|
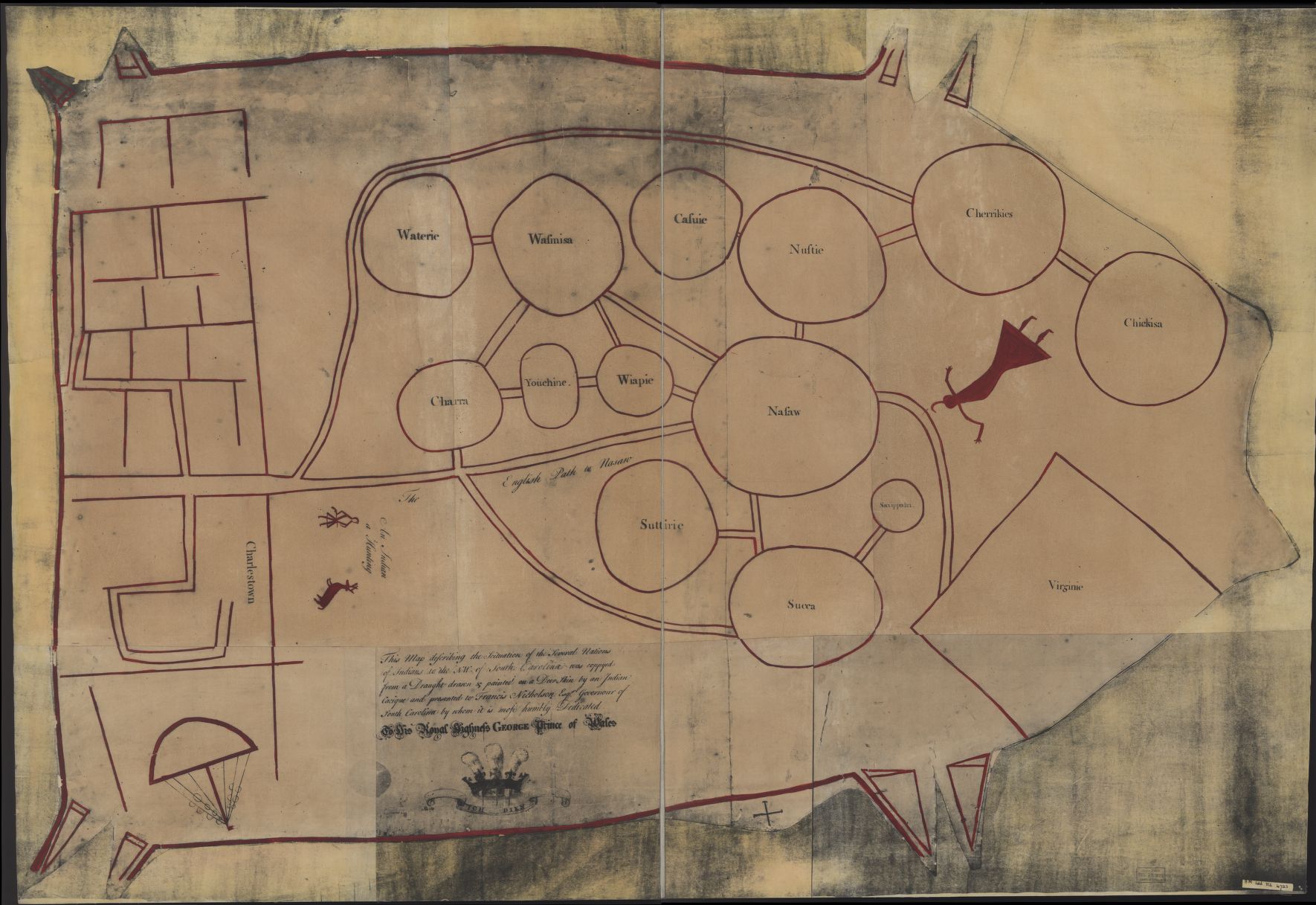
Benjamin Hawkins
Benjamin Hawkins (August 15, 1754June 6, 1816) was an American planter, statesman and a U.S. Indian agent He was a delegate to the Continental Congress and a United States Senator from North Carolina, having grown up among the planter elite. Appointed by George Washington in 1796 as one of three commissioners to the Creeks, in 1801 President Jefferson named him "principal agent for Indian affairs south of the Ohio iver, and was principal Indian agent to the Creek Indians. Hawkins established the Creek Agency and his plantation near present-day Roberta, Georgia, in what became Crawford County. He learned the Muscogee language, and had a Creek woman, Lavinia Downs, as common-law wife, who, in the Creek's matrilineal society, provided an entry into that world. He had seven children with her, although he resisted Creek pressure to marry her until near the end of his life. He wrote extensively about the Creek and other Southeast tribes: the Choctaw, Cherokee and Chickasaw. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and South Carolina to the south, and Tennessee to the west. In the 2020 census, the state had a population of 10,439,388. Raleigh is the state's capital and Charlotte is its largest city. The Charlotte metropolitan area, with a population of 2,595,027 in 2020, is the most-populous metropolitan area in North Carolina, the 21st-most populous in the United States, and the largest banking center in the nation after New York City. The Raleigh-Durham-Cary combined statistical area is the second-largest metropolitan area in the state and 32nd-most populous in the United States, with a population of 2,043,867 in 2020, and is home to the largest research park in the United States, Research Triangle Park. The earliest evidence of human occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was previously the nation's second vice president under John Adams and the first United States secretary of state under George Washington. The principal author of the Declaration of Independence, Jefferson was a proponent of democracy, republicanism, and individual rights, motivating American colonists to break from the Kingdom of Great Britain and form a new nation. He produced formative documents and decisions at state, national, and international levels. During the American Revolution, Jefferson represented Virginia in the Continental Congress that adopted the Declaration of Independence. As a Virginia legislator, he drafted a state law for religious freedom. He served as the second Governor of Virginia from 1779 to 1781, during the Revolutionary War. In 178 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the '' Organisation internationale de la Francopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of the Continental Army, Washington led the Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces to victory in the American Revolutionary War and served as the president of the Constitutional Convention (United States), Constitutional Convention of 1787, which created the Constitution of the United States and the American federal government. Washington has been called the "Father of the Nation, Father of his Country" for his manifold leadership in the formative days of the country. Washington's first public office was serving as the official Surveying, surveyor of Culpeper County, Virginia, from 1749 to 1750. Subsequently, he received his first military training (as well as a command with the Virginia Regiment) d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granville County, North Carolina
Granville County is a county located on the northern border of the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 60,992. Its county seat is Oxford. Granville County encompasses Oxford, NC Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the Raleigh- Durham-Chapel Hill, NC Combined Statistical Area. The county has access to Kerr Lake and Falls Lake and is part of the Roanoke, Tar and Neuse River watersheds. History The county was formed by English colonists in 1746 from Edgecombe County. It was named for John Carteret, 2nd Earl Granville, who as heir to one of the eight original Lords Proprietors of the Province of Carolina, claimed one eighth of the land granted in the charter of 1665. The claim was established as consisting of approximately the northern half of North Carolina, and this territory came to be known as the Granville District, also known as Oxford. In 1752, parts of Granville, Bladen, and Johnston counties were com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantations In The American South
A plantation complex in the Southern United States is the built environment (or complex) that was common on agricultural plantations in the American South from the 17th into the 20th century. The complex included everything from the main residence down to the pens for livestock. Until the abolition of slavery, such plantations were generally self-sufficient settlements that relied on the forced labor of enslaved people. Plantations are an important aspect of the history of the Southern United States, particularly the antebellum era (pre-American Civil War). The mild temperate climate, plentiful rainfall, and fertile soils of the southeastern United States allowed the flourishing of large plantations, where large numbers of enslaved Africans or African Americans were held captive and forced to produce crops to create wealth for a white elite. Today, as was also true in the past, there is a wide range of opinion as to what differentiated a plantation from a farm. Typically, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philemon Hawkins II
Philemon Hawkins II (September 28, 1717 September 10, 1801) was an American planter, military officer and politician who served in the North Carolina militia during the Revolutionary War. Early life and political career Philemon Hawkins II was born on September 28, 1717 in Charles City County, Colony of Virginia. His parents were Philemon Hawkins I and Anne Eleanor Howard. He was initially known as Philemon Hawkins, Jr. His parents were from Devonshire in England, and settled in the Colony of Virginia in 1717. His father reportedly descended from Sir John Hawkins, the English naval commander, and died in Gloucester County, Virginia in 1725. After his father's death, Philemon Hawkins II moved to Bute County Province of North Carolina in 1735, along with his mother and two siblings, John and Ann. In 1743 he married Delia Martin, daughter of Colonel Zachariah Martin of Mecklenburg County, Virginia. He filled many public positions in Bute County and became the wealthiest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Slavery In Georgia
Slavery in Georgia is known to have been practiced by European colonists. During the colonial era, the practice of slavery in Georgia soon became surpassed by industrial-scale plantation slavery. The colony of the Province of Georgia under James Oglethorpe banned slavery in 1735, the only one of the thirteen colonies to have done so. However, it was legalized by royal decree in 1751, in part due to George Whitefield's support for the institution of slavery. Pre-colonial period Native Americans did not commonly enslave members of their own and other tribes before Europeans arrived but this practice became common after European intrusion, continuing into the 1800s; slaves might or might not be adopted eventually, especially if enslaved as children; and the enslavement was rarely if ever hereditary. Native American slaves were most often captives from wars; captives bartered from other tribes, sometimes at great distances; or children sold by their parents during famines. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups Of Africa
The ethnic groups of Africa number in the thousands, with each population generally having its own language (or dialect of a language) and culture. The ethnolinguistic groups include various Afroasiatic, Khoisan, Niger-Congo, and Nilo-Saharan populations. The official population count of the various ethnic groups in Africa is highly uncertain, both due to limited infrastructure to perform censuses and due to the rapid population growth. There have also been accusations of deliberate misreporting in order to give selected ethnicities numerical superiority (as in the case of Nigeria's Hausa, Fulani, Yoruba, and Igbo peoples). A 2009 genetic clustering study, which genotyped 1327 polymorphic markers in various African populations, identified six ancestral clusters. The clustering corresponded closely with ethnicity, culture and language. A 2018 whole genome sequencing study of the world's populations observed similar clusters among the populations in Africa. At K=9, distinct anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as a member of the Muskogean language family. In the present day, they are organized as the federally recognized Chickasaw Nation. Chickasaw people have a migration story in which they moved from a land west of the Mississippi River, where they settled mostly in present-day northeast Mississippi, northwest Alabama, and into Lawrence County, Tennessee. They had interaction with French, English, and Spanish colonists during the colonial period. The United States considered the Chickasaw one of the Five Civilized Tribes of the Southeast, as they adopted numerous practices of European Americans. Resisting European-American settlers encroaching on their territory, they were forced by the U.S. government to sell their traditional lands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, and northeastern Alabama. The Cherokee language is part of the Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian language group. In the 19th century, James Mooney, an early American Ethnography, ethnographer, recorded one oral tradition that told of the Tribe (Native American), tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian peoples have been based. However, anthropologist Thomas R. Whyte, writing in 2007, dated the split among the peoples as occurring earlier. He believes that the ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes: the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, and Jena Band of Choctaw Indians in Louisiana. The Choctaw were first noted by Europeans in French written records of 1675. Their mother mound is Nanih Waiya, a great earthwork platform mound located in central-east Mississippi. Early Spanish explorers of the mid-16th century in the Southeast encountered ancestral Mississippian culture villages and chiefs. The Choctaw coalesced as a people in the 17th century and developed at least three distinct political and geographical divisions: eastern, western, and southern. These different groups sometimes created distinct, independent alliances with nearby European pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |