Zaolzie on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Trans-Olza ( pl, Zaolzie, ; cs, Záolží, ''Záolší''; german: Olsa-Gebiet; Cieszyn Silesian: ''Zaolzi''), also known as Trans-Olza Silesia ( Polish: ''Śląsk Zaolziański''), is a territory in the
 After the fall of Great Moravia in 907 the area could have been under the influence of Bohemian rulers. In the late 10th century
After the fall of Great Moravia in 907 the area could have been under the influence of Bohemian rulers. In the late 10th century
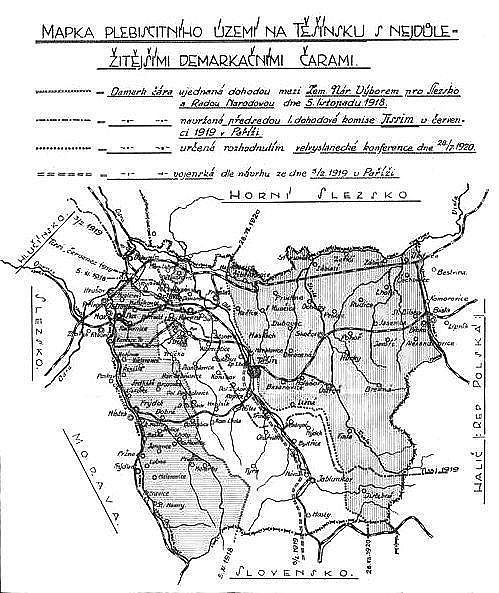
 Cieszyn Silesia was claimed by both Poland and Czechoslovakia: the Polish ''Rada Narodowa Księstwa Cieszyńskiego'' made its claim in its declaration "Ludu śląski!" of 30 October 1918, and the Czech ''Zemský národní výbor pro Slezsko'' did so in its declaration of 1 November 1918.Gawrecká 2004, 21. On 31 October 1918, at the end of World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the majority of the area was taken over by local Polish authorities supported by armed forces. An interim agreement from 2 November 1918 reflected the inability of the two national councils to come to final
Cieszyn Silesia was claimed by both Poland and Czechoslovakia: the Polish ''Rada Narodowa Księstwa Cieszyńskiego'' made its claim in its declaration "Ludu śląski!" of 30 October 1918, and the Czech ''Zemský národní výbor pro Slezsko'' did so in its declaration of 1 November 1918.Gawrecká 2004, 21. On 31 October 1918, at the end of World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the majority of the area was taken over by local Polish authorities supported by armed forces. An interim agreement from 2 November 1918 reflected the inability of the two national councils to come to final
 Historian Richard M. Watt writes, "On 5 November 1918, the Poles and the Czechs in the region disarmed the Austrian garrison (...) The Poles took over the areas that appeared to be theirs, just as the Czechs had assumed administration of theirs. Nobody objected to this friendly arrangement (...) Then came second thoughts in
Historian Richard M. Watt writes, "On 5 November 1918, the Poles and the Czechs in the region disarmed the Austrian garrison (...) The Poles took over the areas that appeared to be theirs, just as the Czechs had assumed administration of theirs. Nobody objected to this friendly arrangement (...) Then came second thoughts in  Watt argues that Beneš strategically waited for Poland's moment of weakness, and moved in during the Polish-Soviet War crisis in July 1920. As Watt writes, "Over the dinner table, Beneš convinced the British and French that the plebiscite should not be held and that the Allies should simply impose their own decision in the Teschen matter. More than that, Beneš persuaded the French and the British to draw a frontier line that gave Czechoslovakia most of the territory of Teschen, the vital railroad and all the important coal fields. With this frontier, 139,000 Poles were to be left in Czech territory, whereas only 2,000 Czechs were left on the Polish side".
"The next morning Beneš visited the Polish delegation at Spa. By giving the impression that the Czechs would accept a settlement favorable to the Poles without a plebiscite, Beneš got the Poles to sign an agreement that Poland would abide by any Allied decision regarding Teschen. The Poles, of course, had no way of knowing that Beneš had already persuaded the Allies to make a decision on Teschen. After a brief interval, to make it appear that due deliberation had taken place, the Allied Council of Ambassadors in Paris imposed its 'decision'. Only then did it dawn on the Poles that at Spa they had signed a blank check. To them, Beneš' stunning triumph was not diplomacy, it was a swindle (...) As Polish Prime Minister
Watt argues that Beneš strategically waited for Poland's moment of weakness, and moved in during the Polish-Soviet War crisis in July 1920. As Watt writes, "Over the dinner table, Beneš convinced the British and French that the plebiscite should not be held and that the Allies should simply impose their own decision in the Teschen matter. More than that, Beneš persuaded the French and the British to draw a frontier line that gave Czechoslovakia most of the territory of Teschen, the vital railroad and all the important coal fields. With this frontier, 139,000 Poles were to be left in Czech territory, whereas only 2,000 Czechs were left on the Polish side".
