Yellow Fever Epidemic Of 1855 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Yellow fever is a viral

 Yellow fever virus is mainly transmitted through the bite of the yellow fever mosquito ''Aedes aegypti'', but other mostly ''
Yellow fever virus is mainly transmitted through the bite of the yellow fever mosquito ''Aedes aegypti'', but other mostly ''


 Control of the yellow fever mosquito ''A. aegypti'' is of major importance, especially because the same mosquito can also transmit dengue fever and
Control of the yellow fever mosquito ''A. aegypti'' is of major importance, especially because the same mosquito can also transmit dengue fever and
 An estimated 90% of yellow fever infections occur on the African continent. In 2016, a large outbreak originated in Angola and spread to neighboring countries before being contained by a massive vaccination campaign. In March and April 2016, 11 imported cases of the Angola genotype in unvaccinated Chinese nationals were reported in China, the first appearance of the disease in Asia in recorded history.
An estimated 90% of yellow fever infections occur on the African continent. In 2016, a large outbreak originated in Angola and spread to neighboring countries before being contained by a massive vaccination campaign. In March and April 2016, 11 imported cases of the Angola genotype in unvaccinated Chinese nationals were reported in China, the first appearance of the disease in Asia in recorded history.
 In South America, two genotypes have been identified (South American genotypes I and II). Based on phylogenetic analysis these two genotypes appear to have originated in West Africa and were first introduced into Brazil. The date of introduction of the predecessor African genotype which gave rise to the South American genotypes appears to be 1822 (95% confidence interval 1701 to 1911). The historical record shows an outbreak of yellow fever occurred in Recife, Brazil, between 1685 and 1690. The disease seems to have disappeared, with the next outbreak occurring in 1849. It was likely introduced with the trafficking of slaves through the
In South America, two genotypes have been identified (South American genotypes I and II). Based on phylogenetic analysis these two genotypes appear to have originated in West Africa and were first introduced into Brazil. The date of introduction of the predecessor African genotype which gave rise to the South American genotypes appears to be 1822 (95% confidence interval 1701 to 1911). The historical record shows an outbreak of yellow fever occurred in Recife, Brazil, between 1685 and 1690. The disease seems to have disappeared, with the next outbreak occurring in 1849. It was likely introduced with the trafficking of slaves through the
(Mitchell's account of the Yellow Fever in Virginia in 1741–2)
, ''The Philadelphia Medical Museum,'' 1 (1) : 1–20. * (John Mitchell) (1814
"Account of the Yellow fever which prevailed in Virginia in the years 1737, 1741, and 1742, in a letter to the late Cadwallader Colden, Esq. of New York, from the late John Mitchell, M.D.F.R.S. of Virginia,"
''American Medical and Philosophical Register'', 4 : 181–215. The term "yellow fever" appears on p. 186. On p. 188, Mitchell mentions "… the distemper was what is generally called yellow fever in America". However, on pages 191–192, he states "… I shall consider the cause of the yellowness which is so remarkable in this distemper, as to have given it the name of the Yellow Fever." However, Dr. Mitchell misdiagnosed the disease that he observed and treated, and the disease was probably Weil's disease or hepatitis. McNeill argues that the environmental and ecological disruption caused by the introduction of sugar plantations created the conditions for mosquito and viral reproduction, and subsequent outbreaks of yellow fever. Deforestation reduced populations of insectivorous birds and other creatures that fed on mosquitoes and their eggs. In
In  The southern city of was plagued with major epidemics during the 19th century, most notably in 1833 and 1853. A major epidemic occurred in both New Orleans and Shreveport, Louisiana in 1873. Its residents called the disease "yellow jack". Urban epidemics continued in the United States until 1905, with the last outbreak affecting New Orleans.
At least 25 major outbreaks took place in the Americas during the 18th and 19th centuries, including particularly serious ones in
The southern city of was plagued with major epidemics during the 19th century, most notably in 1833 and 1853. A major epidemic occurred in both New Orleans and Shreveport, Louisiana in 1873. Its residents called the disease "yellow jack". Urban epidemics continued in the United States until 1905, with the last outbreak affecting New Orleans.
At least 25 major outbreaks took place in the Americas during the 18th and 19th centuries, including particularly serious ones in  In 1853,
In 1853,



 During 1920–1923, the Rockefeller Foundation's
During 1920–1923, the Rockefeller Foundation's
"U.S. Army Yellow Fever Commission."
Claude Moore Health Sciences Library,
disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, chills, loss of appetite
Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetite. While the term in non-scientific publications is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa, many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite, some of which may be harmless, while others i ...
, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In about 15% of people, within a day of improving the fever comes back, abdominal pain occurs, and liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
damage begins causing yellow skin. If this occurs, the risk of bleeding and kidney problems
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
is increased.
The disease is caused by the yellow fever virus and is spread by the bite of an infected mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
. It infects humans, other primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s, and several types of mosquitoes. In cities, it is spread primarily by ''Aedes aegypti
''Aedes aegypti'', the yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that can spread dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, Mayaro and yellow fever viruses, and other disease agents. The mosquito can be recognized by black and white markings on its le ...
'', a type of mosquito found throughout the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referr ...
and subtropics. The virus is an RNA virus of the genus ''Flavivirus
''Flavivirus'' is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Flaviviridae''. The genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cau ...
''. The disease may be difficult to tell apart from other illnesses, especially in the early stages. To confirm a suspected case, blood-sample testing with polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
is required.
A safe and effective vaccine against yellow fever exists, and some countries require vaccinations for travelers. Other efforts to prevent infection include reducing the population of the transmitting mosquitoes. In areas where yellow fever is common, early diagnosis of cases and immunization of large parts of the population are important to prevent outbreak
In epidemiology, an outbreak is a sudden increase in occurrences of a disease when cases are in excess of normal expectancy for the location or season. It may affect a small and localized group or impact upon thousands of people across an entire ...
s. Once a person is infected, management is symptomatic; no specific measures are effective against the virus. Death occurs in up to half of those who get severe disease.
In 2013, yellow fever resulted in about 127,050 severe infections and 45,000 deaths worldwide, with nearly 90 percent of these occurring in Africa. Nearly a billion people live in an area of the world where the disease is common. It is common in tropical areas of the continents of South America and Africa, but not in Asia. Since the 1980s, the number of cases of yellow fever has been increasing. This is believed to be due to fewer people being immune, more people living in cities, people moving frequently, and changing climate increasing the habitat for mosquitoes.
The disease originated in Africa and spread to the Americas starting in the 17th century with the European trafficking of enslaved Africans
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
from sub-Saharan Africa. Since the 17th century, several major outbreaks
In epidemiology, an outbreak is a sudden increase in occurrences of a disease when cases are in excess of normal expectancy for the location or season. It may affect a small and localized group or impact upon thousands of people across an entire ...
of the disease have occurred in the Americas, Africa, and Europe. In the 18th and 19th centuries, yellow fever was considered one of the most dangerous infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
s; numerous epidemics swept through major cities of the US and in other parts of the world.
In 1927, yellow fever virus was the first human virus to be isolated.
Signs and symptoms
Yellow fever begins after an incubation period of three to six days. Most cases cause only a mild infection with fever, headache, chills, back pain, fatigue, loss of appetite, muscle pain, nausea, and vomiting. In these cases, the infection lasts only three to six days. But in 15% of cases, people enter a second, toxic phase of the disease characterized by recurring fever, this time accompanied by jaundice due toliver damage
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the si ...
