Yarkand on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the
 :The Emperor then, using the same envoy that Xian had sent to him, bestowed upon him the seal and ribbon of “Protector General of the Western Regions,” and gave him chariots, standards, gold, brocades and embroideries.
"Pei Zun, the Administrator of Dunhuang, wrote saying that foreigners should not be allowed to employ such great authority and that these decrees would cause the kingdoms to despair. An Imperial decree then ordered that the seal and ribbons of “Protector General” be recovered, and replaced with the seal and ribbon of “Great Han General.” Xian’s envoy refused to make the exchange, and (Pei) Zun took them by force.
:Consequently, Xian became resentful. Furthermore, he falsely named himself “Great Protector General,” and sent letters to all the kingdoms. They all submitted to him, and bestowed the title of Chanyu on him. Xian gradually became arrogant making heavy demands for duties and taxes. Several times he attacked Qiuci (
:The Emperor then, using the same envoy that Xian had sent to him, bestowed upon him the seal and ribbon of “Protector General of the Western Regions,” and gave him chariots, standards, gold, brocades and embroideries.
"Pei Zun, the Administrator of Dunhuang, wrote saying that foreigners should not be allowed to employ such great authority and that these decrees would cause the kingdoms to despair. An Imperial decree then ordered that the seal and ribbons of “Protector General” be recovered, and replaced with the seal and ribbon of “Great Han General.” Xian’s envoy refused to make the exchange, and (Pei) Zun took them by force.
:Consequently, Xian became resentful. Furthermore, he falsely named himself “Great Protector General,” and sent letters to all the kingdoms. They all submitted to him, and bestowed the title of Chanyu on him. Xian gradually became arrogant making heavy demands for duties and taxes. Several times he attacked Qiuci ( :That winter (46 CE), Xian returned and attacked Qiuci (Kucha), killed the king, and annexed the kingdom. The hostage princes of Shanshan, and then Yanqi (Karashahr) and the other kingdoms, were detained a long time at Dunhuang and became worried, so they fled and returned o their kingdoms
:The king of Shanshan wrote a letter to the Emperor expressing his desire to return his son to enter the service of the Emperor, and again pleaded for a Protector General, saying that if a Protector General were not sent, he would be forced to obey the Xiongnu. The Son of Heaven replied:
::“We are not able, at the moment, to send out envoys and Imperial troops so, in spite of their good wishes, each kingdom hould seek help as they please, wherever they can, to the east, west, south, or north.”
:Following this, Shanshan, and Jushi (
:That winter (46 CE), Xian returned and attacked Qiuci (Kucha), killed the king, and annexed the kingdom. The hostage princes of Shanshan, and then Yanqi (Karashahr) and the other kingdoms, were detained a long time at Dunhuang and became worried, so they fled and returned o their kingdoms
:The king of Shanshan wrote a letter to the Emperor expressing his desire to return his son to enter the service of the Emperor, and again pleaded for a Protector General, saying that if a Protector General were not sent, he would be forced to obey the Xiongnu. The Son of Heaven replied:
::“We are not able, at the moment, to send out envoys and Imperial troops so, in spite of their good wishes, each kingdom hould seek help as they please, wherever they can, to the east, west, south, or north.”
:Following this, Shanshan, and Jushi (
Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
, China, located on the southern rim of the Taklamakan Desert
The Taklimakan or Taklamakan Desert (; zh, s=塔克拉玛干沙漠, p=Tǎkèlāmǎgān Shāmò, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Такәламаган Шамә; ug, تەكلىماكان قۇملۇقى, Täklimakan qumluqi; also spelled Taklimakan and T ...
in the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
. It is one of 11 counties administered under Kashgar Prefecture. The county, usually referred to as Yarkand in English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, was the seat of an ancient Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
kingdom on the southern branch of the Silk Road and the Yarkand Khanate
The Yarkent Khanate, also known as the Yarkand Khanate and the Kashghar Khanate, was a Sunni Muslim Turkic state ruled by the Mongol descendants of Chagatai Khan. It was founded by Sultan Said Khan in 1514 as a western offshoot of Moghulistan, ...
. The county sits at an altitude of and had a population of .
The fertile oasis is fed by the Yarkand River
The Yarkand River (or Yarkent River, Yeh-erh-ch'iang Ho) is a river in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of western China. It originates in the Siachen Muztagh in a part of the Karakoram range and flows into the Tarim River or Neinejoung R ...
, which flows north down from the Karakorum mountains and passes through the Kunlun Mountains, known historically as the Congling mountains (lit. 'Onion Mountains' - from the abundance of wild onion Wild onion can refer to
* any uncultivated species in the genus '' Allium'', especially:
**'' Allium bisceptrum''
** '' Allium canadense''
** ''Allium tricoccum
''Allium tricoccum'' (commonly known as ramp, ramps, ramson, wild leek, wood leek, o ...
s found there). The oasis now covers , but was likely far more extensive before a period of desiccation affected the region from the 3rd century CE onwards.
Today, Yarkant is a predominantly Uyghur settlement. The irrigated oasis farmland
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous with bo ...
produces cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, corn, fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
s (especially pomegranates
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between tall.
The pomegranate was originally described throughout the Mediterranean region. It was introduc ...
, pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the family Rosaceae, bearing the po ...
s and apricots
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus '' Prunus''.
Usually, an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are al ...
) and walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of a drupe of any tree of the genus ''Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''.
Although culinarily considered a "nut" and used as such, it is not a true ...
s. Yak and sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated ...
graze in the highland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
s. Mineral deposits include petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO ...
, granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies under ...
and coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
.
History
Han dynasty
The territory of Yārkand is first mentioned in the ''Book of Han
The ''Book of Han'' or ''History of the Former Han'' (Qián Hàn Shū,《前汉书》) is a history of China finished in 111AD, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty from the first emperor in 206 BCE to the fall of Wang Mang in 23 CE. ...
'' (1st century BCE) as "Shaju" (Old Chinese, approximately, *s³a(j)-ka), which is probably related to the name of the Iranian Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
tribes.
Descriptions in the '' Hou Hanshu'' ('History of the Later Han') contain insights into the complex political situation China faced in attempting to open up the "Silk Routes
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
" to the West in the 1st century CE. According to the "Chapter on the Western Regions
The Western Regions or Xiyu (Hsi-yü; ) was a historical name specified in the Chinese chronicles between the 3rd century BC to the 8th century AD that referred to the regions west of Yumen Pass, most often Central Asia or sometimes more sp ...
" in the ''Hou Hanshu'':
:"Going west from the kingdom of Suoju (Yarkand), and passing through the countries of Puli ( Tashkurghan) and Wulei (centred on Sarhad in the Wakhan
Wakhan, or "the Wakhan" (also spelt Vakhan; Persian and ps, واخان, ''Vâxân'' and ''Wāxān'' respectively; tg, Вахон, ''Vaxon''), is a rugged, mountainous part of the Pamir, Hindu Kush and Karakoram regions of Afghanistan. Wakha ...
), you arrive among the Da Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat a ...
(Kushans
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
). To the east, it is 10,950 li (4,553 km) from Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang ...
.
