Blacks And Changing American Institutions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Black is a racialized classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin; in certain countries, often in socially based systems of racial classification in the Western world, the term "black" is used to describe persons who are perceived as dark-skinned compared to other populations. It is most commonly used for people of
 Numerous communities of dark-skinned peoples are present in North Africa, some dating from prehistoric communities. Others descend from migrants via the historical trans-Saharan trade or, after the Arab invasions of North Africa in the 7th century, from slaves from the
Numerous communities of dark-skinned peoples are present in North Africa, some dating from prehistoric communities. Others descend from migrants via the historical trans-Saharan trade or, after the Arab invasions of North Africa in the 7th century, from slaves from the  In the 18th century, the Moroccan Sultan Moulay Ismail "the Warrior King" (1672–1727) raised a corps of 150,000 black soldiers, called his Black Guard.
According to Carlos Moore, resident scholar at Brazil's University of the State of Bahia, in the 21st century Afro-multiracials in the Arab world, including Arabs in North Africa, self-identify in ways that resemble multi-racials in Latin America. He claims that darker-toned Arabs, much like darker-toned Latin Americans, consider themselves white because they have some distant white ancestry.
Egyptian President Anwar Sadat had a mother who was a dark-skinned Nubian Sudanese ( Sudanese Arab) woman and a father who was a lighter-skinned Egyptian. In response to an advertisement for an acting position, as a young man he said, "I am not white but I am not exactly black either. My blackness is tending to reddish".
Due to the
In the 18th century, the Moroccan Sultan Moulay Ismail "the Warrior King" (1672–1727) raised a corps of 150,000 black soldiers, called his Black Guard.
According to Carlos Moore, resident scholar at Brazil's University of the State of Bahia, in the 21st century Afro-multiracials in the Arab world, including Arabs in North Africa, self-identify in ways that resemble multi-racials in Latin America. He claims that darker-toned Arabs, much like darker-toned Latin Americans, consider themselves white because they have some distant white ancestry.
Egyptian President Anwar Sadat had a mother who was a dark-skinned Nubian Sudanese ( Sudanese Arab) woman and a father who was a lighter-skinned Egyptian. In response to an advertisement for an acting position, as a young man he said, "I am not white but I am not exactly black either. My blackness is tending to reddish".
Due to the
 In the
In the
 Historians estimate that between the advent of
Historians estimate that between the advent of

 About 150,000 East African and black people live in Israel, amounting to just over 2% of the nation's population. The vast majority of these, some 120,000, are
About 150,000 East African and black people live in Israel, amounting to just over 2% of the nation's population. The vast majority of these, some 120,000, are
 Beginning several centuries ago, during the period of the Ottoman Empire, tens of thousands of Zanj captives were brought by slave traders to plantations and agricultural areas situated between Antalya and Istanbul, which gave rise to the Afro-Turk population in present-day Turkey. Some of their ancestry remained ''in situ'', and many migrated to larger cities and towns. Other black slaves were transported to Crete, from where they or their descendants later reached the İzmir area through the population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923, or indirectly from Ayvalık in pursuit of work.
Apart from the historical Afro-Turk presence Turkey also hosts a sizeable immigrant black population since the end of the 1990s. The community is composed mostly of modern immigrants from Ghana, Ethiopia, DRC, Sudan, Nigeria, Kenya, Eritrea, Somalia and Senegal. According to official figures 1.5 million Africans live in Turkey and around 25% of them are located in Istanbul. Other studies state the majority of Africans in Turkey lives in Istanbul and report Tarlabaşı, Dolapdere,
Beginning several centuries ago, during the period of the Ottoman Empire, tens of thousands of Zanj captives were brought by slave traders to plantations and agricultural areas situated between Antalya and Istanbul, which gave rise to the Afro-Turk population in present-day Turkey. Some of their ancestry remained ''in situ'', and many migrated to larger cities and towns. Other black slaves were transported to Crete, from where they or their descendants later reached the İzmir area through the population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923, or indirectly from Ayvalık in pursuit of work.
Apart from the historical Afro-Turk presence Turkey also hosts a sizeable immigrant black population since the end of the 1990s. The community is composed mostly of modern immigrants from Ghana, Ethiopia, DRC, Sudan, Nigeria, Kenya, Eritrea, Somalia and Senegal. According to official figures 1.5 million Africans live in Turkey and around 25% of them are located in Istanbul. Other studies state the majority of Africans in Turkey lives in Istanbul and report Tarlabaşı, Dolapdere,
 The
The
 Negritos, are a collection of various, often unrelated peoples, who were once considered a single distinct population of closely related groups, but genetic studies showed that they descended from the same ancient
Negritos, are a collection of various, often unrelated peoples, who were once considered a single distinct population of closely related groups, but genetic studies showed that they descended from the same ancient  Negrito means "little black people" in Spanish (negrito is the Spanish diminutive of negro, i.e., "little black person"); it is what the Spaniards called the aborigines that they encountered in the Philippines. The term ''Negrito'' itself has come under criticism in countries like Malaysia, where it is now interchangeable with the more acceptable Semang, although this term actually refers to a specific group.
They have dark skin, often curly-hair and Asiatic facial characteristics, and are stockily built.
Negritos in the Philippines frequently face discrimination. Because of their traditional hunter-gatherer lifestyle, they are marginalized and live in poverty, unable to find employment.
Negrito means "little black people" in Spanish (negrito is the Spanish diminutive of negro, i.e., "little black person"); it is what the Spaniards called the aborigines that they encountered in the Philippines. The term ''Negrito'' itself has come under criticism in countries like Malaysia, where it is now interchangeable with the more acceptable Semang, although this term actually refers to a specific group.
They have dark skin, often curly-hair and Asiatic facial characteristics, and are stockily built.
Negritos in the Philippines frequently face discrimination. Because of their traditional hunter-gatherer lifestyle, they are marginalized and live in poverty, unable to find employment.
 While census collection of ethnic background is illegal in France, it is estimated that there are about 2.5 – 5 million black people residing there.
While census collection of ethnic background is illegal in France, it is estimated that there are about 2.5 – 5 million black people residing there.
 Indigenous Australians have been referred to as "black people" in Australia since the early days of European settlement. While originally related to skin colour, the term is used today to indicate Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander ancestry in general and can refer to people of any skin pigmentation.
Being identified as either "black" or "white" in
Indigenous Australians have been referred to as "black people" in Australia since the early days of European settlement. While originally related to skin colour, the term is used today to indicate Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander ancestry in general and can refer to people of any skin pigmentation.
Being identified as either "black" or "white" in  The second half of the 20th century to the present has seen a gradual shift towards improved human rights for Aboriginal people. In a 1967 referendum, more than 90% of the Australian population voted to end constitutional discrimination and to include Aborigines in the national census. During this period, many Aboriginal activists began to embrace the term "black" and use their ancestry as a source of pride. Activist Bob Maza said:
In 1978, Aboriginal writer Kevin Gilbert received the National Book Council award for his book ''Living Black: Blacks Talk to Kevin Gilbert'', a collection of Aboriginal people's stories, and in 1998 was awarded (but refused to accept) the Human Rights Award for Literature for ''Inside Black Australia'', a poetry anthology and exhibition of Aboriginal photography. In contrast to previous definitions based solely on the degree of Aboriginal ancestry, the Government changed the legal definition of Aboriginal in 1990 to include any:
This nationwide acceptance and recognition of Aboriginal people led to a significant increase in the number of people self-identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander. The reappropriation of the term "black" with a positive and more inclusive meaning has resulted in its widespread use in mainstream Australian culture, including public media outlets, government agencies, and private companies. In 2012, a number of high-profile cases highlighted the legal and community attitude that identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander is not dependent on skin color, with a well-known boxer Anthony Mundine being widely criticized for questioning the "blackness" of another boxer and journalist Andrew Bolt being successfully sued for publishing discriminatory comments about Aboriginals with light skin.
The second half of the 20th century to the present has seen a gradual shift towards improved human rights for Aboriginal people. In a 1967 referendum, more than 90% of the Australian population voted to end constitutional discrimination and to include Aborigines in the national census. During this period, many Aboriginal activists began to embrace the term "black" and use their ancestry as a source of pride. Activist Bob Maza said:
In 1978, Aboriginal writer Kevin Gilbert received the National Book Council award for his book ''Living Black: Blacks Talk to Kevin Gilbert'', a collection of Aboriginal people's stories, and in 1998 was awarded (but refused to accept) the Human Rights Award for Literature for ''Inside Black Australia'', a poetry anthology and exhibition of Aboriginal photography. In contrast to previous definitions based solely on the degree of Aboriginal ancestry, the Government changed the legal definition of Aboriginal in 1990 to include any:
This nationwide acceptance and recognition of Aboriginal people led to a significant increase in the number of people self-identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander. The reappropriation of the term "black" with a positive and more inclusive meaning has resulted in its widespread use in mainstream Australian culture, including public media outlets, government agencies, and private companies. In 2012, a number of high-profile cases highlighted the legal and community attitude that identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander is not dependent on skin color, with a well-known boxer Anthony Mundine being widely criticized for questioning the "blackness" of another boxer and journalist Andrew Bolt being successfully sued for publishing discriminatory comments about Aboriginals with light skin.
 Melanesians, along with other Pacific Islanders, were frequently deceived or coerced during the 19th and 20th centuries into forced labour for sugarcane, cotton, and coffee planters in countries distant to their native lands in a practice known as blackbirding. In Queensland, some 55,000 to 62,500Tracey Flanagan, Meredith Wilkie, and Susanna Iuliano
Melanesians, along with other Pacific Islanders, were frequently deceived or coerced during the 19th and 20th centuries into forced labour for sugarcane, cotton, and coffee planters in countries distant to their native lands in a practice known as blackbirding. In Queensland, some 55,000 to 62,500Tracey Flanagan, Meredith Wilkie, and Susanna Iuliano
"Australian South Sea Islanders: A Century of Race Discrimination under Australian Law"
Australian Human Rights Commission. were brought from the New Hebrides, the Solomon Islands, and New Guinea to work in sugarcane fields. Under the
 There were eight principal areas used by Europeans to buy and ship slaves to the Western Hemisphere. The number of enslaved people sold to the New World varied throughout the slave trade. As for the distribution of slaves from regions of activity, certain areas produced far more enslaved people than others. Between 1650 and 1900, 10.24 million enslaved West Africans arrived in the Americas from the following regions in the following proportions:Lovejoy, Paul E. ''Transformations in Slavery''. Cambridge University Press, 2000.
*
There were eight principal areas used by Europeans to buy and ship slaves to the Western Hemisphere. The number of enslaved people sold to the New World varied throughout the slave trade. As for the distribution of slaves from regions of activity, certain areas produced far more enslaved people than others. Between 1650 and 1900, 10.24 million enslaved West Africans arrived in the Americas from the following regions in the following proportions:Lovejoy, Paul E. ''Transformations in Slavery''. Cambridge University Press, 2000.