, as well as abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
. Bleeding in the mouth, nose, the eyes, and the gastrointestinal tract cause vomit containing blood, hence the Spanish name for yellow fever, ("black vomit"). There may also be kidney failure, hiccups, and delirium.
Among those who develop jaundice, the fatality rate is 20 to 50%, while the overall fatality rate
In epidemiology, case fatality rate (CFR) – or sometimes more accurately case-fatality risk – is the proportion of people diagnosed with a certain disease, who end up dying of it. Unlike a disease's mortality rate, the CFR does not take int ...
is about 3 to 7.5%. Severe cases may have a mortality greater than 50%.
Surviving the infection provides lifelong immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity desc ...
, and normally results in no permanent organ damage.
Complication
Yellow fever can lead to death for 20% to 50% of those who develop severe disease. Jaundice, fatigue, heart rhythm problems, seizures and internal bleeding may also appear as complications of yellow fever during recovery time.Cause
Yellow fever is caused by yellow fever virus, an enveloped RNA virus 40–50 in width, the type species and namesake of the family ''Flaviviridae
''Flaviviridae'' is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors (mainly ticks and mosquitoes). The family gets its name from the yellow fever viru ...
''. It was the first illness shown to be transmissible by filtered human serum and transmitted by mosquitoes, by American doctor Walter Reed
Walter Reed (September 13, 1851 – November 22, 1902) was a U.S. Army physician who in 1901 led the team that confirmed the theory of Cuban doctor Carlos Finlay that yellow fever is transmitted by a particular mosquito species rather than ...
around 1900. The positive-sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system re ...
, single-stranded RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
is around 10,862 nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecule ...
s long and has a single open reading frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible readin ...
encoding a polyprotein
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called prot ...
.Host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
People
*Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman
* Michel Host ...
protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
s cut this polyprotein into three structural (C, prM, E) and seven nonstructural proteins (NS1, NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5); the enumeration corresponds to the arrangement of the protein coding gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s in the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
. Minimal ''yellow fever virus'' (YFV) 3'UTR region is required for stalling of the host 5'-3' exonuclease XRN1. The UTR contains PKS3 pseudoknot structure, which serves as a molecular signal to stall the exonuclease and is the only viral requirement for subgenomic flavivirus RNA (sfRNA) production. The sfRNAs are a result of incomplete degradation of the viral genome by the exonuclease and are important for viral pathogenicity. Yellow fever belongs to the group of hemorrhagic fevers
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
.
The viruses infect, amongst others, monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
s, macrophages, Schwann cells
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells, olfactory en ...
, and dendritic cells. They attach to the cell surfaces via specific receptors
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a n ...
and are taken up by an endosomal vesicle
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry)
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form nat ...
. Inside the endosome
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can ...
, the decreased pH induces the fusion of the endosomal membrane with the virus envelope. The capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
enters the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
, decays, and releases the genome. Receptor binding, as well as membrane fusion, are catalyzed
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
by the protein E, which changes its conformation at low pH, causing a rearrangement of the 90 homodimer
Dimer may refer to:
* Dimer (chemistry), a chemical structure formed from two similar sub-units
** Protein dimer, a protein quaternary structure
** d-dimer
* Dimer model, an item in statistical mechanics, based on ''domino tiling''
* Julius Dimer ...
s to 60 homo trimers.
After entering the host cell, the viral genome is replicated in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and in the so-called vesicle packets. At first, an immature form of the virus particle is produced inside the ER, whose M-protein is not yet cleaved to its mature form, so is denoted as precursor M (prM) and forms a complex with protein E. The immature particles are processed in the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ...
by the host protein furin
Furin is a protease, a proteolytic enzyme that in humans and other animals is encoded by the ''FURIN'' gene. Some proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized, and must have sections removed in order to become active. Furin cleaves these s ...
, which cleaves prM to M. This releases E from the complex, which can now take its place in the mature, infectious virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's ...
.
Transmission

 Yellow fever virus is mainly transmitted through the bite of the yellow fever mosquito ''Aedes aegypti'', but other mostly ''
Yellow fever virus is mainly transmitted through the bite of the yellow fever mosquito ''Aedes aegypti'', but other mostly ''Aedes
''Aedes'' is a genus of mosquitoes originally found in tropical and subtropical zones, but now found on all continents except perhaps Antarctica. Some species have been spread by human activity: '' Aedes albopictus'', a particularly invasive sp ...
'' mosquitoes such as the tiger mosquito (''Aedes albopictus
''Aedes albopictus'' (''Stegomyia albopicta''), from the mosquito (Culicidae) family, also known as the (Asian) tiger mosquito or forest mosquito, is a mosquito native to the tropical and subtropical areas of Southeast Asia. In the past few cen ...
'') can also serve as a vector
Vector most often refers to:
*Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
*Vector (epidemiology), an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematic ...
for this virus. Like other arbovirus
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo''rne ''virus'') is sometimes used to more sp ...
es, which are transmitted by mosquitoes, ''yellow fever virus'' is taken up by a female mosquito when it ingests the blood of an infected human or another primate. Viruses reach the stomach of the mosquito, and if the virus concentration is high enough, the virions can infect epithelial cells and replicate there. From there, they reach the haemocoel
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
(the blood system of mosquitoes) and from there the salivary gland
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary ...
s. When the mosquito next sucks blood, it injects its saliva into the wound, and the virus reaches the bloodstream of the bitten person. Transovarial transmissionial and transstadial transmission
Transstadial transmission occurs when a pathogen remains with the vector from one life stage ("stadium") to the next. For example, the bacteria '' Borrelia burgdorferi'', the causative agent for Lyme disease, infects the tick vector as a larva, and ...
of yellow fever virus within ''A. aegypti'', that is, the transmission from a female mosquito to its eggs and then larvae, are indicated. This infection of vectors without a previous blood meal seems to play a role in single, sudden breakouts of the disease.
Three epidemiologically different infectious cycles occur in which the virus is transmitted from mosquitoes to humans or other primates. In the "urban cycle", only the yellow fever mosquito ''A. aegypti'' is involved. It is well adapted to urban areas, and can also transmit other diseases, including Zika fever
Zika fever, also known as Zika virus disease or simply Zika, is an infectious disease caused by the Zika virus. Most cases have no symptoms, but when present they are usually mild and can resemble dengue fever. Symptoms may include fever, red ...
, dengue fever, and chikungunya
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the ''Chikungunya virus'' (CHIKV). Symptoms include fever and joint pains. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a ra ...
. The urban cycle is responsible for the major outbreaks of yellow fever that occur in Africa. Except for an outbreak in Bolivia in 1999, this urban cycle no longer exists in South America.
Besides the urban cycle, both in Africa and South America, a sylvatic cycle
The sylvatic cycle, also enzootic or sylvatic transmission cycle, is a portion of the natural transmission cycle of a pathogen. Sylvatic refers to the occurrence of a subject in or affecting wild animals. The sylvatic cycle is the fraction of the ...
(forest or jungle cycle) is present, where ''Aedes africanus
''Aedes africanus'' is a species of mosquito that is found on the continent of Africa with the exclusion of Madagascar. Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit, Systematic Catalog of Culicidae, ''Aedes aegypti'' and ''Aedes africanus'' are the two main ...
'' (in Africa) or mosquitoes of the genus '' Haemagogus'' and ''Sabethes
''Sabethes'' mosquitoes are primarily an arboreal genus, breeding in plant cavities.Ralph E. Harbach. 1994. The subgenus ''Sabethinus'' of ''Sabethes'' (Diptera: Culicidae). ''Systematic Entomology'', 19: 207-234; https://www.researchgate.net/p ...
