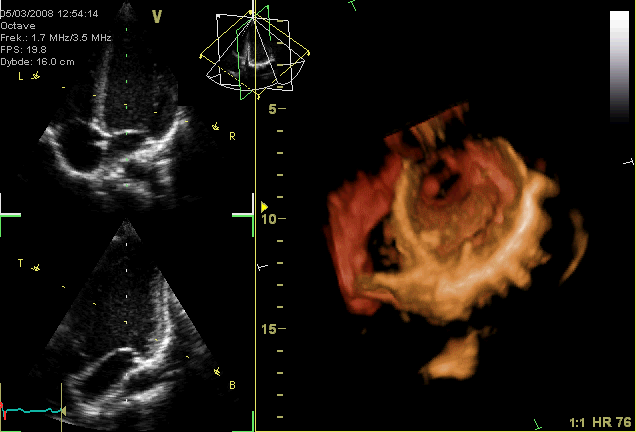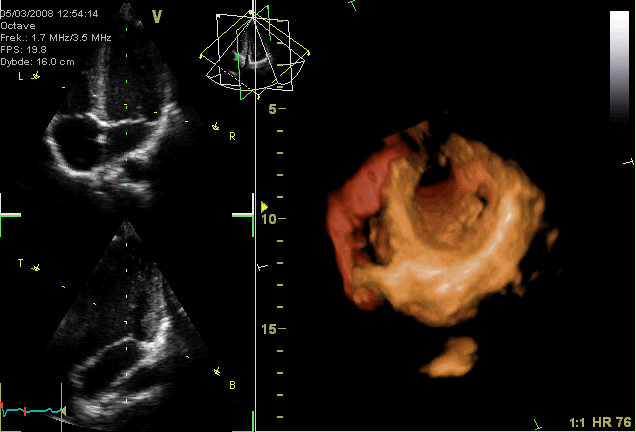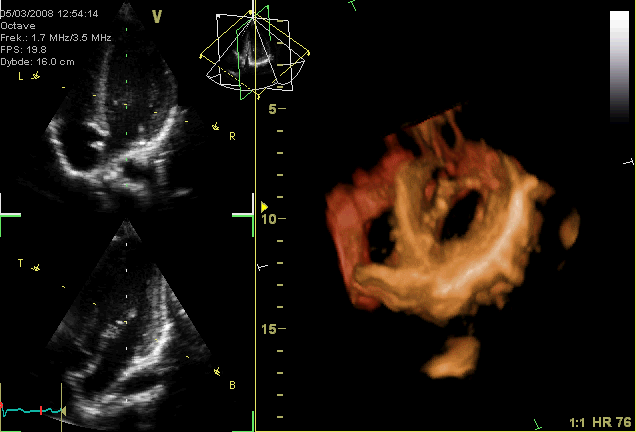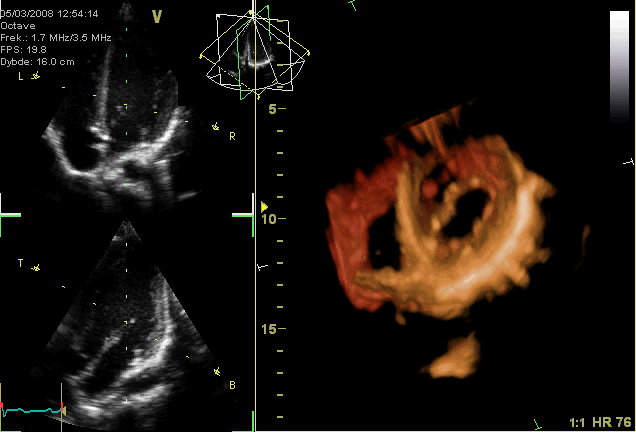 Typically, healthy hearts have only two audible heart sounds, called S1 and S2. The first heart sound S1, is the sound created by the closing of the atrioventricular valves during ventricular contraction and is normally described as "lub". The second heart sound, S2, is the sound of the semilunar valves closing during ventricular diastole and is described as "dub".
Typically, healthy hearts have only two audible heart sounds, called S1 and S2. The first heart sound S1, is the sound created by the closing of the atrioventricular valves during ventricular contraction and is normally described as "lub". The second heart sound, S2, is the sound of the semilunar valves closing during ventricular diastole and is described as "dub".[ Additional heart sounds may also be present and these give rise to gallop rhythms. A third heart sound, S3 usually indicates an increase in ventricular blood volume. A fourth heart sound S4 is referred to as an atrial gallop and is produced by the sound of blood being forced into a stiff ventricle. The combined presence of S3 and S4 give a quadruple gallop.]stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. ...
by which they are heard, and site at which they are heard loudest. Murmurs may be caused by Valvular heart disease, damaged heart valves or congenital heart disease such as ventricular septal defects, or may be heard in normal hearts. A different type of sound, a pericardial friction rub can be heard in cases of pericarditis where the inflamed membranes can rub together.
Blood tests
Blood tests play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of many cardiovascular conditions.
Troponin is a sensitive biomarker for a heart with insufficient blood supply. It is released 4–6 hours after injury and usually peaks at about 12–24 hours.
Electrocardiogram
 Using surface electrodes on the body, it is possible to record the electrical activity of the heart. This tracing of the electrical signal is the electrocardiogram (ECG) or (EKG). An ECG is a bedside test and involves the placement of ten leads on the body. This produces a "12 lead" ECG (three extra leads are calculated mathematically, and one lead is Ground (electricity), electrically ground, or earthed).
There are five prominent features on the ECG: the P wave (electrocardiography), P wave (atrial depolarisation), the QRS complex (ventricular depolarisation) and the T wave (ventricular repolarisation).
Using surface electrodes on the body, it is possible to record the electrical activity of the heart. This tracing of the electrical signal is the electrocardiogram (ECG) or (EKG). An ECG is a bedside test and involves the placement of ten leads on the body. This produces a "12 lead" ECG (three extra leads are calculated mathematically, and one lead is Ground (electricity), electrically ground, or earthed).
There are five prominent features on the ECG: the P wave (electrocardiography), P wave (atrial depolarisation), the QRS complex (ventricular depolarisation) and the T wave (ventricular repolarisation).
