|
Independent Operational Group Silesia
Independent Operational Group Silesia (Polish: Samodzielna Grupa Operacyjna Śląsk, SGO Śląsk) was an Operational Group of the Polish Army, created in September 1938 to annex Trans-Olza (Zaolzie) from Czechoslovakia. History The Group was commanded by General Władysław Bortnowski and comprised several Army units and five air squadrons. Altogether, 35,966 Polish officers and soldiers participated in the annexation of Zaolzie. The Group comprised mostly units of the 4th Infantry Division, as well as regiments of the 14th Infantry Division, 15th Infantry Division, 16th Infantry Division, 23rd Infantry Division, 25th Infantry Division, and 21st Mountain Infantry Division. Additionally, a cavalry regiment was created, comprising units of the Wielkopolska Cavalry Brigade and the Pomeranian Cavalry Brigade. Annexation of Zaolzie region After its creation, the military unit was stationed near the border of Poland and Czechoslovakia. As a result of Munich crisis, the Cze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wielkopolska Cavalry Brigade
Wielkopolska Cavalry Brigade (Polish: ''Wielkopolska Brygada Kawalerii'') was a cavalry unit of the Polish Army in the interbellum period. It was created on April 1, 1937 out of the Cavalry Brigade "Poznań". Its headquarters were stationed in Poznań and the brigade consisted of these units: * 16th Greater Poland Uhlan Regiment * 15th Poznań Uhlans Regiment, stationed in Poznań, * 17th Greater Poland Uhlan Regiment of King Bolesław Chrobry, stationed in Leszno * 7th Greater Poland Mounted Rifles Regiment, stationed in Biedrusko, * 7th Greater Poland Mounted Artillery Regiment, stationed in Poznań, * 3rd Squadron of Pioneers, stationed in Poznań, * 7th Squadron of Communications, stationed in Poznań. Polish September Campaign The Brigade, under General Roman Abraham, was part of the Poznań Army. On the first day of the Polish September Campaign, its forces counterattacked the Wehrmacht in the area of Leszno and Rawicz, together with the 25th Infantry Division. On Septem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Disestablished In 1938
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Units And Formations Of Poland
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by possessing an army aviation component. Within a national military force, the word army may also mean a field army. In some countries, such as France and China, the term "army", especially in its plural form "armies", has the broader meaning of armed forces as a whole, while retaining the colloquial sense of land forces. To differentiate the colloquial army from the formal concept of military force, the term is qualified, for example in France the land force is called ''Armée de terre'', meaning Land Army, and the air and space force is called ''Armée de l'Air et de l’Espace' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Established In 1938
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feliks Ankerstein