*  By the early 1900s, ''nigger'' had become a pejorative word in the United States. In its stead, the term '' colored'' became the mainstream alternative to '' negro'' and its derived terms. After the American Civil Rights Movement, the terms ''colored'' and ''negro'' gave way to "black". ''Negro'' had superseded ''colored'' as the most polite word for
By the early 1900s, ''nigger'' had become a pejorative word in the United States. In its stead, the term '' colored'' became the mainstream alternative to '' negro'' and its derived terms. After the American Civil Rights Movement, the terms ''colored'' and ''negro'' gave way to "black". ''Negro'' had superseded ''colored'' as the most polite word for
 From the late 19th century, the South used a colloquial term, the '' one-drop rule'', to classify as black a person of any known African ancestry. This practice of hypodescent was not put into law until the early 20th century. Legally, the definition varied from state to state. Racial definition was more flexible in the 18th and 19th centuries before the American Civil War. For instance, President Thomas Jefferson held in slavery persons who were legally white (less than 25% black) according to Virginia law at the time, but, because they were born to slave mothers, they were born into slavery, according to the principle of '' partus sequitur ventrem'', which Virginia adopted into law in 1662.
Outside of the United States, some other countries have adopted the one-drop rule, but the definition of who is black and the extent to which the one-drop "rule" applies varies greatly from country to country.
The one-drop rule may have originated as a means of increasing the number of black slaves and was maintained as an attempt to keep the white race "pure". One of the results of the one-drop rule was the uniting of the African-American community. Some of the most prominent abolitionists and civil-rights activists of the 19th century were multiracial, such as Frederick Douglass, Robert Purvis and James Mercer Langston. They advocated equality for all.
From the late 19th century, the South used a colloquial term, the '' one-drop rule'', to classify as black a person of any known African ancestry. This practice of hypodescent was not put into law until the early 20th century. Legally, the definition varied from state to state. Racial definition was more flexible in the 18th and 19th centuries before the American Civil War. For instance, President Thomas Jefferson held in slavery persons who were legally white (less than 25% black) according to Virginia law at the time, but, because they were born to slave mothers, they were born into slavery, according to the principle of '' partus sequitur ventrem'', which Virginia adopted into law in 1662.
Outside of the United States, some other countries have adopted the one-drop rule, but the definition of who is black and the extent to which the one-drop "rule" applies varies greatly from country to country.
The one-drop rule may have originated as a means of increasing the number of black slaves and was maintained as an attempt to keep the white race "pure". One of the results of the one-drop rule was the uniting of the African-American community. Some of the most prominent abolitionists and civil-rights activists of the 19th century were multiracial, such as Frederick Douglass, Robert Purvis and James Mercer Langston. They advocated equality for all.
 The concept of blackness in the United States has been described as the degree to which one associates themselves with mainstream
The concept of blackness in the United States has been described as the degree to which one associates themselves with mainstream
 Approximately 12 million people were shipped from Africa to the
Approximately 12 million people were shipped from Africa to the
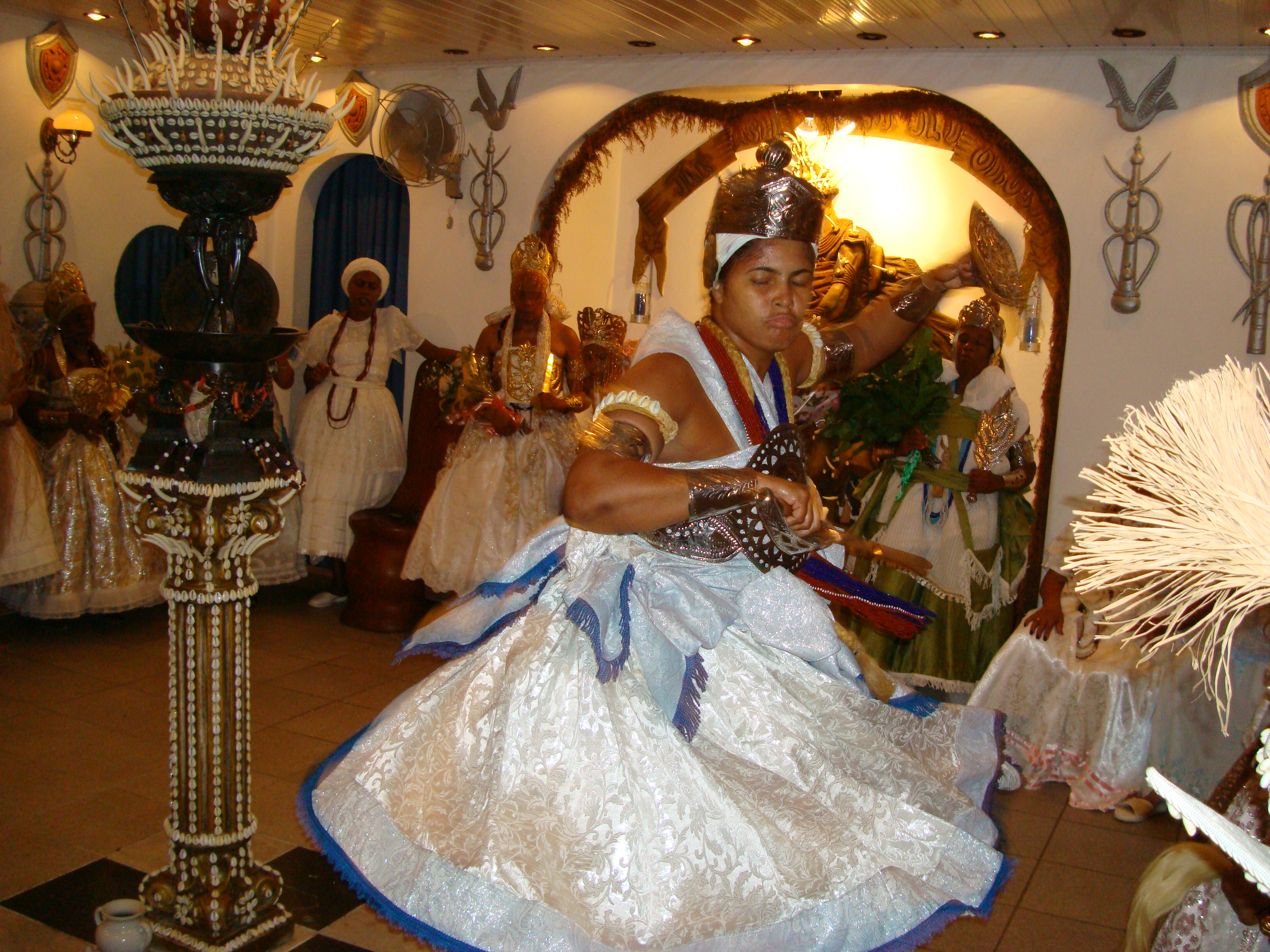 According to the 2010 census, 6.7% of Brazilians said they were black, compared with 6.2% in 2000, and 43.1% said they were racially mixed, up from 38.5%. In 2010, Elio Ferreira de Araujo, Brazil's minister for racial equality, attributed the increases to growing pride among his country's black and indigenous communities.
The philosophy of the racial democracy in Brazil has drawn some criticism, based on economic issues. Brazil has one of the largest gaps in income distribution in the world. The richest 10% of the population earn 28 times the average income of the bottom 40%. The richest 10 percent is almost exclusively white or predominantly European in ancestry. One-third of the population lives under the poverty line, with blacks and other people of color accounting for 70 percent of the poor.
According to the 2010 census, 6.7% of Brazilians said they were black, compared with 6.2% in 2000, and 43.1% said they were racially mixed, up from 38.5%. In 2010, Elio Ferreira de Araujo, Brazil's minister for racial equality, attributed the increases to growing pride among his country's black and indigenous communities.
The philosophy of the racial democracy in Brazil has drawn some criticism, based on economic issues. Brazil has one of the largest gaps in income distribution in the world. The richest 10% of the population earn 28 times the average income of the bottom 40%. The richest 10 percent is almost exclusively white or predominantly European in ancestry. One-third of the population lives under the poverty line, with blacks and other people of color accounting for 70 percent of the poor.
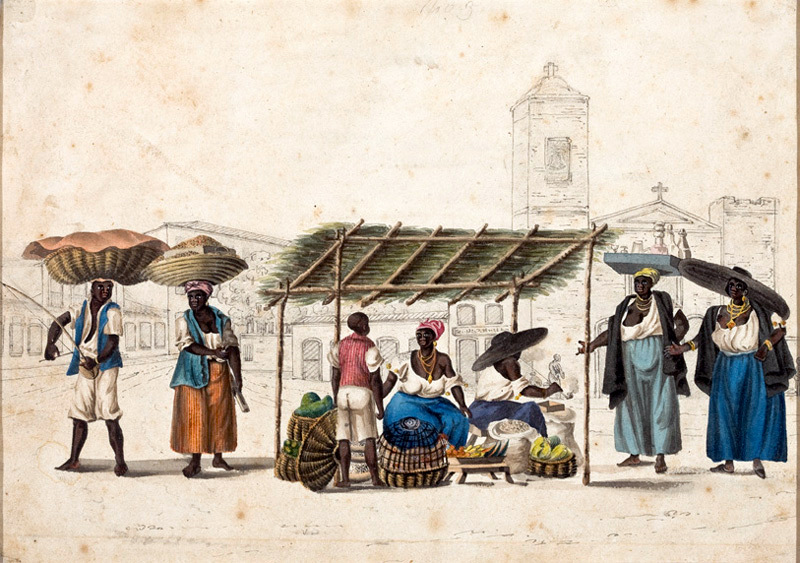 In 2015 United States, African Americans, including multiracial people, earned 76.8% as much as white people. By contrast, black and mixed race Brazilians earned on average 58% as much as whites in 2014. The gap in income between blacks and other non-whites is relatively small compared to the large gap between whites and all people of color. Other social factors, such as illiteracy and education levels, show the same patterns of disadvantage for people of color.
In 2015 United States, African Americans, including multiracial people, earned 76.8% as much as white people. By contrast, black and mixed race Brazilians earned on average 58% as much as whites in 2014. The gap in income between blacks and other non-whites is relatively small compared to the large gap between whites and all people of color. Other social factors, such as illiteracy and education levels, show the same patterns of disadvantage for people of color.
 Some commentators observe that the United States practice of segregation and white supremacy in the South, and discrimination in many areas outside that region, forced many African Americans to unite in the civil rights struggle, whereas the fluid nature of race in Brazil has divided individuals of African ancestry between those with more or less ancestry and helped sustain an image of the country as an example of post-colonial harmony. This has hindered the development of a common identity among black Brazilians.
Though Brazilians of at least partial African heritage make up a large percentageTom Phillips
Some commentators observe that the United States practice of segregation and white supremacy in the South, and discrimination in many areas outside that region, forced many African Americans to unite in the civil rights struggle, whereas the fluid nature of race in Brazil has divided individuals of African ancestry between those with more or less ancestry and helped sustain an image of the country as an example of post-colonial harmony. This has hindered the development of a common identity among black Brazilians.