'' (in South America) serve as vectors. In the jungle, the mosquitoes infect mainly nonhuman primates; the disease is mostly asymptomatic in African primates. In South America, the sylvatic cycle is currently the only way humans can become infected, which explains the low incidence of yellow fever cases on the continent. People who become infected in the jungle can carry the virus to urban areas, where ''A. aegypti'' acts as a vector. Because of this sylvatic cycle, yellow fever cannot be eradicated except by eradicating the mosquitoes that serve as vectors.
In Africa, a third infectious cycle known as "savannah cycle" or intermediate cycle, occurs between the jungle and urban cycles. Different mosquitoes of the genus ''Aedes'' are involved. In recent years, this has been the most common form of transmission of yellow fever in Africa.
Concern exists about yellow fever spreading to southeast Asia, where its vector ''A. aegypti'' already occurs.
Pathogenesis
After transmission from a mosquito, the viruses replicate in the lymph nodes and infect dendritic cells in particular. From there, they reach the liver and infecthepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, ...
s (probably indirectly via Kupffer cell
Kupffer cells, also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer–Browicz cells, are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Ku ...
s), which leads to eosinophilic degradation of these cells and to the release of cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s. Apoptotic masses known as Councilman bodies appear in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
of hepatocytes.
Fatality may occur when cytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a physiological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Norm ...
, shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses Collective noun
*Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names
* Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves
Healthcare
* Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emergen ...
, and multiple organ failure
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is altered organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring medical intervention to achieve homeostasis.
Although Irwin and Rippe cautioned in 2005 that the use of "multiple organ failure" or "multisy ...
follow.
Diagnosis
Yellow fever is most frequently a clinicaldiagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
, based on symptomatology and travel history. Mild cases of the disease can only be confirmed virologically. Since mild cases of yellow fever can also contribute significantly to regional outbreaks, every suspected case of yellow fever (involving symptoms of fever, pain, nausea, and vomiting 6–10 days after leaving the affected area) is treated seriously.
If yellow fever is suspected, the virus cannot be confirmed until 6–10 days following the illness. A direct confirmation can be obtained by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, where the genome of the virus is amplified. Another direct approach is the isolation of the virus and its growth in cell culture using blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intr ...
; this can take 1–4 weeks.
Serologically, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence ...
during the acute phase of the disease using specific IgM
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is one of several isotypes of antibody (also known as immunoglobulin) that are produced by vertebrates. IgM is the largest antibody, and it is the first antibody to appear in the response to initial exposure to an antig ...
against yellow fever or an increase in specific IgG
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG ...
titer
Titer (American English) or titre (British English) is a way of expressing concentration. Titer testing employs serial dilution to obtain approximate quantitative information from an analytical procedure that inherently only evaluates as positiv ...
(compared to an earlier sample) can confirm yellow fever. Together with clinical symptoms, the detection of IgM or a four-fold increase in IgG titer is considered sufficient indication for yellow fever. As these tests can cross-react with other flaviviruses, such as dengue virus, these indirect methods cannot conclusively prove yellow fever infection.
Liver biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
can verify inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
and necrosis of hepatocytes and detect viral antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons ...
s. Because of the bleeding tendency of yellow fever patients, a biopsy is only advisable ''post mortem'' to confirm the cause of death.
In a differential diagnosis, infections with yellow fever must be distinguished from other feverish illnesses such as malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
. Other viral hemorrhagic fever
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of animal and human illnesses in which fever and hemorrhage are caused by a viral infection. VHFs may be caused by five distinct families of RNA viruses: the families '' Filoviridae'', ''Flav ...
s, such as Ebola virus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus '' Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and o ...
, Lassa virus
''Lassa mammarenavirus'' (LASV) is an arenavirus that causes Lassa hemorrhagic fever,
a type of viral hemorrhagic fever (VHF), in humans and other primates. ''Lassa mammarenavirus'' is an emerging virus and a select agent, requiring Biosafet ...
, Marburg virus, and Junin virus
''Argentinian mammarenavirus'', better known as the ''Junin virus'' or ''Junín virus'' (JUNV), is an arenavirus in the '' Mammarenavirus'' genus that causes Argentine hemorrhagic fever (AHF). The virus took its original name from the city of Ju ...
, must be excluded as the cause.
Prevention
Personal prevention of yellow fever includes vaccination and avoidance of mosquito bites in areas where yellow fever is endemic. Institutional measures for prevention of yellow fever include vaccination programmes and measures to control mosquitoes. Programmes for distribution of mosquito nets for use in homes produce reductions in cases of both malaria and yellow fever. Use of EPA-registered insect repellent is recommended when outdoors. Exposure for even a short time is enough for a potential mosquito bite. Long-sleeved clothing, long pants, and socks are useful for prevention. The application of larvicides to water-storage containers can help eliminate potential mosquito breeding sites. EPA-registered insecticide spray decreases the transmission of yellow fever. * Use insect repellent when outdoors such as those containing DEET,picaridin
Icaridin, also known as picaridin, is an insect repellent which can be used directly on skin or clothing. It has broad efficacy against various arthropods such as mosquitos, ticks, gnats, flies and fleas, and is almost colorless and odorless. A s ...
, ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate
Ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate (trade name IR3535) is an insect repellent which is applied topically to prevent bites and stings from mosquitos, ticks, and other insects. It is a colorless and almost odorless oil, has efficacy against a broad ran ...
(IR3535), or oil of lemon eucalyptus on exposed skin.
* Mosquitoes may bite through thin clothing, so spraying clothes with repellent containing permethrin
Permethrin is a medication and an insecticide. As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed onto clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects th ...
or another EPA-registered repellent gives extra protection. Clothing treated with permethrin is commercially available. Mosquito repellents containing permethrin are not approved for application directly to the skin.
* The peak biting times for many mosquito species are dusk to dawn. However, ''A. aegypti'', one of the mosquitoes that transmits yellow fever virus, feeds during the daytime. Staying in accommodations with screened or air-conditioned rooms, particularly during peak biting times, also reduces the risk of mosquito bites.
Vaccination
Vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
is recommended for those traveling to affected areas, because non-native people tend to develop more severe illness when infected. Protection begins by the 10th day after vaccine administration in 95% of people, and had been reported to last for at least 10 years. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO) now states that a single dose of vaccine is sufficient to confer lifelong immunity against yellow fever disease. The attenuated live vaccine stem 17D was developed in 1937 by Max Theiler
Max Theiler (30 January 1899 – 11 August 1972) was a South African-American virologist and physician. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1951 for developing a vaccine against yellow fever in 1937, becoming the first ...
. The WHO recommends routine vaccination for people living in affected areas between the 9th and 12th month after birth.
Up to one in four people experience fever, aches, and local soreness and redness at the site of injection. In rare cases (less than one in 200,000 to 300,000), the vaccination can cause yellow fever vaccine-associated viscerotropic disease, which is fatal in 60% of cases. It is probably due to the genetic morphology of the immune system. Another possible side effect is an infection of the nervous system, which occurs in one in 200,000 to 300,000 cases, causing yellow fever vaccine-associated neurotropic disease, which can lead to meningoencephalitis
Meningoencephalitis (; from ; ; and the medical suffix ''-itis'', "inflammation"), also known as herpes meningoencephalitis, is a medical condition that simultaneously resembles both meningitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the menin ...
and is fatal in less than 5% of cases.