Imaging
Several medical imaging, imaging methods can be used to assess the anatomy and function of the heart, including ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
(echocardiography), angiography, CT scan, CT, MRI, and Positron emission tomography, PET, scans. An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart used to measure the heart's function, assess for valve disease, and look for any abnormalities. Echocardiography can be conducted by a probe on the chest (Transthoracic echocardiogram, transthoracic), or by a probe in the esophagus (Transesophageal echocardiogram, transesophageal). A typical echocardiography report will include information about the width of the valves noting any stenosis, whether there is any backflow of blood (Regurgitation (circulation), regurgitation) and information about the blood volumes at the end of systole and diastole, including an ejection fraction, which describes how much blood is ejected from the left and right ventricles after systole. Ejection fraction can then be obtained by dividing the volume ejected by the heart (stroke volume) by the volume of the filled heart (end-diastolic volume). Echocardiograms can also be conducted under circumstances when the body is more stressed, in order to examine for signs of lack of blood supply. This cardiac stress test involves either direct exercise, or where this is not possible, injection of a drug such as dobutamine.
CT scans, chest X-rays and other forms of imaging can help evaluate the heart's size, evaluate for signs of pulmonary oedema, and indicate whether there is pericardial effusion, fluid around the heart. They are also useful for evaluating the aorta, the major blood vessel which leaves the heart.
Treatment
Diseases affecting the heart can be treated by a variety of methods including lifestyle modification, drug treatment, and surgery.
Ischemic heart disease
Narrowings of the coronary arteries (ischemic heart disease) are treated to relieve symptoms of chest pain caused by a partially narrowed artery (angina pectoris), to minimise heart muscle damage when an artery is completely occluded (myocardial infarction), or to prevent a myocardial infarction from occurring. Medications to improve angina symptoms include Medical use of nitroglycerin, nitroglycerin, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers, while preventative treatments include Antiplatelet drug, antiplatelets such as aspirin and statins, lifestyle measures such as stopping smoking and weight loss, and treatment of risk factors such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
In addition to using medications, narrowed heart arteries can be treated by expanding the narrowings or redirecting the flow of blood to bypass an obstruction. This may be performed using a percutaneous coronary intervention, during which narrowings can be expanded by passing small balloon-tipped wires into the coronary arteries, inflating the balloon to expand the narrowing, and sometimes leaving behind a metal scaffold known as a stent to keep the artery open.aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
) to a point beyond the obstruction.
Valvular heart disease
Diseased heart valves that have become abnormally narrow or abnormally leaky may require surgery. This is traditionally performed as an open surgical procedure to replace the damaged heart valve with a tissue or metallic Artificial heart valve, prosthetic valve. In some circumstances, the Tricuspid valve, tricuspid or Mitral valve, mitral valves can be repaired Mitral valve repair, surgically, avoiding the need for a valve replacement. Heart valves can also be treated percutaneously, using techniques that share many similarities with percutaneous coronary intervention. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement, Transcatheter aortic valve replacement is increasingly used for patients consider very high risk for open valve replacement.
Cardiac arrhythmias
Abnormal heart rhythms (Heart arrhythmia, arrhythmias) can be treated using antiarrhythmic drugs. These may work by manipulating the flow of electrolytes across the cell membrane (such as calcium channel blockers, sodium channel blockers, amiodarone, or digoxin), or modify the autonomic nervous system's effect on the heart (beta blockers and atropine). In some arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation which increase the risk of stroke, this risk can be reduced using anticoagulants such as warfarin or novel oral anticoagulants.
Heart failure
As well as addressing the underlying cause for a patient's heart failure (most commonly Coronary artery disease, ischemic heart disease or hypertension), the mainstay of heart failure treatment is with medication. These include drugs to prevent fluid from accumulating in the lungs by increasing the amount of urine a patient produces (diuretics), and drugs that attempt to preserve the pumping function of the heart (beta blockers, ACE inhibitors and Antimineralocorticoid, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists).
History
Ancient
 Humans have known about the heart since ancient times, although its precise function and anatomy were not clearly understood.
Humans have known about the heart since ancient times, although its precise function and anatomy were not clearly understood.[
These ideas went unchallenged for almost a thousand years.][
]
Pre-modern
The earliest descriptions of the coronary circulation, coronary and pulmonary circulation systems can be found in the ''Commentary on Anatomy in Avicenna's Canon'', published in 1242 by Ibn al-Nafis.
Modern
 A breakthrough in understanding the flow of blood through the heart and body came with the publication of ''Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus, De Motu Cordis'' (1628) by the English physician William Harvey. Harvey's book completely describes the systemic circulation and the mechanical force of the heart, leading to an overhaul of the Galenic doctrines.
A breakthrough in understanding the flow of blood through the heart and body came with the publication of ''Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus, De Motu Cordis'' (1628) by the English physician William Harvey. Harvey's book completely describes the systemic circulation and the mechanical force of the heart, leading to an overhaul of the Galenic doctrines.atrioventricular node
The atrioventricular node or AV node electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of t ...
prompted Arthur Keith and Martin Flack to look for similar structures in the heart, leading to their discovery of the sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node or sinus node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approxi ...
several months later. These structures form the anatomical basis of the electrocardiogram, whose inventor, Willem Einthoven, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology in 1924.
The first Heart transplantation, heart transplant in a human ever performed was by James Hardy (surgeon), James Hardy in 1964, using a chimpanzee heart, but the patient died within 2 hours. The first human to human heart transplantation was performed in 1967 by the South African surgeon Christiaan Barnard at Groote Schuur Hospital in Cape Town. This marked an important milestone in cardiac surgery, capturing the attention of both the medical profession and the world at large. However, long-term survival rates of patients were initially very low. Louis Washkansky, the first recipient of a donated heart, died 18 days after the operation while other patients did not survive for more than a few weeks. The American surgeon Norman Shumway has been credited for his efforts to improve transplantation techniques, along with pioneers Richard Lower (surgeon), Richard Lower, Vladimir Demikhov and Adrian Kantrowitz. As of March 2000, more than 55,000 heart transplantations have been performed worldwide. The first successful transplant of a heart from a Genetically modified organism, genetically modified pig to a human in which the patient lived for a longer time, was performed January 7, 2022 in Baltimore by heart surgeon Bartley P. Griffith, recipient was David Bennett (57) this successfully extended his life until 8 March 2022 (1 month and 30 days).