Though Brazilians of at least partial African heritage make up a large percentageTom Phillips
"Brazil census shows African-Brazilians in the majority for the first time"
''The Guardian'', 17 November 2011. Retrieved 6 May 2018. of the population, few blacks have been elected as politicians. The city of
sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
n ancestry and the indigenous peoples of Oceania, though it has been applied in many contexts to other groups, and is no indicator of any close ancestral relationship whatsoever. Indigenous African societies do not use the term ''black'' as a racial identity outside of influences brought by Western cultures. The term "black" may or may not be capitalized. The ''AP Stylebook
The ''AP Stylebook'', also known by its full name ''The Associated Press Stylebook and Briefing on Media Law'', is an American English grammar style and usage guide created by American journalists working for or connected with the Associated Pr ...
'' changed its guide to capitalize the "b" in ''black'' in 2020. The '' ASA Style Guide'' says that the "b" should not be capitalized. Some perceive the term "black" as a derogatory, outdated, reductive or otherwise unrepresentative label, and as a result neither use nor define it, especially in African countries with little to no history of colonial racial segregation.
Contemporary anthropologist
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and ...
s and other scientists, while recognizing the reality of biological variation between different human populations, regard the concept of a unified, distinguishable "Black race" as socially constructed. Different societies apply different criteria regarding who is classified "black", and these social constructs have changed over time. In a number of countries, societal variables affect classification as much as skin color, and the social criteria for "blackness" vary. In the United Kingdom, "black" was historically equivalent with "person of color
The term "person of color" ( : people of color or persons of color; abbreviated POC) is primarily used to describe any person who is not considered "white". In its current meaning, the term originated in, and is primarily associated with, the U ...
", a general term for non-European peoples. In other regions such as Australasia, settlers applied the term "black" or it was used by local populations with different histories and ancestral backgrounds.
Africa
Northern Africa
 Numerous communities of dark-skinned peoples are present in North Africa, some dating from prehistoric communities. Others descend from migrants via the historical trans-Saharan trade or, after the Arab invasions of North Africa in the 7th century, from slaves from the
Numerous communities of dark-skinned peoples are present in North Africa, some dating from prehistoric communities. Others descend from migrants via the historical trans-Saharan trade or, after the Arab invasions of North Africa in the 7th century, from slaves from the trans-Saharan slave trade
During the Trans-Saharan slave trade, slaves were transported across the Sahara desert. Most were moved from Sub-Saharan Africa to North Africa to be sold to Mediterranean and Middle eastern civilizations; a small percentage went the other ...
in North Africa. In the 18th century, the Moroccan Sultan Moulay Ismail "the Warrior King" (1672–1727) raised a corps of 150,000 black soldiers, called his Black Guard.
According to Carlos Moore, resident scholar at Brazil's University of the State of Bahia, in the 21st century Afro-multiracials in the Arab world, including Arabs in North Africa, self-identify in ways that resemble multi-racials in Latin America. He claims that darker-toned Arabs, much like darker-toned Latin Americans, consider themselves white because they have some distant white ancestry.
Egyptian President Anwar Sadat had a mother who was a dark-skinned Nubian Sudanese ( Sudanese Arab) woman and a father who was a lighter-skinned Egyptian. In response to an advertisement for an acting position, as a young man he said, "I am not white but I am not exactly black either. My blackness is tending to reddish".
Due to the
In the 18th century, the Moroccan Sultan Moulay Ismail "the Warrior King" (1672–1727) raised a corps of 150,000 black soldiers, called his Black Guard.
According to Carlos Moore, resident scholar at Brazil's University of the State of Bahia, in the 21st century Afro-multiracials in the Arab world, including Arabs in North Africa, self-identify in ways that resemble multi-racials in Latin America. He claims that darker-toned Arabs, much like darker-toned Latin Americans, consider themselves white because they have some distant white ancestry.
Egyptian President Anwar Sadat had a mother who was a dark-skinned Nubian Sudanese ( Sudanese Arab) woman and a father who was a lighter-skinned Egyptian. In response to an advertisement for an acting position, as a young man he said, "I am not white but I am not exactly black either. My blackness is tending to reddish".
Due to the patriarchal
Patriarchy is a social system in which positions of Dominance hierarchy, dominance and Social privilege, privilege are primarily held by men. It is used, both as a technical Anthropology, anthropological term for families or clans controll ...
nature of Arab society, Arab men, including during the slave trade in North Africa, enslaved more African women than men. The female slaves were often put to work in domestic service and agriculture. The men interpreted the Quran to permit sexual relations between a male master and his enslaved females outside of marriage (see Ma malakat aymanukum and sex), leading to many mixed-race children. When an enslaved woman became pregnant with her Arab master's child, she was considered as '' umm walad'' or "mother of a child", a status that granted her privileged rights. The child was given rights of inheritance to the father's property, so mixed-race children could share in any wealth of the father. Because the society was patrilineal, the children inherited their fathers' social status at birth and were born free.
Some mixed-race children succeeded their respective fathers as rulers, such as Sultan Ahmad al-Mansur, who ruled Morocco from 1578 to 1608. He was not technically considered as a mixed-race child of a slave; his mother was Fulani and a concubine of his father.
In early 1991, non-Arabs of the Zaghawa people of Sudan attested that they were victims of an intensifying Arab apartheid campaign, segregating Arabs and non-Arabs (specifically, people of Nilotic ancestry). Sudanese Arabs, who controlled the government, were widely referred to as practicing apartheid against Sudan's non-Arab citizens. The government was accused of "deftly manipulat(ing) Arab solidarity" to carry out policies of apartheid and ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
.Vukoni Lupa Lasaga, "The slow, violent death of apartheid in Sudan," 19 September 2006, Norwegian Council for Africa.
Sudanese Arabs are also black people in that they are culturally and linguistically Arabized indigenous peoples of Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
of mostly Nilo-Saharans
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. T ...
, Nubian,Richard A. Lobban Jr. (2004): "Historical Dictionary of Ancient and Medieval Nubia". The Scarecrow Press, p. 37. and CushiticJakobsson, Mattias; Hassan, Hisham Y.; Babiker, Hiba; Günther, Torsten; Schlebusch, Carina M.; Hollfelder, Nina (24 August 2017). "Northeast African genomic variation shaped by the continuity of indigenous groups and Eurasian migrations". ''PLOS Genetics''. 13(8): e1006976. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1006976. ISSN 1553-7404. PMC 5587336. PMID 28837655. ancestry; their skin tone and appearance resembles that of other black people.
American University
The American University (AU or American) is a private federally chartered research university in Washington, D.C. Its main campus spans 90 acres (36 ha) on Ward Circle, mostly in the Spring Valley neighborhood of Northwest D.C. AU was charte ...
economist George Ayittey accused the Arab government of Sudan of practicing acts of racism against black citizens. According to Ayittey, "In Sudan... the Arabs monopolized power and excluded blacks – Arab apartheid." Many African commentators joined Ayittey in accusing Sudan of practicing Arab apartheid.
Sahara
 In the
In the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
, the native Tuareg Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
populations kept " negro" slaves. Most of these captives were of Nilotic extraction, and were either purchased by the Tuareg nobles from slave markets in the Western Sudan or taken during raids. Their origin is denoted via the Ahaggar Berber word '' Ibenheren'' (sing. ''Ébenher''), which alludes to slaves that only spoke a Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. T ...
language. These slaves were also sometimes known by the borrowed Songhay term ''Bella''.
Similarly, the Sahrawi indigenous peoples of the Western Sahara observed a class system consisting of high caste
Caste is a form of social stratification characterised by endogamy, hereditary transmission of a style of life which often includes an occupation, ritual status in a hierarchy, and customary social interaction and exclusion based on cultura ...
s and low castes. Outside of these traditional tribal boundaries were "Negro" slaves, who were drawn from the surrounding areas.
North-Eastern Africa
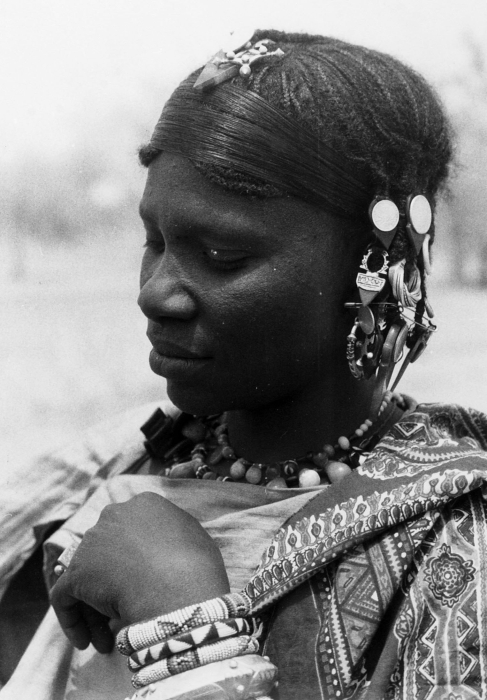
In Ethiopia and Somalia, the slave classes mainly consisted of captured peoples from the Sudanese-Ethiopian and Kenyan-Somali international borders or other surrounding areas of Nilotic andBantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
*Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for Nationali ...
peoples who were collectively known as '' Shanqella'' and ''Adone'' (both analogues to "negro" in an English-speaking context). Some of these slaves were captured during territorial conflicts in the Horn of Africa and then sold off to slave merchants. The earliest representation of this tradition dates from a seventh or eighth century BC inscription belonging to the Kingdom of Damat.
These captives and others of analogous morphology were distinguished as ''tsalim barya'' (dark-skinned slave) in contrast with the Afroasiatic-speaking nobles or ''saba qayh'' ("red men") or light-skinned slave; while on the other hand, western racial category standards do not differentiate between ''saba qayh'' ("red men"—light-skinned) or ''saba tiqur'' ("black men"—dark-skinned) Horn Africans (of either Afroasiatic-speaking, Nilotic-speaking or Bantu origin) thus considering all of them as "black people" (and in some case "negro") according to Western society's notion of race.
Southern Africa
In South Africa, the period of colonization resulted in many unions and marriages between European and Africans ( Bantu peoples of South Africa andKhoisan
Khoisan , or (), according to the contemporary Khoekhoegowab orthography, is a catch-all term for those indigenous peoples of Southern Africa who do not speak one of the Bantu languages, combining the (formerly "Khoikhoi") and the or ( in t ...
s) from various tribes, resulting in mixed-race children. As the European colonialists acquired control of territory, they generally pushed the mixed-race and African populations into second-class status. During the first half of the 20th century, the white-dominated government classified the population according to four main racial groups: ''Black'', ''White'', '' Asian'' (mostly Indian), and ''Coloured
Coloureds ( af, Kleurlinge or , ) refers to members of multiracial ethnic communities in Southern Africa who may have ancestry from more than one of the various populations inhabiting the region, including African, European, and Asian. South ...
''. The Coloured group included people of mixed Bantu, Khoisan, and European ancestry (with some Malay ancestry, especially in the Western Cape). The Coloured definition occupied an intermediary political position between the Black and White definitions in South Africa. It imposed a system of legal racial segregation, a complex of laws known as apartheid.
