Yuchi Ethnic Township on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Yuchi people, also spelled Euchee and Uchee, are a Native American tribe based in
 The term ''Yuchi'' translated to "over there sit/live" or "situated yonder." Their autonym, or name for themselves, Tsoyaha or Coyaha, means "Children of the Sun." Their language is an isolate. The Shawnee called them ''Tahokale,'' and the Cherokee call them ''Aniyutsi.''
The term ''Yuchi'' translated to "over there sit/live" or "situated yonder." Their autonym, or name for themselves, Tsoyaha or Coyaha, means "Children of the Sun." Their language is an isolate. The Shawnee called them ''Tahokale,'' and the Cherokee call them ''Aniyutsi.''
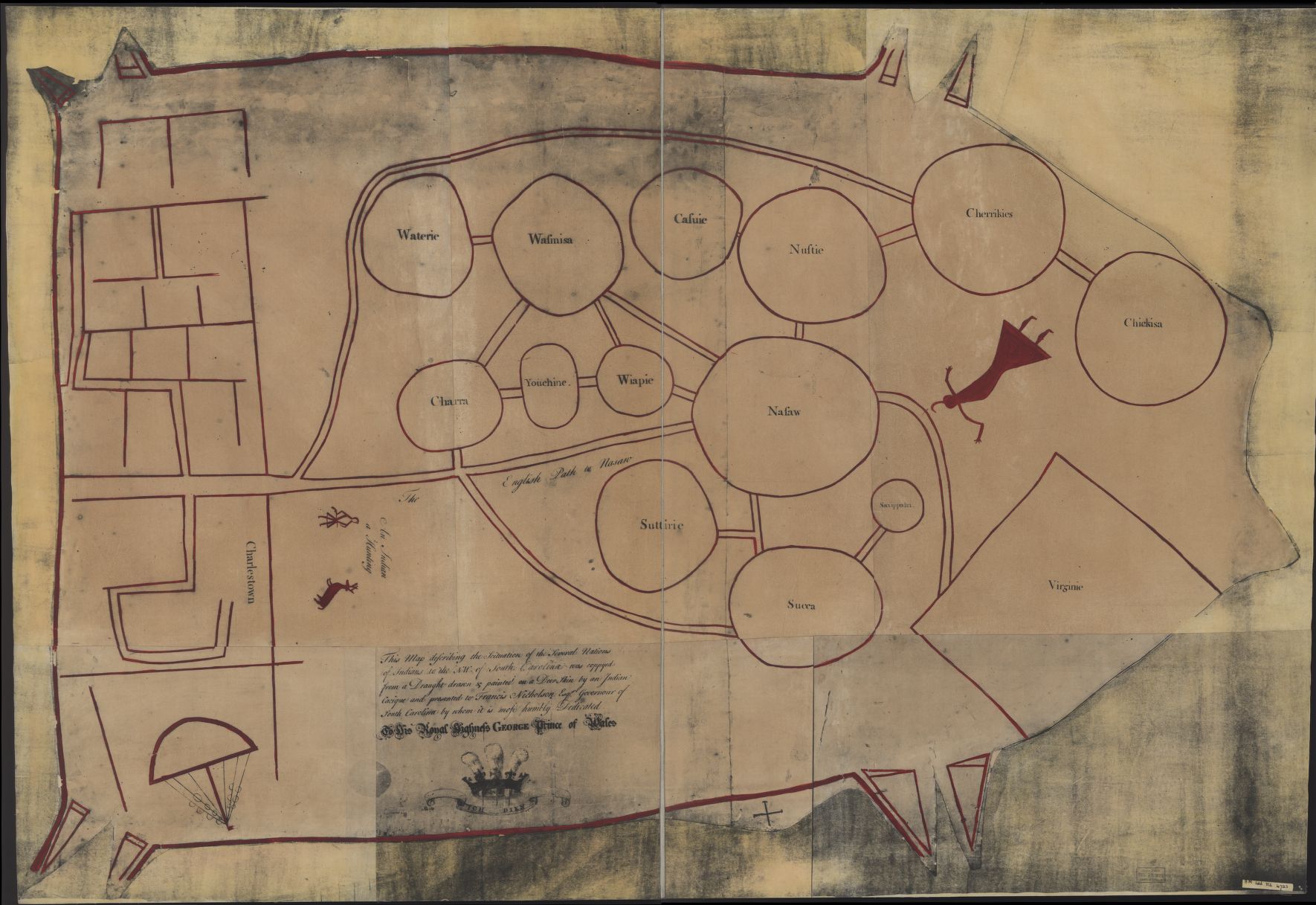 Yuchi towns were later documented in northern Georgia and western South Carolina, where the tribe had migrated to escape pressure from the Cherokee. "Mount Pleasant" was noted as being on the
Yuchi towns were later documented in northern Georgia and western South Carolina, where the tribe had migrated to escape pressure from the Cherokee. "Mount Pleasant" was noted as being on the
Watkinsville, GA: LAMAR Institute Publications, 1990 "Euchee Town" (also called Uche Town), a large settlement on the In the late 18th century, English colonists noted Patsiliga, a settlement on the
In the late 18th century, English colonists noted Patsiliga, a settlement on the
 The Yuchi people are enrolled in federally recognized tribes, particularly the Muscogee (Creek) Nation, who host the Euchee Language Program. In 1990s, the Yuchi Tribal Organization based in Sapulpa, Oklahoma, petitioned the US federal government to gain federal recognition as an independent tribe. In 2000, the
The Yuchi people are enrolled in federally recognized tribes, particularly the Muscogee (Creek) Nation, who host the Euchee Language Program. In 1990s, the Yuchi Tribal Organization based in Sapulpa, Oklahoma, petitioned the US federal government to gain federal recognition as an independent tribe. In 2000, the
 The Yuchi language is a linguistic isolate, not known to be related to any other language. In 2000 the estimated number of fluent Yuchi speakers was 15, but this number dwindled to 7 by 2006.Anderton, Alice, PhD
The Yuchi language is a linguistic isolate, not known to be related to any other language. In 2000 the estimated number of fluent Yuchi speakers was 15, but this number dwindled to 7 by 2006.Anderton, Alice, PhD
"Status of Indian Languages in Oklahoma"