The Yellow Fever Initiative, launched by the WHO in 2006, vaccinated more than 105 million people in 14 countries in West Africa. No outbreaks were reported during 2015. The campaign was supported by the GAVI
GAVI, officially Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance (previously the GAVI Alliance, and before that the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization) is a public–private global health partnership with the goal of increasing access to immunization ...
alliance and governmental organizations in Europe and Africa. According to the WHO, mass vaccination cannot eliminate yellow fever because of the vast number of infected mosquitoes in urban areas of the target countries, but it will significantly reduce the number of people infected.
Demand for yellow fever vaccine has continued to increase due to the growing number of countries implementing yellow fever vaccination as part of their routine immunization programmes. Recent upsurges in yellow fever outbreaks in Angola (2015), the Democratic Republic of Congo (2016), Uganda (2016), and more recently in Nigeria and Brazil in 2017 have further increased demand, while straining global vaccine supply. Therefore, to vaccinate susceptible populations in preventive mass immunization campaigns during outbreaks, fractional dosing of the vaccine is being considered as a dose-sparing strategy to maximize limited vaccine supplies. Fractional dose yellow fever vaccination refers to administration of a reduced volume of vaccine dose, which has been reconstituted as per manufacturer recommendations. The first practical use of fractional dose yellow fever vaccination was in response to a large yellow fever outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in mid-2016.
In March 2017, the WHO launched a vaccination campaign in Brazil with 3.5 million doses from an emergency stockpile. In March 2017 the WHO recommended vaccination for travellers to certain parts of Brazil. In March 2018, Brazil shifted its policy and announced it planned to vaccinate all 77.5 million currently unvaccinated citizens by April 2019.
Compulsory vaccination
Some countries in Asia are considered to be potentially in danger of yellow fever epidemics, as both mosquitoes with the capability to transmit yellow fever as well as susceptible monkeys are present. The disease does not yet occur in Asia. To prevent introduction of the virus, some countries demand previous vaccination of foreign visitors who have passed through yellow fever areas. Vaccination has to be proved by a vaccination certificate, which is valid 10 days after the vaccination and lasts for 10 years. Although the WHO on 17 May 2013 advised that subsequent booster vaccinations are unnecessary, an older (than 10 years) certificate may not be acceptable at all border posts in all affected countries. A list of the countries that require yellow fever vaccination is published by the WHO. If the vaccination cannot be given for some reason, dispensation may be possible. In this case, an exemption certificate issued by a WHO-approved vaccination center is required. Although 32 of 44 countries where yellow fever occurs endemically do have vaccination programmes, in many of these countries, less than 50% of their population is vaccinated.Vector control
 Control of the yellow fever mosquito ''A. aegypti'' is of major importance, especially because the same mosquito can also transmit dengue fever and
Control of the yellow fever mosquito ''A. aegypti'' is of major importance, especially because the same mosquito can also transmit dengue fever and chikungunya
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the ''Chikungunya virus'' (CHIKV). Symptoms include fever and joint pains. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a ra ...
disease. ''A. aegypti'' breeds preferentially in water, for example, in installations by inhabitants of areas with precarious drinking water supplies, or in domestic refuse, especially tires, cans, and plastic bottles. These conditions are common in urban areas in developing countries.
Two main strategies are employed to reduce ''A. aegypti'' populations. One approach is to kill the developing larvae. Measures are taken to reduce the water accumulations in which the larvae develop. Larvicide
A larvicide (alternatively larvacide) is an insecticide that is specifically targeted against the larval life stage of an insect. Their most common use is against mosquitoes. Larvicides may be contact poisons, stomach poisons, growth regulators, o ...
s are used, along with larvae-eating fish and copepods, which reduce the number of larvae. For many years, copepods of the genus ''Mesocyclops
''Mesocyclops'' is a genus of copepod crustaceans in the family Cyclopidae. Because the various species of ''Mesocyclops'' are known to prey on mosquito larvae, it is used as a nontoxic and inexpensive form of biological mosquito control.
Biol ...
'' have been used in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
for preventing dengue fever. This eradicated the mosquito vector in several areas. Similar efforts may prove effective against yellow fever. Pyriproxyfen is recommended as a chemical larvicide, mainly because it is safe for humans and effective in small doses.
The second strategy is to reduce populations of the adult yellow fever mosquito. Lethal ovitraps can reduce ''Aedes'' populations, using lesser amounts of pesticide because it targets the pest directly. Curtains and lids of water tanks can be sprayed with insecticides, but application inside houses is not recommended by the WHO. Insecticide-treated mosquito nets are effective, just as they are against the ''Anopheles
''Anopheles'' () is a genus of mosquito first described and named by J. W. Meigen in 1818. About 460 species are recognised; while over 100 can transmit human malaria, only 30–40 commonly transmit parasites of the genus ''Plasmodium'', which ...
'' mosquito that carries malaria.
Treatment
As with other ''Flavivirus'' infections, no cure is known for yellow fever. Hospitalization is advisable and intensive care may be necessary because of rapid deterioration in some cases. Certain acute treatment methods lack efficacy:passive immunization Passive immunity is the transfer of active humoral immunity of ready-made antibodies. Passive immunity can occur naturally, when maternal antibodies are transferred to the fetus through the placenta, and it can also be induced artificially, when ...
after the emergence of symptoms is probably without effect; ribavirin
Ribavirin, also known as tribavirin, is an antiviral medication used to treat RSV infection, hepatitis C and some viral hemorrhagic fevers. For hepatitis C, it is used in combination with other medications such as simeprevir, sofosbuvir, pe ...
and other antiviral drugs, as well as treatment with interferons, are ineffective in yellow fever patients. Symptomatic treatment includes rehydration and pain relief with drugs such as paracetamol (acetaminophen). Acetylsalicylic acid
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat ...
(aspirin). However, aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
(NSAIDs) are often avoided because of an increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding due to their anticoagulant effects.
Epidemiology
Yellow fever is common in tropical and subtropical areas of South America and Africa. Worldwide, about 600 million people live in endemic areas. The WHO estimates 200,000 cases of yellow fever worldwide each year. About 15% of people infected with yellow fever progress to a severe form of the illness, and up to half of those will die, as there is no cure for yellow fever.Africa
 An estimated 90% of yellow fever infections occur on the African continent. In 2016, a large outbreak originated in Angola and spread to neighboring countries before being contained by a massive vaccination campaign. In March and April 2016, 11 imported cases of the Angola genotype in unvaccinated Chinese nationals were reported in China, the first appearance of the disease in Asia in recorded history.
An estimated 90% of yellow fever infections occur on the African continent. In 2016, a large outbreak originated in Angola and spread to neighboring countries before being contained by a massive vaccination campaign. In March and April 2016, 11 imported cases of the Angola genotype in unvaccinated Chinese nationals were reported in China, the first appearance of the disease in Asia in recorded history.
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
analysis has identified seven genotypes of yellow fever viruses, and they are assumed to be differently adapted to humans and to the vector ''A. aegypti''. Five genotypes (Angola, Central/East Africa, East Africa, West Africa I, and West Africa II) occur only in Africa. West Africa genotype I is found in Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
and the surrounding region. West Africa genotype I appears to be especially infectious, as it is often associated with major outbreaks. The three genotypes found outside of Nigeria and Angola occur in areas where outbreaks are rare. Two outbreaks, in Kenya (1992–1993) and Sudan (2003 and 2005), involved the East African genotype, which had remained undetected in the previous 40 years.