By the middle of the 20th century, Cardiovascular disease, heart disease had surpassed infectious disease as the leading cause of death in the United States, and it is currently the leading cause of deaths worldwide. Since 1948, the ongoing Framingham Heart Study has shed light on the effects of various influences on the heart, including diet, exercise, and common medications such as aspirin. Although the introduction of ACE inhibitors and beta blockers has improved the management of chronic heart failure, the disease continues to be an enormous medical and societal burden, with 30 to 40% of patients dying within a year of receiving the diagnosis.
Society and culture
Symbolism
 As one of the vital organs, the heart was long identified as the center of the entire body, the seat of life, or emotion, or reason, will, intellect, purpose or the mind.
As one of the vital organs, the heart was long identified as the center of the entire body, the seat of life, or emotion, or reason, will, intellect, purpose or the mind.
Food
Animal hearts are widely consumed as food. As they are almost entirely muscle, they are high in protein. They are often included in dishes with other offal, for example in the Ottoman cuisine, pan-Ottoman kokoretsi.
Chicken (food), Chicken hearts are considered to be giblets, and are often grilled on skewers; examples of this are Japanese cuisine, Japanese yakitori, ''hāto yakitori'', Brazilian cuisine, Brazilian churrasco, ''churrasco de coração'', and Indonesian cuisine, Indonesian satay, chicken heart satay. They can also be pan-fried, as in Jerusalem mixed grill. In Egyptian cuisine, they can be used, finely chopped, as part of stuffing for chicken. Many recipes combined them with other giblets, such as the Mexican cuisine, Mexican ''pollo en menudencias'' and the Russian cuisine, Russian ''ragu iz kurinyikh potrokhov''.
The hearts of beef, pork, and mutton can generally be interchanged in recipes. As heart is a hard-working muscle, it makes for "firm and rather dry" meat, so is generally slow-cooked. Another way of dealing with toughness is to Julienning, julienne the meat, as in Chinese cuisine, Chinese stir-fried heart.
Beef heart may be grilled or braised.[Irma S. Rombauer, Rombauer, Irma S. and Rombauer Becker, Marion (1975) ''The Joy of Cooking'', p. 508] In the Peruvian cuisine, Peruvian anticuchos, ''anticuchos de corazón'', barbecued beef hearts are grilled after being tenderized through long marination in a spice and vinegar mixture. An Australian cuisine, Australian recipe for "mock goose" is actually braised stuffed beef heart.
Pork, Pig heart is stewed, poached, braised, or made into sausage. The Balinese cuisine, Balinese ''oret'' is a sort of blood sausage made with pig heart and blood. A French cuisine, French recipe for ''cœur de porc à l'orange'' is made of braised heart with an orange sauce.
Other animals
Vertebrates
The size of the heart varies among the different animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
phylum, groups, with hearts in vertebrates ranging from those of the smallest mice (12 mg) to the blue whale (600 kg). In vertebrates, the heart lies in the middle of the ventral part of the body, surrounded by a pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of ...
.
Double circulatory systems
 Adult amphibians and most reptiles have a double circulatory system, meaning a circulatory system divided into arterial and venous parts. However, the heart itself is not completely separated into two sides. Instead, it is separated into three chambers—two atria and one ventricle. Blood returning from both the systemic circulation and the lungs is returned, and blood is pumped simultaneously into the systemic circulation and the lungs. The double system allows blood to circulate to and from the lungs which deliver oxygenated blood directly to the heart.
Adult amphibians and most reptiles have a double circulatory system, meaning a circulatory system divided into arterial and venous parts. However, the heart itself is not completely separated into two sides. Instead, it is separated into three chambers—two atria and one ventricle. Blood returning from both the systemic circulation and the lungs is returned, and blood is pumped simultaneously into the systemic circulation and the lungs. The double system allows blood to circulate to and from the lungs which deliver oxygenated blood directly to the heart.
Full division
Archosaurs (crocodilians and birds) and mammals show complete separation of the heart into two pumps for a total of four heart chambers; it is thought that the four-chambered heart of archosaurs evolved independently from that of mammals. In crocodilians, there is a small opening, the foramen of Panizza, at the base of the arterial trunks and there is some degree of mixing between the blood in each side of the heart, during a dive underwater;
Fish
 The heart evolved no less than 380 million years ago in fish.
The heart evolved no less than 380 million years ago in fish.
Invertebrates
 Arthropods and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. In this system, deoxygenated blood collects around the heart in cavities (:wikt:sinus, sinuses). This blood slowly permeates the heart through many small one-way channels. The heart then pumps the blood into the hemocoel, a cavity between the organs. The heart in arthropods is typically a muscular tube that runs the length of the body, under the back and from the base of the head. Instead of blood the circulatory fluid is haemolymph which carries the most commonly used respiratory pigment, copper-based haemocyanin as the oxygen transporter. Haemoglobin is only used by a few arthropods.
Arthropods and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. In this system, deoxygenated blood collects around the heart in cavities (:wikt:sinus, sinuses). This blood slowly permeates the heart through many small one-way channels. The heart then pumps the blood into the hemocoel, a cavity between the organs. The heart in arthropods is typically a muscular tube that runs the length of the body, under the back and from the base of the head. Instead of blood the circulatory fluid is haemolymph which carries the most commonly used respiratory pigment, copper-based haemocyanin as the oxygen transporter. Haemoglobin is only used by a few arthropods. In some other invertebrates such as earthworms, the circulatory system is not used to transport oxygen and so is much reduced, having no veins or arteries and consisting of two connected tubes. Oxygen travels by diffusion and there are five small muscular vessels that connect these vessels that contract at the front of the animals that can be thought of as "hearts".
In some other invertebrates such as earthworms, the circulatory system is not used to transport oxygen and so is much reduced, having no veins or arteries and consisting of two connected tubes. Oxygen travels by diffusion and there are five small muscular vessels that connect these vessels that contract at the front of the animals that can be thought of as "hearts".[
Cephalopod, Squids and other cephalopods have two "gill hearts" also known as branchial hearts, and one "systemic heart". The branchial hearts have two atria and one ventricle each, and pump to the gills, whereas the systemic heart pumps to the body.]aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
and contracts to pump blood. This suggests a presence of it in the last deuterostome, common ancestor of these groups (may have been lost in the echinoderms).