"The next morning Beneš visited the Polish delegation at Spa. By giving the impression that the Czechs would accept a settlement favorable to the Poles without a plebiscite, Beneš got the Poles to sign an agreement that Poland would abide by any Allied decision regarding Teschen. The Poles, of course, had no way of knowing that Beneš had already persuaded the Allies to make a decision on Teschen. After a brief interval, to make it appear that due deliberation had taken place, the Allied Council of Ambassadors in Paris imposed its 'decision'. Only then did it dawn on the Poles that at Spa they had signed a blank check. To them, Beneš' stunning triumph was not diplomacy, it was a swindle (...) As Polish Prime Minister
 The local Polish population felt that Warsaw had betrayed them and they were not satisfied with the division of Cieszyn Silesia. About 12,000 to 14,000 Poles were forced to leave to Poland.Gabal 1999, 120. It is not quite clear how many Poles were in Zaolzie in Czechoslovakia. Estimates (depending mainly whether the
The local Polish population felt that Warsaw had betrayed them and they were not satisfied with the division of Cieszyn Silesia. About 12,000 to 14,000 Poles were forced to leave to Poland.Gabal 1999, 120. It is not quite clear how many Poles were in Zaolzie in Czechoslovakia. Estimates (depending mainly whether the

 Within the region originally demanded from Czechoslovakia by Nazi Germany in 1938 was the important railway junction city of Bohumín ( pl, Bogumin). The Poles regarded the city as of crucial importance to the area and to Polish interests. On 28 September,
Within the region originally demanded from Czechoslovakia by Nazi Germany in 1938 was the important railway junction city of Bohumín ( pl, Bogumin). The Poles regarded the city as of crucial importance to the area and to Polish interests. On 28 September,
 On 1 September 1939
On 1 September 1939
 Immediately after World War II, Zaolzie was returned to Czechoslovakia within its 1920 borders, although local Poles had hoped it would again be given to Poland. Most Czechoslovaks of German ethnicity were expelled, and the local Polish population again suffered discrimination, as many Czechs blamed them for the discrimination by the Polish authorities in 1938–1939. Polish organizations were banned, and the Czechoslovak authorities carried out many arrests and dismissed many Poles from work. The situation had somewhat improved when the
Immediately after World War II, Zaolzie was returned to Czechoslovakia within its 1920 borders, although local Poles had hoped it would again be given to Poland. Most Czechoslovaks of German ethnicity were expelled, and the local Polish population again suffered discrimination, as many Czechs blamed them for the discrimination by the Polish authorities in 1938–1939. Polish organizations were banned, and the Czechoslovak authorities carried out many arrests and dismissed many Poles from work. The situation had somewhat improved when the

 The entry of both the Czech Republic and
The entry of both the Czech Republic and
Jarosław Jot-Drużycki: Poles living in Zaolzie identify themselves better with Czechs
. ''European Foundation of Human Rights.'' 3 September 2014. *
Documents and photographs about the situation in Zaolzie in 1938
*
{{good article Cieszyn Silesia Czech Republic–Poland border Czechoslovakia–Poland border Czechoslovakia–Poland relations History of Czech Silesia Moravian-Silesian Region Polish minority in Zaolzie Territorial disputes of Czechoslovakia Territorial disputes of Poland Historical regions in the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
, which was disputed between Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
and Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
during the Interwar Period. Its name comes from the Olza River.
The Trans-Olza region was created in 1920, when Cieszyn Silesia
Cieszyn Silesia, Těšín Silesia or Teschen Silesia ( pl, Śląsk Cieszyński ; cs, Těšínské Slezsko or ; german: Teschener Schlesien or ) is a historical region in south-eastern Silesia, centered on the towns of Cieszyn and Český ...
was divided between Czechoslovakia and Poland. Trans-Olza forms the eastern part of the Czech portion of Cieszyn Silesia
Cieszyn Silesia, Těšín Silesia or Teschen Silesia ( pl, Śląsk Cieszyński ; cs, Těšínské Slezsko or ; german: Teschener Schlesien or ) is a historical region in south-eastern Silesia, centered on the towns of Cieszyn and Český ...
. The division did not satisfy any side, and persisting conflict over the region led to its annexation by Poland in October 1938, following the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
. After the invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
in 1939, the area became a part of Nazi Germany until 1945. After the war, the 1920 borders were restored.
Historically, the largest specified ethnic group inhabiting this area were Poles. Under Austrian rule, Cieszyn Silesia was initially divided into three ( Bielitz, Friedek and Teschen), and later into four districts (plus Freistadt
Freistadt (, literally "Freetown") is a small Austrian town in the state of Upper Austria in the region Mühlviertel. With a population of approximately 7,500 residents, it is a trade centre for local villages. Freistadt is the economic centre o ...
). One of them, Frýdek, had a mostly Czech population, the other three were mostly inhabited by Poles. During the 19th century the number of ethnic Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
grew. After declining at the end of the 19th century,The 1880, 1890, 1900 and 1910 Austrian censuses asked people about the language they use. (Siwek 1996, 31.) at the beginning of the 20th century and later from 1920 to 1938 the Czech population grew significantly to rival the Poles. Another significant ethnic group were the Jews, but almost the entire Jewish population was murdered during World War II by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
.
In addition to the Polish, Czech and German national orientations there was another group of Silesians
Silesians ( szl, Ślōnzŏki or Ślůnzoki; Silesian German: ''Schläsinger'' ''or'' ''Schläsier''; german: Schlesier; pl, Ślązacy; cz, Slezané) is a geographical term for the inhabitants of Silesia, a historical region in Central Eur ...
, who claimed to be of a distinct national identity. This group enjoyed popular support throughout the whole of Cieszyn Silesia
Cieszyn Silesia, Těšín Silesia or Teschen Silesia ( pl, Śląsk Cieszyński ; cs, Těšínské Slezsko or ; german: Teschener Schlesien or ) is a historical region in south-eastern Silesia, centered on the towns of Cieszyn and Český ...
although its strongest supporters were among the Protestants
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
in the eastern part of the Cieszyn Silesia (now part of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
) and not in Trans-Olza itself.
Name and territory
The term ''Zaolzie'' (meaning "the trans-Olza", i.e. "lands beyond the Olza") is used predominantly in Poland and also commonly by the Polish minority living in the territory. The term ''Zaolzie'' was first used in 1930s by Polish writer Paweł Hulka-Laskowski. In Czech it is mainly referred to as ''České Těšínsko''/''Českotěšínsko'' ("land around Český Těšín"), or as ''Těšínsko'' or ''Těšínské Slezsko'' (meaningCieszyn Silesia
Cieszyn Silesia, Těšín Silesia or Teschen Silesia ( pl, Śląsk Cieszyński ; cs, Těšínské Slezsko or ; german: Teschener Schlesien or ) is a historical region in south-eastern Silesia, centered on the towns of Cieszyn and Český ...
). The Czech equivalent of Zaolzie (''Zaolší'' or ''Zaolží'') is rarely used. The term of ''Zaolzie'' is also used by some foreign scholars, e.g. American ethnolinguist Kevin Hannan
Kevin J. Hannan (January 22, 1954 – January 5, 2008) was an American ethnolinguist and slavicist.