The apartheid bureaucracy devised complex (and often arbitrary) criteria in the Population Registration Act
The Population Registration Act of 1950 required that each inhabitant of South Africa be classified and registered in accordance with their racial characteristics as part of the system of apartheid.
Social rights, political rights, educational ...
of 1945 to determine who belonged in which group. Minor officials administered tests to enforce the classifications. When it was unclear from a person's physical appearance whether the individual should be considered Coloured or Black, the " pencil test" was used. A pencil was inserted into a person's hair to determine if the hair was kinky enough to hold the pencil, rather than having it pass through, as it would with smoother hair. If so, the person was classified as Black. Such classifications sometimes divided families.
Sandra Laing is a South African woman who was classified as Coloured by authorities during the apartheid era, due to her skin colour and hair texture, although her parents could prove at least three generations of European ancestors. At age 10, she was expelled from her all-white school. The officials' decisions based on her anomalous appearance disrupted her family and adult life. She was the subject of the 2008 biographical dramatic film '' Skin'', which won numerous awards. During the apartheid era, those classed as "Coloured" were oppressed and discriminated against. But, they had limited rights and overall had slightly better socioeconomic conditions than those classed as "Black". The government required that Blacks and Coloureds live in areas separate from Whites, creating large townships located away from the cities as areas for Blacks.
In the post-apartheid era, the Constitution of South Africa has declared the country to be a "Non-racial democracy". In an effort to redress past injustices, the ANC government has introduced laws in support of affirmative action policies for Blacks; under these they define "Black" people to include "Africans", "Coloureds" and "Asians". Some affirmative action policies favor "Africans" over "Coloureds" in terms of qualifying for certain benefits. Some South Africans categorized as "African Black" say that "Coloureds" did not suffer as much as they did during apartheid. "Coloured" South Africans are known to discuss their dilemma by saying, "we were not white enough under apartheid, and we are not black enough under the ANC ( African National Congress)".
In 2008, the High Court in South Africa ruled that Chinese South Africans who were residents during the apartheid era (and their descendants) are to be reclassified as "Black people," solely for the purposes of accessing affirmative action benefits, because they were also "disadvantaged" by racial discrimination. Chinese people who arrived in the country after the end of apartheid do not qualify for such benefits.
Other than by appearance, "Coloureds" can usually be distinguished from "Blacks" by language. Most speak Afrikaans or English as a first language, as opposed to Bantu languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀) are a large family of languages spoken by the Bantu people of Central, Southern, Eastern africa and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.
The t ...
such as Zulu or Xhosa. They also tend to have more European-sounding names than Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
*Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for Nationali ...
names.
Asia
Western Asia
Arab world
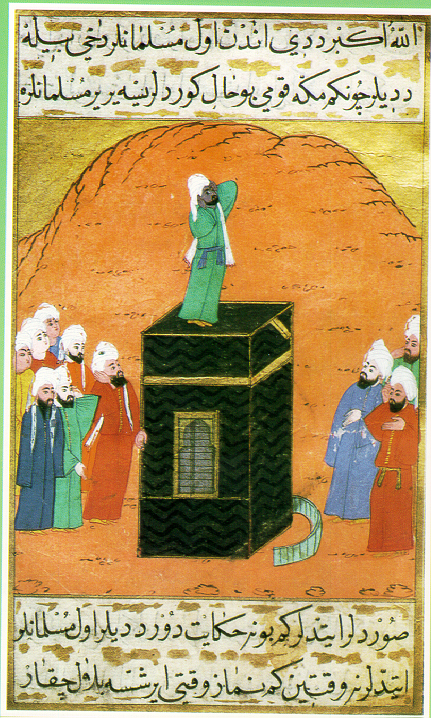
 Historians estimate that between the advent of
Historians estimate that between the advent of Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
in 650 CE and the abolition of slavery in the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
in the mid-20th century, 10 to 18 million black Africans (known as the Zanj) were enslaved by east African slave traders and transported to the Arabian Peninsula and neighboring countries. This number far exceeded the number of slaves who were taken to the Americas. Several factors affected the visibility of descendants of this diaspora in 21st-century Arab societies: The traders shipped more female slaves than males, as there was a demand for them to serve as concubines in harems in the Arabian Peninsula and neighboring countries. Male slaves were castrated in order to serve as harem guards. The death toll of black African slaves from forced labor was high. The mixed-race children of female slaves and Arab owners were assimilated into the Arab owners' families under the patrilineal kinship system. As a result, few distinctive Afro-Arab communities have survived in the Arabian Peninsula and neighboring countries.
Distinctive and self-identified black communities have been reported in countries such as Iraq, with a reported 1.2 million black people ( Afro-Iraqis), and they attest to a history of discrimination. These descendants of the Zanj have sought minority status from the government, which would reserve some seats in Parliament for representatives of their population. According to Alamin M. Mazrui et al., generally in the Arabian Peninsula and neighboring countries, most of these communities identify as both black and Arab.
Iran
Afro-Iranians are people of black African ancestry residing in Iran. During theQajar dynasty
The Qajar dynasty (; fa, دودمان قاجار ', az, Qacarlar ) was an IranianAbbas Amanat, ''The Pivot of the Universe: Nasir Al-Din Shah Qajar and the Iranian Monarchy, 1831–1896'', I. B. Tauris, pp 2–3 royal dynasty of Turkic peoples ...
, many wealthy households imported black African women and children as slaves to perform domestic work. This slave labor was drawn exclusively from the Zanj, who were Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
*Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for Nationali ...
-speaking peoples that lived along the African Great Lakes, in an area roughly comprising modern-day Tanzania, Mozambique and Malawi.F.R.C. Bagley et al., ''The Last Great Muslim Empires'', (Brill: 1997), p.174.Bethwell A. Ogot, ''Zamani: A Survey of East African History'', (East African Publishing House: 1974), p.104.
Israel

 About 150,000 East African and black people live in Israel, amounting to just over 2% of the nation's population. The vast majority of these, some 120,000, are
About 150,000 East African and black people live in Israel, amounting to just over 2% of the nation's population. The vast majority of these, some 120,000, are Beta Israel
The Beta Israel ( he, בֵּיתֶא יִשְׂרָאֵל, ''Bēteʾ Yīsrāʾēl''; gez, ቤተ እስራኤል, , modern ''Bēte 'Isrā'ēl'', EAE: "Betä Ǝsraʾel", "House of Israel" or "Community of Israel"), also known as Ethiopian Jews ...
, most of whom are recent immigrants who came during the 1980s and 1990s from Ethiopia. In addition, Israel is home to more than 5,000 members of the African Hebrew Israelites of Jerusalem
African Hebrew Israelites in Israel, officially known as The African Hebrew Israelite Nation of Jerusalem (also known as the Hebrew Israelites of Jerusalem, the Hebrew Israelites, the Black Hebrew Israelites, or simply the Black Hebrews or the B ...
movement that are ancestry of African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
who emigrated to Israel in the 20th century, and who reside mainly in a distinct neighborhood in the Negev town of Dimona. Unknown numbers of black converts to Judaism reside in Israel, most of them converts from the United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States.
Additionally, there are around 60,000 non-Jewish African immigrants in Israel, some of whom have sought asylum. Most of the migrants are from communities in Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
and Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
, particularly the Niger-Congo-speaking Nuba groups of the southern Nuba Mountains; some are illegal immigrants.
Turkey
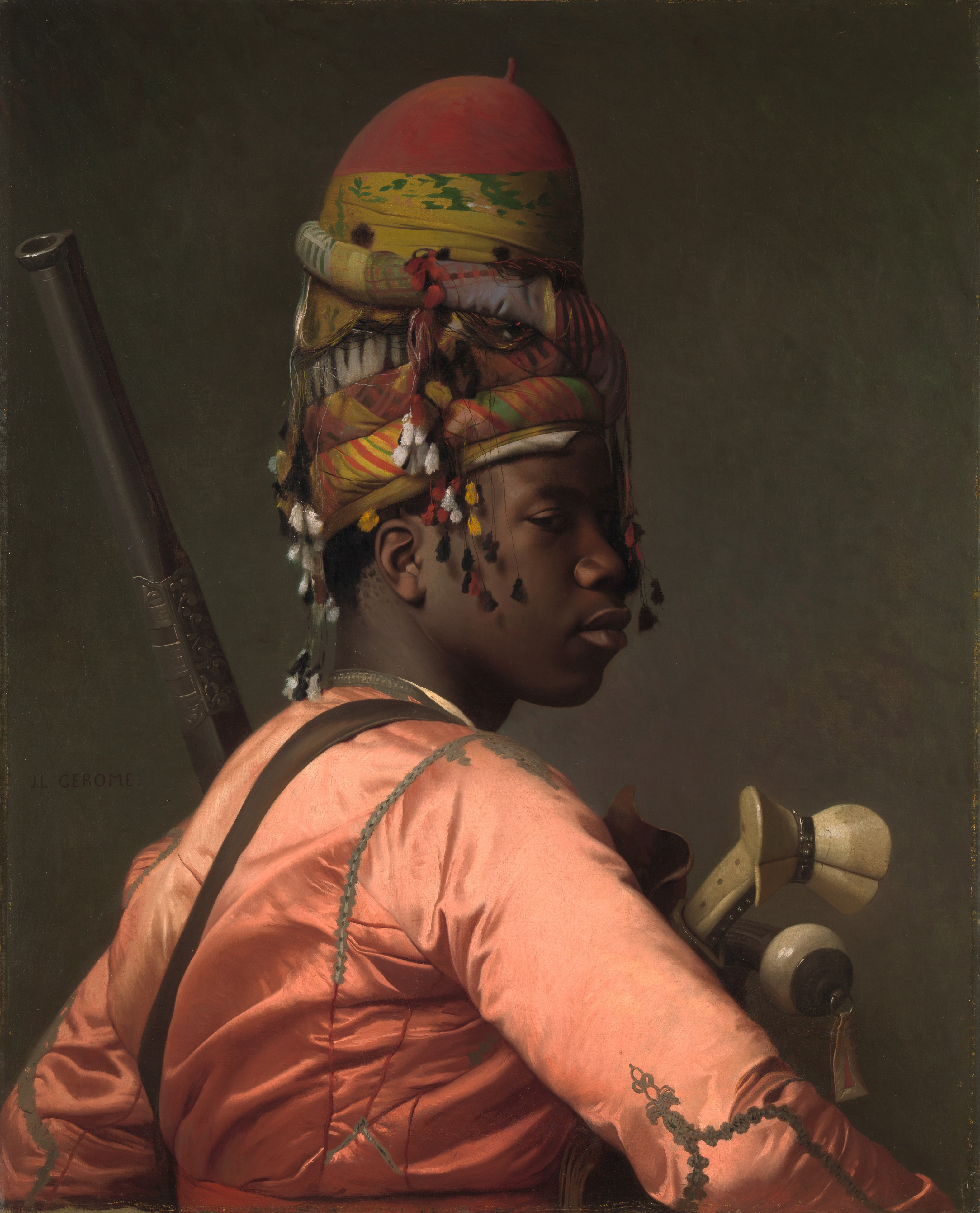
 Beginning several centuries ago, during the period of the Ottoman Empire, tens of thousands of Zanj captives were brought by slave traders to plantations and agricultural areas situated between Antalya and Istanbul, which gave rise to the Afro-Turk population in present-day Turkey. Some of their ancestry remained ''in situ'', and many migrated to larger cities and towns. Other black slaves were transported to Crete, from where they or their descendants later reached the İzmir area through the population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923, or indirectly from Ayvalık in pursuit of work.