Additional images
File:Blausen 0451 Heart Anterior.png, The human heart viewed from the front
File:Blausen 0456 Heart Posterior.png, The human heart viewed from behind
File:Blausen 0260 CoronaryVessels Anterior.png, The coronary circulation
File:2008 Internal Anatomy of the HeartN.jpg, Frontal section of the human heart
File:Slide2aaaaaa.JPG, An anatomical specimen of the heart
File:Human Heart and Circulatory System.png, Heart illustration with circulatory system
File:Animated Heart.gif, Animated heart 3D model rendered in computer
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
External links
Transplantation of pig heart to human. BBC, 11 Jan 2022.
Heart surgeon Bartley P Griffith talks about the unique transplant of pig heart to human.
– NIH
Atlas of Human Cardiac Anatomy
Dissection review of the anatomy of the Human Heart including vessels, internal and external features
The Heart
BBC Radio 4 interdisciplinary discussion with David Wootton, Fay Bound Alberti & Jonathan Sawday (''In Our Time'', 1 June 2006)
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Human Heart
Heart,
Cardiac anatomy
Articles containing video clips
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
Organs (anatomy)


 The human heart is situated in the
The human heart is situated in the  The heart has four chambers, two upper atria, the receiving chambers, and two lower ventricles, the discharging chambers. The atria open into the ventricles via the
The heart has four chambers, two upper atria, the receiving chambers, and two lower ventricles, the discharging chambers. The atria open into the ventricles via the  The heart has four valves, which separate its chambers. One valve lies between each atrium and ventricle, and one valve rests at the exit of each ventricle.
The valves between the atria and ventricles are called the atrioventricular valves. Between the right atrium and the right ventricle is the
The heart has four valves, which separate its chambers. One valve lies between each atrium and ventricle, and one valve rests at the exit of each ventricle.
The valves between the atria and ventricles are called the atrioventricular valves. Between the right atrium and the right ventricle is the  The heart wall is made up of three layers: the inner
The heart wall is made up of three layers: the inner  The middle layer of the heart wall is the myocardium, which is the
The middle layer of the heart wall is the myocardium, which is the  The heart receives nerve signals from the vagus nerve and from nerves arising from the sympathetic trunk. These nerves act to influence, but not control, the heart rate. Sympathetic nervous system, Sympathetic nerves also influence the force of heart contraction. Signals that travel along these nerves arise from two paired cardiovascular centres in the medulla oblongata. The vagus nerve of the parasympathetic nervous system acts to decrease the heart rate, and nerves from the sympathetic trunk act to increase the heart rate. These nerves form a network of nerves that lies over the heart called the cardiac plexus.
The vagus nerve is a long, wandering nerve that emerges from the brainstem and provides parasympathetic stimulation to a large number of organs in the thorax and abdomen, including the heart. The nerves from the sympathetic trunk emerge through the T1-T4 thoracic ganglia and travel to both the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes, as well as to the atria and ventricles. The ventricles are more richly innervated by sympathetic fibers than parasympathetic fibers. Sympathetic stimulation causes the release of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (also known as noradrenaline) at the neuromuscular junction of the cardiac nerves. This shortens the repolarisation period, thus speeding the rate of depolarisation and contraction, which results in an increased heart rate. It opens chemical or ligand-gated sodium and calcium ion channels, allowing an influx of cation, positively charged ions. Norepinephrine binds to the beta-1 adrenergic receptor, beta–1 receptor.
The heart receives nerve signals from the vagus nerve and from nerves arising from the sympathetic trunk. These nerves act to influence, but not control, the heart rate. Sympathetic nervous system, Sympathetic nerves also influence the force of heart contraction. Signals that travel along these nerves arise from two paired cardiovascular centres in the medulla oblongata. The vagus nerve of the parasympathetic nervous system acts to decrease the heart rate, and nerves from the sympathetic trunk act to increase the heart rate. These nerves form a network of nerves that lies over the heart called the cardiac plexus.
The vagus nerve is a long, wandering nerve that emerges from the brainstem and provides parasympathetic stimulation to a large number of organs in the thorax and abdomen, including the heart. The nerves from the sympathetic trunk emerge through the T1-T4 thoracic ganglia and travel to both the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes, as well as to the atria and ventricles. The ventricles are more richly innervated by sympathetic fibers than parasympathetic fibers. Sympathetic stimulation causes the release of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (also known as noradrenaline) at the neuromuscular junction of the cardiac nerves. This shortens the repolarisation period, thus speeding the rate of depolarisation and contraction, which results in an increased heart rate. It opens chemical or ligand-gated sodium and calcium ion channels, allowing an influx of cation, positively charged ions. Norepinephrine binds to the beta-1 adrenergic receptor, beta–1 receptor.
 The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at about three weeks into human embryogenesis, embryogenesis. This early start is crucial for subsequent embryonic and prenatal development.
The heart derives from splanchnopleuric mesenchyme in the neural plate which forms the cardiogenic region. Two endocardial tubes form here that fuse to form a primitive heart tube known as the tubular heart. Between the third and fourth week, the heart tube lengthens, and begins to fold to form an S-shape within the pericardium. This places the chambers and major vessels into the correct alignment for the developed heart. Further development will include the formation of the septa and the valves and the remodeling of the heart chambers. By the end of the fifth week, the septa are complete, and by the ninth week, the heart valves are complete.
Before the fifth week, there is an opening in the fetal heart known as the
The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at about three weeks into human embryogenesis, embryogenesis. This early start is crucial for subsequent embryonic and prenatal development.
The heart derives from splanchnopleuric mesenchyme in the neural plate which forms the cardiogenic region. Two endocardial tubes form here that fuse to form a primitive heart tube known as the tubular heart. Between the third and fourth week, the heart tube lengthens, and begins to fold to form an S-shape within the pericardium. This places the chambers and major vessels into the correct alignment for the developed heart. Further development will include the formation of the septa and the valves and the remodeling of the heart chambers. By the end of the fifth week, the septa are complete, and by the ninth week, the heart valves are complete.