South America
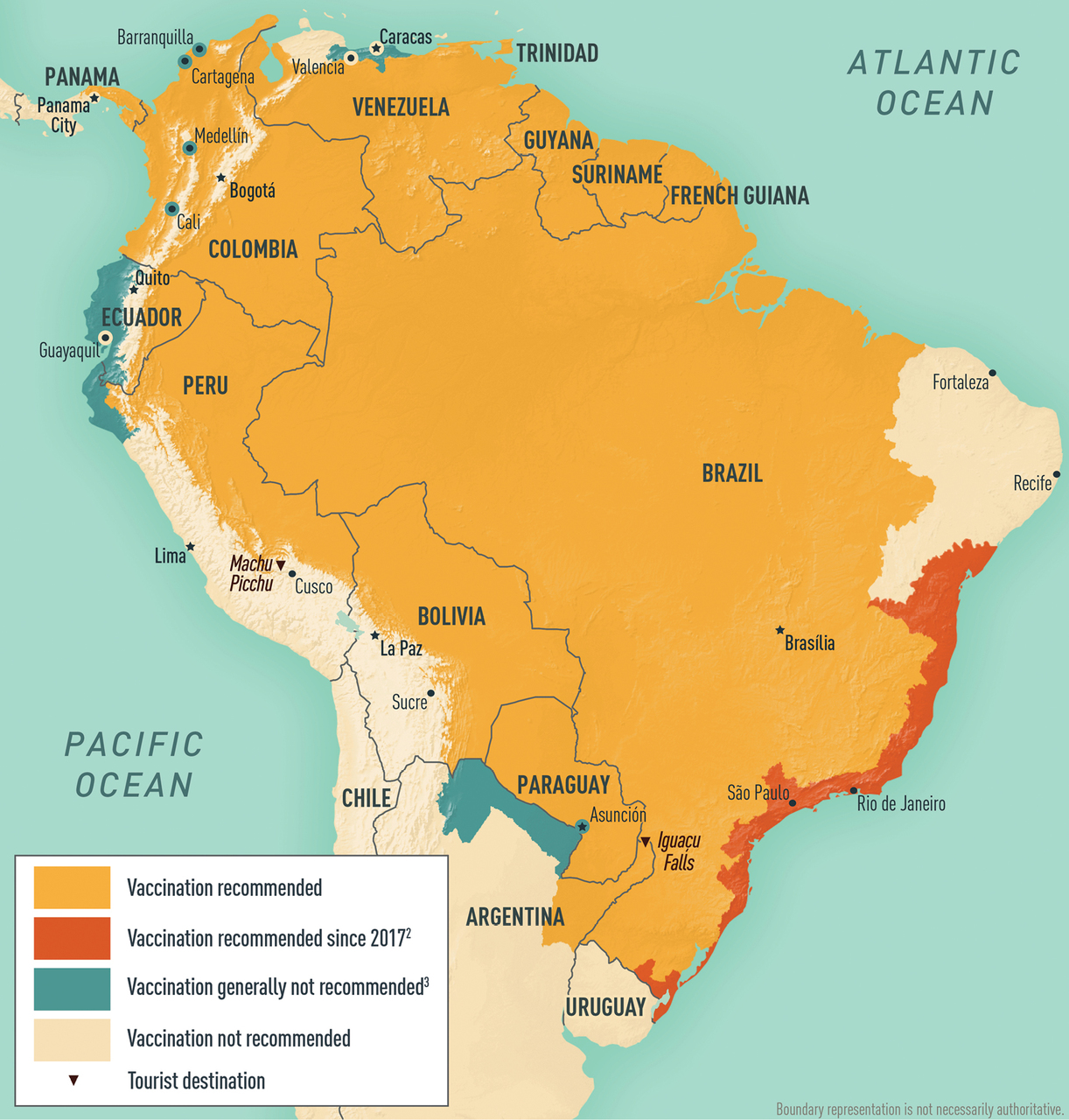
 In South America, two genotypes have been identified (South American genotypes I and II). Based on phylogenetic analysis these two genotypes appear to have originated in West Africa and were first introduced into Brazil. The date of introduction of the predecessor African genotype which gave rise to the South American genotypes appears to be 1822 (95% confidence interval 1701 to 1911). The historical record shows an outbreak of yellow fever occurred in Recife, Brazil, between 1685 and 1690. The disease seems to have disappeared, with the next outbreak occurring in 1849. It was likely introduced with the trafficking of slaves through the
In South America, two genotypes have been identified (South American genotypes I and II). Based on phylogenetic analysis these two genotypes appear to have originated in West Africa and were first introduced into Brazil. The date of introduction of the predecessor African genotype which gave rise to the South American genotypes appears to be 1822 (95% confidence interval 1701 to 1911). The historical record shows an outbreak of yellow fever occurred in Recife, Brazil, between 1685 and 1690. The disease seems to have disappeared, with the next outbreak occurring in 1849. It was likely introduced with the trafficking of slaves through the slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
from Africa. Genotype I has been divided into five subclades, A through E.
In late 2016, a large outbreak began in Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literally ...
state of Brazil that was characterized as a sylvan or jungle epizootic
In epizoology, an epizootic (from Greek: ''epi-'' upon + ''zoon'' animal) is a disease event in a nonhuman animal population analogous to an epidemic in humans. An epizootic may be restricted to a specific locale (an "outbreak"), general (an "epi ...
. It began as an outbreak in brown howler monkeys, which serve as a sentinel species
Sentinel species are organisms, often animals, used to detect risks to humans by providing advance warning of a danger. The terms primarily apply in the context of environmental hazards rather than those from other sources. Some animals can act ...
for yellow fever, that then spread to men working in the jungle. No cases had been transmitted between humans by the ''A. aegypti'' mosquito, which can sustain urban outbreaks that can spread rapidly. In April 2017, the sylvan outbreak continued moving toward the Brazilian coast, where most people were unvaccinated. By the end of May the outbreak appeared to be declining after more than 3,000 suspected cases, 758 confirmed and 264 deaths confirmed to be yellow fever. The Health Ministry launched a vaccination campaign and was concerned about spread during the Carnival season in February and March. The CDC issued a Level 2 alert (practice enhanced precautions.)
A Bayesian analysis of genotypes I and II has shown that genotype I accounts for virtually all the current infections in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Colombia, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, and Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
and Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
, while genotype II accounted for all cases in Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
. Genotype I originated in the northern Brazilian region around 1908 (95% highest posterior density interval PD 1870–1936). Genotype II originated in Peru in 1920 (95% HPD: 1867–1958). The estimated rate of mutation for both genotypes was about 5 × 10−4 substitutions/site/year, similar to that of other RNA viruses.
Asia
The main vector (''A. aegypti'') also occurs in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, the Pacific, and Australia, but yellow fever has never occurred there, until jet travel introduced 11 cases from the2016 Angola and DR Congo yellow fever outbreak
On 20 January 2016, the health minister of Angola reported 23 cases of yellow fever with 7 deaths among Eritrean and Congolese citizens living in Angola in Viana municipality, a suburb of the capital of Luanda. The first cases (hemorrhagic feve ...
in Africa. Proposed explanations include:
* That the strains of the mosquito in the east are less able to transmit ''yellow fever virus''.
* That immunity is present in the populations because of other diseases caused by related viruses (for example, dengue
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic ...
).
* That the disease was never introduced because the shipping trade was insufficient.
But none is considered satisfactory. Another proposal is the absence of a slave trade to Asia on the scale of that to the Americas. The trans-Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
probably introduced yellow fever into the Western Hemisphere from Africa.