Personal life
He was born into a family of Silesian and Irish ancestry. Kevin Hannan married Hanna, a Polish American, and had two daughters ...
.
The term ''Zaolzie'' denotes the territory of the former districts of Český Těšín and Fryštát, in which the Polish population formed a majority according to the 1910 Austrian census.Szymeczek 2008, 63. It makes up the eastern part of the Czech portion of Cieszyn Silesia. However, Polish historian Józef Szymeczek notes that the term is often mistakenly used for the whole Czech part of Cieszyn Silesia.
Since the 1960 reform of administrative divisions of Czechoslovakia, Zaolzie has consisted of Karviná District
Karviná District ( cs, okres Karviná, pl, powiat Karwina) is a district (''okres'') within the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. Its administrative center is the city of Karviná. It was created by 1960 reform of administrative ...
and the eastern part of Frýdek-Místek District.
History
After theMigration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
the area was settled by West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic la ...
, which were later organized into the Golensizi tribe. The tribe had a large and important gord situated in contemporary Chotěbuz. In the 880s or the early 890s the gord was raided and burned, most probably by an army of Svatopluk I of Moravia, and afterwards the area could have been subjugated by Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavs, Wes ...
, which is however questioned by historians like Zdeněk Klanica, Idzi Panic, Stanisław Szczur.
 After the fall of Great Moravia in 907 the area could have been under the influence of Bohemian rulers. In the late 10th century
After the fall of Great Moravia in 907 the area could have been under the influence of Bohemian rulers. In the late 10th century Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
, ruled by Bolesław I Chrobry, began to contend for the region, which was crossed by important international routes. From 950 to 1060 it was under the rule of the Duchy of Bohemia, and from 1060 it was part of Poland. The written history explicitly about the region begins on 23 April 1155 when Cieszyn/Těšín was first mentioned in a written document, a letter from Pope Adrian IV issued for Walter, Bishop of Wrocław, where it was listed amongst other centres of castellanies. The castellany was then a part of Duchy of Silesia
The Duchy of Silesia ( pl, Księstwo śląskie, german: Herzogtum Schlesien, cs, Slezské knížectví) with its capital at Wrocław was a medieval duchy located in the historic Silesian region of Poland. Soon after it was formed under the Pi ...
. In 1172 it became a part of Duchy of Racibórz, and from 1202 of Duchy of Opole and Racibórz. In the first half of the 13th century the Moravian settlement organised by Arnold von Hückeswagen from Starý Jičín castle and later accelerated by Bruno von Schauenburg, Bishop of Olomouc, began to press close to Silesian settlements. This prompted signing of a special treaty between Duke Władysław of Opole and King Ottokar II of Bohemia
Ottokar II ( cs, Přemysl Otakar II.; , in Městec Králové, Bohemia – 26 August 1278, in Dürnkrut, Lower Austria), the Iron and Golden King, was a member of the Přemyslid dynasty who reigned as King of Bohemia from 1253 until his d ...
on December 1261 which regulated a local border between their states along the Ostravice River. In order to strengthen the border Władysław of Opole decided to found Orlová monastery
The Orlová monastery ( cs, benediktinský klášter v Orlové, pl, klasztor benedyktynów w Orłowej) was a Benedictine abbey established around 1268 in what is now a town of Orlová in the Karviná District, Moravian-Silesian Region, Czech R ...
in 1268. In the continued process of feudal fragmentation of Poland the Castellany of Cieszyn was eventually transformed in 1290 into the Duchy of Cieszyn, which in 1327 became an autonomic fiefdom
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of ...
of the Bohemian crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were a number of incorporated states in Central Europe during the medieval and early modern periods connected by feudal relations under the Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted of the Kingdom of Bo ...
. Upon the death of Elizabeth Lucretia, its last ruler from the Polish Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branc ...
in 1653, it passed directly to the Czech kings from the Habsburg dynasty. When most of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is spli ...
was conquered by Prussian king Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the S ...
in 1742, the Cieszyn region was part of the small southern portion that was retained by the Habsburg monarchy (Austrian Silesia
Austrian Silesia, (historically also ''Oesterreichisch-Schlesien, Oesterreichisch Schlesien, österreichisch Schlesien''); cs, Rakouské Slezsko; pl, Śląsk Austriacki officially the Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia, (historically ''Herzogth ...
).
Up to the mid-19th century members of the local Slav population did not identify themselves as members of larger ethnolinguistic entities. In Cieszyn Silesia (as in all West Slavic borderlands) various territorial identities pre-dated ethnic and national identity. Consciousness of membership within a greater Polish or Czech nation spread slowly in Silesia.
From 1848 to the end of the 19th century, local Polish and Czech people co-operated, united against the Germanizing tendencies of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
and later of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
. At the end of the century, ethnic tensions arose as the area's economic significance grew. This growth caused a wave of immigration from Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
. About 60,000 people arrived between 1880 and 1910. The new immigrants were Polish and poor, about half of them being illiterate. They worked in coal mining and metallurgy. For these people the most important factor was material well-being; they cared little about the homeland from which they had fled. Almost all of them assimilated into the Czech population. Many of them settled in Ostrava
Ostrava (; pl, Ostrawa; german: Ostrau ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic, and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 280,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four ri ...
(west of the ethnic border), as heavy industry was spread through the whole western part of Cieszyn Silesia. Even today, ethnographers find that about 25,000 people in Ostrava (about 8% of the population) have Polish surnames.
The Czech population (living mainly in the northern part of the area: Bohumín, Orlová, etc.) declined numerically at the end of the 19th century, assimilating with the prevalent Polish population. This process shifted with the industrial boom in the area.