Before the fifth week, there is an opening in the fetal heart known as the  The heart functions as a pump in the
The heart functions as a pump in the  The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in which the heart contracts and relaxes with every heartbeat. The period of time during which the ventricles contract, forcing blood out into the aorta and main pulmonary artery, is known as systole, while the period during which the ventricles relax and refill with blood is known as diastole. The atria and ventricles work in concert, so in systole when the ventricles are contracting, the atria are relaxed and collecting blood. When the ventricles are relaxed in diastole, the atria contract to pump blood to the ventricles. This coordination ensures blood is pumped efficiently to the body.
At the beginning of the cardiac cycle, the ventricles are relaxing. As they do so, they are filled by blood passing through the open Mitral valve, mitral and Tricuspid valve, tricuspid valves. After the ventricles have completed most of their filling, the atria contract, forcing further blood into the ventricles and priming the pump. Next, the ventricles start to contract. As the pressure rises within the cavities of the ventricles, the mitral and tricuspid valves are forced shut. As the pressure within the ventricles rises further, exceeding the pressure with the aorta and pulmonary arteries, the aortic and pulmonary valves open. Blood is ejected from the heart, causing the pressure within the ventricles to fall. Simultaneously, the atria refill as blood flows into the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cavae, and into the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. Finally, when the pressure within the ventricles falls below the pressure within the aorta and pulmonary arteries, the aortic and pulmonary valves close. The ventricles start to relax, the mitral and tricuspid valves open, and the cycle begins again.
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in which the heart contracts and relaxes with every heartbeat. The period of time during which the ventricles contract, forcing blood out into the aorta and main pulmonary artery, is known as systole, while the period during which the ventricles relax and refill with blood is known as diastole. The atria and ventricles work in concert, so in systole when the ventricles are contracting, the atria are relaxed and collecting blood. When the ventricles are relaxed in diastole, the atria contract to pump blood to the ventricles. This coordination ensures blood is pumped efficiently to the body.
At the beginning of the cardiac cycle, the ventricles are relaxing. As they do so, they are filled by blood passing through the open Mitral valve, mitral and Tricuspid valve, tricuspid valves. After the ventricles have completed most of their filling, the atria contract, forcing further blood into the ventricles and priming the pump. Next, the ventricles start to contract. As the pressure rises within the cavities of the ventricles, the mitral and tricuspid valves are forced shut. As the pressure within the ventricles rises further, exceeding the pressure with the aorta and pulmonary arteries, the aortic and pulmonary valves open. Blood is ejected from the heart, causing the pressure within the ventricles to fall. Simultaneously, the atria refill as blood flows into the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cavae, and into the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. Finally, when the pressure within the ventricles falls below the pressure within the aorta and pulmonary arteries, the aortic and pulmonary valves close. The ventricles start to relax, the mitral and tricuspid valves open, and the cycle begins again.
 Cardiac output (CO) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle (stroke volume) in one minute. This is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (SV) by the beats per minute of the heart rate (HR). So that: CO = SV x HR.
The cardiac output is normalized to body size through body surface area and is called the cardiac index.
The average cardiac output, using an average stroke volume of about 70mL, is 5.25 L/min, with a normal range of 4.0–8.0 L/min. The stroke volume is normally measured using an
Cardiac output (CO) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle (stroke volume) in one minute. This is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume (SV) by the beats per minute of the heart rate (HR). So that: CO = SV x HR.
The cardiac output is normalized to body size through body surface area and is called the cardiac index.
The average cardiac output, using an average stroke volume of about 70mL, is 5.25 L/min, with a normal range of 4.0–8.0 L/min. The stroke volume is normally measured using an  The normal rhythmical heart beat, called sinus rhythm, is established by the heart's own pacemaker, the
The normal rhythmical heart beat, called sinus rhythm, is established by the heart's own pacemaker, the  The normal resting heart rate is called the sinus rhythm, created and sustained by the
The normal resting heart rate is called the sinus rhythm, created and sustained by the  Typically, healthy hearts have only two audible heart sounds, called S1 and S2. The first heart sound S1, is the sound created by the closing of the atrioventricular valves during ventricular contraction and is normally described as "lub". The second heart sound, S2, is the sound of the semilunar valves closing during ventricular diastole and is described as "dub". Each sound consists of two components, reflecting the slight difference in time as the two valves close. S2 may split S2, split into two distinct sounds, either as a result of inspiration or different valvular or cardiac problems. Additional heart sounds may also be present and these give rise to gallop rhythms. A third heart sound, S3 usually indicates an increase in ventricular blood volume. A fourth heart sound S4 is referred to as an atrial gallop and is produced by the sound of blood being forced into a stiff ventricle. The combined presence of S3 and S4 give a quadruple gallop.
Heart murmurs are abnormal heart sounds which can be either related to disease or benign, and there are several kinds. There are normally two heart sounds, and abnormal heart sounds can either be extra sounds, or "murmurs" related to the flow of blood between the sounds. Murmurs are graded by volume, from 1 (the quietest), to 6 (the loudest), and evaluated by their relationship to the heart sounds, position in the cardiac cycle, and additional features such as their radiation to other sites, changes with a person's position, the frequency of the sound as determined by the side of the
Typically, healthy hearts have only two audible heart sounds, called S1 and S2. The first heart sound S1, is the sound created by the closing of the atrioventricular valves during ventricular contraction and is normally described as "lub". The second heart sound, S2, is the sound of the semilunar valves closing during ventricular diastole and is described as "dub". Each sound consists of two components, reflecting the slight difference in time as the two valves close. S2 may split S2, split into two distinct sounds, either as a result of inspiration or different valvular or cardiac problems. Additional heart sounds may also be present and these give rise to gallop rhythms. A third heart sound, S3 usually indicates an increase in ventricular blood volume. A fourth heart sound S4 is referred to as an atrial gallop and is produced by the sound of blood being forced into a stiff ventricle. The combined presence of S3 and S4 give a quadruple gallop.