Intertribal Wordpath Society, Ahalenia.com, 2006-2009 (retrieved 7 Feb 2009) According to a 2011 documentary on the Yuchi language, the number of first-language speakers has declined to five. Young Yuchi people have learned the language in recent years and are continuing to do so. Yuchi language classes are being taught in Sapulpa, Oklahoma, in an effort led by Richard Grounds and the Euchee Language Project. As of 2011, the Administration for Native Americans awarded the Yuchi tribe a grant for the years 2011 to 2014 in an effort to provide after-school programs for the youth to improve proficiency in their native language and develop a young generation of speakers. The Yuchi people and language are featured in a chapter in Mark Abley's ''Spoken Here: Travels Among Threatened Languages'', a book on endangered languages.
Ethnology of the Yuchi Indians
(reprint)'', University of Nebraska Press, 2004.
Daniel Elliott, ''Ye Pleasant Mount: 1989&1990 Excavations.''
The LAMAR Institute, University of Georgia, 1991.
The Euchee Language Project
''Memoirs of Jeremiah Curtin in the Indian Territory''
pp. 327, 333-335. 19th century ethnographer's account of learning Yuchi language in 1883 in a Yuchi settlement 55 miles from
Uchee Path
historical marker
Joseph Mahan Collection
Columbus State University Archives {{authority control Native American history of Tennessee Native American tribes in Tennessee Native American tribes in Alabama Native American tribes in Georgia (U.S. state) Native American tribes in Oklahoma Unrecognized tribes in the United States
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
.
In the 16th century, Yuchi people lived in the eastern Tennessee River valley in Tennessee. In the late 17th century, they moved south to Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina, settling near the Muscogee Creek people.Jackson 416 Some also migrated to the panhandle of Florida. After suffering many fatalities from epidemic disease and warfare in the 18th century, several surviving Yuchi bands were removed to Indian Territory in the 1830s, together with their allies the Muscogee Creek.
Today, the Yuchi live primarily in the northeastern Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
area, where many are enrolled citizens of the federally recognized Muscogee (Creek) Nation. They maintain a distinct cultural identity, and some speak the Yuchi language, a linguistic isolate.
Name
 The term ''Yuchi'' translated to "over there sit/live" or "situated yonder." Their autonym, or name for themselves, Tsoyaha or Coyaha, means "Children of the Sun." Their language is an isolate. The Shawnee called them ''Tahokale,'' and the Cherokee call them ''Aniyutsi.''
The term ''Yuchi'' translated to "over there sit/live" or "situated yonder." Their autonym, or name for themselves, Tsoyaha or Coyaha, means "Children of the Sun." Their language is an isolate. The Shawnee called them ''Tahokale,'' and the Cherokee call them ''Aniyutsi.''
History
At the time of first European contact, the Yuchi people lived in what is now eastern Tennessee. In 1541, Spanish explorerHernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire ...
described them as a powerful tribe known as the ''Uchi,'' that were also associated with the Chisca tribe.