Decision time (1918–1920)

 Cieszyn Silesia was claimed by both Poland and Czechoslovakia: the Polish ''Rada Narodowa Księstwa Cieszyńskiego'' made its claim in its declaration "Ludu śląski!" of 30 October 1918, and the Czech ''Zemský národní výbor pro Slezsko'' did so in its declaration of 1 November 1918.Gawrecká 2004, 21. On 31 October 1918, at the end of World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the majority of the area was taken over by local Polish authorities supported by armed forces. An interim agreement from 2 November 1918 reflected the inability of the two national councils to come to final
Cieszyn Silesia was claimed by both Poland and Czechoslovakia: the Polish ''Rada Narodowa Księstwa Cieszyńskiego'' made its claim in its declaration "Ludu śląski!" of 30 October 1918, and the Czech ''Zemský národní výbor pro Slezsko'' did so in its declaration of 1 November 1918.Gawrecká 2004, 21. On 31 October 1918, at the end of World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the majority of the area was taken over by local Polish authorities supported by armed forces. An interim agreement from 2 November 1918 reflected the inability of the two national councils to come to final delimitation
Boundary delimitation (or simply delimitation) is the drawing of boundaries, particularly of electoral precincts, states, counties or other municipalities.
and on 5 November 1918, the area was divided between Poland and Czechoslovakia by an agreement of the two councils. In early 1919 both councils were absorbed by the newly created and independent central governments in Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
and Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is official ...
.
Following an announcement that elections to the Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
(parliament) of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
would be held in the entirety of Cieszyn Silesia, the Czechoslovak government requested that the Poles cease their preparations as no elections were to be held in the disputed territory until a final agreement could be reached. When their demands were rejected by the Poles, the Czechs decided to resolve the issue by force and on 23 January 1919 invaded the area.
The Czechoslovak offensive was halted after pressure from the Entente
Entente, meaning a diplomatic "understanding", may refer to a number of agreements:
History
* Entente (alliance), a type of treaty or military alliance where the signatories promise to consult each other or to cooperate with each other in case o ...
following the Battle of Skoczów
The Battle of Skoczów took place in late January 1919, during the Polish–Czechoslovak War. Czechoslovak units were halted only under pressure from the Entente. The result of the war was to set a new demarcation line, which extended the territory ...
, and a ceasefire was signed on 3 February. The new Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
claimed the area partly on historic and ethnic grounds, but especially on economic grounds.Mamatey 1973, 34. The area was important for the Czechs as the crucial railway line connecting Czech Silesia
Czech Silesia (, also , ; cs, České Slezsko; szl, Czeski Ślōnsk; sli, Tschechisch-Schläsing; german: Tschechisch-Schlesien; pl, Śląsk Czeski) is the part of the historical region of Silesia now in the Czech Republic. Czech Silesia is ...
with Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
crossed the area (the Košice–Bohumín Railway, which was one of only two railroads that linked the Czech provinces to Slovakia at that time). The area is also very rich in black coal. Many important coal mines, facilities and metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sci ...
factories are located there. The Polish side based its claim to the area on ethnic criteria: a majority (69.2%) of the area's population was Polish according to the last (1910) Austrian census.Dariusz Miszewski. ''Aktywność polityczna mniejszości polskiej w Czechosłowacji w latach 1920-1938''. Wyd. Adam Marszałek. 2002. p. 346.
In this very tense atmosphere it was decided that a plebiscite would be held in the area asking people which country this territory should join. Plebiscite commissioners arrived there at the end of January 1920, and after analysing the situation declared a state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state du ...
in the territory on 19 May 1920. The situation in the area remained very tense, with mutual intimidation, acts of terror, beatings and even killings. A plebiscite could not be held in this atmosphere. On 10 July both sides renounced the idea of a plebiscite and entrusted the Conference of Ambassadors with the decision.Zahradnik 1992, 64. Eventually, on 28 July 1920, by a decision of the Spa Conference, Czechoslovakia received 58.1% of the area of Cieszyn Silesia, containing 67.9% of the population. It was this territory that became known from the Polish standpoint as ''Zaolzie'' – the Olza River marked the boundary between the Polish and Czechoslovak parts of the territory.
The most vocal support for union with Poland had come from within the territory awarded to Czechoslovakia, while some of the strongest opponents of Polish rule came from the territory awarded to Poland.
View of Richard M. Watt
 Historian Richard M. Watt writes, "On 5 November 1918, the Poles and the Czechs in the region disarmed the Austrian garrison (...) The Poles took over the areas that appeared to be theirs, just as the Czechs had assumed administration of theirs. Nobody objected to this friendly arrangement (...) Then came second thoughts in
Historian Richard M. Watt writes, "On 5 November 1918, the Poles and the Czechs in the region disarmed the Austrian garrison (...) The Poles took over the areas that appeared to be theirs, just as the Czechs had assumed administration of theirs. Nobody objected to this friendly arrangement (...) Then came second thoughts in Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
. It was observed that under the agreement of 5 November, the Poles controlled about a third of the duchy's coal mines. The Czechs realized that they had given away rather a lot (...) It was recognized that any takeover in Teschen would have to be accomplished in a manner acceptable by the victorious Allies (...), so the Czechs cooked up a tale that the Teschen area was becoming Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
(...) The Czechs put together a substantial body of infantry – about 15,000 men – and on 23 January 1919, they invaded the Polish-held areas. To confuse the Poles, the Czechs recruited some Allied officers of Czech background and put these men in their respective wartime uniforms at the head of the invasion forces. After a little skirmishing, the tiny Polish defense force was nearly driven out."
In 1919, the matter went to consideration in Paris before the World War I Allies. Watt claims the Poles based their claims on ethnographical reasons and the Czechs based their need on the Teschen coal, useful in order to influence the actions of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
, whose capitals were fuelled by coal from the duchy. The Allies finally decided that the Czechs should get 60 percent of the coal fields and the Poles were to get most of the people and the strategic rail line. Watt writes: "Czech envoy Edvard Beneš
Edvard Beneš (; 28 May 1884 – 3 September 1948) was a Czech politician and statesman who served as the president of Czechoslovakia from 1935 to 1938, and again from 1945 to 1948. He also led the Czechoslovak government-in-exile 1939 to 194 ...
proposed a plebiscite. The Allies were shocked, arguing that the Czechs were bound to lose it. However, Beneš was insistent and a plebiscite was announced in September 1919. As it turned out, Beneš knew what he was doing. A plebiscite would take some time to set up, and a lot could happen in that time – particularly when a nation's affairs were conducted as cleverly as were Czechoslovakia's."Watt 1998, 163.
