|
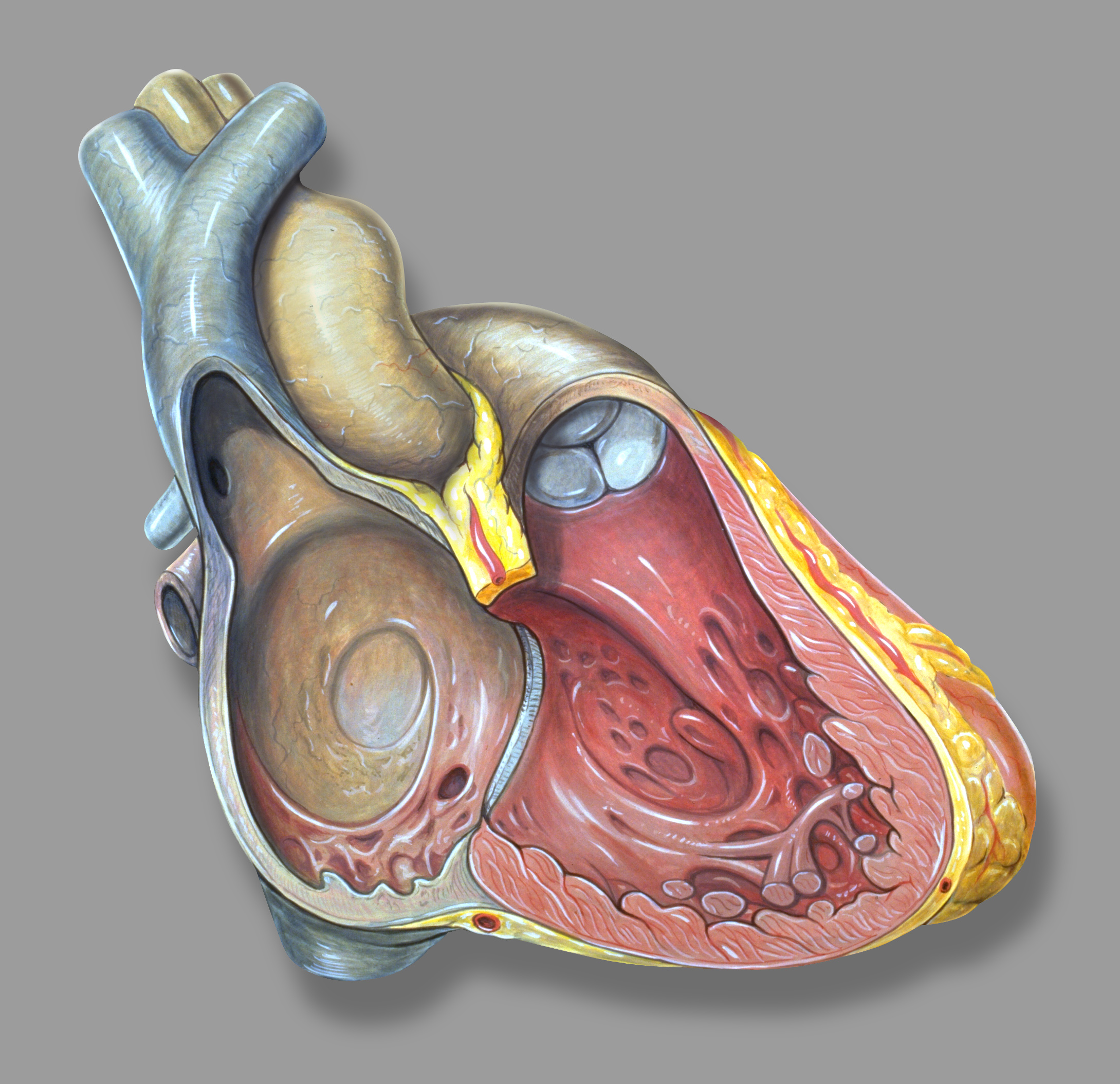
Atrioventricular Septum
The atrioventricular septum is a septum of the heart between the right atrium (RA) and the left ventricle (LV). Although the name "atrioventricular septum" implies any septum between an atrium and a ventricle, in practice the divisions from RA to RV and from LA to LV are mediated by valves, not by septa. Also, there is usually no communication between the LA and the RV. Structure It has a membranous and muscular part. When considering only the membranous septum, it is also known as the "atrioventricular component of the membranous septum". Development It is formed by the union of the dorsal AV cushion and ventral AV cushion. This septum divides the atrioventricular canal. Clinical relevance In some cases, defects can be identified with an echocardiogram. Incomplete formation of the endocardial cushions can lead to atrioventricular septal defect Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" (CAVC) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate. Examples Human anatomy * Interatrial septum, the wall of tissue that is a sectional part of the left and right atria of the heart * Interventricular septum, the wall separating the left and right ventricles of the heart * Lingual septum, a vertical layer of fibrous tissue that separates the halves of the tongue. *Nasal septum: the cartilage wall separating the nostrils of the nose * Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the alveoli from each other in the lungs * Orbital septum, a palpebral ligament in the upper and lower eyelids * Septum pellucidum or septum lucidum, a thin structure separating two fluid pockets in the brain * Uterine septum, a malformation of the uterus * Vaginal septum, a lateral or transverse partition inside the vagina * Intermuscular sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the atria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiogram
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnormality in patients with suspected cardiac disease. It is a tool which helps in reaching an early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocardial Cushions
Endocardial cushions, or atrioventricular cushions, refer to a subset of cells in the development of the heart that play a vital role in the proper formation of the heart septa. They develop on the atrioventricular canal and conotruncal region of the bulbus cordis. During heart development, the heart starts out as a tube. As heart development continues, this tube undergoes remodeling to eventually form the four-chambered heart. The endocardial cushions are a subset of cells found in the developing