Both historical and archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
evidence exists documenting several Yuchi towns of the 18th century. Among these was Chestowee in present-day Bradley County, Tennessee. In 1714, instigated by two English fur trader
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mos ...
s from South Carolina, the Cherokee attacked and destroyed Chestowee. The Cherokee were prepared to carry their attacks further to Yuchi settlements south on the Savannah River
The Savannah River is a major river in the southeastern United States, forming most of the border between the states of South Carolina and Georgia. Two tributaries of the Savannah, the Tugaloo River and the Chattooga River, form the norther ...
, but the colonial government of South Carolina did not condone this. The Cherokee destruction of Chestowee marked their emergence as a major power in the Southeast.
 Yuchi towns were later documented in northern Georgia and western South Carolina, where the tribe had migrated to escape pressure from the Cherokee. "Mount Pleasant" was noted as being on the
Yuchi towns were later documented in northern Georgia and western South Carolina, where the tribe had migrated to escape pressure from the Cherokee. "Mount Pleasant" was noted as being on the Savannah River
The Savannah River is a major river in the southeastern United States, forming most of the border between the states of South Carolina and Georgia. Two tributaries of the Savannah, the Tugaloo River and the Chattooga River, form the norther ...
in present-day Effingham County, Georgia
Effingham County ( ) is a county located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2010 census, the population was 52,250. The seat is Springfield.
Effingham County is included in the Savannah metropolitan area.
In 200 ...
, from about 1722 to about 1750. To take advantage of trade, the British established a trading post and small military garrison there, which they called Mount Pleasant.Daniel T. Elliott and Rita Folse Elliott, "Mount Pleasant. An Eighteenth-Century Yuchi Indian Town, British Trader Outpost, and Military Garrison in Georgia"Watkinsville, GA: LAMAR Institute Publications, 1990 "Euchee Town" (also called Uche Town), a large settlement on the
Chattahoochee River
The Chattahoochee River forms the southern half of the Alabama and Georgia border, as well as a portion of the Florida - Georgia border. It is a tributary of the Apalachicola River, a relatively short river formed by the confluence of the Chatta ...
, was documented from the middle to late 18th century. It was located near Euchee (or Uche) Creek, about ten miles downriver from the Muscogee Creek settlement of ''Coweta'' Old Town. The naturalist William Bartram
William Bartram (April 20, 1739 – July 22, 1823) was an American botanist, ornithologist, natural historian and explorer. Bartram was the author of an acclaimed book, now known by the shortened title ''Bartram's Travels'', which chronicled ...
visited Euchee Town in 1778. In his letters he ranked it as the largest and most compact Indian town he had ever encountered, with large, well-built houses.John T. Ellisor, ''The Second Creek War'', p. 31 US Indian agent Benjamin Hawkins
Benjamin Hawkins (August 15, 1754June 6, 1816) was an American planter, statesman and a U.S. Indian agent He was a delegate to the Continental Congress and a United States Senator from North Carolina, having grown up among the planter elite. ...
also visited the town and described the Yuchi as "more orderly and industrious" than the other tribes of the Muscogee Creek Confederacy. The Yuchi began to move on, some into the Florida panhandle.
 In the late 18th century, English colonists noted Patsiliga, a settlement on the
In the late 18th century, English colonists noted Patsiliga, a settlement on the Flint River
The Flint River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 15, 2011 river in the U.S. state of Georgia. The river drains of western Georgia, flowing south from the u ...
. Other Yuchi settlements may have been those villages noted on the Oconee River near Uchee Creek in Wilkinson County, Georgia, and on Brier Creek in Burke
Burke is an Anglo-Norman Irish surname, deriving from the ancient Anglo-Norman and Hiberno-Norman noble dynasty, the House of Burgh. In Ireland, the descendants of William de Burgh (–1206) had the surname ''de Burgh'' which was gaelicised ...
or Screven counties, also in Georgia. A Yuchi town was known to exist from 1746 to 1751 at the site of present-day Silver Bluff in Aiken County, South Carolina, which developed in the later 18th century.