 Watt argues that Beneš strategically waited for Poland's moment of weakness, and moved in during the Polish-Soviet War crisis in July 1920. As Watt writes, "Over the dinner table, Beneš convinced the British and French that the plebiscite should not be held and that the Allies should simply impose their own decision in the Teschen matter. More than that, Beneš persuaded the French and the British to draw a frontier line that gave Czechoslovakia most of the territory of Teschen, the vital railroad and all the important coal fields. With this frontier, 139,000 Poles were to be left in Czech territory, whereas only 2,000 Czechs were left on the Polish side".
"The next morning Beneš visited the Polish delegation at Spa. By giving the impression that the Czechs would accept a settlement favorable to the Poles without a plebiscite, Beneš got the Poles to sign an agreement that Poland would abide by any Allied decision regarding Teschen. The Poles, of course, had no way of knowing that Beneš had already persuaded the Allies to make a decision on Teschen. After a brief interval, to make it appear that due deliberation had taken place, the Allied Council of Ambassadors in Paris imposed its 'decision'. Only then did it dawn on the Poles that at Spa they had signed a blank check. To them, Beneš' stunning triumph was not diplomacy, it was a swindle (...) As Polish Prime Minister
Watt argues that Beneš strategically waited for Poland's moment of weakness, and moved in during the Polish-Soviet War crisis in July 1920. As Watt writes, "Over the dinner table, Beneš convinced the British and French that the plebiscite should not be held and that the Allies should simply impose their own decision in the Teschen matter. More than that, Beneš persuaded the French and the British to draw a frontier line that gave Czechoslovakia most of the territory of Teschen, the vital railroad and all the important coal fields. With this frontier, 139,000 Poles were to be left in Czech territory, whereas only 2,000 Czechs were left on the Polish side".
"The next morning Beneš visited the Polish delegation at Spa. By giving the impression that the Czechs would accept a settlement favorable to the Poles without a plebiscite, Beneš got the Poles to sign an agreement that Poland would abide by any Allied decision regarding Teschen. The Poles, of course, had no way of knowing that Beneš had already persuaded the Allies to make a decision on Teschen. After a brief interval, to make it appear that due deliberation had taken place, the Allied Council of Ambassadors in Paris imposed its 'decision'. Only then did it dawn on the Poles that at Spa they had signed a blank check. To them, Beneš' stunning triumph was not diplomacy, it was a swindle (...) As Polish Prime Minister Wincenty Witos
Wincenty Witos (; 22 January 1874 – 31 October 1945) was a Polish politician, prominent member and leader of the Polish People's Party (PSL), who served three times as the Prime Minister of Poland in the 1920s.
He was a member of the Polish Pe ...
warned: 'The Polish nation has received a blow which will play an important role in our relations with the Czechoslovak Republic. The decision of the Council of Ambassadors has given the Czechs a piece of Polish land containing a population which is mostly Polish.... The decision has caused a rift between these two nations which are ordinarily politically and economically united' (
...."
View of Victor S. Mamatey
Another account of the situation in 1918–1919 is given by historianVictor S. Mamatey
Victor Samuel Mamatey (February 2, 1917 - January 18, 2007) was an American professor of history.
Biography
Mamatey was born in North Braddock, Pennsylvania. His father, Albert Mamatey, was a Slovak immigrant to the United States, active in Sl ...
. He notes that when the French government recognised Czechoslovakia's right to the "boundaries of Bohemia, Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
Th ...
, and Austrian Silesia
Austrian Silesia, (historically also ''Oesterreichisch-Schlesien, Oesterreichisch Schlesien, österreichisch Schlesien''); cs, Rakouské Slezsko; pl, Śląsk Austriacki officially the Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia, (historically ''Herzogth ...
" in its note to Austria of 19 December, the Czechoslovak government acted under the impression it had French support for its claim to Cieszyn Silesia as part of Austrian Silesia. However, Paris believed it gave that assurance only against German-Austrian claims, not Polish ones. Paris, however, viewed both Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
as potential allies against Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
and did not want to cool relations with either. Mamatey writes that the Poles "brought the matter before the peace conference that had opened in Paris on 18 January. On 29 January, the Council of Ten summoned Beneš and the Polish delegate Roman Dmowski to explain the dispute, and on 1 February obliged them to sign an agreement redividing the area pending its final disposition by the peace conference. Czechoslovakia thus failed to gain her objective in Teschen."
With respect to the arbitration decision itself, Mamatey writes that "On 25 March, to expedite the work of the peace conference, the Council of Ten was divided into the Council of Four (The "Big Four") and the Council of Five (the foreign ministers). Early in April the two councils considered and approved the recommendations of the Czechoslovak commission without a change – with the exception of Teschen, which they referred to Poland and Czechoslovakia to settle in bilateral negotiations." When the Polish-Czechoslovak negotiations failed, the Allied powers proposed plebiscites in the Cieszyn Silesia and also in the border districts of Orava and Spiš
Spiš (Latin: ''Cips/Zepus/Scepus/Scepusia'', german: Zips, hu, Szepesség/Szepes, pl, Spisz) is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland (14 villages). Spiš is an informal designation of the territory ...
(now in Slovakia) to which the Poles had raised claims. In the end, however, no plebiscites were held due to the rising mutual hostilities of Czechs and Poles in Cieszyn Silesia. Instead, on 28 July 1920 the Spa Conference (also known as the Conference of Ambassadors) divided each of the three disputed areas between Poland and Czechoslovakia.