Apart from the historical Afro-Turk presence Turkey also hosts a sizeable immigrant black population since the end of the 1990s. The community is composed mostly of modern immigrants from Ghana, Ethiopia, DRC, Sudan, Nigeria, Kenya, Eritrea, Somalia and Senegal. According to official figures 1.5 million Africans live in Turkey and around 25% of them are located in Istanbul. Other studies state the majority of Africans in Turkey lives in Istanbul and report Tarlabaşı, Dolapdere,
Beginning several centuries ago, during the period of the Ottoman Empire, tens of thousands of Zanj captives were brought by slave traders to plantations and agricultural areas situated between Antalya and Istanbul, which gave rise to the Afro-Turk population in present-day Turkey. Some of their ancestry remained ''in situ'', and many migrated to larger cities and towns. Other black slaves were transported to Crete, from where they or their descendants later reached the İzmir area through the population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923, or indirectly from Ayvalık in pursuit of work.
Apart from the historical Afro-Turk presence Turkey also hosts a sizeable immigrant black population since the end of the 1990s. The community is composed mostly of modern immigrants from Ghana, Ethiopia, DRC, Sudan, Nigeria, Kenya, Eritrea, Somalia and Senegal. According to official figures 1.5 million Africans live in Turkey and around 25% of them are located in Istanbul. Other studies state the majority of Africans in Turkey lives in Istanbul and report Tarlabaşı, Dolapdere, Kumkapı
Kumkapı (meaning 'sand gate' in Turkish) is a quarter in Fatih district of Istanbul. It is located along the northern shore of Marmara Sea. Up to recent times, Kumkapı is the center of the Armenian community of the city, boasting a school and s ...
, Yenikapı and Kurtuluş as having a strong African presence.
Most of the African immigrants in Turkey come to Turkey to further migrate to Europe. Immigrants from Eastern Africa are usually refugees, meanwhile Western and Central African immigration is reported to be economically driven. It is reported that African immigrants in Turkey regularly face economic and social challenges, notably racism and opposition to immigration
Opposition to immigration, also known as anti-immigration, has become a significant political ideology in many countries. In the modern sense, immigration refers to the entry of people from one state or territory into another state or territory ...
by locals.
Southern Asia
 The
The Siddi
The Siddi (), also known as the Sheedi, Sidi, or Siddhi, or Habshi are an ethnic group inhabiting India and Pakistan. They are primarily descended from the Bantu peoples of the Zanj coast in Southeast Africa and Ethiopia, most whom arrived to ...
are an ethnic group inhabiting India and Pakistan. Members are descended from the Bantu peoples of Southeast Africa. Some were merchants, sailors, indentured servants, slaves or mercenaries. The Siddi population is currently estimated at around 270,000–350,000 individuals, living mostly in Karnataka, Gujarat, and Hyderabad in India and Makran
Makran ( fa, مكران), mentioned in some sources as Mecran and Mokrān, is the coastal region of Baluchistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in Balochistan, in Pakistan and Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. It extends westwards, ...
and Karachi in Pakistan. In the Makran
Makran ( fa, مكران), mentioned in some sources as Mecran and Mokrān, is the coastal region of Baluchistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in Balochistan, in Pakistan and Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. It extends westwards, ...
strip of the Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and Balochistan provinces in southwestern Pakistan, these Bantu descendants are known as the Makrani. There was a brief "Black Power" movement in Sindh in the 1960s and many Siddi are proud of and celebrate their African ancestry.
Southeastern Asia
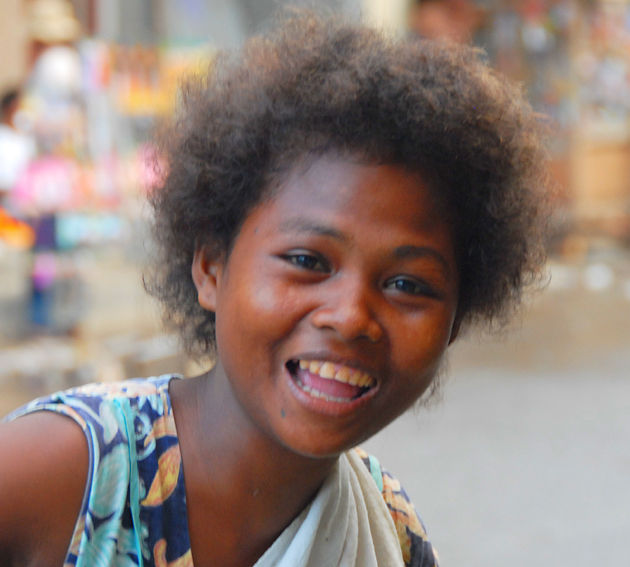
 Negritos, are a collection of various, often unrelated peoples, who were once considered a single distinct population of closely related groups, but genetic studies showed that they descended from the same ancient
Negritos, are a collection of various, often unrelated peoples, who were once considered a single distinct population of closely related groups, but genetic studies showed that they descended from the same ancient East Eurasian
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
meta-population which gave rise to modern East Asian peoples
East Asian people (East Asians) are the people from East Asia, which consists of China, Taiwan, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, and South Korea. The total population of all countries within this region is estimated to be 1.677 billion and 21% of t ...
, and consist of several separate groups, as well as displaying genetic heterogeneity. They inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia, and are now confined primarily to Southern Thailand, the Malay Peninsula, and the Andaman Islands of India. Negrito means "little black people" in Spanish (negrito is the Spanish diminutive of negro, i.e., "little black person"); it is what the Spaniards called the aborigines that they encountered in the Philippines. The term ''Negrito'' itself has come under criticism in countries like Malaysia, where it is now interchangeable with the more acceptable Semang, although this term actually refers to a specific group.
They have dark skin, often curly-hair and Asiatic facial characteristics, and are stockily built.
Negritos in the Philippines frequently face discrimination. Because of their traditional hunter-gatherer lifestyle, they are marginalized and live in poverty, unable to find employment.
Negrito means "little black people" in Spanish (negrito is the Spanish diminutive of negro, i.e., "little black person"); it is what the Spaniards called the aborigines that they encountered in the Philippines. The term ''Negrito'' itself has come under criticism in countries like Malaysia, where it is now interchangeable with the more acceptable Semang, although this term actually refers to a specific group.
They have dark skin, often curly-hair and Asiatic facial characteristics, and are stockily built.
Negritos in the Philippines frequently face discrimination. Because of their traditional hunter-gatherer lifestyle, they are marginalized and live in poverty, unable to find employment.
Afro-Asians
" Afro-Asians" or "African-Asians" are persons of mixed sub-Saharan African and Asian ancestry. In the United States, they are also called "black Asians" or "Blasians". Historically, Afro-Asian populations have been marginalized as a result of human migration and social conflict.Europe
Western Europe
France
 While census collection of ethnic background is illegal in France, it is estimated that there are about 2.5 – 5 million black people residing there.
While census collection of ethnic background is illegal in France, it is estimated that there are about 2.5 – 5 million black people residing there.
Germany
As of 2020, there are approximately one million black people living in Germany.Netherlands
Afro-Dutch are residents of the Netherlands who are of Black African orAfro-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the ...
ancestry. They tend to be from the former and present Dutch overseas territories of Aruba
Aruba ( , , ), officially the Country of Aruba ( nl, Land Aruba; pap, Pais Aruba) is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands physically located in the mid-south of the Caribbean Sea, about north of the Venezuela peninsula of ...
, Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC i ...
, Curaçao
Curaçao ( ; ; pap, Kòrsou, ), officially the Country of Curaçao ( nl, Land Curaçao; pap, Pais Kòrsou), is a Lesser Antilles island country in the southern Caribbean Sea and the Dutch Caribbean region, about north of the Venezuela coast ...
, Sint Maarten and Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
. The Netherlands also has sizable Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
an and other African communities.
Spain
The term " Moors" has been used in Europe in a broader, somewhat derogatory sense to refer toMuslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s,Menocal, María Rosa (2002). ''Ornament of the World: How Muslims, Jews and Christians Created a Culture of Tolerance in Medieval Spain'', Little, Brown, & Co., p. 241. . especially those of Arab or Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
ancestry, whether living in North Africa or Iberia. Moors were not a distinct or self-defined people. Medieval and early modern Europeans applied the name to Muslim Arabs, Berbers, Sub-Saharan Africans and Europeans alike.
Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
, writing in the 7th century, claimed that the Latin word Maurus was derived from the Greek ''mauron'', μαύρον, which is the Greek word for "black". Indeed, by the time Isidore of Seville came to write his ''Etymologies'', the word Maurus or "Moor" had become an adjective in Latin, "for the Greeks call black, mauron". "In Isidore's day, Moors were black by definition..."
Afro-Spaniards are Spanish nationals of West/ Central African ancestry. Today, they mainly come from Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoria ...
, Ghana, Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
, Mali, Nigeria and Senegal. Additionally, many Afro-Spaniards born in Spain are from the former Spanish colony Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoria ...
. Today, there are an estimated 683,000 Afro-Spaniards in Spain.
United Kingdom
According to the Office for National Statistics, at the 2001 census there were more than a million black people in the United Kingdom; 1% of the total population described themselves as "Black Caribbean", 0.8% as "Black African", and 0.2% as "Black other". Britain encouraged the immigration of workers from the Caribbean after World War II; the first symbolic movement was of those who came on the ship the ''Empire Windrush
HMT ''Empire Windrush'', originally MV ''Monte Rosa'', was a passenger liner and cruise ship launched in Germany in 1930. She was owned and operated by the German shipping line in the 1930s under the name ''Monte Rosa''. During World War II she ...
'' and, hence, those who migrated between 1948 and 1970 are known as the Windrush generation. The preferred official umbrella term is "black and minority ethnic" ( BAME), but sometimes the term "black" is used on its own, to express unified opposition to racism, as in the Southall Black Sisters, which started with a mainly British Asian constituency, and the National Black Police Association, which has a membership of "African, African-Caribbean and Asian origin".
Eastern Europe
As African states became independent in the 1960s, the Soviet Union offered many of their citizens the chance to study in Russia. Over a period of 40 years, about 400,000 African students from various countries moved to Russia to pursue higher studies, including many black Africans. This extended beyond the Soviet Union to many countries of theEastern bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
.