During the 18th century, the Yuchi established an alliance with white settlers in the Southern Colonies, trading deerskins and Indian slaves
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
with them. The Yuchi population plummeted during the 18th century due to Eurasian infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
, to which they had no immunity, and to war with the Cherokee, who were moving into their territory. After the American Revolution, Yuchi people maintained close relations with the Muscogee Creek Confederacy, into which federally recognized members were later absorbed. Some Yuchi migrated south to Florida along with the Muscogee, where they became part of the newly formed Seminole people.Jackson 415
During the Creek War
The Creek War (1813–1814), also known as the Red Stick War and the Creek Civil War, was a regional war between opposing Indigenous American Creek factions, European empires and the United States, taking place largely in modern-day Alabama ...
of 1813–1814, which overlapped the War of 1812, many Yuchi joined the Red Sticks
Red Sticks (also Redsticks, Batons Rouges, or Red Clubs), the name deriving from the red-painted war clubs of some Native American Creeks—refers to an early 19th-century traditionalist faction of these people in the American Southeast. Made u ...
party, traditionalists opposed to the Muscogee people of the Lower Towns, who had adopted aspects of European-American culture. Euchee Town decayed. The Yuchi tribe became one of the poorest of the Muscogee communities, at the same time gaining a bad reputation. The archaeological site of the town, designated a National Historic Landmark, is within the boundaries of present-day Fort Benning, Georgia.
In the 1830s, the US government forcibly removed the Yuchi, along with the Muscogee, from Alabama and Georgia to Indian Territory (present day Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
), west of the Mississippi River. The Yuchi settled in the north and northwestern parts of the Muscogee Nation. Three tribal towns which the Yuchi established there in the 19th century continue today: Duck Creek, Polecat, and Sand Creek.
Second Seminole War
Prior to 1818 some Yuchi moved to near Lake Miccosukee in northern Florida, settling near Muscogee refugees. Andrew Jackson's invasion of the area during the First Seminole War resulted in the Yuchi moving to eastern Florida. They fought alongside the Seminole during theSecond Seminole War
The Second Seminole War, also known as the Florida War, was a conflict from 1835 to 1842 in Florida between the United States and groups collectively known as Seminoles, consisting of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans and ...
under their chief Uchee Billy Uchee Billy or Yuchi Billy (unknown–November 25, 1837, St. Augustine, Florida) was a chief of a Yuchi band in Florida during the first half of the 19th century. Uchee Billy's band was living near Lake Miccosukee when Andrew Jackson invaded Spanis ...
. He was captured in 1837 with his brother Jack by General Joseph Marion Hernandez
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
, who also captured Osceola. The two leaders were imprisoned for years in Fort Marion in St. Augustine, Florida
St. Augustine ( ; es, San Agustín ) is a city in the Southeastern United States and the county seat of St. Johns County on the Atlantic coast of northeastern Florida. Founded in 1565 by Spanish explorers, it is the oldest continuously inhabit ...
.
From 1890 to 1895, the Dawes Commission considered the Yuchi in Indian Territory to be an autonomous tribe. It registered tribal members preparatory to allotment of communal tribal lands in Indian Territory to individual households of members. Some 1200 tribal members were registered in those years. The Dawes Commission later decided to legally classify the Yuchi as part of the Muscogee (Creek) Nation, in an effort to simplify the process of land allotment. But this decision interrupted the autonomy of the people and their record of historical continuity as a recognized tribe.
Current status
 The Yuchi people are enrolled in federally recognized tribes, particularly the Muscogee (Creek) Nation, who host the Euchee Language Program. In 1990s, the Yuchi Tribal Organization based in Sapulpa, Oklahoma, petitioned the US federal government to gain federal recognition as an independent tribe. In 2000, the
The Yuchi people are enrolled in federally recognized tribes, particularly the Muscogee (Creek) Nation, who host the Euchee Language Program. In 1990s, the Yuchi Tribal Organization based in Sapulpa, Oklahoma, petitioned the US federal government to gain federal recognition as an independent tribe. In 2000, the Bureau of Indian Affairs
The Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA), also known as Indian Affairs (IA), is a United States federal agency within the Department of the Interior. It is responsible for implementing federal laws and policies related to American Indians and A ...
denied the petition.
As of 1997, the Yuchi tribe had a formal enrollment of 249 members. Other Yuchi descendants are already enrolled in other tribes, such as the Muscogee. Most Yuchi are of multi-tribal descent; some are citizens of other tribes, such as the Shawnee.
The Euchee Tribe of Indians, while not recognized, has their headquarters in Sapulpa, Oklahoma. Their tribal chairmen are co-chairs Felix Brown Jr. and Clinton Sago.
James Anaya, United Nations (UN) Special Rapporteur on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, visited the Yuchi community. Tracie Revis (Yuchi) gave a speech defining the importance of federal recognition. He acknowledged the declaration by the UN on the Rights of Indigenous People that states "that we have the right of self-determination and by virtue of that right- we may freely determine our political status and freely pursue our economic, social and cultural development."