Part of Czechoslovakia (1920–1938)
 The local Polish population felt that Warsaw had betrayed them and they were not satisfied with the division of Cieszyn Silesia. About 12,000 to 14,000 Poles were forced to leave to Poland.Gabal 1999, 120. It is not quite clear how many Poles were in Zaolzie in Czechoslovakia. Estimates (depending mainly whether the
The local Polish population felt that Warsaw had betrayed them and they were not satisfied with the division of Cieszyn Silesia. About 12,000 to 14,000 Poles were forced to leave to Poland.Gabal 1999, 120. It is not quite clear how many Poles were in Zaolzie in Czechoslovakia. Estimates (depending mainly whether the Silesians
Silesians ( szl, Ślōnzŏki or Ślůnzoki; Silesian German: ''Schläsinger'' ''or'' ''Schläsier''; german: Schlesier; pl, Ślązacy; cz, Slezané) is a geographical term for the inhabitants of Silesia, a historical region in Central Eur ...
are included as Poles or not) range from 110,000 to 140,000 people in 1921. The 1921 and 1930 census numbers are not accurate since nationality depended on self-declaration and many Poles filled in Czech nationality mainly as a result of fear of the new authorities and as compensation for some benefits. Czechoslovak law guaranteed rights for national minorities but reality in Zaolzie was quite different.Zahradnik 1992, 76–79. Local Czech authorities made it more difficult for local Poles to obtain citizenship, while the process was expedited when the applicant pledged to declare Czech nationality and send his children to a Czech school. Newly built Czech schools were often better supported and equipped, thus inducing some Poles to send their children there. Czech schools were built in ethnically almost entirely Polish municipalities. This and other factors contributed to the cultural assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or assume the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group whether fully or partially.
The different types of cultural as ...
of Poles and also to significant emigration to Poland. After a few years, the heightened nationalism typical for the years around 1920 receded and local Poles increasingly co-operated with Czechs. Still, Czechization was supported by Prague, which did not follow certain laws related to language, legislative and organizational issues. Polish deputies in the Czechoslovak National Assembly frequently tried to put those issues on agenda. One way or another, more and more local Poles thus assimilated into the Czech population.
Part of Poland (1938–1939)
 Within the region originally demanded from Czechoslovakia by Nazi Germany in 1938 was the important railway junction city of Bohumín ( pl, Bogumin). The Poles regarded the city as of crucial importance to the area and to Polish interests. On 28 September,
Within the region originally demanded from Czechoslovakia by Nazi Germany in 1938 was the important railway junction city of Bohumín ( pl, Bogumin). The Poles regarded the city as of crucial importance to the area and to Polish interests. On 28 September, Edvard Beneš
Edvard Beneš (; 28 May 1884 – 3 September 1948) was a Czech politician and statesman who served as the president of Czechoslovakia from 1935 to 1938, and again from 1945 to 1948. He also led the Czechoslovak government-in-exile 1939 to 194 ...
composed a note to the Polish administration offering to reopen the debate surrounding the territorial demarcation in Těšínsko in the interest of mutual relations, but he delayed in sending it in hopes of good news from London and Paris, which came only in a limited form. Beneš then turned to the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
leadership in Moscow, which had begun a partial mobilisation in eastern Belarus and the Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
on 22 September and threatened Poland with the dissolution of the Soviet-Polish non-aggression pact. The Czech government was offered 700 fighter planes if room for them could be found on the Czech airfields. On 28 September, all the military districts west of the Urals were ordered to stop releasing men for leave. On 29 September 330,000 reservists were up throughout the western USSR.
Nevertheless, the Polish Foreign Minister, Colonel Józef Beck, believed that Warsaw should act rapidly to forestall the German occupation of the city. At noon on 30 September, Poland gave an ultimatum to the Czechoslovak government. It demanded the immediate evacuation of Czechoslovak troops and police and gave Prague time until noon the following day. At 11:45 a.m. on 1 October the Czechoslovak foreign ministry called the Polish ambassador in Prague and told him that Poland could have what it wanted. The Polish Army, commanded by General Władysław Bortnowski, annexed an area of 801.5 km2 with a population of 227,399 people. Administratively the annexed area was divided between two counties: Frysztat and Cieszyn County. At the same time Slovakia lost to Hungary 10,390 km2 with 854,277 inhabitants.
The Germans were delighted with this outcome, and were happy to give up the sacrifice of a small provincial rail centre to Poland in exchange for the ensuing propaganda benefits. It spread the blame of the partition of the Republic of Czechoslovakia, made Poland a participant in the process and confused political expectations. Poland was accused of being an accomplice of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
– a charge that Warsaw was hard-put to deny.Watt 1998, 386.
The Polish side argued that Poles in Zaolzie deserved the same ethnic rights and freedom as the Sudeten Germans under the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
. The vast local Polish population enthusiastically welcomed the change, seeing it as a liberation and a form of historical justice, but they quickly changed their mood. The new Polish authorities appointed people from Poland to various key positions from which locals were fired.Gabal 1999, 123. The Polish language became the sole official language. Using Czech (or German) by Czechs (or Germans) in public was prohibited and Czechs and Germans were being forced to leave the annexed area or become subject to Polonization
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
. Rapid Polonization policies then followed in all parts of public and private life. Czech organizations were dismantled and their activity was prohibited. The Roman Catholic parishes in the area belonged either to the Archdiocese of Breslau (Archbishop Bertram Bertram may refer to:
Places
* Bertram, Western Australia, a suburb of Perth, Australia
*Bertram, Iowa, United States, a city
* Bertram, Texas, United States, a city
* Bertram Building, a historic building in Austin, Texas
* Bertram Glacier, Palmer ...
) or to the Archdiocese of Olomouc (Archbishop Leopold Prečan), respectively, both traditionally comprising cross-border diocesan territories in Czechoslovakia and Germany. When the Polish government demanded after its takeover that the parishes there be disentangled from these two archdioceses, the Holy See complied. Pope Pius XI
Pope Pius XI ( it, Pio XI), born Ambrogio Damiano Achille Ratti (; 31 May 1857 – 10 February 1939), was head of the Catholic Church from 6 February 1922 to his death in February 1939. He was the first sovereign of Vatican City fr ...