Balkans
Due to the slave trade in the Ottoman Empire that had flourished in the Balkans, the coastal town of Ulcinj in Montenegro had its own black community. In 1878, that community consisted of about 100 people.Oceania
Indigenous Australians
 Indigenous Australians have been referred to as "black people" in Australia since the early days of European settlement. While originally related to skin colour, the term is used today to indicate Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander ancestry in general and can refer to people of any skin pigmentation.
Being identified as either "black" or "white" in
Indigenous Australians have been referred to as "black people" in Australia since the early days of European settlement. While originally related to skin colour, the term is used today to indicate Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander ancestry in general and can refer to people of any skin pigmentation.
Being identified as either "black" or "white" in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
during the 19th and early 20th centuries was critical in one's employment and social prospects. Various state-based Aboriginal Protection Boards were established which had virtually complete control over the lives of Indigenous Australians – where they lived, their employment, marriage, education and included the power to separate children from their parents. Aborigines were not allowed to vote and were often confined to reserves and forced into low paid or effectively slave labour. The social position of mixed-race or " half-caste" individuals varied over time. A 1913 report by Baldwin Spencer states that:
After the First World War, however, it became apparent that the number of mixed-race people was growing at a faster rate than the white population, and, by 1930, fear of the "half-caste menace" undermining the White Australia
The White Australia policy is a term encapsulating a set of historical policies that aimed to forbid people of non-European ethnic origin, especially Asians (primarily Chinese) and Pacific Islanders, from immigrating to Australia, starting i ...
ideal from within was being taken as a serious concern. Cecil Cook, the Northern Territory Protector of Natives, noted that:
The official policy became one of biological and cultural assimilation: "Eliminate the full-blood and permit the white admixture to half-castes and eventually the race will become white". This led to different treatment for "black" and "half-caste" individuals, with lighter-skinned individuals targeted for removal from their families to be raised as "white" people and prohibited from speaking their native language and practicing traditional customs, a process now known as the Stolen Generation
The Stolen Generations (also known as Stolen Children) were the children of Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander descent who were removed from their families by the Australian federal and state government agencies and church miss ...
.
 The second half of the 20th century to the present has seen a gradual shift towards improved human rights for Aboriginal people. In a 1967 referendum, more than 90% of the Australian population voted to end constitutional discrimination and to include Aborigines in the national census. During this period, many Aboriginal activists began to embrace the term "black" and use their ancestry as a source of pride. Activist Bob Maza said:
In 1978, Aboriginal writer Kevin Gilbert received the National Book Council award for his book ''Living Black: Blacks Talk to Kevin Gilbert'', a collection of Aboriginal people's stories, and in 1998 was awarded (but refused to accept) the Human Rights Award for Literature for ''Inside Black Australia'', a poetry anthology and exhibition of Aboriginal photography. In contrast to previous definitions based solely on the degree of Aboriginal ancestry, the Government changed the legal definition of Aboriginal in 1990 to include any:
This nationwide acceptance and recognition of Aboriginal people led to a significant increase in the number of people self-identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander. The reappropriation of the term "black" with a positive and more inclusive meaning has resulted in its widespread use in mainstream Australian culture, including public media outlets, government agencies, and private companies. In 2012, a number of high-profile cases highlighted the legal and community attitude that identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander is not dependent on skin color, with a well-known boxer Anthony Mundine being widely criticized for questioning the "blackness" of another boxer and journalist Andrew Bolt being successfully sued for publishing discriminatory comments about Aboriginals with light skin.
The second half of the 20th century to the present has seen a gradual shift towards improved human rights for Aboriginal people. In a 1967 referendum, more than 90% of the Australian population voted to end constitutional discrimination and to include Aborigines in the national census. During this period, many Aboriginal activists began to embrace the term "black" and use their ancestry as a source of pride. Activist Bob Maza said:
In 1978, Aboriginal writer Kevin Gilbert received the National Book Council award for his book ''Living Black: Blacks Talk to Kevin Gilbert'', a collection of Aboriginal people's stories, and in 1998 was awarded (but refused to accept) the Human Rights Award for Literature for ''Inside Black Australia'', a poetry anthology and exhibition of Aboriginal photography. In contrast to previous definitions based solely on the degree of Aboriginal ancestry, the Government changed the legal definition of Aboriginal in 1990 to include any:
This nationwide acceptance and recognition of Aboriginal people led to a significant increase in the number of people self-identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander. The reappropriation of the term "black" with a positive and more inclusive meaning has resulted in its widespread use in mainstream Australian culture, including public media outlets, government agencies, and private companies. In 2012, a number of high-profile cases highlighted the legal and community attitude that identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander is not dependent on skin color, with a well-known boxer Anthony Mundine being widely criticized for questioning the "blackness" of another boxer and journalist Andrew Bolt being successfully sued for publishing discriminatory comments about Aboriginals with light skin.
Melanesians
The region of Melanesia is named from Greek , ''black'', and , ''island'',etymologically
Etymology () The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words ...
meaning "islands of black eople, in reference to the dark skin of the indigenous peoples. Early European settlers, such as Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez, noted the resemblance of the people to those in Africa.
 Melanesians, along with other Pacific Islanders, were frequently deceived or coerced during the 19th and 20th centuries into forced labour for sugarcane, cotton, and coffee planters in countries distant to their native lands in a practice known as blackbirding. In Queensland, some 55,000 to 62,500Tracey Flanagan, Meredith Wilkie, and Susanna Iuliano
Melanesians, along with other Pacific Islanders, were frequently deceived or coerced during the 19th and 20th centuries into forced labour for sugarcane, cotton, and coffee planters in countries distant to their native lands in a practice known as blackbirding. In Queensland, some 55,000 to 62,500Tracey Flanagan, Meredith Wilkie, and Susanna Iuliano"Australian South Sea Islanders: A Century of Race Discrimination under Australian Law"
Australian Human Rights Commission. were brought from the New Hebrides, the Solomon Islands, and New Guinea to work in sugarcane fields. Under the
Pacific Island Labourers Act 1901
The Pacific Island Labourers Act 1901 was an Act of the Parliament of Australia which was designed to facilitate the mass deportation of nearly all the Pacific Islanders (called " Kanakas") working in Australia, especially in the Queensland s ...
, most islanders working in Queensland were repatriated back to their homelands.
Those who remained in Australia, commonly called South Sea Islanders, often faced discrimination similarly to Indigenous Australians by white-dominated society. Many indigenous rights activists have South Sea Islander ancestry, including Faith Bandler, Evelyn Scott and Bonita Mabo
Ernestine Bonita Mabo (née Neehow) ( – 26 November 2018), was an Australian educator and activist for Aboriginal Australians, Torres Strait Islanders, and Australian South Sea Islanders. She was the wife of Eddie Mabo until his death in 199 ...
.
Many Melanesians have taken up the term 'Melanesia' as a way to empower themselves as a collective people. Stephanie Lawson writes that the term "moved from a term of denigration to one of affirmation, providing a positive basis for contemporary subregional identity as well as a formal organisation". For instance, the term is used in the Melanesian Spearhead Group, which seeks to promote economic growth among Melanesian countries.
Other
John Caesar, nicknamed "Black Caesar", a convict andbushranger
Bushrangers were originally escaped convicts in the early years of the British settlement of Australia who used the bush as a refuge to hide from the authorities. By the 1820s, the term had evolved to refer to those who took up "robbery under ...
with parents born in an unknown area in Africa, was one of the first people of recent black African ancestry to arrive in Australia.
At the 2006 Census, 248,605 residents declared that they were born in Africa. This figure pertains to all immigrants to Australia who were born in nations in Africa regardless of race, and includes white Africans.
North America
Canada
"Black Canadians" is a designation used for people of black African ancestry who are citizens or permanent residents of Canada. The majority of black Canadians are ofCaribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
origin, though the population also consists of African American immigrants and their descendants (including black Nova Scotians), as well as many African immigrants.
Black Canadians often draw a distinction between those of Afro-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the ...
ancestry and those of other African roots. The term ''African Canadian'' is occasionally used by some black Canadians who trace their heritage to the first slaves brought by British and French colonists to the North American mainland. Promised freedom by the British during the American Revolutionary War, thousands of Black Loyalists
Black Loyalists were people of African descent who sided with the Loyalists during the American Revolutionary War. In particular, the term refers to men who escaped enslavement by Patriot masters and served on the Loyalist side because of the Cro ...
were resettled by the Crown in Canada afterward, such as Thomas Peters. In addition, an estimated ten to thirty thousand fugitive slaves reached freedom in Canada from the Southern United States during the Antebellum years, aided by people along the Underground Railroad.
Many black people of Caribbean origin in Canada reject the term "African Canadian" as an elision of the uniquely Caribbean aspects of their heritage, Rinaldo Walcott, ''Black Like Who?: Writing Black Canada''. 2003, Insomniac Press. . and instead identify as ''Caribbean Canadian''. Unlike in the United States, where "African American" has become a widely used term, in Canada controversies associated with distinguishing African or Caribbean heritage have resulted in the term "black Canadian" being widely accepted there."As for terminology, in Canada, it is still appropriate to say Black Canadians." Valerie Pruegger, "Black History Month". ''Culture and Community Spirit'', Government of Alberta.
United States
 There were eight principal areas used by Europeans to buy and ship slaves to the Western Hemisphere. The number of enslaved people sold to the New World varied throughout the slave trade. As for the distribution of slaves from regions of activity, certain areas produced far more enslaved people than others. Between 1650 and 1900, 10.24 million enslaved West Africans arrived in the Americas from the following regions in the following proportions:Lovejoy, Paul E. ''Transformations in Slavery''. Cambridge University Press, 2000.
*
There were eight principal areas used by Europeans to buy and ship slaves to the Western Hemisphere. The number of enslaved people sold to the New World varied throughout the slave trade. As for the distribution of slaves from regions of activity, certain areas produced far more enslaved people than others. Between 1650 and 1900, 10.24 million enslaved West Africans arrived in the Americas from the following regions in the following proportions:Lovejoy, Paul E. ''Transformations in Slavery''. Cambridge University Press, 2000.
* Senegambia
The Senegambia (other names: Senegambia region or Senegambian zone,Barry, Boubacar, ''Senegambia and the Atlantic Slave Trade'', (Editors: David Anderson, Carolyn Brown; trans. Ayi Kwei Armah; contributors: David Anderson, American Council of Le ...
(Senegal and The Gambia): 4.8%
* Upper Guinea ( Guinea-Bissau, Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
and Sierra Leone): 4.1%
* Windward Coast
The Windward Coast was used to describe an area of West Africa located on the coast between Cape Mount and Assini, i.e. the coastlines of the modern states of Liberia and Ivory Coast, to the west of what was called the Gold Coast. A related reg ...
(Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
and Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
): 1.8%
* Gold Coast ( Ghana and east of Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
): 10.4%
* Bight of Benin
The Bight of Benin or Bay of Benin is a bight in the Gulf of Guinea area on the western African coast that derives its name from the historical Kingdom of Benin.
Geography
It extends eastward for about from Cape St. Paul to the Nun outlet of t ...