An estimated 2,000 persons are ethnically Yuchi. They are descendants of some 1,100 persons recorded by the Indian Claims Commission in 1950, which was settling compensation claims dating from allotments.
The Yuchi continue their important ceremonies, such as the Green Corn Ceremony of late summer. They maintain three ceremonial grounds in Oklahoma. Some members belong to the Native American Church and Methodist congregations.
In 2008, the Yuchi tribe received a grant from President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
's administration for a Native Americans Comprehensive Community Survey and Plan. The grant was used to developed the Tribal History Project, which began in October 2010.
The Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a ...
acknowledged the importance of the Yuchi's distinct culture and language and approached the Yuchi in order to collect genetic data (DNA). The Yuchi tribe declined to participate in the Project due to cultural conflict and uncertainty over the uses of government ownership of tribal DNA.
Yuchi language
 The Yuchi language is a linguistic isolate, not known to be related to any other language. In 2000 the estimated number of fluent Yuchi speakers was 15, but this number dwindled to 7 by 2006.Anderton, Alice, PhD
The Yuchi language is a linguistic isolate, not known to be related to any other language. In 2000 the estimated number of fluent Yuchi speakers was 15, but this number dwindled to 7 by 2006.Anderton, Alice, PhD"Status of Indian Languages in Oklahoma"
Intertribal Wordpath Society, Ahalenia.com, 2006-2009 (retrieved 7 Feb 2009) According to a 2011 documentary on the Yuchi language, the number of first-language speakers has declined to five. Young Yuchi people have learned the language in recent years and are continuing to do so. Yuchi language classes are being taught in Sapulpa, Oklahoma, in an effort led by Richard Grounds and the Euchee Language Project. As of 2011, the Administration for Native Americans awarded the Yuchi tribe a grant for the years 2011 to 2014 in an effort to provide after-school programs for the youth to improve proficiency in their native language and develop a young generation of speakers. The Yuchi people and language are featured in a chapter in Mark Abley's ''Spoken Here: Travels Among Threatened Languages'', a book on endangered languages.
Notable Yuchi people
*Uchee Billy Uchee Billy or Yuchi Billy (unknown–November 25, 1837, St. Augustine, Florida) was a chief of a Yuchi band in Florida during the first half of the 19th century. Uchee Billy's band was living near Lake Miccosukee when Andrew Jackson invaded Spanis ...
(died 1837), warrior and chief
* Sam Story, 19th-century chief
*Richard Ray Whitman
Richard Ray Whitman (born 1949) is a Yuchi-Muscogee multidisciplinary visual artist, poet, and actor. He is enrolled in the Muscogee Nation and lives in Oklahoma.Lester, 619Lippard, 216
Early life and education
Whitman was born in Claremore, Okl ...
(born 1949), artist, poet, actor
See also
*Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands
Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the nor ...
* Yuchi language
References
Citations
Bibliography
*Jackson, Jason Baird. "Yuchi." ''Handbook of North American Indians: Southeast.'' Eds. William C. Sturtevant and Raymond D. Fogelson. Volume 14. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution, 2004. .Further reading
* Mark Abley, ''Spoken Here: Travels Among Threatened Languages'', Houghton Mifflin, 2003. * Jason Jackson, ''Yuchi Ceremonial Life: Performance, Meaning, and Tradition in a Contemporary American Indian Community'', University of Nebraska Press, 2003. * Jason Baird Jackson (ed.), ''Yuchi Indian Histories Before the Removal Era.'' Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press, 2012. * Frank Speck,Ethnology of the Yuchi Indians
(reprint)'', University of Nebraska Press, 2004.
Daniel Elliott, ''Ye Pleasant Mount: 1989&1990 Excavations.''
The LAMAR Institute, University of Georgia, 1991.
External links
The Euchee Language Project
''Memoirs of Jeremiah Curtin in the Indian Territory''
pp. 327, 333-335. 19th century ethnographer's account of learning Yuchi language in 1883 in a Yuchi settlement 55 miles from
Muskogee, Oklahoma
Muskogee () is the thirteenth-largest city in Oklahoma and the county seat of Muskogee County. Home to Bacone College, it lies approximately southeast of Tulsa. The population of the city was 36,878 as of the 2020 census, a 6.0 percent decrease ...
. Electronic record maintained by Library of Congress, accessed January 15, 2007.
Uchee Path
historical marker
Joseph Mahan Collection
Columbus State University Archives {{authority control Native American history of Tennessee Native American tribes in Tennessee Native American tribes in Alabama Native American tribes in Georgia (U.S. state) Native American tribes in Oklahoma Unrecognized tribes in the United States