, former nuncio to Poland, subjected the Catholic parishes in Zaolzie to an apostolic administration under Stanisław Adamski, Bishop of Katowice.Jerzy Pietrzak, "Die politischen und kirchenrechtlichen Grundlagen der Einsetzung Apostolischer Administratoren in den Jahren 1939–1942 und 1945 im Vergleich", in: ''Katholische Kirche unter nationalsozialistischer und kommunistischer Diktatur: Deutschland und Polen 1939–1989'', Hans-Jürgen Karp and Joachim Köhler (eds.), (=Forschungen und Quellen zur Kirchen- und Kulturgeschichte Ostdeutschlands; vol. 32), Cologne: Böhlau, 2001, pp. 157–174, here p. 160. .
Czechoslovak education in the Czech and German language ceased to exist. About 35,000 Czechoslovaks emigrated to core Czechoslovakia (the later Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
The Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia; cs, Protektorát Čechy a Morava; its territory was called by the Nazis ("the rest of Czechia"). was a partially annexed territory of Nazi Germany established on 16 March 1939 following the German oc ...
) by choice or forcibly. The behaviour of the new Polish authorities was different but similar in nature to that of the Czechoslovak ones before 1938. Two political factions appeared: socialists (the opposition) and rightists (loyal to the new Polish national authorities). Leftist politicians and sympathizers were discriminated against and often fired from work. The Polish political system was artificially implemented in Zaolzie. The local Poles continued to feel like second-class citizens and a majority of them were dissatisfied with the situation after October 1938. Zaolzie remained a part of Poland for only 11 months until the invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
started on 1 September 1939.
Reception
When Poland entered the Western camp in April 1939,General Gamelin
Maurice Gustave Gamelin (, 20 September 1872 – 18 April 1958) was an army general in the French Army. Gamelin is remembered for his disastrous command (until 17 May 1940) of the French military during the Battle of France (10 May–22 June 194 ...
reminded General Kasprzycki of the Polish role in the dismemberment of Czechoslovakia. According to historian Paul N. Hehn
Paul N. Hehn (April 8, 1927 – January 4, 2015) was an American historian who specialized in the Second World War. The son of a German immigrant father and a French-Canadian mother, Hehn was born in Manhattan and served as a US Navy Seabee in the ...
, Poland's annexation of Teschen may have contributed to the British and French reluctance to attack the Germans with greater forces in September 1939.
Richard M. Watt
Richard M. Watt (November 10, 1930 – January 25, 2015) was an American historian and writer.
Biography
Richard Martin Watt was born on November 10, 1930, in La Grange, Illinois, United States. Watt attended Glen Ridge High School in Essex Co ...
describes the Polish capture of Teschen in these words:
Amid the general euphoria in Poland – the acquisition of Teschen was a very popular development – no one paid attention to the bitter comment of the Czechoslovak general who handed the region over to the incoming Poles. He predicted that it would not be long before the Poles would themselves be handing Teschen over to the Germans.Watt also writes that
the Polish 1938 ultimatum to Czechoslovakia and its acquisition of Teschen were gross tactical errors. Whatever justice there might have been to the Polish claim upon Teschen, its seizure in 1938 was an enormous mistake in terms of the damage done to Poland's reputation among the democratic powers of the world.Daladier, the French Prime Minister, told the US ambassador to France that "he hoped to live long enough to pay Poland for her cormorant attitude in the present crisis by proposing a new partition." The Soviet Union was so hostile to Poland over Munich that there was a real prospect that war between the two states might break out quite separate from the wider conflict over Czechoslovakia. The Soviet Prime Minister, Molotov, denounced the Poles as "Hitler's jackals". In his postwar memoirs, Winston Churchill compared Germany and Poland to vultures landing on the dying carcass of Czechoslovakia and lamented that "over a question so minor as Teschen, they
he Poles
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
sundered themselves from all those friends in France, Britain and the United States who had lifted them once again to a national, coherent life, and whom they were soon to need so sorely. ... It is a mystery and tragedy of European history that a people capable of every heroic virtue ... as individuals, should repeatedly show such inveterate faults in almost every aspect of their governmental life."
In 2009 Polish president Lech Kaczyński declared during 70th anniversary of start of World War II, which was welcomed by the Czech and Slovak diplomatic delegations:
The Polish annexation is frequently brought up by Russian diplomacy as a counter-argument to Soviet-German cooperation.
World War II
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
invaded Poland, starting World War II in Europe, and subsequently made Zaolzie part of the ''Military district of Upper Silesia''. On 26 October 1939 Nazi Germany unilaterally annexed Zaolzie as part of Landkreis Teschen East Upper Silesia (german: Ostoberschlesien) is the easternmost extremity of Silesia, the eastern part of the Upper Silesian region around the city of Katowice (german: Kattowitz).Isabel Heinemann, ''"Rasse, Siedlung, deutsches Blut": das Rasse- ...
. During the war, strong Germanization was introduced by the authorities. The Jews were in the worst position, followed by the Poles.Zahradnik 1992, 99. Poles received lower food rations, they were supposed to pay extra taxes, they were not allowed to enter theatres, cinemas, etc. Polish and Czech education ceased to exist, Polish organizations were dismantled and their activity was prohibited. Katowice's Bishop Adamski was deposed as apostolic administrator for the Catholic parishes in Zaolzie and on 23 December 1939 Cesare Orsenigo, nuncio to Germany, returned them to their original archdioceses of Breslau or Olomouc, respectively, with effect of 1 January 1940.
The German authorities introduced terror into Zaolzie. The Nazis especially targeted the Polish intelligentsia, many of whom died during the war. Mass killings, executions, arrests, taking locals to forced labour and deportations to concentration camps
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simpl ...
all happened on a daily basis. The most notorious war crime was a murder of 36 villagers in and around Żywocice
Żywocice (German ''Zywodczütz'') is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Krapkowice, within Krapkowice County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately south of Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, ...
on 6 August 1944. This massacre is known as the Żywocice tragedy ( pl, Tragedia Żywocicka). The resistance movement
A resistance movement is an organized effort by some portion of the civil population of a country to withstand the legally established government or an occupying power and to disrupt civil order and stability. It may seek to achieve its objective ...