:The Chanyu (Khan) of the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
took advantage of the chaos caused by Wang Mang
Wang Mang () (c. 45 – 6 October 23 CE), courtesy name Jujun (), was the founder and the only emperor of the short-lived Chinese Xin dynasty. He was originally an official and consort kin of the Han dynasty and later seized the thron ...
(9-24 CE) and invaded the Western Regions. Only Yan, the king of Suoju, who was more powerful than the others, did not consent to being annexed. Previously, during the time of Emperor Yuan (48-33 BCE), he was a hostage prince and grew up in the capital. He admired and loved the Middle Kingdom and extended the rules of Chinese administration to his own country. He ordered all his sons to respectfully serve the Han dynasty generation by generation, and to never turn their backs on it. Yan died in the fifth Tianfeng year (18 CE). He was awarded the posthumous title of 'Faithful and Martial King'. His son, Kang, succeeded him on the throne.
:At the beginning of Emperor Guangwu's reign (25-57 CE), Kang led the neighboring kingdoms to resist the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
. He escorted, and protected, more than a thousand people including the officers, the soldiers, the wife and children of the former Protector General. He sent a letter to Hexi (Chinese territory west of the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
) to inquire about the activities of the Middle Kingdom, and personally expressed his attachment to, and admiration for, the Han dynasty.
:In the fifth Jianwu year (29 CE) the General-in-Chief of Hexi, Dou Rong, following Imperial instructions, bestowed on Kang the titles of: “King of Chinese Suoju, Performer of Heroic Deeds Who Cherishes Virtue ndCommandant-in-Chief of the Western Regions.” The fifty-five kingdoms were all made dependencies after that.
:In the ninth year (33 CE) Kang died. He was awarded the posthumous
Posthumous may refer to:
* Posthumous award - an award, prize or medal granted after the recipient's death
* Posthumous publication – material published after the author's death
* ''Posthumous'' (album), by Warne Marsh, 1987
* ''Posthumous'' ...
title of “Greatly Accomplished King.” His younger brother, Xian
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqin ...
, succeeded him on the throne. Xian attacked and conquered the kingdoms of Jumi (Keriya) and Xiye ( Karghalik). He killed both their kings, and installed two sons of his elder brother, Kang, as the kings of Jumi and Xiye.
:In the fourteenth year (38 CE), together with An, the king of Shanshan
Shanshan (; ug, پىچان, Pichan, Piqan) was a kingdom located at the north-eastern end of the Taklamakan Desert near the great, but now mostly dry, salt lake known as Lop Nur.
The kingdom was originally an independent city-state, known in ...
(the Lop Nor
Lop Nur or Lop Nor (from a Mongolian name meaning "Lop Lake", where "Lop" is a toponym of unknown origin) is a former salt lake, now largely dried up, located in the eastern fringe of the Tarim Basin, between the Taklamakan and Kumtag deserts ...
region), he sent envoys to the Imperial Palace to offer tribute. Following this, the Western Regions were (again) in communication with China. All the kingdoms to the east of the Congling (Pamirs) were dependent on Xian.
:In the seventeenth year (41 CE), Xian again sent an envoy to present offerings o the Emperor and to ask that a Protector General be appointed. The Son of Heaven questioned the Excellency of Works, Dou Rong, about this. He was of the opinion that Xian, and his sons and brothers who had pledged to serve the Han were truly sincere. Therefore, e suggested thatit would be appropriate to give him higher rank to maintain order and security.
 :The Emperor then, using the same envoy that Xian had sent to him, bestowed upon him the seal and ribbon of “Protector General of the Western Regions,” and gave him chariots, standards, gold, brocades and embroideries.
"Pei Zun, the Administrator of Dunhuang, wrote saying that foreigners should not be allowed to employ such great authority and that these decrees would cause the kingdoms to despair. An Imperial decree then ordered that the seal and ribbons of “Protector General” be recovered, and replaced with the seal and ribbon of “Great Han General.” Xian’s envoy refused to make the exchange, and (Pei) Zun took them by force.
:Consequently, Xian became resentful. Furthermore, he falsely named himself “Great Protector General,” and sent letters to all the kingdoms. They all submitted to him, and bestowed the title of Chanyu on him. Xian gradually became arrogant making heavy demands for duties and taxes. Several times he attacked Qiuci (
:The Emperor then, using the same envoy that Xian had sent to him, bestowed upon him the seal and ribbon of “Protector General of the Western Regions,” and gave him chariots, standards, gold, brocades and embroideries.
"Pei Zun, the Administrator of Dunhuang, wrote saying that foreigners should not be allowed to employ such great authority and that these decrees would cause the kingdoms to despair. An Imperial decree then ordered that the seal and ribbons of “Protector General” be recovered, and replaced with the seal and ribbon of “Great Han General.” Xian’s envoy refused to make the exchange, and (Pei) Zun took them by force.
:Consequently, Xian became resentful. Furthermore, he falsely named himself “Great Protector General,” and sent letters to all the kingdoms. They all submitted to him, and bestowed the title of Chanyu on him. Xian gradually became arrogant making heavy demands for duties and taxes. Several times he attacked Qiuci (Kucha
Kucha, or Kuche (also: ''Kuçar'', ''Kuchar''; ug, كۇچار, Кучар; zh, t= 龜茲, p=Qiūcí, zh, t= 庫車, p=Kùchē; sa, कूचीन, translit=Kūcīna), was an ancient Buddhist kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road ...
) and the other kingdoms. All the kingdoms were anxious and fearful.
:In the winter of the twenty-first year (45 CE), eighteen kings, including the king of Nearer Jushi (Turpan
Turpan (also known as Turfan or Tulufan, , ug, تۇرپان) is a prefecture-level city located in the east of the autonomous region of Xinjiang, China. It has an area of and a population of 632,000 (2015).
Geonyms
The original name of the cit ...
), Shanshan
Shanshan (; ug, پىچان, Pichan, Piqan) was a kingdom located at the north-eastern end of the Taklamakan Desert near the great, but now mostly dry, salt lake known as Lop Nur.
The kingdom was originally an independent city-state, known in ...
, Yanqi (Karashahr
Karasahr or Karashar ( ug, قاراشەھەر, Qarasheher, 6=Қарашәһәр), which was originally known, in the Tocharian languages as ''Ārśi'' (or Arshi) and Agni or the Chinese derivative Yanqi ( zh, s=焉耆, p=Yānqí, w=Yen-ch'i), is an ...
), and others, sent their sons to enter the service of the Emperor and offered treasure. As a result, they were granted audience when they circulated weeping, prostrating with their foreheads to the ground, in the hope of obtaining a Protector General. The Son of Heaven, considering that the Middle Kingdom was just beginning to return to peace and that the northern frontier regions were still unsettled, returned all the hostage princes with generous gifts.
:At the same time, Xian, infatuated with his military power, wanted to annex the Western Regions, and greatly increased his attacks. The kingdoms, informed that no Protector General would be sent, and that the hostage princes were all returning, were very worried and frightened. Therefore, they sent a letter to the Administrator of Dunhuang to ask him to detain their hostage sons with him, so that they could point this out to the ing of
Ing, ING or ing may refer to:
Art and media
* ''...ing'', a 2003 Korean film
* i.n.g, a Taiwanese girl group
* The Ing, a race of dark creatures in the 2004 video game ''Metroid Prime 2: Echoes''
* "Ing", the first song on The Roches' 1992 al ...