Heart murmurs are abnormal heart sounds which can be either related to disease or benign, and there are several kinds. There are normally two heart sounds, and abnormal heart sounds can either be extra sounds, or "murmurs" related to the flow of blood between the sounds. Murmurs are graded by volume, from 1 (the quietest), to 6 (the loudest), and evaluated by their relationship to the heart sounds, position in the cardiac cycle, and additional features such as their radiation to other sites, changes with a person's position, the frequency of the sound as determined by the side of the  Using surface electrodes on the body, it is possible to record the electrical activity of the heart. This tracing of the electrical signal is the electrocardiogram (ECG) or (EKG). An ECG is a bedside test and involves the placement of ten leads on the body. This produces a "12 lead" ECG (three extra leads are calculated mathematically, and one lead is Ground (electricity), electrically ground, or earthed).
There are five prominent features on the ECG: the P wave (electrocardiography), P wave (atrial depolarisation), the QRS complex (ventricular depolarisation) and the T wave (ventricular repolarisation). As the heart cells contract, they create a current that travels through the heart. A downward deflection on the ECG implies cells are becoming more positive in charge ("depolarising") in the direction of that lead, whereas an upward inflection implies cells are becoming more negative ("repolarising") in the direction of the lead. This depends on the position of the lead, so if a wave of depolarising moved from left to right, a lead on the left would show a negative deflection, and a lead on the right would show a positive deflection. The ECG is a useful tool in detecting arrythmia, rhythm disturbances and in detecting insufficient blood supply to the heart. Sometimes abnormalities are suspected, but not immediately visible on the ECG. Cardiac stress test, Testing when exercising can be used to provoke an abnormality or an ECG can be worn for a longer period such as a 24-hour Holter monitor if a suspected rhythm abnormality is not present at the time of assessment.
Using surface electrodes on the body, it is possible to record the electrical activity of the heart. This tracing of the electrical signal is the electrocardiogram (ECG) or (EKG). An ECG is a bedside test and involves the placement of ten leads on the body. This produces a "12 lead" ECG (three extra leads are calculated mathematically, and one lead is Ground (electricity), electrically ground, or earthed).
There are five prominent features on the ECG: the P wave (electrocardiography), P wave (atrial depolarisation), the QRS complex (ventricular depolarisation) and the T wave (ventricular repolarisation). As the heart cells contract, they create a current that travels through the heart. A downward deflection on the ECG implies cells are becoming more positive in charge ("depolarising") in the direction of that lead, whereas an upward inflection implies cells are becoming more negative ("repolarising") in the direction of the lead. This depends on the position of the lead, so if a wave of depolarising moved from left to right, a lead on the left would show a negative deflection, and a lead on the right would show a positive deflection. The ECG is a useful tool in detecting arrythmia, rhythm disturbances and in detecting insufficient blood supply to the heart. Sometimes abnormalities are suspected, but not immediately visible on the ECG. Cardiac stress test, Testing when exercising can be used to provoke an abnormality or an ECG can be worn for a longer period such as a 24-hour Holter monitor if a suspected rhythm abnormality is not present at the time of assessment.
 Humans have known about the heart since ancient times, although its precise function and anatomy were not clearly understood. From the primarily religious views of earlier societies towards the heart, ancient Greece, ancient Greeks are considered to have been the primary seat of scientific understanding of the heart in the ancient world. Aristotle considered the heart to be the organ responsible for creating blood; Plato considered the heart as the source of circulating blood and Hippocrates noted blood circulating cyclically from the body through the heart to the lungs. Erasistratos (304–250 BCE) noted the heart as a pump, causing dilation of blood vessels, and noted that arteries and veins both radiate from the heart, becoming progressively smaller with distance, although he believed they were filled with air and not blood. He also discovered the heart valves.
The Greek physician Galen (2nd century CE) knew blood vessels carried blood and identified venous (dark red) and arterial (brighter and thinner) blood, each with distinct and separate functions. Galen, noting the heart as the hottest organ in the body, concluded that it provided heat to the body. The heart did not pump blood around, the heart's motion sucked blood in during diastole and the blood moved by the pulsation of the arteries themselves. Galen believed the arterial blood was created by venous blood passing from the left ventricle to the right through 'pores' between the ventricles. Air from the lungs passed from the lungs via the pulmonary artery to the left side of the heart and created arterial blood.
These ideas went unchallenged for almost a thousand years.
Humans have known about the heart since ancient times, although its precise function and anatomy were not clearly understood. From the primarily religious views of earlier societies towards the heart, ancient Greece, ancient Greeks are considered to have been the primary seat of scientific understanding of the heart in the ancient world. Aristotle considered the heart to be the organ responsible for creating blood; Plato considered the heart as the source of circulating blood and Hippocrates noted blood circulating cyclically from the body through the heart to the lungs. Erasistratos (304–250 BCE) noted the heart as a pump, causing dilation of blood vessels, and noted that arteries and veins both radiate from the heart, becoming progressively smaller with distance, although he believed they were filled with air and not blood. He also discovered the heart valves.
The Greek physician Galen (2nd century CE) knew blood vessels carried blood and identified venous (dark red) and arterial (brighter and thinner) blood, each with distinct and separate functions. Galen, noting the heart as the hottest organ in the body, concluded that it provided heat to the body. The heart did not pump blood around, the heart's motion sucked blood in during diastole and the blood moved by the pulsation of the arteries themselves. Galen believed the arterial blood was created by venous blood passing from the left ventricle to the right through 'pores' between the ventricles. Air from the lungs passed from the lungs via the pulmonary artery to the left side of the heart and created arterial blood.
These ideas went unchallenged for almost a thousand years.
 A breakthrough in understanding the flow of blood through the heart and body came with the publication of ''Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus, De Motu Cordis'' (1628) by the English physician William Harvey. Harvey's book completely describes the systemic circulation and the mechanical force of the heart, leading to an overhaul of the Galenic doctrines. Otto Frank (physiologist), Otto Frank (1865–1944) was a German physiologist; among his many published works are detailed studies of this important heart relationship. Ernest Starling (1866–1927) was an important English physiologist who also studied the heart. Although they worked largely independently, their combined efforts and similar conclusions have been recognized in the name "Frank–Starling mechanism".