History
Early history
The evolutionary origins of yellow fever most likely lie in Africa, with transmission of the disease from nonhuman primates to humans. The virus is thought to have originated in East or Central Africa and spread from there to West Africa. As it was endemic in Africa, local populations had developed some immunity to it. When an outbreak of yellow fever would occur in an African community where colonists resided, most Europeans died, while the indigenous Africans usually developed nonlethal symptoms resembling influenza. This phenomenon, in which certain populations develop immunity to yellow fever due to prolonged exposure in their childhood, is known asacquired immunity
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
. The virus, as well as the vector ''A. aegypti,'' were probably transferred to North and South America with the trafficking of slaves from Africa, part of the Columbian exchange following European exploration and colonization. However, some researchers have argued that yellow fever might have existed in the Americas during the pre-Columbian period as mosquitoes of the genus ''Haemagogus'', which is indigenous to the Americas, have been known to carry the disease.
The first definitive outbreak of yellow fever in the New World was in 1647 on the island of Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
. An outbreak was recorded by Spanish colonists in 1648 in the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
, where the indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
Mayan people
Mayan most commonly refers to:
* Maya peoples, various indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Maya civilization, pre-Columbian culture of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Mayan languages, language family spoken ...
called the illness ''xekik'' ("blood vomit"). In 1685, Brazil suffered its first epidemic in Recife
That it may shine on all ( Matthew 5:15)
, image_map = Brazil Pernambuco Recife location map.svg
, mapsize = 250px
, map_caption = Location in the state of Pernambuco
, pushpin_map = Brazil#South A ...
. The first mention of the disease by the name "yellow fever" occurred in 1744.
* (John Mitchell) (1805(Mitchell's account of the Yellow Fever in Virginia in 1741–2)
, ''The Philadelphia Medical Museum,'' 1 (1) : 1–20. * (John Mitchell) (1814
"Account of the Yellow fever which prevailed in Virginia in the years 1737, 1741, and 1742, in a letter to the late Cadwallader Colden, Esq. of New York, from the late John Mitchell, M.D.F.R.S. of Virginia,"
''American Medical and Philosophical Register'', 4 : 181–215. The term "yellow fever" appears on p. 186. On p. 188, Mitchell mentions "… the distemper was what is generally called yellow fever in America". However, on pages 191–192, he states "… I shall consider the cause of the yellowness which is so remarkable in this distemper, as to have given it the name of the Yellow Fever." However, Dr. Mitchell misdiagnosed the disease that he observed and treated, and the disease was probably Weil's disease or hepatitis. McNeill argues that the environmental and ecological disruption caused by the introduction of sugar plantations created the conditions for mosquito and viral reproduction, and subsequent outbreaks of yellow fever. Deforestation reduced populations of insectivorous birds and other creatures that fed on mosquitoes and their eggs.
Colonial times
The ''Colonial Times'' was a newspaper in what is now the Australian state of Tasmania. It was established as the ''Colonial Times, and Tasmanian Advertiser'' in 1825 in Hobart, Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colon ...
and during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, the West Indies were known as a particularly dangerous posting for soldiers due to yellow fever being endemic in the area. The mortality rate in British garrisons in Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
was seven times that of garrisons in Canada, mostly because of yellow fever and other tropical diseases. Both English and French forces posted there were seriously affected by the "yellow jack". Wanting to regain control of the lucrative sugar trade in Saint-Domingue (Hispaniola), and with an eye on regaining France's New World empire, Napoleon sent an army under the command of his brother-in-law General Charles Leclerc
Charles Marc Hervé Perceval Leclerc (; born 16 October 1997) is a Monégasque racing driver, currently racing in Formula One for Scuderia Ferrari. He won the GP3 Series championship in 2016 and the FIA Formula 2 Championship in .
Leclerc ...
to Saint-Domingue to seize control after a slave revolt. The historian J. R. McNeill asserts that yellow fever accounted for about 35,000 to 45,000 casualties of these forces during the fighting. Only one third of the French troops survived for withdrawal and return to France. Napoleon gave up on the island and his plans for North America, selling the Louisiana Purchase to the US in 1803. In 1804, Haiti proclaimed its independence as the second republic in the Western Hemisphere. Considerable debate exists over whether the number of deaths caused by disease in the Haitian Revolution was exaggerated.
Although yellow fever is most prevalent in tropical-like climates, the northern United States were not exempted from the fever. The first outbreak in English-speaking North America occurred in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
in 1668. English colonists in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, largest city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the List of United States cities by population, sixth-largest city i ...
and the French in the Mississippi River Valley
The Mississippi embayment is a physiographic feature in the south-central United States, part of the Mississippi Alluvial Plain. It is essentially a northward continuation of the fluvial sediments of the Mississippi River Delta to its conflue ...
recorded major outbreaks in 1669, as well as additional yellow fever epidemics in Philadelphia, Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...
, and New York City in the 18th and 19th centuries. The disease traveled along steamboat routes from New Orleans, causing some 100,000–150,000 deaths in total. The yellow fever epidemic of 1793
During the 1793 yellow fever epidemic in Philadelphia, 5,000 or more people were listed in the official register of deaths between August 1 and November 9. The vast majority of them died of yellow fever, making the epidemic in the city of 50,000 ...
in Philadelphia, which was then the capital of the United States, resulted in the deaths of several thousand people, more than 9% of the population. One of these deaths was James Hutchinson, a physician helping to treat the population of the city. The national government fled the city to Trenton, New Jersey, including President George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
.
 The southern city of was plagued with major epidemics during the 19th century, most notably in 1833 and 1853. A major epidemic occurred in both New Orleans and Shreveport, Louisiana in 1873. Its residents called the disease "yellow jack". Urban epidemics continued in the United States until 1905, with the last outbreak affecting New Orleans.
At least 25 major outbreaks took place in the Americas during the 18th and 19th centuries, including particularly serious ones in
The southern city of was plagued with major epidemics during the 19th century, most notably in 1833 and 1853. A major epidemic occurred in both New Orleans and Shreveport, Louisiana in 1873. Its residents called the disease "yellow jack". Urban epidemics continued in the United States until 1905, with the last outbreak affecting New Orleans.
At least 25 major outbreaks took place in the Americas during the 18th and 19th centuries, including particularly serious ones in Cartagena, Chile
Cartagena is a Chilean commune located in the San Antonio Province, Valparaíso Region. The commune spans an area of .
History
In the seventeenth century the area surrounding the town became a major producer of wheat, which was shipped to Peru a ...
, in 1741; Cuba in 1762 and 1900; Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total
, population_density_km2 = auto
, timezone = AST (UTC −4)
, area_code_type = Area codes
, area_code = 809, 829, 849
, postal_code_type = Postal codes
, postal_code = 10100–10699 ( Distrito Nacional)
, webs ...
in 1803; and Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the seat of Shelby County in the southwest part of the state; it is situated along the Mississippi River. With a population of 633,104 at the 2020 U.S. census, Memphis is the second-mos ...
, in 1878.
In the early nineteenth century, the prevalence of yellow fever in the Caribbean "led to serious health problems" and alarmed the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
as numerous deaths and sickness curtailed naval operations and destroyed morale. One episode began in April 1822 when the frigate USS Macedonian left Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
and became part of Commodore James Biddle's West India Squadron. Unbeknownst to all, they were about to embark on a cruise to disaster and their assignment "would prove a cruise through hell". Secretary of the Navy Smith Thompson
Smith Thompson (January 17, 1768 – December 18, 1843) was a US Secretary of the Navy from 1819 to 1823 and a US Supreme Court Associate Justice from 1823 to his death.