Suoju (Yarkand), and tell him that their young hostage sons were detained because a Protector General was to be sent. Then he he king of Yarkand
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
would stop his hostilities. Pei Zun sent an official report informing the Emperor f this proposal which he approved.
:In the twenty-second year (46 CE Xian, aware that no Protector General was coming, sent a letter to An, king of Shanshan, ordering him to cut the route to the Han. An did not accept his order and killed the envoy. Xian was furious and sent soldiers to attack Shanshan. An gave battle but was defeated and fled into the mountains. Xian killed or captured more than a thousand men, and then withdrew.
 :That winter (46 CE), Xian returned and attacked Qiuci (Kucha), killed the king, and annexed the kingdom. The hostage princes of Shanshan, and then Yanqi (Karashahr) and the other kingdoms, were detained a long time at Dunhuang and became worried, so they fled and returned o their kingdoms
:The king of Shanshan wrote a letter to the Emperor expressing his desire to return his son to enter the service of the Emperor, and again pleaded for a Protector General, saying that if a Protector General were not sent, he would be forced to obey the Xiongnu. The Son of Heaven replied:
::“We are not able, at the moment, to send out envoys and Imperial troops so, in spite of their good wishes, each kingdom hould seek help as they please, wherever they can, to the east, west, south, or north.”
:Following this, Shanshan, and Jushi (
:That winter (46 CE), Xian returned and attacked Qiuci (Kucha), killed the king, and annexed the kingdom. The hostage princes of Shanshan, and then Yanqi (Karashahr) and the other kingdoms, were detained a long time at Dunhuang and became worried, so they fled and returned o their kingdoms
:The king of Shanshan wrote a letter to the Emperor expressing his desire to return his son to enter the service of the Emperor, and again pleaded for a Protector General, saying that if a Protector General were not sent, he would be forced to obey the Xiongnu. The Son of Heaven replied:
::“We are not able, at the moment, to send out envoys and Imperial troops so, in spite of their good wishes, each kingdom hould seek help as they please, wherever they can, to the east, west, south, or north.”
:Following this, Shanshan, and Jushi (Turpan
Turpan (also known as Turfan or Tulufan, , ug, تۇرپان) is a prefecture-level city located in the east of the autonomous region of Xinjiang, China. It has an area of and a population of 632,000 (2015).
Geonyms
The original name of the cit ...
/Jimasa
Jimsar County is a county in Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. It contains an area of . According to the 2002 census, it has a population of 130,000.
Near the town of Jimsar are the ruins of the ancient city of Beiting () or Tin ...
) again submitted to the Xiongnu. Meanwhile, Xian became increasingly violent.
:The king of Guisai, reckoning that his kingdom was far enough away, killed Xian’s envoy. Xian then attacked and killed him. He appointed a nobleman from that country, Sijian, king of Guisai. Furthermore, Xian appointed his own son, Zeluo, to be king of Qiuci (Kucha). Xian, taking account of the youth of Zeluo, detached a part of the territory from Qiuci (Kucha) from which he made the kingdom of Wulei (Yengisar). He transferred Sijian to the post of king of Wulei, and appointed another noble to the post of king of Guisai.
:Several years later, the people of the kingdom of Qiuci (Kucha), killed Zeluo and Sijian, and sent envoys to the Xiongnu to ask them to appoint a king to replace them. The Xiongnu established a nobleman of Qiuci (Kucha), Shendu, to be king of Qiuci (Kucha), making it dependent on the Xiongnu.
:Because Dayuan ( Ferghana) had reduced their tribute and taxes, Xian personally took command of several tens of thousands of men taken from several kingdoms, and attacked Dayuan (Ferghana). Yanliu, the king of Dayuan, came before him to submit. Xian took advantage of this to take him back to his own kingdom. Then he transferred Qiaosaiti, the king of Jumi (Keriya), to the post of king of Dayuan (Ferghana). Then Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in
 There is very little information on Yarkant's history for many centuries, apart from a couple of brief references in
There is very little information on Yarkant's history for many centuries, apart from a couple of brief references in  At the end of the 16th century Yarkant was incorporated into the Khanate of Kashgar and became its capital. The Jesuit Benedict Göez, who sought a route from the
At the end of the 16th century Yarkant was incorporated into the Khanate of Kashgar and became its capital. The Jesuit Benedict Göez, who sought a route from the
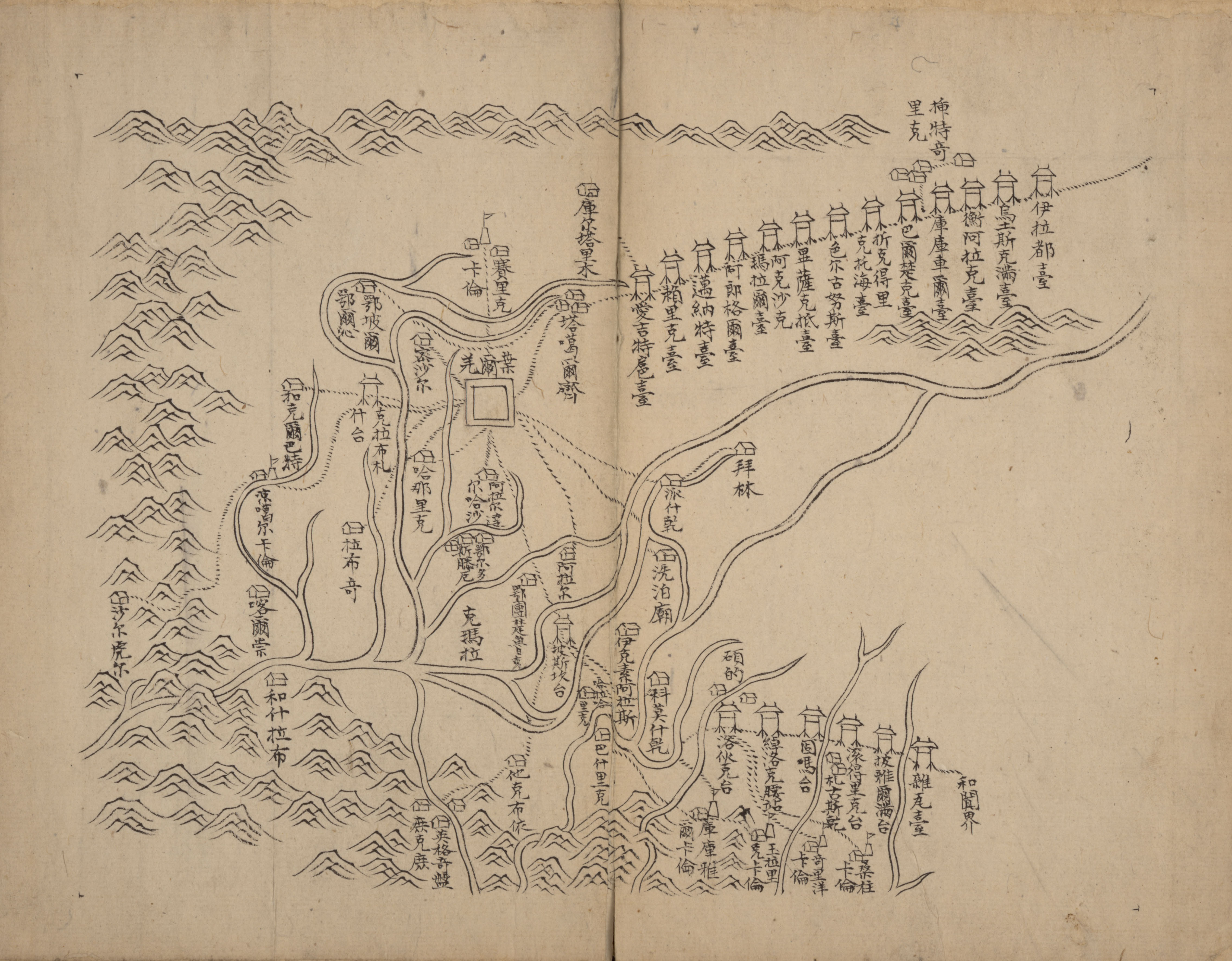 The
The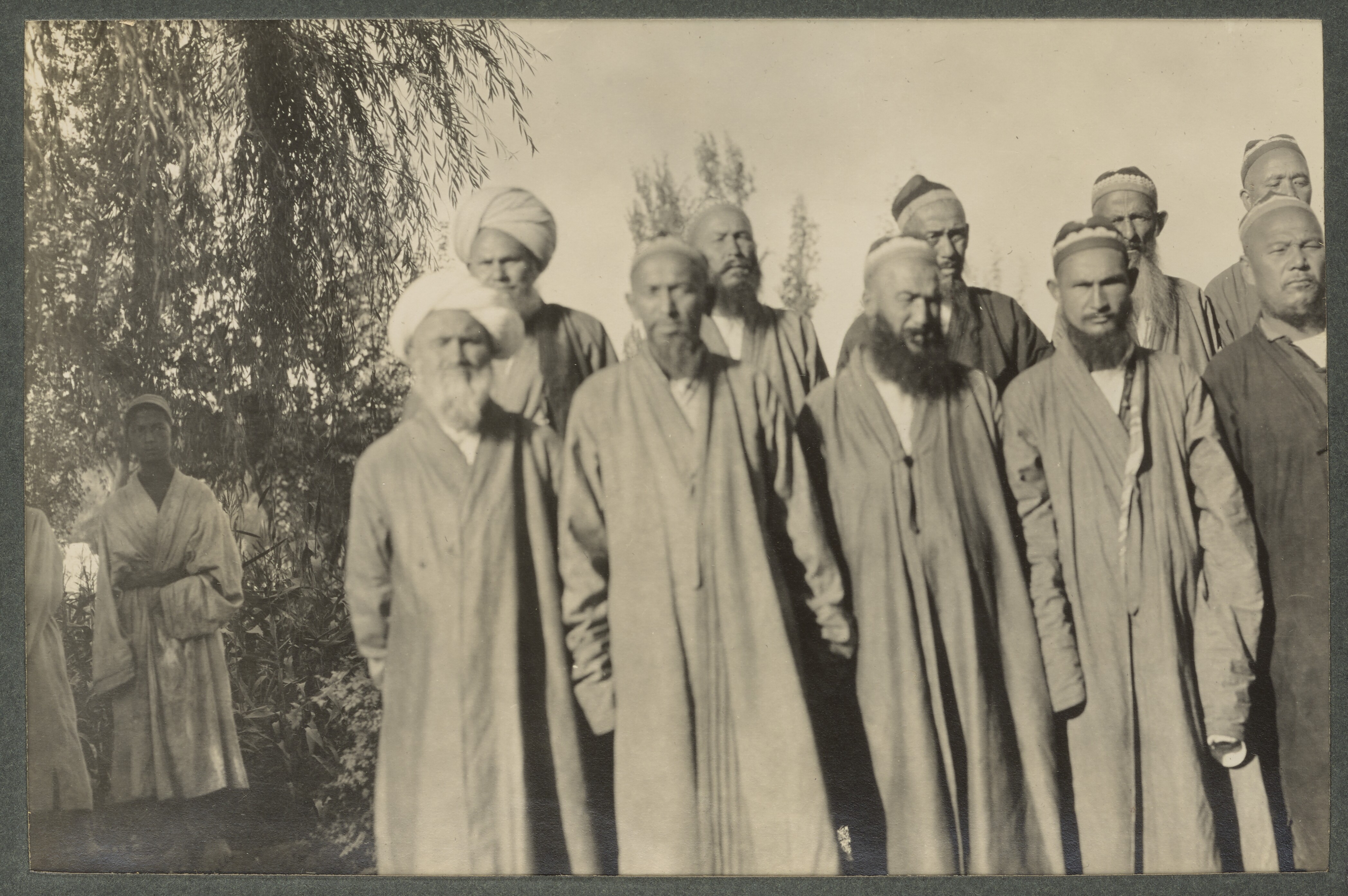  By the 19th century, due to its active trade with
By the 19th century, due to its active trade with

 The
The
File:NJ-43-8 Shache, China.jpg, Map including Yarkant (labeled as SHACHE (SHA-CH'E) ( DMA, 1980)
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nj-43-5th-ed.jpg, Map including Yarkant (labeled as SO-CH'E (YARKAND)) ( AMS, 1966)
File:Operational Navigation Chart G-7, 6th edition.jpg, From the Operational Navigation Chart; map including Yarkant (labeled as SHACHE (SO-CH'E)) ( DMA, 1980)
File:Txu-pclmaps-oclc-22834566 g-7a.jpg, Map including Yarkant (labeled as SHACHE (SO-CH'E)) ( DMA, 1984)
The Roof of the World: Being the Narrative of a Journey over the high plateau of Tibet to the Russian Frontier and the Oxus sources on Pamir
'' Edinburgh. Edmonston and Douglas. Reprint: Ch’eng Wen Publishing Company. Taipei. 1971. * Hill, John E. (2015). ''Through the Jade Gate - China to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes 1st to 2nd Centuries CE''. Volumes I and II. CreateSpace, Charleston, SC. and . *Hulsewé, A. F. P. and Loewe, M. A. N. 1979. ''China in Central Asia: The Early Stage 125 BC – AD 23: an annotated translation of chapters 61 and 96 of the History of the Former Han Dynasty''. E. J. Brill, Leiden. *Puri, B. N. ''Buddhism in Central Asia'', Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, Delhi, 1987. (2000 reprint). *Shaw, Robert. 1871. Visits to High Tartary, Yarkand and Kashgar. Reprint with introduction by Peter Hopkirk, Oxford University Press, 1984. . *Stein, Aurel M. 1907. ''Ancient Khotan: Detailed report of archaeological explorations in Chinese Turkestan'', 2 vols. Clarendon Press. Oxford
*Stein, Aurel M. 1921. ''Serindia: Detailed report of explorations in Central Asia and westernmost China'', 5 vols. London & Oxford. Clarendon Press. Reprint: Delhi. Motilal Banarsidass. 1980
Introduction to Yarkent County
official website of Kashgar Prefecture government
Yarkand Pictures
Washington University
contains many useful resources including a number of full-text historical works) {{Authority control Central Asian Buddhist kingdoms Central Asian Buddhist sites Populated places along the Silk Road County-level divisions of Xinjiang Oases of China Former countries in Chinese history Kashgar Prefecture
Central Asia< ...
(Tashkent plus the Chu, Talas, and middle Jaxartes basins) attacked him there several times and Qiaosaiti fled home o Keriyamore than a year later. Xian appointed him king of Jumi (Keriya) and sent Yanliu back to Dayuan again, ordering him to bring the customary tribute and offerings.
:Xian also banished the king of Yutian (Khotan
Hotan (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Western China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become ...
), Yulin, to be king of Ligui and set up his younger brother, Weishi, as king of Yutian.
:More than a year later Xian became suspicious that the kingdoms wanted to rebel against him. He summoned Weishi, and the kings of Jumi (Keriya), Gumo (Aksu), and Zihe (Shahidulla), and killed them all. He didn’t set up any more kings, he just sent generals to maintain order and guard these kingdoms. Rong, the son of Weishi, fled and made submission to the Han, who named him: “Marquis Who Maintains Virtue.” A general from Suoju (Yarkand), named Junde, had been posted to Yutian (Khotan), and tyrannised the people there who became indignant.
:In the third Yongping year (60 CE), during the reign of Emperor Ming, a high official of this country, called Dumo, had left town when he saw a wild pig. He wanted to shoot it, but the pig said to him: “Do not shoot me, I will undertake to kill Junde for you.” Following this, Dumo plotted with his brothers and killed Junde. However, another high official, Xiumo Ba, plotted, in his turn, with a Chinese man, Han Rong, and others, to kill Dumo and his brothers, then he named himself king of Yutian (Khotan). Together with men from the kingdom of Jumi (Keriya), he attacked and killed the Suoju (Yarkand) general who was at Pishan (modern Pishan or Guma). He then returned with the soldiers.
:Then Xian sent his Heir Apparent, and his State Chancellor, leading 20,000 soldiers from several kingdoms, to attack Xiumo Ba. iumoBa came to meet them and gave battle, defeating the soldiers of Suoju (Yarkand) who fled, and more than 10,000 of them were killed.
:Xian again fielded several tens of thousands of men from several kingdoms, and personally led them to attack Xiumo Ba. iumoBa was again victorious and beheaded more than half of the enemy. Xian escaped and fled, returning to his kingdom. Xiumo Ba advanced and encircled Suoju (Yarkand), but he was hit and killed by an arrow, and his soldiers retreated to Yutian (Khotan).
:Suyule, State Chancellor f Khotan and others, appointed Guangde
Guangde is a county-level city in the southeast of Anhui Province, People's Republic of China, bordering the provinces of Jiangsu to the north and Zhejiang to the east. It is the easternmost county-level division of Anhui and is under the jurisdi ...
, the son of Xiumo Ba’s elder brother, king. The Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
, with Qiuci (Kucha) and the other kingdoms, attacked Suoju (Yarkand), but were unable to take it.
:Later, Guangde recognising of the exhaustion of Suoju (Yarkand), sent his younger brother, the Marquis who Supports the State, Ren, commanding an army, to attack Xian. As he had suffered war continuously, Xian sent an envoy to make peace with Guangde. Guangde's father had previously been detained for several years in Suoju (Yarkand). Xian returned Guangde's father and also gave one of his daughters in marriage and swore brotherhood to Guangde, so the soldiers withdrew and left.
:In the following year (61 CE), Qieyun, the Chancellor of Suoju (Yarkand), and others, worried by Xian's arrogance, plotted to get the town to submit to Yutian (Khotan). Guangde, the king of Yutian (Khotan), then led 30,000 men from several kingdoms to attack Suoju (Yarkand). Xian stayed in the town to defend it and sent a messenger to say to Guangde: “I have given you your father and a wife. Why are you attacking me?” Guangde replied to him: “O king, you are the father of my wife. It has been a long time since we met. I want us to meet, each of us escorted by only two men, outside the town wall to make an alliance.”
:Xian consulted Qieyun about this. Qieyun said to him: “Guangde, your son-in-law is a very close relation; you should go out to see him.” Xian then rashly went out. Guangde advanced and captured him. In addition, Qieyun and his colleagues let the soldiers of Yutian (Khotan) into the town to capture Xian’s wife and children. (Guangde) annexed his kingdom. He put Xian in chains, and took him home with him. More than a year later, he killed him.
:When the Xiongnu heard that Guangde had defeated Suoju (Yarkand), they sent five generals leading more than 30,000 men from fifteen kingdoms including Yanqi (Karashahr), Weili (Korla), and Qiuci (Kucha), to besiege Yutian (Khotan). Guangde asked to submit. He sent his Heir Apparent as a hostage and promised to give felt carpets each year. In winter, the Xiongnu ordered soldiers to take Xian’s son, Bujuzheng, who was a hostage with them, to appoint him king of Suoju (Yarkand).
:Guangde then attacked and killed ujuzheng and put his younger brother, Qili, on the throne. This was in the third Yuanhe year (86 CE) of Emperor Zhang.
:At this time Chief Clerk Ban Chao brought the troops of several kingdoms to attack Suoju (Yarkand). He soundly defeated Suoju (Yarkand) so it submitted to Han."
In 90 CE the Yuezhi or Kushans invaded the region with an army of reportedly 70,000 men, under their Viceroy, Xian, but they were forced to withdraw without a battle after Ban Chao instigated a "burnt earth" policy.
After the Yuanchu period (114-120 CE), when the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
or Kushans placed a hostage prince on the throne of Kashgar:
:"... Suoju arkandfollowed by resisting Yutian hotan and put themselves under Shule ashgar Thus Shule ashgar became powerful and a rival to Qiuci ucha
Ucha is a Portuguese parish, located in the municipality of Barcelos. The population in 2011 was 1,420, in an area of 4.27 km².
References
Freguesias of Barcelos, Portugal
{{braga-geo-stub ...
and Yutian hotan"
:"In the second Yongjian year 27 CEof the reign of Emperor Shun, anYong once again attacked and subdued Yanqi arashahr and then Qiuci ucha
Ucha is a Portuguese parish, located in the municipality of Barcelos. The population in 2011 was 1,420, in an area of 4.27 km².
References
Freguesias of Barcelos, Portugal
{{braga-geo-stub ...
Shule ashgar Yutian hotan Suoju arkand and other kingdoms, seventeen altogether, came to submit. Following this, the Wusun li River Basin and Issyk Kul
Li, li, or LI may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects
* Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political te ...
and the countries of the Congling amir Mountains put an end to their disruptions to communications with the west."
In 130 CE, Yarkand, along with Ferghana and Kashgar, sent tribute and offerings to the Chinese Emperor.
Later history
 There is very little information on Yarkant's history for many centuries, apart from a couple of brief references in
There is very little information on Yarkant's history for many centuries, apart from a couple of brief references in Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom ...
(618-907) histories and it appears to have been of less note than the oasis of Kharghalik (see Yecheng and Yecheng County
Kargilik County ( transliterated from ; ); from Mandarin Chinese Yecheng County (), is a county in southwest of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region and is under the administration of the Kashgar Prefecture. It contains an area of 28,600 km ...
) to its south.
It was possibly captured by the Muslims soon after they subdued Kashgar in the early 10/11th century.
The area became the main base in the region for Chagatai Khan
Chagatai Khan ( Mongolian: ''; Čaɣatay''; mn, Цагадай, translit=Tsagadai; chg, , ''Čaġatāy''; ug, چاغاتاي خان, ''Chaghatay-Xan''; zh, 察合台, ''Chágětái''; fa, , ''Joghatây''; 22 December 1183 – 1 July 1242) ...
(died 1241), who inherited Kashgaria
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan. ...
(and also much of the land between the Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
(Amu Darya) and Jaxartes
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known ...
(Syr Darya) rivers) after his father, Genghis Khan, died in 1227.
Marco Polo described Yarkant in 1273, but said only that this "province" (of Kublai Khan's nephew, Kaidu
Kaidu (Middle Mongol: , Modern Mongol: / , ; ; c. 1230 – 1301) was a grandson of the Mongol khagan Ögedei (1185–1241) and thus leader of the House of Ögedei and the ''de facto'' khan of the Chagatai Khanate, a division of the Mongol Em ...
, d. 1301) was, "five days' journey in extent. The inhabitants follow the law of Mahomet, and there are also some Nestorian Christians
Nestorianism is a term used in Christian theology and Church history to refer to several mutually related but doctrinarily distinct sets of teachings. The first meaning of the term is related to the original teachings of Christian theologian N ...
. They are subject to the Great Khan's nephew. It is amply stocked with the means of life, especially cotton."
 At the end of the 16th century Yarkant was incorporated into the Khanate of Kashgar and became its capital. The Jesuit Benedict Göez, who sought a route from the
At the end of the 16th century Yarkant was incorporated into the Khanate of Kashgar and became its capital. The Jesuit Benedict Göez, who sought a route from the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
to Cathay (which, according to his superiors, may or may not have been the same place as China), arrived in Yarkant with a caravan from Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
in late 1603. He remained there for about a year, making a short trip to Khotan
Hotan (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Western China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become ...
during that time. He reported:
:"Hiarchan arkant the capital of the kingdom of Cascar
The Canadian Association for Stock Car Auto Racing (CASCAR) was an auto racing sanctioning body for amateur and professional stock car racing in Canada. The company was founded in 1981 and was headquartered in Delaware, Ontario. In 2006, NASCAR p ...
, is a mart of much note, both for the great concourse of merchants, and for the variety of wares. At this capital the caravan of Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
merchants reaches its terminus; and a new one is formed for the journey to Cathay. The command of this caravan is sold by the king, who invests the chiefs with a kind of royal authority over the merchants for the whole journey. A twelvemonth passed away however before the new company was formed, for the way is long and perilous, and the caravan is not formed every year, but only when a large number arrange to join it, and when it is known that they will be allowed to enter Cathay."
During his journey, Göez also noted the presence of large marble quarries in the area, leading him to write that amongst native travellers from Yarkant to Cathay:
:"no article of traffic is more valuable or more generally adopted as an investment for this journey than lumps of a certain transparent kind of marble called by the Chinese "jusce" ( jade). They carry these to the Emperor of Cathay, attracted by the high prices which he deems it obligatory on his dignity to give ; and such pieces as the Emperor does not fancy they are free to dispose of to private individuals."
Yarkent Khanate
Yarkent served as capital for theYarkent Khanate
The Yarkent Khanate, also known as the Yarkand Khanate and the Kashghar Khanate, was a Sunni Muslim Turkic state ruled by the Mongol descendants of Chagatai Khan. It was founded by Sultan Said Khan in 1514 as a western offshoot of Moghulistan, ...
, also known as ''Yarkent State'', from the establishment of Yarkent Khanate to its fall (1514–1713).
The Khanate was predominantly Uyghur/Turki; some of its most populated cities were Hotan, Yarkent, Kashgar, Yangihissar, Aksu, Uchturpan, Kucha, Karashar, Turpan and Kumul. It enjoyed continued dominance in the region for about 200 years until it was conquered by the Dzungar Khan, Tsewang Rabtan in 1705.
In the first half of the 14th century the Chagatai Khanate had collapsed; on the western part of the collapsed Chagatai Khanate, the Empire of Timur emerged in 1370, and became the dominant power in the region until its conquest in 1508 by the Shaybanids. Its eastern part became Moghulistan, which was created by Tughluk Timur Khan in 1347 with the capital centered in Almalik, around the Ili River Valley. It comprised all the settled lands of Eastern Kashgaria, as well as regions of Turpan and Kumul which were known at the time as Uyghurstan, according to Balkh and Indian sources of the 16th and 17th centuries. The reigning dynasty of the Yarkent Khanate originated from this state, which existed for more than a century.
In 1509 the Dughlats, vassal rulers of the Tarim basin, rebelled against the Moghulistan Khanate and broke away. Five years later Sultan Said Khan, a brother of the Khan of Moghulistan in Turfan, conquered the Dughlats but established his own Yarkent khanate instead.
This put an end to the dominance in the cities of Kashgaria of the Dughlat emirs, who had controlled them since 1220, when most of Kashgaria had been granted to the Dughlat by Chagatai Khan himself. The conquest of the Dughlats allowed the Yarkent state to become the foremost power in the region.
Qing dynasty
 The
The Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
gained control of the region in the middle of the 18th century.
 By the 19th century, due to its active trade with
By the 19th century, due to its active trade with Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu ...
, and an influx of foreign merchants, it became "the largest and most populous of all the States of Káshghar."( Kashgar). Yakub Beg
Muhammad Yaqub Bek (محمد یعقوب بیگ; uz, Яъқуб-бек, ''Ya’qub-bek''; ; 182030 May 1877) was a Khoqandi ruler of Yettishar (Kashgaria) during his invasion of Xinjiang from 1865 to 1877. He held the title of Atalik Ghazi (" ...
(1820–1877) conquered Khotan
Hotan (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Western China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become ...
, Aksu, Kashgar, and neighbouring towns with the help of the Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
in the 1860s. He made Yarkant the capital of the newly founded Turkic state of Yettishar
Yettishar ( Uyghur: يەتتىشەر دۆلەتى; ; meaning "Seven Cities" or "Heptapolis"), commonly known as Kashgaria, was a short-lived Sunni Muslim Turkic state that existed in Xinjiang between 1865 and 1877 during the Dungan Revolt agai ...
, where he received embassies from England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
in 1870 and 1873. The Qing dynasty defeated Yakub at Turpan
Turpan (also known as Turfan or Tulufan, , ug, تۇرپان) is a prefecture-level city located in the east of the autonomous region of Xinjiang, China. It has an area of and a population of 632,000 (2015).
Geonyms
The original name of the cit ...
in 1877 after which he committed suicide. Thus ended the Yettishar kingdom, and the region returned to Qing Chinese control.
Chinese merchants and soldiers, foreigners like Russians, foreign Muslims, and other Turki merchants all engaged in temporary marriages with Turki (Uyghur) women, since a lot of foreigners lived in Yarkand, temporary marriage flourished there more than it did towards areas with fewer foreigners like areas towards Kucha's east. The Earl of Dunmore
Earl of Dunmore is a title in the Peerage of Scotland.
History
The title was created in 1686 for Lord Charles Murray, second son of John Murray, 1st Marquess of Atholl. He was made Lord Murray of Blair, Moulin and Tillimet (or Tullimet) and ...
wrote in 1894:
''Almost every Chinaman in Yarkand, soldier or civilian, takes unto himself a temporary wife, dispensing entirely with the services of the clergy, as being superfluous, and most of the high officials also give way to the same amiable weakness, their mistresses being in almost all cases natives of Khotan, which city enjoys the unenviable distinction of supplying every large city in Turkestan with courtesans.'' ''When a Chinaman is called back to his own home in China proper, or a Chinese soldier has served his time in Turkestan and has to return to his native city of Pekin or Shanghai, he either leaves his temporary wife behind to shift for herself, or he sells her to a friend. If he has a family he takes the boys with him~—if he can afford it—failing that, the sons are left alone and unprotected to fight the battle of life, While in the case of daughters, he sells them to one of his former companions for a trifling sum.'' ''The natives, although all Mahammadans, have a strong predilection for the Chinese, and seem to like their manners and customs, and never seem to resent this behaviour to their womankind, their own manners, customs, and morals (?) being of the very loosest description.''
Twentieth century

 The
The Battle of Yarkand
The Battle of Yarkhand () was a confrontation that took place in April 1934 at Yarkand, Xinjiang, China. Gen. Ma Zhancang's Chinese Muslim army defeated Uighur and Afghan volunteers sent by King Mohammed Zahir Shah, and killed them all. The emir A ...
took place in Yarkant county, in April 1934. Ma Zhancang
Ma Zhancang (, Xiao'erjing: ) was a Hui Chinese Muslim general of the New 36th Division (National Revolutionary Army), who served under Generals Ma Zhongying and Ma Hushan. At the Battle of Kashgar (1933), he repulsed an attack of Uighurs led b ...
's Chinese Muslim
Islam has been practiced in China since the 7th century CE.. Muslims are a minority group in China, representing 1.6-2 percent of the total population (21,667,000- 28,210,795) according to various estimates. Though Hui Muslims are the most nume ...
army defeated the Turkic Uighur and Kirghiz army, and the Afghan volunteers sent by king Mohammed Zahir Shah
Mohammed Zahir Shah (Pashto/Dari: , 15 October 1914 – 23 July 2007) was the last king of Afghanistan, reigning from 8 November 1933 until he was deposed on 17 July 1973. Serving for 40 years, Zahir was the longest-serving ruler of Afghanistan ...
, and exterminated them all. The emir Abdullah Bughra
Abdullah Bughra ( ug, (Kona Yëziq) ئابدۇللا بۇغرا, عبد الله بغرا; zh, c=阿不都拉·布格拉, p=Ābùdūlā·Bùgélā; died 1934) was a Uighur Emir of the First East Turkestan Republic. He was the younger brother of ...
was killed and beheaded, his head was sent to Idgah mosque
The Id Kah Mosque ( ug, ھېيتگاھ مەسچىتى, translit=Hëytgah Meschiti, ; zh, s=艾提尕尔清真寺, t=艾提尕爾清真寺, p=Àitígǎěr Qīngzhēnsì; from Persian language, Persian: عیدگاه, Eidgah, Eidgāh, meaning "Pl ...
.
Almost all the ancient buildings of the old city were destroyed during the Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goa ...
(1966–1968) with only the central mosque, the main gate of the old palace and the royal cemetery surviving.
Following riots around Yarkant in summer 2014, many scores of people, including Hans and Uyghurs, died, with estimates ranging from the state media total of 96 to about 3,000 according to some residents and Rebiya Kadeer
Rebiya Kadeer ( ug, رابىيە قادىر, translit=Rabiye Qadir; born 15 November 1946) is an ethnic Uyghur businesswoman and political activist. Born in Altay City, Xinjiang, Kadeer became a millionaire in the 1980s through her real estate ...
, president of the Germany-based World Uyghur Congress (WUC). This has been labelled Yarkand Massacre
The Yarkand Massacre was an episode of violence that began on 28 July 2014 in Yarkant County, Kashgar Region of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China, and lasted for several days, as Chinese police quelled the local unrest. While Chinese s ...
.
In August 2015, it was reported by Chinese media that the amount of farmland per capita was increased from 2.6 mu per person to 3.5 mu after clearing up more arable lands.
Geography
Yarkant is strategically located about half way between Kashgar andKhotan
Hotan (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Western China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become ...
, at the junction of a branch road north to Aksu. It also was the terminus for caravans coming from Kashmir via Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu ...
and then over the Karakoram Pass to the oasis of Niya in the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
. The Xinjiang-Tibet Highway China National Highway 219
China National Highway 219 (G219; Chinese: '' Guódào219'') is a highway which runs along the entire western and southern border of the People's Republic of China, from Kom-Kanas Mongolian ethnic township in Xinjiang to Dongxing in Guangxi. ...
, built in 1956 commences in Yecheng/Yarkant and heads south and west, across Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is a region administered by China as part of Hotan County, Hotan Prefecture, Xinjiang and Rutog County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet. It is claimed by India to be a part of its Leh District, Ladakh Union Territory. It is a part of t ...
and into central Tibet.
From Yarkant another important route headed southwest via Tashkurgan Town
Tashkurgan ( ug, تاشقورغان بازىرى; zh, s=塔什库尔干镇, p=Tǎshíkù'ěrgān Zhèn; ) is a town in the far northwest of China, close to the country's border with Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. It is the principal tow ...
to the Wakhan
Wakhan, or "the Wakhan" (also spelt Vakhan; Persian and ps, واخان, ''Vâxân'' and ''Wāxān'' respectively; tg, Вахон, ''Vaxon''), is a rugged, mountainous part of the Pamir, Hindu Kush and Karakoram regions of Afghanistan. Wakha ...
corridor from where travellers could cross the relatively easy Baroghil Pass and Badakshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising parts of modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic Ba ...
.
Climate
As with much of southern Xinjiang, Yarkant has atemperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
zone, continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''BWk''), with a mean total of only of precipitation per annum. As spring and autumn are short, winter and summer are the main seasons. The monthly daily average temperature ranges from in January to in July; the annual mean is . The diurnal temperature variation
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day.
Temperature lag
Temperature lag is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation: peak da ...
is not particularly large for a desert, averaging annually. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 56% in March to 75% in October, the county seat receives 2,860 hours of bright sunshine annually.
Administrative divisions
County controlled District (县辖区) * Tuomuwusitang District (托木吾斯塘区) , Yishikuli District (伊什库力区) , Wudalike District (乌达力克区) , Huoshilapu District (霍什拉甫区) , Awati District (阿瓦提区) , Ailixihu District (艾力西湖区) , Baishikante District (白什坎特区) Subdistricts * Yarkant Subdistrict (Ye'erqiang; ), Chengzhong Subdistrict (),Chengdong Subdistrict
Chengdong District () is one of four districts of the prefecture-level city of Xining, the capital of Qinghai Province, Northwest China.
Subdivisions
* Dongguan Street Subdistrict ()
* Qingzhen Alley Subdistrict ()
* Dazhong Street Subdistri ...
(), Chengxi Subdistrict (), Chengbei Subdistrict ()
Towns ( / )
* Yarkant Town (Shache; / ), Charak Charak may refer to:
*Bandar Charak, a city in Iran
* Charak, Bushehr, a village in Iran
*Charaka, ancient Ayurveda figure
*Charak Puja
Charak Puja or Charak Mela (also known as ''Cadak'', ''Chadak'', ''Nil Puja'' and ''Hajrha Puja'') is a Hind ...
(Qiareke; / ), Awat (Awati; / ), Elishku (Ailixihu, Elishqu; / ), Hangdi (Huangdi; / ), Beshkent (Baishikante; / ), Egerchi (Yigai'erqi; / ), Tomosteng (Tuomu Wusitang, Tuomuwusitang; , formerly Tomosteng Township / ), Misha
Misha (russian: Миша), also known as Mishka (russian: Мишка) or The Olympic Mishka (russian: Олимпийский Мишка), is the name of the Russian Bear mascot of the 1980 Moscow Olympic Games (the XXII Summer Olympics). He wa ...
(Mixia; / , formerly Misha Township ), Odanlik (Wudalike; , formerly Odanlik Township / ), Alamet (Alamaiti; , formerly a Alamet Township / )
Townships ( / )
* Gulbagh Township (Gulebage; / ), Yengiostang Township (Yingwusitang; / ), Aral Township (Arele; / ), Charbagh Township (Qia'erbage; / ), Ishkul Township (Yishikuli; / ), Tagharchi Township (Taga'erqi; / ), Pekichi Township (Paikeqi; / ), Arslanbagh Township (A'ersilanbage; / ), Yaqaerik Township (Yaka'airike; / ), Kachung Township (Kaqun; / ), Koshirap Township (Huoshilafu; / /), Damsi Township (Damusi; / ), Azadbagh Township (Azhatibage; / ), Kosh’erik Township (Kuoshi'airike; / ), Dongbagh Township (Dunbage; / ), Baghawat Township (Bage'awati; / ), Karasu Township (Kalasu; / )
Ethnic Townships (民族乡)
*孜热甫夏提塔吉克族乡 Zerepshat Tajik township
Other (其他)
*莎车农场 , 莎车县良种场 , 莎车县国营农场 , 喀什监狱
莎车县各县辖区管辖乡镇
Tuomuwusitang District (托木吾斯塘区)
*古勒巴格乡 , 托木吾斯塘乡 , 英吾斯塘乡 , 阿热勒乡 , 恰尔巴格乡
Tuomuwusitang District (托木吾斯塘区)
*伊什库力乡 , 米夏乡 , 塔尕尔其乡 , 拍克其乡
Wudalike District (乌达力克区)
*热克镇 , 乌达力克乡 , 阿尔斯兰巴格乡 , 亚喀艾日克乡 , 孜热甫夏提塔吉克族乡
Huoshilafu District (霍什拉甫区)
*喀群乡 , 霍什拉甫乡 , 达木斯乡
Awat District (阿瓦提区)
*Awat Town (阿瓦提镇) , Alamaiti Township (阿拉买提乡) , Azatibage Township (阿扎提巴格乡)
Aili West Lake District (艾力西湖区)
*Ailixihu Town (艾力西湖镇) , Huangdi Town (荒地镇) , Kuoshiairike Township (阔什艾日克乡) , Dunbage Township (墩巴格乡)
Baishikan Special District (白什坎特区)
*白什坎特镇 , 依盖尔其镇 , 巴格阿瓦提乡 , 喀拉苏乡
Economy
Yarkant County is an important producer of wheat, corn, rice, rapeseed, and cotton in southern Xinjiang. The area also produces grapes, rugs, and leather products. Industries include electronics, coal, silk, tractor repair, and cotton and cooking oil processing. , there was about 154,600 acres (1,021,500 '' mu'') of cultivated land in Yarkant.Demographics
As of 2015, 818,379 of the 851,374 residents of the county were Uyghur, 25,404 wereHan Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
and 7,591 were from other ethnic groups.
As of 1999, 95.71% of the population of Yarkant (Shache) County was Uyghur and 3.47% of the population was Han Chinese.
Transportation
Yarkant is served by China National Highway 315, the Kashgar-Hotan Railway andShache Airport
Shache Airport is an airport that serves Yarkant County (Shache) in Kashgar Prefecture of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in northwestern China. It is located near Zirefuxiati Village () of Zirefuxiati Tajik Township. The airport received app ...
.
Historical maps
Historical English-language maps including Yarkant:See also
* Altyn Mosque *Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
* Mount Imeon
Mount Imeon () is an ancient name for the Central Asian complex of mountain ranges comprising the present Hindu Kush, Pamir and Tian Shan, extending from the Zagros Mountains in the southwest to the Altay Mountains in the northeast, and linked to ...
* Shaksgam River
Notes
References
References
*Dorje, Gyurme (2009). ''Tibet Handbook''. 4th Edition. Footprint, Bath, England. . * * Forsyth, T. D. ''Report on A Mission to Yarkund in 1873''. Foreign Department Press, Calcutta, 1875. Downloadable from: https://archive.org/details/reportamissiont00forsgoog. * Gordon, T. E. 1876.The Roof of the World: Being the Narrative of a Journey over the high plateau of Tibet to the Russian Frontier and the Oxus sources on Pamir
'' Edinburgh. Edmonston and Douglas. Reprint: Ch’eng Wen Publishing Company. Taipei. 1971. * Hill, John E. (2015). ''Through the Jade Gate - China to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes 1st to 2nd Centuries CE''. Volumes I and II. CreateSpace, Charleston, SC. and . *Hulsewé, A. F. P. and Loewe, M. A. N. 1979. ''China in Central Asia: The Early Stage 125 BC – AD 23: an annotated translation of chapters 61 and 96 of the History of the Former Han Dynasty''. E. J. Brill, Leiden. *Puri, B. N. ''Buddhism in Central Asia'', Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, Delhi, 1987. (2000 reprint). *Shaw, Robert. 1871. Visits to High Tartary, Yarkand and Kashgar. Reprint with introduction by Peter Hopkirk, Oxford University Press, 1984. . *Stein, Aurel M. 1907. ''Ancient Khotan: Detailed report of archaeological explorations in Chinese Turkestan'', 2 vols. Clarendon Press. Oxford
*Stein, Aurel M. 1921. ''Serindia: Detailed report of explorations in Central Asia and westernmost China'', 5 vols. London & Oxford. Clarendon Press. Reprint: Delhi. Motilal Banarsidass. 1980
External links
Introduction to Yarkent County
official website of Kashgar Prefecture government
Yarkand Pictures
Washington University
contains many useful resources including a number of full-text historical works) {{Authority control Central Asian Buddhist kingdoms Central Asian Buddhist sites Populated places along the Silk Road County-level divisions of Xinjiang Oases of China Former countries in Chinese history Kashgar Prefecture