Feliks Józef Ankerstein (1897 – ? 1955) was a Polish Army major and intelligence officer. Career Ankerstein served during World War I in the Polish Legions and the Polish Military Organization, and after the war in the Polish Army. He participated in the Silesian Uprisings. He became an officer in the Second Department of Polish General Staff (the intelligence section), serving as deputy to the chief of its Office 2, Edmund Charaszkiewicz (1929–39), and as a member of the secret K-7 organization (''Komitet Siedmiu'', "Committee of Seven") that supervised certain covert operations. He was engaged in covert operations from 16 September 1928, including the 1938 annexation of Zaolzie and operations conducted in autumn 1938 in collaboration with Hungary in Carpathian Rus. After the invasion of Poland in September 1939, Ankerstein worked in Section II's Office (''Ekspozytura'') "R" in Romania. He later made his way to London, where he reportedly about 1940 entered the service of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Charaszkiewicz
Edmund Kalikst Eugeniusz Charaszkiewicz (; Poniec, 14 October 1895 – 22 December 1975, London) was a Polish military intelligence officer who specialized in clandestine warfare. Between the World Wars, he helped establish Poland's interbellum borders in conflicts over territory with Poland's neighbours. Also, for a dozen years before World War II, he coordinated Marshal Józef Piłsudski's Promethean movement, aimed at liberating the non-Russian peoples of the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union—an objective that Piłsudski deemed crucial if Poland, sandwiched between Germany and the Soviet Union, were to preserve her just-regained independence. Early career Edmund Charaszkiewicz was born on 14 October 1895 in Punitz (in Polish, Poniec), in the Province of Posen, an area of the German Empire that had been annexed from Poland by Prussia in the Third Partition of Poland (1795). He was the son of Stanisław Charaszkiewicz, a building contractor, and Bronisława, née Rajew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Poland (1918-1939)
The history of Poland spans over a thousand years, from medieval tribes, Christianization and monarchy; through Poland's Golden Age, expansionism and becoming one of the largest European powers; to its collapse and partitions, two world wars, communism, and the restoration of democracy. The roots of Polish history can be traced to ancient times, when the territory of present-day Poland was settled by various tribes including Celts, Scythians, Germanic clans, Sarmatians, Slavs and Balts. However, it was the West Slavic Lechites, the closest ancestors of ethnic Poles, who established permanent settlements in the Polish lands during the Early Middle Ages.. The Lechitic Western Polans, a tribe whose name means "people living in open fields", dominated the region and gave Poland - which lies in the North-Central European Plain - its name. The first ruling dynasty, the Piasts, emerged in the 10th century AD. Duke Mieszko I is considered the ''de facto'' creator of the Polish sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cieszyn Silesia
Cieszyn Silesia, Těšín Silesia or Teschen Silesia ( pl, Śląsk Cieszyński ; cs, Těšínské Slezsko or ; german: Teschener Schlesien or ) is a historical region in south-eastern Silesia, centered on the towns of Cieszyn and Český Těšín and bisected by the Olza River. Since 1920 it has been divided between Poland and Czechoslovakia, and later the Czech Republic. It covers an area of about and has about 810,000 inhabitants, of which (44%) is in Poland, while (56%) is in the Czech Republic. The historical boundaries of the region are roughly the same as those of the former independent Duchy of Teschen/Cieszyn. Currently, over half of Cieszyn Silesia forms one of the