Early life and the law
Born in Amenia, New York, Thompson graduated ...
had assigned the squadron to guard United States merchant shipping and suppress piracy. During their time on deployment from 26 May to 3 August 1822, 76 of the Macedonian's officers and men died, including John Cadle, surgeon USN. Seventy-four of these deaths were attributed to yellow fever. Biddle reported that another 52 of his crew were on sick-list. In their report to the secretary of the Navy, Biddle and Surgeon's Mate Charles Chase stated the cause as "fever". As a consequence of this loss, Biddle noted that his squadron was forced to return to Norfolk Navy Yard early. Upon arrival, the Macedonian's crew were provided medical care and quarantined at Craney Island, Virginia.
 In 1853,
In 1853, Cloutierville, Louisiana
Cloutierville is an unincorporated community in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana, United States. It lies approximately south of the city of Natchitoches on the Cane River. The community is part of the Natchitoches Micropolitan Statistical Are ...
, had a late-summer outbreak of yellow fever that quickly killed 68 of the 91 inhabitants. A local doctor concluded that some unspecified infectious agent had arrived in a package from New Orleans. In 1854, 650 residents of Savannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia and is the county seat of Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the British colonial capital of the Province of Georgia and later t ...
, died from yellow fever. In 1858, St. Matthew's German Evangelical Lutheran Church in Charleston, South Carolina, had 308 yellow fever deaths, reducing the congregation by half. A ship carrying persons infected with the virus arrived in Hampton Roads in southeastern Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
in June 1855. (undated newspaper clipping). The disease spread quickly through the community, eventually killing over 3,000 people, mostly residents of Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the No ...
and Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
. In 1873, Shreveport, Louisiana, lost 759 citizens in an 80-day period to a yellow fever epidemic, with over 400 additional victims eventually succumbing. The total death toll from August through November was approximately 1,200.
In 1878, about 20,000 people died in a widespread epidemic in the Mississippi River Valley. That year, Memphis had an unusually large amount of rain, which led to an increase in the mosquito population. The result was a huge epidemic of yellow fever. The steamship John D. Porter took people fleeing Memphis northward in hopes of escaping the disease, but passengers were not allowed to disembark due to concerns of spreading yellow fever. The ship roamed the Mississippi River for the next two months before unloading her passengers.
Major outbreaks have also occurred in southern Europe. Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
lost many lives to outbreaks in 1804, 1814, and 1828. Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
suffered the loss of several thousand citizens during an outbreak in 1821. The Duke de Richelieu deployed 30,000 French troops to the border between France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
in the Pyrenees Mountains
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to C ...
, to establish a ''cordon sanitaire
''Cordon sanitaire'' () is French for "sanitary cordon". It may refer to:
*Cordon sanitaire (medicine), a cordon that quarantines an area during an infectious disease outbreak
*Cordon sanitaire (politics), refusal to cooperate with certain politic ...
'' in order to prevent the epidemic from spreading from Spain into France.James Taylor, ''The age we live in: a history of the nineteenth century,'' Oxford University, 1882; p. 222.
Causes and transmission



Ezekiel Stone Wiggins
Ezekiel Stone Wiggins (December 4, 1839 – August 14, 1910) was a Canadian weather and earthquake predictor known as the "Ottawa Prophet". He was the author of several scientific, educational and religious works.
Early life and education
Ezeki ...
, known as the Ottawa Prophet, proposed that the cause of a yellow fever epidemic in Jacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
, in 1888, was astrological.
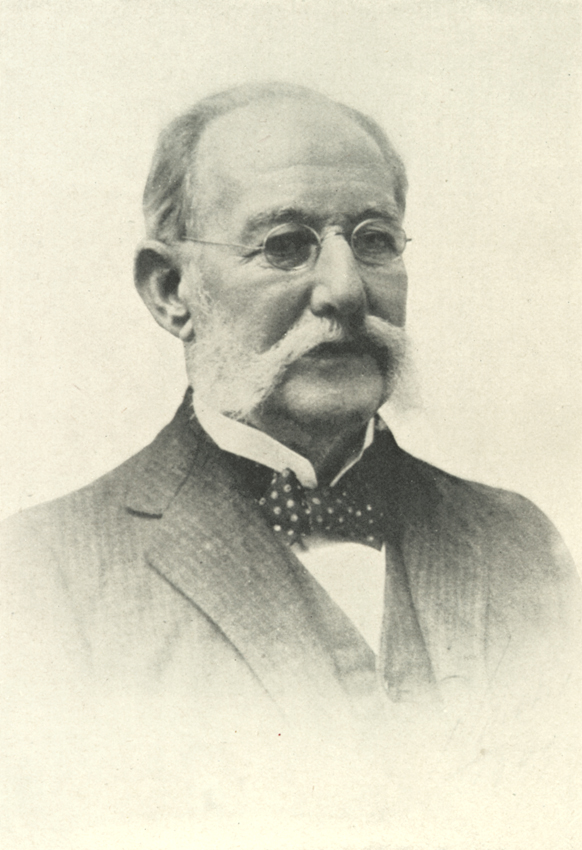
In 1848, Josiah C. Nott
Josiah Clark Nott (March 31, 1804March 31, 1873) was an American surgeon and anthropologist. He is known for his studies into the etiology of yellow fever and malaria, including the theory that they originate from germs.
Nott, who owned slaves ...
suggested that yellow fever was spread by insects such as moths or mosquitoes, basing his ideas on the pattern of transmission of the disease. Carlos Finlay
Carlos Juan Finlay (December 3, 1833 – August 20, 1915) was a Cuban epidemiologist recognized as a pioneer in the research of yellow fever, determining that it was transmitted through mosquitoes ''Aedes aegypti''.
Biography
Early life and ...
, a Cuban doctor and scientist, proposed in 1881 that yellow fever might be transmitted by previously infected mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
es rather than by direct contact from person to person, as had long been believed. Since the losses from yellow fever in the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
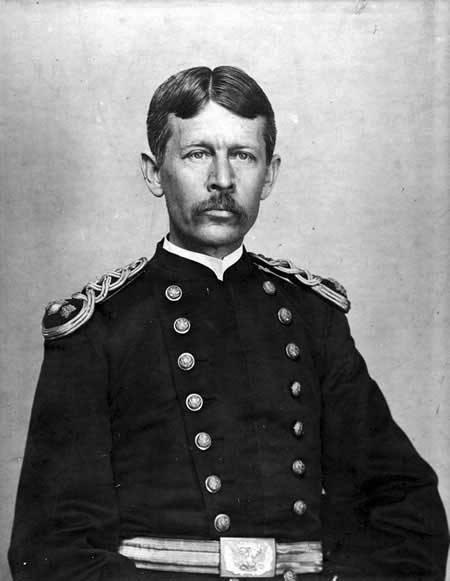
in the 1890s were extremely high, Army doctors began research experiments with a team led by Walter Reed
Walter Reed (September 13, 1851 – November 22, 1902) was a U.S. Army physician who in 1901 led the team that confirmed the theory of Cuban doctor Carlos Finlay that yellow fever is transmitted by a particular mosquito species rather than ...
, and composed of doctors James Carroll, Aristides Agramonte
Aristides Agramonte y Simoni (June 3, 1868 – August 19, 1931) was a Cuban American physician, pathologist and bacteriologist with expertise in tropical medicine. In 1898 George Miller Sternberg appointed him as an Acting Assistant Surgeon ...
, and Jesse William Lazear
Jesse William Lazear (2 May 1866, in Baltimore – 25 September 1900, in Quemados, Cuba) was an American physician.
Background
Lazear was the son of William and Charlotte née Pettigrew. He attended Trinity Hall Military Academy and Washington ...