Although Purkinje fibers and the bundle of His were discovered as early as the 19th century, their specific role in the electrical conduction system of the heart remained unknown until Sunao Tawara published his monograph, titled ''Das Reizleitungssystem des Säugetierherzens'', in 1906. Tawara's discovery of the
A breakthrough in understanding the flow of blood through the heart and body came with the publication of ''Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus, De Motu Cordis'' (1628) by the English physician William Harvey. Harvey's book completely describes the systemic circulation and the mechanical force of the heart, leading to an overhaul of the Galenic doctrines. Otto Frank (physiologist), Otto Frank (1865–1944) was a German physiologist; among his many published works are detailed studies of this important heart relationship. Ernest Starling (1866–1927) was an important English physiologist who also studied the heart. Although they worked largely independently, their combined efforts and similar conclusions have been recognized in the name "Frank–Starling mechanism".
Although Purkinje fibers and the bundle of His were discovered as early as the 19th century, their specific role in the electrical conduction system of the heart remained unknown until Sunao Tawara published his monograph, titled ''Das Reizleitungssystem des Säugetierherzens'', in 1906. Tawara's discovery of the  As one of the vital organs, the heart was long identified as the center of the entire body, the seat of life, or emotion, or reason, will, intellect, purpose or the mind. The heart is an emblematic symbol in many religions, signifying "truth, conscience or moral courage in many religions—the temple or throne of God in Islamic and Judeo-Christian thought; the divine centre, or Ātman (Hinduism), atman, and the third eye of transcendent wisdom in Hinduism; the diamond of purity and essence of the Buddha; the Taoism, Taoist centre of understanding."
In the Hebrew Bible, the word for heart, ''lev'', is used in these meanings, as the seat of emotion, the mind, and referring to the anatomical organ. It is also connected in function and symbolism to the stomach.
An important part of the concept of the Egyptian soul, soul in Ancient Egyptian religion was thought to be the heart, or ''ib''. The ''ib'' or metaphysical heart was believed to be formed from one drop of blood from the child's mother's heart, taken at conception. To ancient Egyptians, the heart was the seat of emotion, thought, will, and intention. This is evidenced by Egyptian language, Egyptian expressions which incorporate the word ''ib'', such as ''Awi-ib'' for "happy" (literally, "long of heart"), ''Xak-ib'' for "estranged" (literally, "truncated of heart"). In Egyptian religion, the heart was the key to the afterlife. It was conceived as surviving death in the nether world, where it gave evidence for, or against, its possessor. The heart was therefore not removed from the body during mummification, and was believed to be the center of intelligence and feeling, and needed in the afterlife. It was thought that the heart was examined by Anubis and a variety of ancient Egyptian deities, deities during the ''Weighing of the Heart'' ceremony. If the heart weighed more than the feather of Maat, which symbolized the ideal standard of behavior. If the scales balanced, it meant the heart's possessor had lived a just life and could enter the afterlife; if the heart was heavier, it would be devoured by the monster Ammit.
The Chinese language, Chinese character for "heart", 心, derives from a comparatively realistic depiction of a heart (indicating the heart chambers) in seal script. The Chinese word :wikt:心#Mandarin, ''xīn'' also takes the metaphorical meanings of "mind", "intention", or "core", and is often translated as "heart-mind" as the ancient Chinese believed the heart was the center of human cognition. Heart (Chinese medicine), In Chinese medicine, the heart is seen as the center of Shen (Chinese religion), 神 ''shén'' "spirit, consciousness". The heart is associated with the small intestine, tongue, governs the Zang-fu, six organs and five viscera, and belongs to fire in the five elements.
The Sanskrit word for heart is ''hṛd'' or ''hṛdaya'', found in the oldest surviving Sanskrit text, the Rigveda. In Sanskrit, it may mean both the anatomical object and "mind" or "soul", representing the seat of emotion. ''Hrd'' may be a cognate of the word for heart in Greek, Latin, and English.
Many classical antiquity, classical philosophers and scientists, including Aristotle, considered the heart the seat of thought, reason, or emotion, often disregarding the brain as contributing to those functions. The identification of the heart as the seat of emotions in particular is due to the Roman Empire, Roman physician Galen, who also located the seat of the passions in the liver, and the seat of reason in the brain.
The heart also played a role in the Aztec system of belief. The most common form of human sacrifice practiced by the Aztecs was heart-extraction. The Aztec believed that the heart (''tona'') was both the seat of the individual and a fragment of the Sun's heat (''istli''). To this day, the Nahua consider the Sun to be a heart-soul (''tona-tiuh''): "round, hot, pulsating".
Indigenous leaders from Alaska to Australia came together in 2020 to deliver a message to the world that humanity needs to shift from the mind to the heart, and let our heart be in charge of what we do. The message was made into a film, which highlighted that humanity must open their hearts to restore balance to the world. Kumu Sabra Kauka, a Hawaiian studies educator and tradition bearer summed up the message of the film saying "Listen to your heart. Follow your path. May it be clear, and for the good of all." The film was led by Illarion Merculieff from the Aleut (Unangan) tribe. Merculieff has written that Unangan Elders referred to the heart as a "source of wisdom", "a deeper portal of profound interconnectedness and awareness that exists between humans and all living things".
In Catholicism, there has been a long tradition of veneration of the heart, stemming from worship of the wounds of Jesus Christ which gained prominence from the mid sixteenth century. This tradition influenced the development of the medieval Christian Catholic devotions, devotion to the Sacred Heart of Jesus and the parallel veneration of the Immaculate Heart of Mary, made popular by John Eudes. There are also many references to the heart in the Christian Bible, including "Blessed are the pure in heart, for they will see God", "Above all else, guard your heart, for everything you do flows from it", "For where your treasure is, there your heart will be also", "For as a man thinks in his heart, so shall he be."
The expression of a broken heart is a cross-cultural reference to grief for a lost one or to unfulfilled romantic love.
The notion of "Cupid's arrows" is ancient, due to Ovid, but while Ovid describes Cupid as wounding his victims with his arrows, it is not made explicit that it is the ''heart'' that is wounded. The familiar iconography of Cupid shooting little heart shape, heart symbols is a Renaissance theme that became tied to Valentine's Day.
In certain Trans–New Guinea languages, Trans-New Guinea languages, such as Foi language, Foi and Momoona, the heart and seat of emotions are Colexification, colexified, meaning they share the same word.
As one of the vital organs, the heart was long identified as the center of the entire body, the seat of life, or emotion, or reason, will, intellect, purpose or the mind. The heart is an emblematic symbol in many religions, signifying "truth, conscience or moral courage in many religions—the temple or throne of God in Islamic and Judeo-Christian thought; the divine centre, or Ātman (Hinduism), atman, and the third eye of transcendent wisdom in Hinduism; the diamond of purity and essence of the Buddha; the Taoism, Taoist centre of understanding."
In the Hebrew Bible, the word for heart, ''lev'', is used in these meanings, as the seat of emotion, the mind, and referring to the anatomical organ. It is also connected in function and symbolism to the stomach.
An important part of the concept of the Egyptian soul, soul in Ancient Egyptian religion was thought to be the heart, or ''ib''. The ''ib'' or metaphysical heart was believed to be formed from one drop of blood from the child's mother's heart, taken at conception. To ancient Egyptians, the heart was the seat of emotion, thought, will, and intention. This is evidenced by Egyptian language, Egyptian expressions which incorporate the word ''ib'', such as ''Awi-ib'' for "happy" (literally, "long of heart"), ''Xak-ib'' for "estranged" (literally, "truncated of heart"). In Egyptian religion, the heart was the key to the afterlife. It was conceived as surviving death in the nether world, where it gave evidence for, or against, its possessor. The heart was therefore not removed from the body during mummification, and was believed to be the center of intelligence and feeling, and needed in the afterlife. It was thought that the heart was examined by Anubis and a variety of ancient Egyptian deities, deities during the ''Weighing of the Heart'' ceremony. If the heart weighed more than the feather of Maat, which symbolized the ideal standard of behavior. If the scales balanced, it meant the heart's possessor had lived a just life and could enter the afterlife; if the heart was heavier, it would be devoured by the monster Ammit.
The Chinese language, Chinese character for "heart", 心, derives from a comparatively realistic depiction of a heart (indicating the heart chambers) in seal script. The Chinese word :wikt:心#Mandarin, ''xīn'' also takes the metaphorical meanings of "mind", "intention", or "core", and is often translated as "heart-mind" as the ancient Chinese believed the heart was the center of human cognition. Heart (Chinese medicine), In Chinese medicine, the heart is seen as the center of Shen (Chinese religion), 神 ''shén'' "spirit, consciousness". The heart is associated with the small intestine, tongue, governs the Zang-fu, six organs and five viscera, and belongs to fire in the five elements.
The Sanskrit word for heart is ''hṛd'' or ''hṛdaya'', found in the oldest surviving Sanskrit text, the Rigveda. In Sanskrit, it may mean both the anatomical object and "mind" or "soul", representing the seat of emotion. ''Hrd'' may be a cognate of the word for heart in Greek, Latin, and English.
Many classical antiquity, classical philosophers and scientists, including Aristotle, considered the heart the seat of thought, reason, or emotion, often disregarding the brain as contributing to those functions. The identification of the heart as the seat of emotions in particular is due to the Roman Empire, Roman physician Galen, who also located the seat of the passions in the liver, and the seat of reason in the brain.
The heart also played a role in the Aztec system of belief. The most common form of human sacrifice practiced by the Aztecs was heart-extraction. The Aztec believed that the heart (''tona'') was both the seat of the individual and a fragment of the Sun's heat (''istli''). To this day, the Nahua consider the Sun to be a heart-soul (''tona-tiuh''): "round, hot, pulsating".
Indigenous leaders from Alaska to Australia came together in 2020 to deliver a message to the world that humanity needs to shift from the mind to the heart, and let our heart be in charge of what we do. The message was made into a film, which highlighted that humanity must open their hearts to restore balance to the world. Kumu Sabra Kauka, a Hawaiian studies educator and tradition bearer summed up the message of the film saying "Listen to your heart. Follow your path. May it be clear, and for the good of all." The film was led by Illarion Merculieff from the Aleut (Unangan) tribe. Merculieff has written that Unangan Elders referred to the heart as a "source of wisdom", "a deeper portal of profound interconnectedness and awareness that exists between humans and all living things".
In Catholicism, there has been a long tradition of veneration of the heart, stemming from worship of the wounds of Jesus Christ which gained prominence from the mid sixteenth century. This tradition influenced the development of the medieval Christian Catholic devotions, devotion to the Sacred Heart of Jesus and the parallel veneration of the Immaculate Heart of Mary, made popular by John Eudes. There are also many references to the heart in the Christian Bible, including "Blessed are the pure in heart, for they will see God", "Above all else, guard your heart, for everything you do flows from it", "For where your treasure is, there your heart will be also", "For as a man thinks in his heart, so shall he be."
The expression of a broken heart is a cross-cultural reference to grief for a lost one or to unfulfilled romantic love.
The notion of "Cupid's arrows" is ancient, due to Ovid, but while Ovid describes Cupid as wounding his victims with his arrows, it is not made explicit that it is the ''heart'' that is wounded. The familiar iconography of Cupid shooting little heart shape, heart symbols is a Renaissance theme that became tied to Valentine's Day.
In certain Trans–New Guinea languages, Trans-New Guinea languages, such as Foi language, Foi and Momoona, the heart and seat of emotions are Colexification, colexified, meaning they share the same word.
 Arthropods and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. In this system, deoxygenated blood collects around the heart in cavities (:wikt:sinus, sinuses). This blood slowly permeates the heart through many small one-way channels. The heart then pumps the blood into the hemocoel, a cavity between the organs. The heart in arthropods is typically a muscular tube that runs the length of the body, under the back and from the base of the head. Instead of blood the circulatory fluid is haemolymph which carries the most commonly used respiratory pigment, copper-based haemocyanin as the oxygen transporter. Haemoglobin is only used by a few arthropods.
Arthropods and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. In this system, deoxygenated blood collects around the heart in cavities (:wikt:sinus, sinuses). This blood slowly permeates the heart through many small one-way channels. The heart then pumps the blood into the hemocoel, a cavity between the organs. The heart in arthropods is typically a muscular tube that runs the length of the body, under the back and from the base of the head. Instead of blood the circulatory fluid is haemolymph which carries the most commonly used respiratory pigment, copper-based haemocyanin as the oxygen transporter. Haemoglobin is only used by a few arthropods.