, mostly composed of Poles, was fairly strong in Zaolzie. So-called ''Volksliste
The Deutsche Volksliste (German People's List), a Nazi Party institution, aimed to classify inhabitants of Nazi-occupied territories (1939-1945) into categories of desirability according to criteria systematised by ''Reichsführer-SS'' Heinrich Hi ...
'' – a document in which a non-German citizen declared that he had some German ancestry by signing it; refusal to sign this document could lead to deportation to a concentration camp – were introduced. Local people who took them were later on enrolled in the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previou ...
. Many local people with no German ancestry were also forced to take them. The World War II death toll in Zaolzie is estimated at about 6,000 people: about 2,500 Jews, 2,000 other citizens (80% of them being Poles)Zahradnik 1992, 103. and more than 1,000 locals who died in the Wehrmacht (those who took the Volksliste). Also a few hundred Poles from Zaolzie were murdered by Soviets in the Katyn massacre.
Percentage-wise, Zaolzie suffered the worst human loss from the whole of Czechoslovakia – about 2.6% of the total population.
Since 1945
 Immediately after World War II, Zaolzie was returned to Czechoslovakia within its 1920 borders, although local Poles had hoped it would again be given to Poland. Most Czechoslovaks of German ethnicity were expelled, and the local Polish population again suffered discrimination, as many Czechs blamed them for the discrimination by the Polish authorities in 1938–1939. Polish organizations were banned, and the Czechoslovak authorities carried out many arrests and dismissed many Poles from work. The situation had somewhat improved when the
Immediately after World War II, Zaolzie was returned to Czechoslovakia within its 1920 borders, although local Poles had hoped it would again be given to Poland. Most Czechoslovaks of German ethnicity were expelled, and the local Polish population again suffered discrimination, as many Czechs blamed them for the discrimination by the Polish authorities in 1938–1939. Polish organizations were banned, and the Czechoslovak authorities carried out many arrests and dismissed many Poles from work. The situation had somewhat improved when the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia
The Communist Party of Czechoslovakia (Czech language, Czech and Slovak language, Slovak: ''Komunistická strana Československa'', KSČ) was a communist and Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist political party in Czechoslovakia that existed be ...
took power in February 1948. Polish property deprived by the German occupants during the war was never returned.
As to the Catholic parishes in Zaolzie pertaining to the Archdiocese of Breslau Archbishop Bertram, then residing in the episcopal Jánský vrch castle in Czechoslovak Javorník, appointed František Onderek (1888–1962) as ''vicar general
A vicar general (previously, archdeacon) is the principal deputy of the bishop of a diocese for the exercise of administrative authority and possesses the title of local ordinary. As vicar of the bishop, the vicar general exercises the bishop's ...
for the Czechoslovak portion of the Archdiocese of Breslau'' on 21 June 1945. In July 1946 Pope Pius XII elevated Onderek to ''Apostolic Administrator for the Czechoslovak portion of the Archdiocese of Breslau'' (colloquially: Apostolic Administration of Český Těšín; cs, Apoštolská administratura českotěšínská), seated in Český Těšín, thus disentangling the parishes from Breslau's jurisdiction. On 31 May 1978 Pope Paul VI
Pope Paul VI ( la, Paulus VI; it, Paolo VI; born Giovanni Battista Enrico Antonio Maria Montini, ; 26 September 18976 August 1978) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 21 June 1963 to his death in Augus ...
merged the apostolic administration into the Archdiocese of Olomouc through his Apostolic constitution ''Olomoucensis et aliarum''.
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
signed a treaty with Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
in Warsaw on 13 June 1958 confirming the border as it existed on 1 January 1938. After the Communist takeover of power, the industrial boom continued and many immigrants arrived in the area (mostly from other parts of Czechoslovakia, mainly from Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
). The arrival of Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 ...
significantly changed the ethnic structure of the area, as almost all the Slovak immigrants assimilated into the Czech majority in the course of time. The number of self-declared Slovaks is rapidly declining. The last Slovak elementary school was closed in Karviná several years ago. Since the dissolution of Czechoslovakia
The dissolution of Czechoslovakia ( cs, Rozdělení Československa, sk, Rozdelenie Česko-Slovenska) took effect on December 31, 1992, and was the self-determined split of the federal republic of Czechoslovakia into the independent countries ...
in 1993, Zaolzie has been part of the independent Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
. However, a significant Polish minority still remains there.
In the European Union

 The entry of both the Czech Republic and
The entry of both the Czech Republic and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
to the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
in May 2004, and especially the entry of the countries to the EU's passport-free Schengen zone in late 2007, reduced the significance of territorial disputes, ending systematic controls on the border between the countries. Signs prohibiting passage across the state border were removed, with people now allowed to cross the border freely at any point of their choosing.
The area belongs mostly to the Cieszyn Silesia Euroregion
Euroregion Cieszyn Silesia ( pl, Euroregion Śląsk Cieszyński, cs, Euroregion Těšínské Slezsko) is one of the euroregions (transnational co-operation structures) between Poland and Czech Republic. It has area of 1741,34 km² and 658,2 ...
with a few municipalities in the Euroregion Beskydy.
Census data
Ethnic structure of Zaolzie based on census results: Sources: Zahradnik 1992, 178–179. Siwek 1996, 31–38.See also
* History of Cieszyn and Těšín *Polonia Karwina
Polski Klub Sportowy Polonia Karwina (PKS Polonia Karwina) was a Polish multi-sport club, located in the town of Karviná (Karwina), Zaolzie, Czechoslovakia. It affiliated nine sport clubs and an amateur theatre group. Most successful and most ...
* Independent Operational Group Silesia
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* *External links
*Jarosław Jot-Drużycki: Poles living in Zaolzie identify themselves better with Czechs
. ''European Foundation of Human Rights.'' 3 September 2014. *
Documents and photographs about the situation in Zaolzie in 1938
*
{{good article Cieszyn Silesia Czech Republic–Poland border Czechoslovakia–Poland border Czechoslovakia–Poland relations History of Czech Silesia Moravian-Silesian Region Polish minority in Zaolzie Territorial disputes of Czechoslovakia Territorial disputes of Poland Historical regions in the Czech Republic