. They successfully proved Finlay's "mosquito hypothesis". Yellow fever was the first virus shown to be transmitted by mosquitoes. The physician William Gorgas
William Crawford Gorgas KCMG (October 3, 1854 – July 3, 1920) was a United States Army physician and 22nd Surgeon General of the U.S. Army (1914–1918). He is best known for his work in Florida, Havana and at the Panama Canal in abating ...
applied these insights and eradicated yellow fever from Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
. He also campaigned against yellow fever during the construction of the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a condui ...
. A previous effort of canal building by the French had failed in part due to mortality from the high incidence of yellow fever and malaria, which killed many workers.
Although Reed has received much of the credit in United States history books for "beating" yellow fever, he had fully credited Finlay with the discovery of the yellow fever vector, and how it might be controlled. Reed often cited Finlay's papers in his own articles, and also credited him for the discovery in his personal correspondence. The acceptance of Finlay's work was one of the most important and far-reaching effects of the U.S. Army Yellow Fever Commission of 1900. Applying methods first suggested by Finlay, the United States government and Army eradicated yellow fever in Cuba and later in Panama, allowing completion of the Panama Canal. While Reed built on the research of Finlay, historian François Delaporte notes that yellow fever research was a contentious issue. Scientists, including Finlay and Reed, became successful by building on the work of less prominent scientists, without always giving them the credit they were due. Reed's research was essential in the fight against yellow fever. He is also credited for using the first type of medical consent form during his experiments in Cuba, an attempt to ensure that participants knew they were taking a risk by being part of testing.
Like Cuba and Panama, Brazil also led a highly successful sanitation campaign against mosquitoes and yellow fever. Beginning in 1903, the campaign led by Oswaldo Cruz
Oswaldo Gonçalves Cruz, better known as Oswaldo Cruz (; August 5, 1872 – February 11, 1917), was a Brazilian physician, pioneer bacteriologist, epidemiologist and public health officer and the founder of the Oswaldo Cruz Institute.
He occup ...
, then director general of public health, resulted not only in eradicating the disease but also in reshaping the physical landscape of Brazilian cities such as Rio de Janeiro. During rainy seasons, Rio de Janeiro had regularly suffered floods, as water from the bay surrounding the city overflowed into Rio's narrow streets. Coupled with the poor drainage systems found throughout Rio, this created swampy conditions in the city's neighborhoods. Pools of stagnant water stood year-long in city streets and proved to be a fertile ground for disease-carrying mosquitoes. Thus, under Cruz's direction, public health units known as "mosquito inspectors" fiercely worked to combat yellow fever throughout Rio by spraying, exterminating rats, improving drainage, and destroying unsanitary housing. Ultimately, the city's sanitation and renovation campaigns reshaped Rio de Janeiro's neighborhoods. Its poor residents were pushed from city centers to Rio's suburbs, or to towns found in the outskirts of the city. In later years, Rio's most impoverished inhabitants would come to reside in ''favelas''.
 During 1920–1923, the Rockefeller Foundation's
During 1920–1923, the Rockefeller Foundation's International Health Board
The Rockefeller Foundation is an American private foundation and philanthropic medical research and arts funding organization based at 420 Fifth Avenue, New York City. The second-oldest major philanthropic institution in America, after the Car ...
undertook an expensive and successful yellow fever eradication campaign in Mexico. The IHB gained the respect of Mexico's federal government because of the success. The eradication of yellow fever strengthened the relationship between the US and Mexico, which had not been very good in the years prior. The eradication of yellow fever was also a major step toward better global health.
In 1927, scientists isolated the ''yellow fever virus'' in West Africa. Following this, two vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
s were developed in the 1930s. Max Theiler
Max Theiler (30 January 1899 – 11 August 1972) was a South African-American virologist and physician. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1951 for developing a vaccine against yellow fever in 1937, becoming the first ...
led the completion of the 17D yellow fever vaccine
Yellow fever vaccine is a vaccine that protects against yellow fever. Yellow fever is a viral infection that occurs in Africa and South America. Most people begin to develop immunity within ten days of vaccination and 99 percent are protected ...
in 1937, for which he was subsequently awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord ...
. That vaccine, 17D, is still in use, although newer vaccines, based on vero cell
Vero cells are a lineage of cells used in cell cultures. The 'Vero' lineage was isolated from kidney epithelial cells extracted from an African green monkey (''Chlorocebus'' sp.; formerly called ''Cercopithecus aethiops'', this group of monkeys ha ...
s, are in development (as of 2018)..
Current status
Using vector control and strict vaccination programs, the urban cycle of yellow fever was nearly eradicated from South America. Since 1943, only a single urban outbreak inSanta Cruz de la Sierra
Santa Cruz de la Sierra (; "Holy Cross of the Mountain Range"), commonly known as Santa Cruz, is the largest city in Bolivia and the capital of the Santa Cruz department.
Situated on the Pirai River in the eastern Tropical Lowlands of Bolivia ...
, Bolivia, has occurred. Since the 1980s, however, the number of yellow fever cases has been increasing again, and ''A. aegypti'' has returned to the urban centers of South America. This is partly due to limitations on available insecticides, as well as habitat dislocations caused by climate change. It is also because the vector control program was abandoned. Although no new urban cycle has yet been established, scientists believe this could happen again at any point. An outbreak in Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th ...
in 2008 was thought to be urban in nature, but this ultimately proved not to be the case.
In Africa, virus eradication programs have mostly relied upon vaccination. These programs have largely been unsuccessful because they were unable to break the sylvatic cycle
The sylvatic cycle, also enzootic or sylvatic transmission cycle, is a portion of the natural transmission cycle of a pathogen. Sylvatic refers to the occurrence of a subject in or affecting wild animals. The sylvatic cycle is the fraction of the ...
involving wild primates. With few countries establishing regular vaccination programs, measures to fight yellow fever have been neglected, making the future spread of the virus more likely.
Research
In the hamster model of yellow fever, early administration of the antiviralribavirin
Ribavirin, also known as tribavirin, is an antiviral medication used to treat RSV infection, hepatitis C and some viral hemorrhagic fevers. For hepatitis C, it is used in combination with other medications such as simeprevir, sofosbuvir, pe ...
is an effective treatment of many pathological features of the disease. Ribavirin treatment during the first five days after virus infection improved survival rates, reduced tissue damage in the liver and spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
, prevented hepatocellular steatosis
Steatosis, also called fatty change, is abnormal retention of fat (lipids) within a cell or organ. Steatosis most often affects the liver – the primary organ of lipid metabolism – where the condition is commonly referred to as fatty liver disea ...
, and normalised levels of alanine aminotransferase, a liver damage marker. The mechanism of action of ribavirin in reducing liver pathology in ''yellow fever virus'' infection may be similar to its activity in treatment of hepatitis C, a related virus. Because ribavirin had failed to improve survival in a virulent rhesus model of yellow fever infection, it had been previously discounted as a possible therapy. Infection was reduced in mosquitoes with the wMel strain of ''Wolbachia
''Wolbachia'' is a genus of intracellular bacteria that infects mainly arthropod species, including a high proportion of insects, and also some nematodes. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes, and is possibly the most common reproducti ...
''.
Yellow fever has been researched by several countries as a potential biological weapon
A biological agent (also called bio-agent, biological threat agent, biological warfare agent, biological weapon, or bioweapon) is a bacterium, virus, protozoan, parasite, fungus, or toxin that can be used purposefully as a weapon in bioterroris ...
.
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
* *"U.S. Army Yellow Fever Commission."
Claude Moore Health Sciences Library,
University of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia. Founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson, the university is ranked among the top academic institutions in the United States, with highly selective ad ...
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Yellow Fever
Biological weapons
Epidemics
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate
Tropical diseases
Vaccine-preventable diseases