euroregions, the Cieszyn Silesia Euroregion, with the rest of it belonging to Euroregion Beskydy. Administrative division From an administrative point of view, the Polish part of Cieszyn Silesia lies within the Silesian Voivodeship and comprises Cieszyn County, the western part of Bielsko Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Nazi Germany, Germany, the United Kingdom, French Third Republic, France, and Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italy. It provided "cession to Germany of the Sudeten German territory" of First Czechoslovak Republic, Czechoslovakia, despite the existence of a 1924 alliance agreement and 1925 military pact between France and the Czechoslovak Republic, for which it is also known as the Munich Betrayal (; ). Most of Europe celebrated the Munich agreement, which was presented as a way to prevent a major war on the continent. The four powers agreed to German occupation of Czechoslovakia, the German annexation of the Czechoslovak borderland areas named the Sudetenland, where more than three million people, mainly Sudeten Germans, ethnic Germans, lived. Adolf Hitler announced that it was his last territorial claim in Northern Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decree On Official Language On Annexed Territory
A decree is a legal proclamation, usually issued by a head of state (such as the president of a republic or a monarch), according to certain procedures (usually established in a constitution). It has the force of law. The particular term used for this concept may vary from country to country. The ''executive orders'' made by the President of the United States, for example, are decrees (although a decree is not exactly an order). Decree by jurisdiction Belgium In Belgium, a decree is a law of a community or regional parliament, e.g. the Flemish Parliament. France The word ''décret'', literally "decree", is an old legal usage in France and is used to refer to executive orders issued by the French President or Prime Minister. Any such order must not violate the French Constitution or Civil Code, and a party has the right to request an order be annulled in the French Council of State. Orders must be ratified by Parliament before they can be modified into legislative Acts. Special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
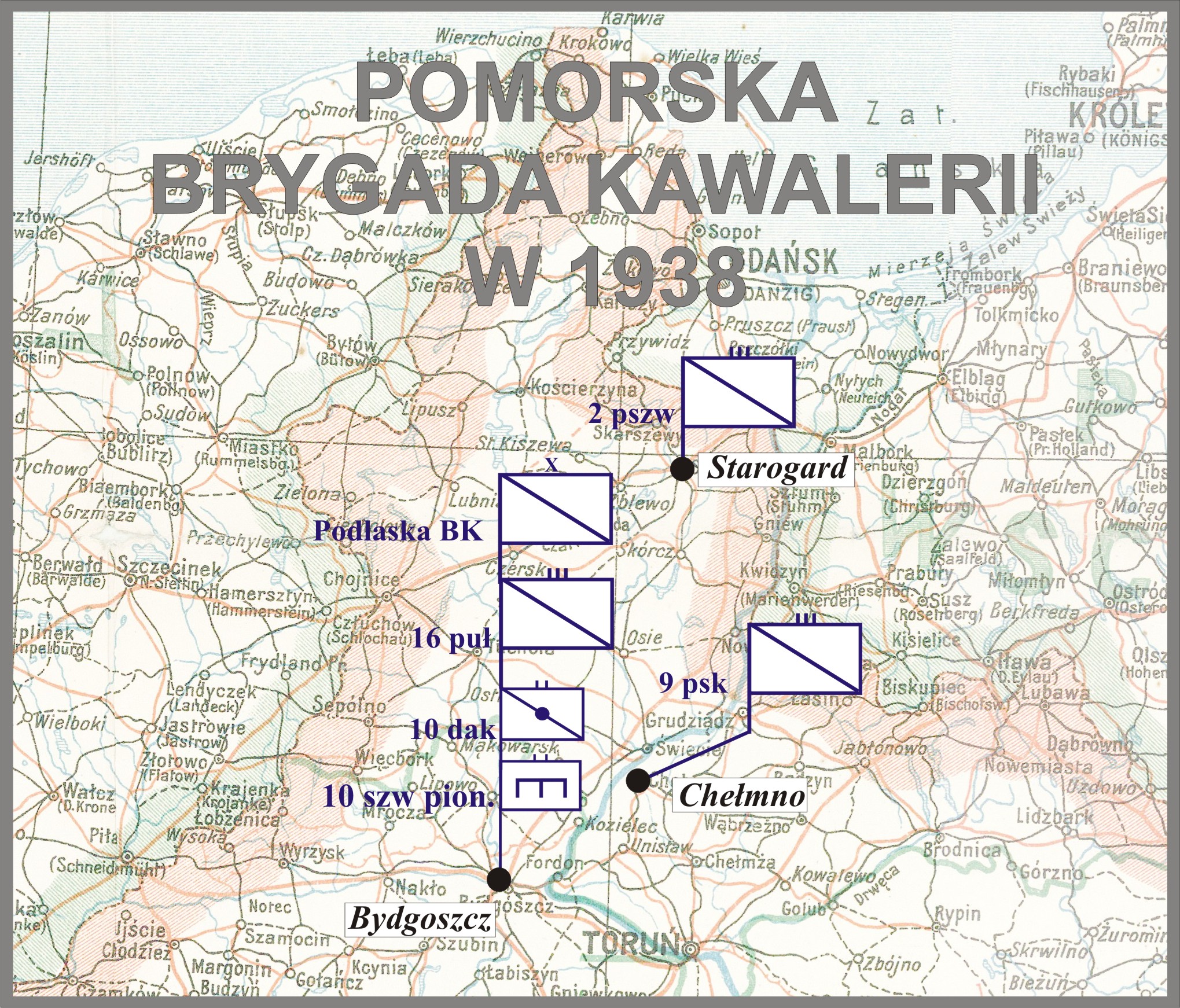
Pomeranian Cavalry Brigade
Pomeranian Cavalry Brigade (Polish: ''Pomorska Brygada Kawalerii'') was a cavalry unit of the Polish Army in the interbellum period. It was created on April 1, 1937 out of the Cavalry Brigade "Bydgoszcz". Its headquarters were stationed in Bydgoszcz and the brigade consisted of these units: * 2nd Rokitno Chevau-légers Regiment, garrisoned in Starogard, * 16th Greater Poland Uhlan Regiment of General Gustaw Orlicz-Dreszer, stationed in Bydgoszcz, * 18th Pomeranian Uhlan Regiment, stationed in Grudziądz, * 8th Mounted Rifles Regiment, stationed in Chełmno, * 11th Mounted Artillery Regiment, stationed in Bydgoszcz, * 10th Pioneers Squadron, stationed in Bydgoszcz, * 8th Communications Squadron, stationed in Bydgoszcz. Polish September Campaign The Brigade, under Colonel Adam Zakrzewski, was part of the Pomorze Army. On September 1, 1939, parts of the 18th Regiment of Pomeranian Uhlans made the legendary charge at Krojanty, during which unit's commandant, Colonel Kazimierz Mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)