( Togo, Benin and Nigeria west of the Niger Delta): 20.2%
* Bight of Biafra
The Bight of Biafra (known as the Bight of Bonny in Nigeria) is a bight off the West African coast, in the easternmost part of the Gulf of Guinea.
Geography
The Bight of Biafra, or Mafra (named after the town Mafra in southern Portugal), between ...
( Nigeria east of the Niger Delta, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoria ...
and Gabon): 14.6%
* West Central Africa (Republic of the Congo
The Republic of the Congo (french: République du Congo, ln, Republíki ya Kongó), also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply either Congo or the Congo, is a country located in the western coast of Central Africa to the w ...
, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Angola): 39.4%
* Southeastern Africa ( Mozambique and Madagascar): 4.7%
 By the early 1900s, ''nigger'' had become a pejorative word in the United States. In its stead, the term '' colored'' became the mainstream alternative to '' negro'' and its derived terms. After the American Civil Rights Movement, the terms ''colored'' and ''negro'' gave way to "black". ''Negro'' had superseded ''colored'' as the most polite word for
By the early 1900s, ''nigger'' had become a pejorative word in the United States. In its stead, the term '' colored'' became the mainstream alternative to '' negro'' and its derived terms. After the American Civil Rights Movement, the terms ''colored'' and ''negro'' gave way to "black". ''Negro'' had superseded ''colored'' as the most polite word for African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
at a time when ''black'' was considered more offensive. This term was accepted as normal, including by people classified as Negroes, until the later Civil Rights movement in the late 1960s. One well-known example is the use by Dr. Rev. Martin Luther King Jr. of "Negro" in his famous speech of 1963, I Have a Dream
"I Have a Dream" is a public speech that was delivered by American civil rights activist and Baptist minister, Martin Luther King Jr., during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom on August 28, 1963. In the speech, King called ...
. During the American civil rights movement of the 1950s and 1960s, some African-American leaders in the United States, notably Malcolm X, objected to the word ''Negro'' because they associated it with the long history of slavery, segregation, and discrimination that treated African Americans as second-class citizens, or worse. Malcolm X preferred ''Black'' to ''Negro'', but later gradually abandoned that as well for ''Afro-American'' after leaving the Nation of Islam
The Nation of Islam (NOI) is a religious and political organization founded in the United States by Wallace Fard Muhammad in 1930.
A black nationalist organization, the NOI focuses its attention on the African diaspora, especially on African ...
.
Since the late 1960s, various other terms for African Americans have been more widespread in popular usage. Aside from ''black American'', these include ''Afro-American'' (in use from the late 1960s to 1990) and ''African American'' (used in the United States to refer to Black Americans, people often referred to in the past as ''American Negroes'').
In the first 200 years that black people were in the United States, they primarily identified themselves by their specific ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
(closely allied to language) and not by skin color. Individuals identified themselves, for example, as Ashanti, Igbo, Bakongo
The Kongo people ( kg, Bisi Kongo, , singular: ; also , singular: ) are a Bantu ethnic group primarily defined as the speakers of Kikongo. Subgroups include the Beembe, Bwende, Vili, Sundi, Yombe, Dondo, Lari, and others.
They have lived ...
, or Wolof. However, when the first captives were brought to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
, they were often combined with other groups from West Africa, and individual ethnic affiliations were not generally acknowledged by English colonists. In areas of the Upper South, different ethnic groups were brought together. This is significant as the captives came from a vast geographic region: the West African coastline stretching from Senegal to Angola and in some cases from the south-east coast such as Mozambique. A new ''African-American'' identity and culture was born that incorporated elements of the various ethnic groups and of European cultural heritage, resulting in fusions such as the Black church and African-American English. This new identity was based on provenance and slave status rather than membership in any one ethnic group.
By contrast, slave records from Louisiana show that the French and Spanish colonists recorded more complete identities of the West Africans, including ethnicities and given tribal names.
The U.S. racial or ethnic classification "black" refers to people with all possible kinds of skin pigmentation, from the darkest through to the very lightest skin colors, including albinos, if they are believed by others to have African ancestry (in any discernible percentage). There are also certain cultural traits associated with being " African American", a term used effectively as a synonym for "black person" within the United States.
In March 1807, Great Britain, which largely controlled the Atlantic, declared the transatlantic slave trade illegal, as did the United States. (The latter prohibition took effect 1 January 1808, the earliest date on which Congress had the power to do so after protecting the slave trade under Article I, Section 9 of the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
.)
By that time, the majority of black people in the United States were native-born, so the use of the term "African" became problematic. Though initially a source of pride, many blacks feared that the use of African as an identity would be a hindrance to their fight for full citizenship in the United States. They also felt that it would give ammunition to those who were advocating repatriating black people back to Africa. In 1835, black leaders called upon Black Americans to remove the title of "African" from their institutions and replace it with " Negro" or "Colored American". A few institutions chose to keep their historic names, such as the African Methodist Episcopal Church. African Americans popularly used the terms "Negro" or "colored" for themselves until the late 1960s.
The term ''black'' was used throughout but not frequently since it carried a certain stigma. In his 1963 "I Have a Dream
"I Have a Dream" is a public speech that was delivered by American civil rights activist and Baptist minister, Martin Luther King Jr., during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom on August 28, 1963. In the speech, King called ...
" speech, Martin Luther King Jr. uses the terms ''negro'' fifteen times and ''black'' four times. Each time that he uses ''black'', it is in parallel construction with ''white''; for example, "black men and white men".
With the successes of the American Civil Rights Movement, a new term was needed to break from the past and help shed the reminders of legalized discrimination. In place of ''Negro'', activists promoted the use of ''black'' as standing for racial pride, militancy, and power. Some of the turning points included the use of the term " Black Power" by Kwame Ture ( Stokely Carmichael) and the popular singer James Brown
James Joseph Brown (May 3, 1933 – December 25, 2006) was an American singer, dancer, musician, record producer and bandleader. The central progenitor of funk music and a major figure of 20th century music, he is often referred to by the honor ...
's song " Say It Loud – I'm Black and I'm Proud".
In 1988, the civil rights leader Jesse Jackson
Jesse Louis Jackson (né Burns; born October 8, 1941) is an American political activist, Baptist minister, and politician. He was a candidate for the Democratic presidential nomination in 1984 and 1988 and served as a shadow U.S. senator ...
urged Americans to use instead the term "African American" because it had a historical cultural base and was a construction similar to terms used by European descendants, such as German American, Italian American, etc. Since then, African American and black have often had parallel status. However, controversy continues over which, if any, of the two terms is more appropriate. Maulana Karenga argues that the term African-American is more appropriate because it accurately articulates their geographical and historical origin. Others have argued that "black" is a better term because "African" suggests foreignness, although black Americans helped found the United States. Still others believe that the term "black" is inaccurate because African Americans have a variety of skin tones. Some surveys suggest that the majority of Black Americans have no preference for "African American" or "black", although they have a slight preference for "black" in personal settings and "African American" in more formal settings.
In the U.S. census race definitions, black and African Americans are citizens and residents of the United States with origins in the black racial groups of Africa. According to the Office of Management and Budget, the grouping includes individuals who self-identify as African American, as well as persons who emigrated from nations in the Caribbean and sub-Saharan Africa. The grouping is thus based on geography, and may contradict or misrepresent an individual's self-identification, since not all immigrants from sub-Saharan Africa are "black". The Census Bureau also notes that these classifications are socio-political constructs and should not be interpreted as scientific or anthropological.
According to U.S. Census Bureau data, African immigrants
The African diaspora is the worldwide collection of communities descended from native Africans or people from Africa, predominantly in the Americas. The term most commonly refers to the descendants of the West and Central Africans who were e ...
generally do not self-identify as African American. The overwhelming majority of African immigrants identify instead with their own respective ethnicities (~95%). Immigrants from some Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
, Central American and South American nations and their descendants may or may not also self-identify with the term.
Recent surveys of African Americans using a genetic testing service have found varied ancestries that show different tendencies by region and sex of ancestors. These studies found that on average, African Americans have 73.2–80.9% West African, 18–24% European, and 0.8–0.9% Native American genetic heritage, with large variation between individuals.
According to studies in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, U.S. residents consistently overestimate the size, physical strength, and formidability of young black men.
One-drop rule
 From the late 19th century, the South used a colloquial term, the '' one-drop rule'', to classify as black a person of any known African ancestry. This practice of hypodescent was not put into law until the early 20th century. Legally, the definition varied from state to state. Racial definition was more flexible in the 18th and 19th centuries before the American Civil War. For instance, President Thomas Jefferson held in slavery persons who were legally white (less than 25% black) according to Virginia law at the time, but, because they were born to slave mothers, they were born into slavery, according to the principle of '' partus sequitur ventrem'', which Virginia adopted into law in 1662.
Outside of the United States, some other countries have adopted the one-drop rule, but the definition of who is black and the extent to which the one-drop "rule" applies varies greatly from country to country.
The one-drop rule may have originated as a means of increasing the number of black slaves and was maintained as an attempt to keep the white race "pure". One of the results of the one-drop rule was the uniting of the African-American community. Some of the most prominent abolitionists and civil-rights activists of the 19th century were multiracial, such as Frederick Douglass, Robert Purvis and James Mercer Langston. They advocated equality for all.
From the late 19th century, the South used a colloquial term, the '' one-drop rule'', to classify as black a person of any known African ancestry. This practice of hypodescent was not put into law until the early 20th century. Legally, the definition varied from state to state. Racial definition was more flexible in the 18th and 19th centuries before the American Civil War. For instance, President Thomas Jefferson held in slavery persons who were legally white (less than 25% black) according to Virginia law at the time, but, because they were born to slave mothers, they were born into slavery, according to the principle of '' partus sequitur ventrem'', which Virginia adopted into law in 1662.
Outside of the United States, some other countries have adopted the one-drop rule, but the definition of who is black and the extent to which the one-drop "rule" applies varies greatly from country to country.
The one-drop rule may have originated as a means of increasing the number of black slaves and was maintained as an attempt to keep the white race "pure". One of the results of the one-drop rule was the uniting of the African-American community. Some of the most prominent abolitionists and civil-rights activists of the 19th century were multiracial, such as Frederick Douglass, Robert Purvis and James Mercer Langston. They advocated equality for all.
Blackness
 The concept of blackness in the United States has been described as the degree to which one associates themselves with mainstream
The concept of blackness in the United States has been described as the degree to which one associates themselves with mainstream African-American culture
African-American culture refers to the contributions of African Americans to the culture of the United States, either as part of or distinct from mainstream American culture. The culture is both distinct and enormously influential on Ame ...
, politics, and values. To a certain extent, this concept is not so much about race but more about political orientation, culture and behavior. Blackness can be contrasted with " acting white", where black Americans are said to behave with assumed characteristics of stereotypical white Americans with regard to fashion, dialect, taste in music, and possibly, from the perspective of a significant number of black youth, academic achievement.
Due to the often political and cultural contours of blackness in the United States, the notion of blackness can also be extended to non-black people. Toni Morrison once described Bill Clinton as the first black President of the United States, because, as she put it, he displayed "almost every trope of blackness". Clinton welcomed the label.
The question of blackness also arose in the Democrat Barack Obama's 2008 presidential campaign. Commentators questioned whether Obama, who was elected the first president with black ancestry, was "black enough", contending that his background is not typical because his mother was a white American and his father was a black student visitor from Kenya. Obama chose to identify as black and African American.
Mexico
Caribbean
Dominican Republic
The first Afro-Dominican slaves were shipped to the Dominican Republic by Spanish conquistadors during the Transatlantic slave trade.Puerto Rico
Spanish conquistadors shipped slaves from West Africa to Puerto Rico. Afro-Puerto Ricans in part trace ancestry to this colonization of the island.South America
 Approximately 12 million people were shipped from Africa to the
Approximately 12 million people were shipped from Africa to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
during the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
from 1492 to 1888. Of these, 11.5 million of those shipped to South America and the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
. Brazil was the largest importer in the Americas, with 5.5 million African slaves imported, followed by the British Caribbean with 2.76 million, the Spanish Caribbean and Spanish Mainland with 1.59 million Africans, and the French Caribbean with 1.32 million. Today their descendants number approximately 150 million in South America and the Caribbean. In addition to skin color, other physical characteristics such as facial features and hair texture are often variously used in classifying peoples as black in South America and the Caribbean. In South America and the Caribbean, classification as black is also closely tied to social status and socioeconomic variables, especially in light of social conceptions of " blanqueamiento" (racial whitening) and related concepts.
Brazil
The concept of race in Brazil is complex. A Brazilian child was never automatically identified with the racial type of one or both of their parents, nor were there only two categories to choose from. Between an individual of unmixed West African ancestry and a very lightmulatto
(, ) is a racial classification to refer to people of mixed African and European ancestry. Its use is considered outdated and offensive in several languages, including English and Dutch, whereas in languages such as Spanish and Portuguese is ...
individual, more than a dozen racial categories were acknowledged, based on various combinations of hair color, hair texture, eye color, and skin color. These types grade into each other like the colors of the spectrum, and no one category stands significantly isolated from the rest. In Brazil, people are classified by appearance, not heredity.
Scholars disagree over the effects of social status on racial classifications in Brazil. It is generally believed that achieving upward mobility and education results in individuals being classified as a category of lighter skin. The popular claim is that in Brazil, poor whites are considered black and wealthy blacks are considered white. Some scholars disagree, arguing that " whitening" of one's social status may be open to people of mixed race, a large part of the population known as '' pardo'', but a person perceived as ''preto'' (black) will continue to be classified as black regardless of wealth or social status.
Statistics
From the years 1500 to 1850, an estimated 3.5 million captives were forcibly shipped from West/Central Africa to Brazil. The territory received the highest number of slaves of any country in the Americas. Scholars estimate that more than half of the Brazilian population is at least in part descended from these individuals. Brazil has the largest population of Afro-ancestry outside Africa. In contrast to the US, during the slavery period and after, the Portuguese colonial government in Brazil and the later Brazilian government did not pass formal anti- miscegenation or segregation laws. As in other Latin American countries,intermarriage
Mixed marriage or intermarriage may refer to:
* Exogamy, the act of marrying outside of one's own social group (the opposite of endogamy)
** Interracial marriage, between people of different races
*** Miscegenation, a pejorative term for inter ...
was prevalent during the colonial period and continued afterward. In addition, people of mixed race (''pardo'') often tended to marry white spouses, and their descendants became accepted as white. As a result, some of the European descended population also has West African or Amerindian blood. According to the last census of the 20th century, in which Brazilians could choose from five color/ethnic categories with which they identified, 54% of individuals identified as white, 6.2% identified as black, and 39.5% identified as pardo (brown)—a broad multi-racial category, including tri-racial persons.
In the 19th century, a philosophy of racial whitening emerged in Brazil, related to the assimilation of mixed-race people into the white population through intermarriage. Until recently the government did not keep data on race. However, statisticians estimate that in 1835, roughly 50% of the population was ''preto'' (black; most were enslaved), a further 20% was ''pardo'' (brown), and 25% white, with the remainder Amerindian. Some classified as pardo were tri-racial.
By the 2000 census, demographic changes including the end to slavery, immigration from Europe and Asia, assimilation of multiracial persons, and other factors resulted in a population in which 6.2% of the population identified as black, 40% as pardo, and 55% as white. Essentially most of the black population was absorbed into the multi-racial category by intermixing. A 2007 genetic study found that at least 29% of the middle-class, white Brazilian population had some recent (since 1822 and the end of the colonial period) African ancestry.
Race relations in Brazil
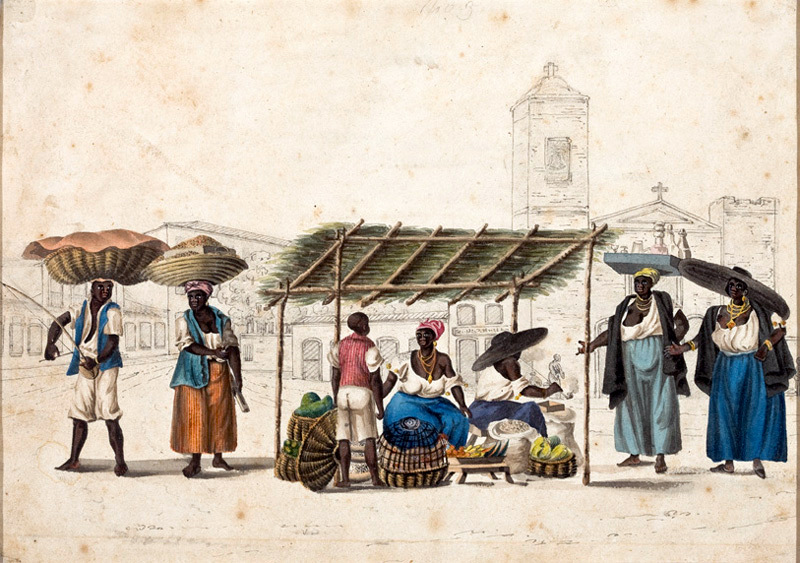 In 2015 United States, African Americans, including multiracial people, earned 76.8% as much as white people. By contrast, black and mixed race Brazilians earned on average 58% as much as whites in 2014. The gap in income between blacks and other non-whites is relatively small compared to the large gap between whites and all people of color. Other social factors, such as illiteracy and education levels, show the same patterns of disadvantage for people of color.
In 2015 United States, African Americans, including multiracial people, earned 76.8% as much as white people. By contrast, black and mixed race Brazilians earned on average 58% as much as whites in 2014. The gap in income between blacks and other non-whites is relatively small compared to the large gap between whites and all people of color. Other social factors, such as illiteracy and education levels, show the same patterns of disadvantage for people of color.
 Some commentators observe that the United States practice of segregation and white supremacy in the South, and discrimination in many areas outside that region, forced many African Americans to unite in the civil rights struggle, whereas the fluid nature of race in Brazil has divided individuals of African ancestry between those with more or less ancestry and helped sustain an image of the country as an example of post-colonial harmony. This has hindered the development of a common identity among black Brazilians.
Though Brazilians of at least partial African heritage make up a large percentageTom Phillips
Some commentators observe that the United States practice of segregation and white supremacy in the South, and discrimination in many areas outside that region, forced many African Americans to unite in the civil rights struggle, whereas the fluid nature of race in Brazil has divided individuals of African ancestry between those with more or less ancestry and helped sustain an image of the country as an example of post-colonial harmony. This has hindered the development of a common identity among black Brazilians.
Though Brazilians of at least partial African heritage make up a large percentageTom Phillips"Brazil census shows African-Brazilians in the majority for the first time"
''The Guardian'', 17 November 2011. Retrieved 6 May 2018. of the population, few blacks have been elected as politicians. The city of
Salvador, Bahia
Salvador (English: ''Savior'') is a Brazilian municipality and capital city of the state of Bahia. Situated in the Zona da Mata in the Northeast Region of Brazil, Salvador is recognized throughout the country and internationally for its cuisine ...
, for instance, is 80% people of color, but voters have not elected a mayor of color.
Patterns of discrimination against non-whites have led some academic and other activists to advocate for use of the Portuguese term ''negro'' to encompass all African-descended people, in order to stimulate a "black" consciousness and identity.
Colombia
Afro-Colombians are the third-largest African diaspora population in Latin America after Afro-Brazilians and Afro-Haitians
Haitians ( French: , ht, Ayisyen) are the citizens of Haiti and the descendants in the diaspora through direct parentage. An ethnonational group, Haitians generally comprise the modern descendants of self-liberated Africans in the Caribbean te ...
.
Venezuela
Most black Venezuelans descend from people brought as slaves to Venezuela directly from Africa during colonization; others have been descendants of immigrants from the Antilles and Colombia. Many blacks were part of the independence movement, and several managed to be heroes. There is a deep-rooted heritage of African culture in Venezuelan culture, as demonstrated in many traditional Venezuelan music and dances, such as theTambor
Tambor can refer to:
* Tambor, Costa Rica, a town in Costa Rica
** Tambor Airport, an airport that serves Tambor, Costa Rica
* El Tambor River, river in Guatemala
* Jeffrey Tambor (born 1944), American actor
* Tambor (dance), Afro-Venezuelan mus ...
, a musical genre inherited from black members of the colony, or the Llanera music
A (, ‘plainsman’) is a South American herder. The name is taken from the Llanos grasslands occupying eastern Colombia and western-central Venezuela.
During the Spanish American wars of independence, lancers and cavalry served in both a ...
or the Gaita zuliana that both are a fusion of all the three major peoples that contribute to the cultural heritage. Also, black inheritance is present in the country's gastronomy.
There are entire communities of blacks in the Barlovento zone, as well as part of the Bolívar state and in other small towns; they also live peaceably among the general population in the rest of Venezuela. Currently, blacks represent a plurality of the Venezuelan population, although many are actually mixed people.
See also
*African diaspora
The African diaspora is the worldwide collection of communities descended from native Africans or people from Africa, predominantly in the Americas. The term most commonly refers to the descendants of the West and Central Africans who were e ...
* Afrophobia
* Black elite
* Black supremacy
Black supremacy or black supremacism is a racial supremacist belief which maintains that black people are superior to people of other races. In the 1960s, Martin Luther King Jr. said that a doctrine of black supremacy was as dangerous as white ...
* Black women
* Lists of black people
Lists of black people include:
Achievements
* List of black Academy Award winners and nominees
* List of black Golden Globe Award winners and nominees
* List of first black Major League Baseball players
* List of black Nobel Laureates
Fiction ...
* Mulatto
(, ) is a racial classification to refer to people of mixed African and European ancestry. Its use is considered outdated and offensive in several languages, including English and Dutch, whereas in languages such as Spanish and Portuguese is ...
* Negrito
* San Basilio de Palenque, the first free African town in the Americas
* Scientific racism
* Zambo
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Black (human racial classification) Indigenous peoples of Oceania Latin American caste system People of African descent Person of color