heart tube that will give rise to the heart's primitive valves and septa, critical to the proper formation of a four-chambered heart. Development The endocardial cushions are thought to arise from a subset of endothelial cells that undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition, a process whereby these cells break cell-to-cell contacts and migrate into the cardiac jelly (towards the interior of the heart tube). These migrated cells form the "swellings" called the endocardial cushions seen in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrioventricular Septal Defect
Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" (CAVC) or "endocardial cushion defect" (ECD), is characterized by a deficiency of the atrioventricular septum of the heart that creates connections between all four of its chambers. It is caused by an abnormal or inadequate fusion of the superior and inferior endocardial cushions with the mid portion of the atrial septum and the muscular portion of the ventricular septum. Symptoms and signs Symptoms include difficulty breathing (dyspnea) and bluish discoloration on skin, fingernails, and lips (cyanosis). A newborn baby will show signs of heart failure such as edema, fatigue, wheezing, sweating and irregular heartbeat. Complications Normally, the four chambers of the heart divide oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood into separate pools. When holes form between the chambers, as in AVSD, the pools can mix. Consequently, arterial blood supplies become less oxygena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostium Primum Atrial Septal Defect
The ostium primum atrial septal defect is a defect in the atrial septum at the level of the tricuspid and mitral valves. This is sometimes known as an endocardial cushion defect because it often involves the endocardial cushion, which is the portion of the heart where the atrial septum meets the ventricular septum and the mitral valve meets the tricuspid valve. Endocardial cushion defects are associated with abnormalities of the atrioventricular valves (the mitral valve and the tricuspid valve). These include the cleft mitral valve, and the single atrioventricular valve (a single large, deformed valve that flows into both the right ventricle and the left ventricle). Endocardial cushion defects are the most common congenital heart defect that is associated with Down syndrome. Signs and symptoms On ECG a left axis deviation is generally found in ostium primum ASD, but an RSR pattern (M pattern) in V1 is characteristic. Fixed splitting of the second heart sound (S2) occurs becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |