Yreka Western Railroad on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Yreka Western Railroad Company is a
The Yreka Western Railroad Company is a
 The Yreka Western Railroad Company is a
The Yreka Western Railroad Company is a shortline railroad
:''Short Line is also one of the four railroads in the American version of the popular board game Monopoly, named after the Shore Fast Line, an interurban streetcar line.''
A shortline railroad is a small or mid-sized railroad company that opera ...
operating freight
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including transp ...
trains between the Union Pacific Railroad
The Union Pacific Railroad , legally Union Pacific Railroad Company and often called simply Union Pacific, is a freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Paci ...
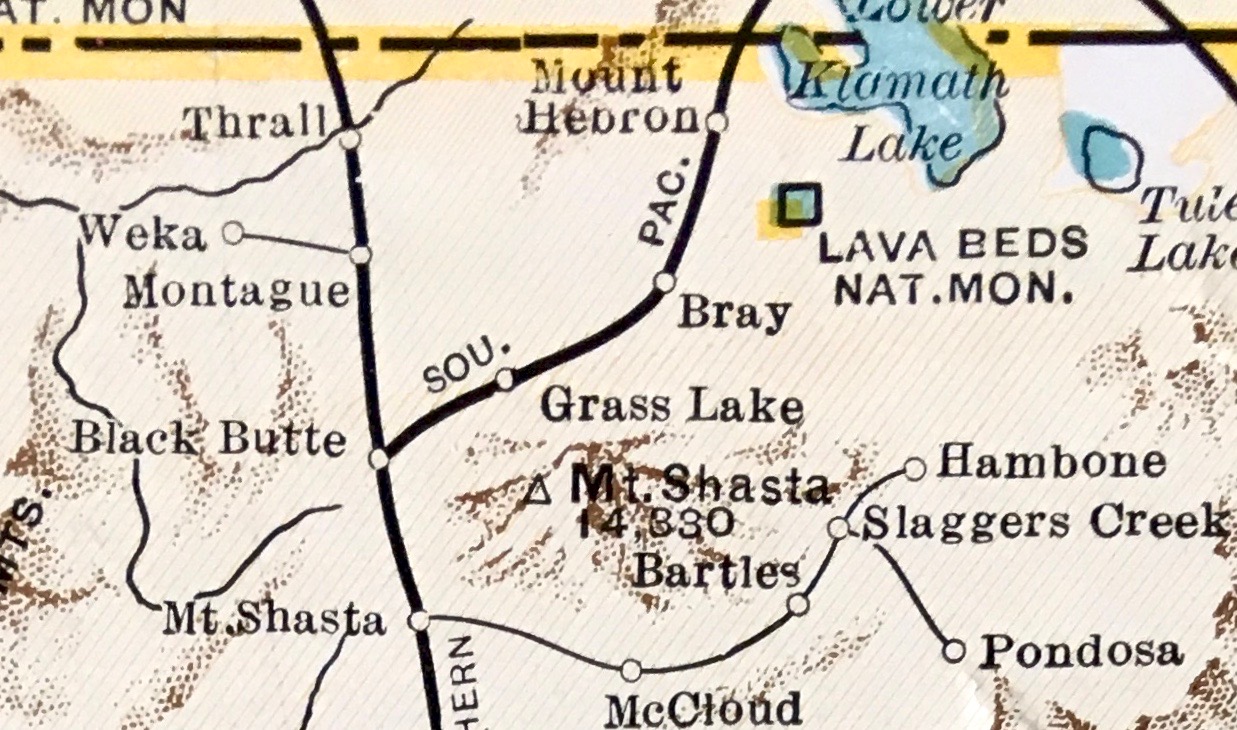
interchange at Montague and the City of Yreka, California
Yreka ( ) is the county seat of Siskiyou County, California, United States, near the Shasta River; the city has an area of about , most of it land. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 7,807, reflecting a meager increase fro ...
. Railmark Holdings
Railmark Holdings, Inc. is an American rail industry holding company whose subsidiaries provide railroad services in railroad operations, track construction and maintenance, rail freight logistics, rail development, and railroad mechanical service ...
acquired the Yreka Western Railroad in 2017.
The Yreka Railroad Company was incorporated in May 1888, with a capital stock of $100,000, and opened in January 1889, connecting Yreka to the Southern Pacific Company
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
lessor Central Pacific Railroad
The Central Pacific Railroad (CPRR) was a rail company chartered by Pacific Railroad Acts, U.S. Congress in 1862 to build a railroad eastwards from Sacramento, California, to complete the western part of the "First transcontinental railroad" in N ...
(ex-California and Oregon Railroad
The Oregon and California Railroad was formed from the Oregon Central Railroad when it was the first to operate a stretch south of Portland in 1869. This qualified the railroad for land grants in California, whereupon the name of the railroad s ...
). The decision to build the Yreka Railroad was due in part to the Southern Pacific's decision to bypass Yreka in favor of a shorter, and more level route through the Shasta Valley and the city of Montague. Not to be left without a rail connection, the citizens of Yreka formed their own railroad. The railroad hauled passengers and local freight. In August 1933, the railroad was re-incorporated as the Yreka Western Railroad Company. The railroad was acquired by Willis Kyle in 1953 who eventually formed the Kyle Railways empire. Eventually, the Union Pacific Railroad
The Union Pacific Railroad , legally Union Pacific Railroad Company and often called simply Union Pacific, is a freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Paci ...
acquired the SP connection at Montague in 1995. In 1999 Kyle Railways sold the Yreka Western Railroad to the Rocky Mountain Railway and Mining Museum of Denver Colorado, who in turn, sold the company to Railmark Holdings, Inc. in December 2016.
Operations
The railroad is an active freight railroad offering direct rail services to the customers on its line, as well as rail logistics and rail transloading services to industrial customers in the northern California and southern Oregon area who are not direct served by rail. The Yreka Western performs mechanical services to freight railcars. Under Railmark's ownership and operation the railroad does not provide excursion passenger rail services. In recent years before 2016, the railroad was operated by The Rocky Mountain Railway and Mining Museum of Denver, Colorado and had provided both freight service and passenger train excursions. The freight traffic on the Yreka Western Railroad is primarily wood chips, forest products, propane, and machinery and bulk commodities. The railroad had provided excursion trains pulled by steam and diesel locomotives from the 1950s until 2007. In 1986 the YW started operating a steam passenger train excursion known as the "Blue Goose" between Yreka and Montague. The railroad offered scenic views ofMount Shasta
Mount Shasta ( Shasta: ''Waka-nunee-Tuki-wuki''; Karuk: ''Úytaahkoo'') is a potentially active volcano at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California. At an elevation of , it is the second-highest peak in the Cascades ...
, the Shasta Valley and the Siskiyou Mountains
The Siskiyou Mountains are a coastal subrange of the Klamath Mountains, and located in northwestern California and southwestern Oregon in the United States. They extend in an arc for approximately from east of Crescent City, California, northea ...
. The trip took about one hour in either direction, with a 60 layover in Montague for lunch. While passengers explored and ate in Montague, the crew took the train to perform a runaround move so the locomotive would pull the train back to Yreka.
The most famous locomotive to run on the line is 2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wheel ...
Baldwin 90 ton logging mikado #19. #19 is nicknamed "Pancho" due to its time spent in Mexico in the 1920s and possible squabble with the Mexican revolutionary Pancho Villa
Francisco "Pancho" Villa (,"Villa"
''Collins English Dictionary''. ; ;
. #19 has starred in many movies, the two most famous being " Emperor of the North" and " Stand By Me". The locomotive was built in April 1915 by the Baldwin for the Caddo & Choctaw River Lumber Company in Arkansas. She served there until being sent to Mexico in 1920 where she is believed to have been converted to oil. In 1924 she was purchased by the ''Collins English Dictionary''. ; ;
McCloud River Railroad
The McCloud Railway was a class III railroad operated around Mount Shasta, California. It began operations on July 1, 1992, when it took over operations from the McCloud River Railroad. The MCR was Incorporation (business), incorporated on April ...
. She served many years there hauling log trains until being sold to the Yreka Western Railroad in 1953. On September 19, 2016, it was announced that #19 would be up for sale in an upcoming auction and on October 6, 2016, was purchased by the Age of Steam Roundhouse
The Age of Steam Roundhouse Museum, Sugarcreek, Ohio, United States, is a museum roundhouse housing steam and diesel locomotives, passenger cars and other railroad equipment.
History
The roundhouse was built by Jerry Joe Jacobson, former CEO of ...
, and is currently being restored in her Emperor of the North paint scheme.
Other locomotives include an SW8 #21 (Former Southern Pacific
The Southern Pacific (or Espee from the railroad initials- SP) was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the ...
#1115). #21 is unique because it has dynamic brakes, not usually found on switching locomotives.
See also
*List of heritage railroads in the United States
This is a list of heritage railroads in the United States. There are currently no such railroads in the states of Mississippi or North Dakota.
Heritage railroads by state
Alabama
* Heart of Dixie Railroad Museum, Shelby & Southern Railroad and ...
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Yreka Western Railroad Heritage railroads in California Transportation in Siskiyou County, California Railway companies established in 1933 1933 establishments in California Tourist attractions in Siskiyou County, California American companies established in 1933