Wrath (Ultraverse Comics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
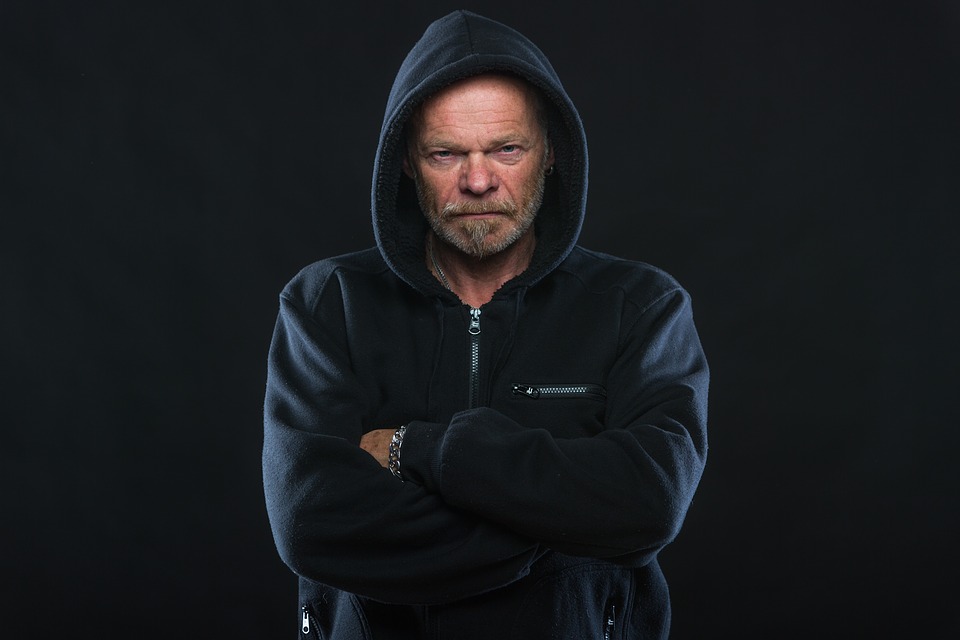 Anger, also known as wrath or
Anger, also known as wrath or
 Three types of anger are recognized by psychologists:Paul M. Hughes, ''Anger'', Encyclopedia of Ethics, Vol I, Second Edition, Rutledge Press
#''Hasty and sudden anger'' is connected to the impulse for self-preservation. It is shared by human and other animals, and it occurs when the animal feels tormented or trapped. This form of anger is episodic.
#''Settled and deliberate anger'' is a reaction to perceived ''deliberate'' harm or unfair treatment by others. This form of anger is episodic.
#''Dispositional anger'' is related more to character traits than to instincts or cognitions. Irritability, sullenness, and churlishness are examples of the last form of anger.
Anger can potentially mobilize psychological resources and boost determination toward correction of wrong behaviors, promotion of social justice, communication of negative sentiment, and redress of grievances. It can also facilitate patience. In contrast, anger can be destructive when it does not find its appropriate outlet in expression. Anger, in its strong form, impairs one's ability to process information and to exert cognitive control over one's
Three types of anger are recognized by psychologists:Paul M. Hughes, ''Anger'', Encyclopedia of Ethics, Vol I, Second Edition, Rutledge Press
#''Hasty and sudden anger'' is connected to the impulse for self-preservation. It is shared by human and other animals, and it occurs when the animal feels tormented or trapped. This form of anger is episodic.
#''Settled and deliberate anger'' is a reaction to perceived ''deliberate'' harm or unfair treatment by others. This form of anger is episodic.
#''Dispositional anger'' is related more to character traits than to instincts or cognitions. Irritability, sullenness, and churlishness are examples of the last form of anger.
Anger can potentially mobilize psychological resources and boost determination toward correction of wrong behaviors, promotion of social justice, communication of negative sentiment, and redress of grievances. It can also facilitate patience. In contrast, anger can be destructive when it does not find its appropriate outlet in expression. Anger, in its strong form, impairs one's ability to process information and to exert cognitive control over one's
 William DeFoore, an anger management writer, described anger as a pressure cooker, stating that "we can only suppress or apply pressure against our happy for so long before it erupts".
One simple dichotomy of anger expression is ''passive anger'' versus ''aggressive anger'' versus ''assertive anger''. These three types of anger have some characteristic symptoms:
William DeFoore, an anger management writer, described anger as a pressure cooker, stating that "we can only suppress or apply pressure against our happy for so long before it erupts".
One simple dichotomy of anger expression is ''passive anger'' versus ''aggressive anger'' versus ''assertive anger''. These three types of anger have some characteristic symptoms:
 Neuroscience has shown that emotions are generated by multiple structures in the brain. The rapid, minimal, and evaluative processing of the emotional significance of the sensory data is done when the data passes through the amygdala in its travel from the sensory organs along certain neural pathways towards the limbic forebrain. Emotion caused by discrimination of stimulus features, thoughts, or memories occurs when its information is relayed from the thalamus to the
Neuroscience has shown that emotions are generated by multiple structures in the brain. The rapid, minimal, and evaluative processing of the emotional significance of the sensory data is done when the data passes through the amygdala in its travel from the sensory organs along certain neural pathways towards the limbic forebrain. Emotion caused by discrimination of stimulus features, thoughts, or memories occurs when its information is relayed from the thalamus to the

Anger
 Wrath is one of the Seven Deadly Sins in Catholicism; and yet the
Wrath is one of the Seven Deadly Sins in Catholicism; and yet the
 Everyone experiences anger, Andrew D. Lester observes, and furthermore anger can serve as "a spiritual friend, a spiritual guide, and a spiritual ally". Denying and suppressing anger is contrary to St. Paul's admonition in his
Everyone experiences anger, Andrew D. Lester observes, and furthermore anger can serve as "a spiritual friend, a spiritual guide, and a spiritual ally". Denying and suppressing anger is contrary to St. Paul's admonition in his
March 9, 2004 Most often a spiritual person is aware of the emotion and the way it can be handled. Thus, in response to the question: "Is any anger acceptable in Buddhism?' the Dalai Lama answered: Buddhist scholar and author Geshe Kelsang Gyatso has also explained Buddha's teaching on the spiritual imperative to identify anger and overcome it by transforming difficulties: The Buddha himself on anger:"Kodhana Sutta: An Angry Person"(AN 7.60), translated from the Pali by Thanissaro Bhikkhu. Access to Insight
June 8, 2010
 In many religions, anger is frequently attributed to God or gods. Primitive people held that gods were subject to anger and revenge in anthropomorphic fashion. The Hebrew Bible says that opposition to God's will results in God's anger.Shailer Mathews, Gerald Birney Smith, A Dictionary of Religion and Ethics, Kessinger Publishing, p.17 Reform
In many religions, anger is frequently attributed to God or gods. Primitive people held that gods were subject to anger and revenge in anthropomorphic fashion. The Hebrew Bible says that opposition to God's will results in God's anger.Shailer Mathews, Gerald Birney Smith, A Dictionary of Religion and Ethics, Kessinger Publishing, p.17 Reform
Maintaining A Good and Healthy Anger
Managing emotions in the workplace
What Your Anger May Be Hiding – Leon F Seltzer Ph.D.
The Interpersonal Effects of Anger and Happiness in Negotiations
Get mad and get more than even: When and why anger expression is effective in negotiations
How To Manage Anger, Stay Calm And Live A Good Life
Anger and advancement versus sadness and subjugation: the effect of negative emotion expressions on social status conferral
{{Authority control Emotions Seven deadly sins Violence
 Anger, also known as wrath or
Anger, also known as wrath or rage
Rage may refer to:
* Rage (emotion), an intense form of anger
Games
* Rage (collectible card game), a collectible card game
* Rage (trick-taking card game), a commercial variant of the card game Oh Hell
* ''Rage'' (video game), a 2011 first-per ...
, is an intense emotional state involving a strong uncomfortable and non-cooperative response to a perceived provocation, hurt or threat.
A person experiencing anger will often experience physical effects, such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and increased levels of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Some view anger as an emotion which triggers part of the fight or flight response. Anger becomes the predominant feeling behaviorally, cognitively, and physiologically when a person makes the conscious choice to take action to immediately stop the threatening behavior of another outside force. The English word originally comes from the term ''anger'' from the Old Norse language.
Anger can have many physical and mental consequences. The external expression of anger can be found in facial expressions, body language, physiological responses, and at times public acts of aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
. Facial expressions can range from inward angling of the eyebrows to a full frown.Michael Kent, ''Anger'', The Oxford Dictionary of Sports Science & Medicine, Oxford University Press, While most of those who experience anger explain its arousal as a result of "what has happened to them", psychologists point out that an angry person can very well be mistaken because anger causes a loss in self-monitoring capacity and objective observability.Raymond W. Novaco, ''Anger'', Encyclopedia of Psychology, Oxford University Press, 2000
Modern psychologists view anger as a normal, natural, and mature emotion experienced by virtually all humans at times, and as something that has functional value for survival. Uncontrolled anger can negatively affect personal or social well-beingJohn W. Fiero, ''Anger'', Ethics, Revised Edition, Vol 1 and negatively impact those around them. While many philosophers and writers have warned against the spontaneous and uncontrolled fits of anger, there has been disagreement over the intrinsic value of anger. The issue of dealing with anger has been written about since the times of the earliest philosophers, but modern psychologists, in contrast to earlier writers, have also pointed out the possible harmful effects of suppressing anger.
Psychology and sociology
 Three types of anger are recognized by psychologists:Paul M. Hughes, ''Anger'', Encyclopedia of Ethics, Vol I, Second Edition, Rutledge Press
#''Hasty and sudden anger'' is connected to the impulse for self-preservation. It is shared by human and other animals, and it occurs when the animal feels tormented or trapped. This form of anger is episodic.
#''Settled and deliberate anger'' is a reaction to perceived ''deliberate'' harm or unfair treatment by others. This form of anger is episodic.
#''Dispositional anger'' is related more to character traits than to instincts or cognitions. Irritability, sullenness, and churlishness are examples of the last form of anger.
Anger can potentially mobilize psychological resources and boost determination toward correction of wrong behaviors, promotion of social justice, communication of negative sentiment, and redress of grievances. It can also facilitate patience. In contrast, anger can be destructive when it does not find its appropriate outlet in expression. Anger, in its strong form, impairs one's ability to process information and to exert cognitive control over one's
Three types of anger are recognized by psychologists:Paul M. Hughes, ''Anger'', Encyclopedia of Ethics, Vol I, Second Edition, Rutledge Press
#''Hasty and sudden anger'' is connected to the impulse for self-preservation. It is shared by human and other animals, and it occurs when the animal feels tormented or trapped. This form of anger is episodic.
#''Settled and deliberate anger'' is a reaction to perceived ''deliberate'' harm or unfair treatment by others. This form of anger is episodic.
#''Dispositional anger'' is related more to character traits than to instincts or cognitions. Irritability, sullenness, and churlishness are examples of the last form of anger.
Anger can potentially mobilize psychological resources and boost determination toward correction of wrong behaviors, promotion of social justice, communication of negative sentiment, and redress of grievances. It can also facilitate patience. In contrast, anger can be destructive when it does not find its appropriate outlet in expression. Anger, in its strong form, impairs one's ability to process information and to exert cognitive control over one's behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as wel ...
. An angry person may lose their objectivity, empathy, prudence or thoughtfulness and may cause harm to themselves or others. There is a sharp distinction between anger and aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
(verbal or physical, direct or indirect) even though they mutually influence each other. While anger can activate aggression or increase its probability or intensity, it is neither a necessary nor a sufficient condition for aggression.
Neuropsychological perspective
Extension of the stimuli of the fighting reactions: At the beginning of life, the human infant struggles indiscriminately against any restraining force, whether it be another human being or a blanket which confines their movements. There is no inherited susceptibility to social stimuli as distinct from other stimulation, in anger. At a later date the child learns that certain actions, such as striking, scolding, and screaming, are effective toward persons, but not toward things. In adults, though the infantile response is still sometimes seen, the fighting reaction becomes fairly well limited to stimuli whose hurting or restraining influence can be thrown off by physical violence.Fundamental Activities—Inherited and LearnedDifferences between related concepts
Raymond Novaco of University of California Irvine, who since 1975 has published a plethora of literature on the subject, stratified anger into three modalities: cognitive (appraisals),somatic
Somatic may refer to:
* Somatic (biology), referring to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells
** Somatic cell, a non-gametic cell in a multicellular organism
* Somatic nervous system, the portion of the vertebrate nervous sys ...
- affective (tension and agitations), and behavioral (withdrawal and antagonism).
The words annoyance and rage
Rage may refer to:
* Rage (emotion), an intense form of anger
Games
* Rage (collectible card game), a collectible card game
* Rage (trick-taking card game), a commercial variant of the card game Oh Hell
* ''Rage'' (video game), a 2011 first-per ...
are often imagined to be at opposite ends of an emotional continuum: mild irritation and annoyance at the low end and fury or murderous rage at the high end. Rage problems are conceptualized as "the inability to process emotions or life's experiences"Parker Hall, 2008, ''Anger, Rage and Relationship: An Empathic Approach to Anger Management'', Routledge either because the capacity to regulate emotion (Schore, 1994) has never been sufficiently developed or because it has been temporarily lost due to more recent trauma. Rage is understood as raw, undifferentiated emotions, that spill out when another life event that cannot be processed, no matter how trivial, puts more stress on the organism than it can bear.
Anger, when viewed as a protective response or instinct to a perceived threat, is considered as positive. The negative expression of this state is known as aggression. Acting on this misplaced state is rage due to possible potential errors in perception and judgment.
Examples
Characteristics
 William DeFoore, an anger management writer, described anger as a pressure cooker, stating that "we can only suppress or apply pressure against our happy for so long before it erupts".
One simple dichotomy of anger expression is ''passive anger'' versus ''aggressive anger'' versus ''assertive anger''. These three types of anger have some characteristic symptoms:
William DeFoore, an anger management writer, described anger as a pressure cooker, stating that "we can only suppress or apply pressure against our happy for so long before it erupts".
One simple dichotomy of anger expression is ''passive anger'' versus ''aggressive anger'' versus ''assertive anger''. These three types of anger have some characteristic symptoms:
Passive anger
Passive anger can be expressed in the following ways: * '' Dispassion'', such as giving someone the cold shoulder or a fake smile, looking unconcerned or " sitting on the fence" while others sort things out, dampening feelings withsubstance abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
, overreacting, oversleeping, not responding to another's anger, frigidity, indulging in sexual practices that depress spontaneity and make objects of participants, giving inordinate amounts of time to machines, objects or intellectual pursuits, talking of frustrations but showing no feeling.
* '' Evasiveness'', such as turning one's back in a crisis, avoiding conflict, not arguing back, becoming phobic
A phobia is an anxiety disorder defined by a persistent and excessive fear of an object or situation. Phobias typically result in a rapid onset of fear and are usually present for more than six months. Those affected go to great lengths to avo ...
.
* '' Defeatism'', such as setting people up for failure, choosing unreliable people to depend on, being accident prone, underachieving, sexual impotence, expressing frustration at insignificant things but ignoring serious ones.
* '' Obsessive behavior'', such as needing to be inordinately clean and tidy, making a habit of constantly checking things, over-dieting or overeating, demanding that all jobs be done perfectly.
* '' Psychological manipulation'', such as provoking people to aggression and then patronizing them, provoking aggression but staying on the sidelines, emotional blackmail, false tearfulness, feigning illness, sabotaging relationships, using sexual provocation, using a third party to convey negative feelings, withholding money or resources.
* '' Secretive behavior'', such as stockpiling resentments that are expressed behind people's backs, giving the silent treatment or under-the-breath mutterings, avoiding eye contact, putting people down, gossiping, anonymous complaints, poison pen letters, stealing
Theft is the act of taking another person's property or services without that person's permission or consent with the intent to deprive the rightful owner of it. The word ''theft'' is also used as a synonym or informal shorthand term for some ...
, and conning.
* '' Self-blame'', such as apologizing too often, being overly critical, inviting criticism
Criticism is the construction of a judgement about the negative qualities of someone or something. Criticism can range from impromptu comments to a written detailed response. , ''"the act of giving your opinion or judgment about the good or bad q ...
.
Aggressive anger
The symptoms of aggressive anger are: * ''Bullying
Bullying is the use of force, coercion, hurtful teasing or threat, to abuse, aggressively dominate or intimidate. The behavior is often repeated and habitual. One essential prerequisite is the perception (by the bully or by others) of an imba ...
'', such as threatening people directly, persecuting, insulting, pushing or shoving, using power to oppress, shouting, driving someone off the road, playing on people's weaknesses
Weakness or asthenia is a symptom of a number of different conditions.
Weakness may also refer to:
* Muscle weakness, the inability to exert force with one's muscles
* '' The Weakness'', the thirty-seventh book in the ''Animorphs'' series
* "Wea ...
.
* ''Destruction'', such as destroying objects as in vandalism, harming animals, child abuse
Child abuse (also called child endangerment or child maltreatment) is physical, sexual, and/or psychological maltreatment or neglect of a child or children, especially by a parent or a caregiver. Child abuse may include any act or failure to a ...
, destroying a relationship, reckless driving
In United States law, reckless driving is a major moving traffic violation that generally consists in driving a vehicle with willful or wanton disregard for the safety of persons or property. It is usually a more serious offense than careless ...
, substance abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
.
* '' Grandiosity'', such as showing off, expressing mistrust, not delegating, being a sore loser, wanting center stage all the time, not listening, talking over people's heads, expecting kiss and make-up sessions to solve problems.
* ''Hurtfulness'', such as violence, including sexual abuse and rape, verbal abuse, biased or vulgar jokes, breaking confidence, using foul language
Profanity, also known as cursing, cussing, swearing, bad language, foul language, obscenities, expletives or vulgarism, is a socially offensive use of language. Accordingly, profanity is language use that is sometimes deemed impolite, rud ...
, ignoring people's feelings, willfully discriminating, blaming
Blame is the act of censuring, holding responsible, or making negative statements about an individual or group that their actions or inaction are socially or morally irresponsible, the opposite of praise. When someone is morally responsible for d ...
, punishing people for unwarranted deeds, labeling others.
* ''Risk-taking behavior'', such as speaking too fast, walking too fast, driving too fast, reckless spending.
* '' Selfishness'', such as ignoring others' needs, not responding to requests for help, queue jumping
Cutting in line, also known as line/queue jumping, butting, barging, budging, bunking, skipping, breaking, ditching, shorting, pushing in, or cutsies, is the act of entering a queue or line at any position other than the end. The act is extremely ...
.
* '' Threats'', such as frightening people by saying how one could harm them, their property or their prospects, finger pointing, fist shaking, wearing clothes or symbols associated with violent behavior, tailgating, excessively blowing a car horn, slamming doors.
* ''Unjust blaming
Blame is the act of censuring, holding responsible, or making negative statements about an individual or group that their actions or inaction are socially or morally irresponsible, the opposite of praise. When someone is morally responsible for d ...
'', such as accusing other people for one's own mistakes, blaming people for person's own feelings, making general accusations.
* '' Unpredictability'', such as explosive rages over minor frustrations, attacking indiscriminately, dispensing unjust punishment
Punishment, commonly, is the imposition of an undesirable or unpleasant outcome upon a group or individual, meted out by an authority—in contexts ranging from child discipline to criminal law—as a response and deterrent to a particular acti ...
, inflicting harm on others for the sake of it, illogical arguments.
* ''Vengeance
Vengeance may refer to:
*Vengeance (concept) or revenge, a harmful action against a person or group in response to a grievance
Film
* ''Vengeance'' (1930 film), action adventure film directed by Archie Mayo
* ''Vengeance'' (1937 film) or ''W ...
'', such as being over-punitive. This differs from retributive justice, as vengeance is personal, and possibly unlimited in scale.
Assertive anger
* '' Blame'', such as after a particular individual commits an action that's possibly frowned upon, the particular person will resort to scolding. This is in fact, common in discipline terms. * ''Punishment
Punishment, commonly, is the imposition of an undesirable or unpleasant outcome upon a group or individual, meted out by an authority—in contexts ranging from child discipline to criminal law—as a response and deterrent to a particular acti ...
'', the angry person will give a temporary punishment to an individual like further limiting a child's will to do anything they want like playing video games, reading, (excluding schoolwork) etc., after they did something to cause trouble.
* ''Sternness'', such as calling out a person on their behaviour, with their voices raised with utter disapproval/disappointment.
Six dimensions of anger expression
Anger expression can take on many more styles than passive or aggressive. Ephrem Fernandez has identified six dimensions of anger expression. They relate to the direction of anger, its locus, reaction, modality, impulsivity, and objective. Coordinates on each of these dimensions can be connected to generate a profile of a person's anger expression style. Among the many profiles that are theoretically possible in this system, are the familiar profile of the person with explosive anger, profile of the person with repressive anger, profile of thepassive aggressive
Passive-aggressive behavior is characterized by a pattern of passive hostility and an avoidance of direct communication. Inaction where some action is socially customary is a typical passive-aggressive strategy (showing up late for functions, st ...
person, and the profile of constructive anger expression.
Ethnicity and culture
Much research has explored whether the emotion of anger is experienced and expressed differently depending on the culture. Matsumoto (2007) conducted a study in which White-American and Asian participants needed to express the emotions from a program called JACFEE (Japanese and Caucasian Facial Expression of Emotion) in order to determine whether Caucasian observers noticed any differences in expression of participants of a different nationality. He found that participants were unable to assign a nationality to people demonstrating expression of anger, i.e. they could not distinguish ethnic-specific expressions of anger. Hatfield, Rapson, and Le (2009) conducted a study that measured ethnic differences in emotional expression using participants from the Philippines, Hawaii, China, and Europe. They concluded that there was a difference between how someone expresses an emotion, especially the emotion of anger in people with different ethnicities, based on frequency, with Europeans showing the lowest frequency of expression of negative emotions. Other research investigates anger within different ethnic groups who live in the same country. Researchers explored whether Black Americans experience and express greater anger than Whites (Mabry & Kiecolt, 2005). They found that, after controlling for sex and age, Black participants did not feel or express more anger than Whites. Deffenbacher and Swaim (1999) compared the expression of anger in Mexican American people and White non-Hispanic American people. They concluded that White non-Hispanic Americans expressed more verbal aggression than Mexican Americans, although when it came to physical aggression expressions there was no significant difference between both cultures when it came to anger.Causes
Some animals make loud sounds, attempt to look physically larger, bare their teeth, and stare.Primate Ethology, 1967, Desmond Morris (Ed.). Weidenfeld & Nicolson Publishers: London, p. 55 The behaviors associated with anger are designed to warn aggressors to stop their threatening behavior. Rarely does a physical altercation occur without the prior expression of anger by at least one of the participants. Displays of anger can be used as amanipulation
Manipulation may refer to:
* Manipulation (psychology) - the action of manipulating someone in a clever or unscrupulous way
* Crowd manipulation - use of crowd psychology to direct the behavior of a crowd toward a specific action
::*Internet mani ...
strategy for social influence.
People feel really angry when they sense that they or someone they care about has been offended, when they are certain about the nature and cause of the angering event, when they are convinced someone else is responsible, and when they feel they can still influence the situation or cope with it.International Handbook of Anger. p. 290 For instance, if a person's car is damaged, they will feel angry if someone else did it (e.g. another driver rear-ended it), but will feel sadness instead if it was caused by situational forces (e.g. a hailstorm) or guilt and shame if they were personally responsible (e.g. they crashed into a wall out of momentary carelessness). Psychotherapist Michael C. Graham defines anger in terms of our expectations and assumptions about the world. Graham states anger almost always results when we are caught up "...expecting the world to be different than it is".
Usually, those who experience anger explain its arousal as a result of "what has happened to them" and in most cases the described provocations occur immediately before the anger experience. Such explanations confirm the illusion that anger has a discrete external cause. The angry person usually finds the cause of their anger in an intentional, personal, and controllable aspect of another person's behavior. This explanation is based on the intuitions of the angry person who experiences a loss in self-monitoring capacity and objective observability as a result of their emotion. Anger can be of multicausal origin, some of which may be remote events, but people rarely find more than ''one'' cause for their anger. According to Novaco, "Anger experiences are embedded or nested within an environmental-temporal context. Disturbances that may not have involved anger at the outset leave residues that are not readily recognized but that operate as a lingering backdrop for focal provocations (of anger)." According to Encyclopædia Britannica, an internal infection can cause pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
which in turn can activate anger."emotion". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Encyclopædia Britannica Online, p. 11 According to cognitive consistency theory, anger is caused by an inconsistency between a desired, or expected, situation and the actually perceived situation, and triggers responses, such as aggressive behavior, with the expected consequence of reducing the inconsistency.
Cognitive effects
Anger causes a reduction in cognitive ability and the accurate processing of external stimuli. Dangers seem smaller, actions seem less risky, ventures seem more likely to succeed, and unfortunate events seem less likely. Angry people are more likely to make risky decisions, and make less realistic risk assessments. In one study, test subjects primed to feel angry felt less likely to have heart disease, and more likely to receive a pay raise, compared to fearful people. This tendency can manifest in retrospective thinking as well: in a 2005 study, angry subjects said they thought the risks of terrorism in the year following9/11
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial ...
in retrospect were low, compared to what the fearful and neutral subjects thought.
In inter-group relationships, anger makes people think in more negative and prejudiced terms about outsiders. Anger makes people less trusting, and slower to attribute good qualities to outsiders.
When a group is in conflict with a rival group, it will feel more anger if it is the politically stronger group and less anger when it is the weaker.
Unlike other negative emotions like sadness and fear, angry people are more likely to demonstrate correspondence bias
In social psychology, fundamental attribution error (FAE), also known as correspondence bias or attribution effect, is the tendency for people to under-emphasize situational and environmental explanations for an individual's observed behavior whil ...
– the tendency to blame a person's behavior more on his nature than on his circumstances. They tend to rely more on stereotypes, and pay less attention to details and more attention to the superficial. In this regard, anger is unlike other "negative" emotions such as sadness and fear, which promote analytical thinking.
An angry person tends to anticipate other events that might cause them anger. They will tend to rate anger-causing events (e.g. being sold a faulty car) as more likely than sad events (e.g. a good friend moving away).
A person who is angry tends to place more blame on another person for their misery. This can create a feedback, as this extra blame can make the angry person angrier still, so they in turn place yet more blame on the other person.
When people are in a certain emotional state, they tend to pay more attention to, or remember, things that are charged with the same emotion; so it is with anger. For instance, if a person is trying to persuade someone that a tax increase is necessary, if the person is currently feeling angry, they would do better to use an argument that elicits anger ("more criminals will escape justice") than, say, an argument that elicits sadness ("there will be fewer welfare benefits for disabled children"). Also, unlike other negative emotions, which focus attention on all negative events, anger only focuses attention on anger-causing events.
Anger can make a person more desiring of an object to which his anger is tied. In a 2010 Dutch study, test subjects were primed to feel anger or fear by being shown an image of an angry or fearful face, and then were shown an image of a random object. When subjects were made to feel angry, they expressed more desire to possess that object than subjects who had been primed to feel fear.
Expressive strategies
As with any emotion, the display of anger can be feigned or exaggerated. Studies by Hochschild and Sutton have shown that the show of anger is likely to be an effective manipulation strategy in order to change and design attitudes. Anger is a distinct strategy of social influence and its use (e.g. belligerent behaviors) as a goal achievement mechanism proves to be a successful strategy.Sutton, R.I. ''Maintaining norms about expressed emotions: The case of bill collectors'', Administrative Science Quarterly, 1991, 36:245–268Hochschild, AR, ''The managed heart: Commercialization of human feeling'', University of California Press, 1983 Larissa Tiedens, known for her studies of anger, claimed that expression of feelings would cause a powerful influence not only on the perception of the expresser but also on theirpower position
Power position is a concept from Feng Shui, the ancient Chinese practice of studying one's position within one's surroundings.
In Feng Shui, the Power Position or "Dragon Seat" is the physical position in the room for a business meeting, which ...
in the society. She studied the correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics ...
between anger expression and social influence perception. Previous researchers, such as Keating, 1985 have found that people with angry face expression were perceived as powerful and as in a high social position
Social position is the position of an individual in a given society and culture. A given position (for example, the occupation of ''priest'') may belong to many individuals.
Definition
Stanley Wasserman and Katherine Faust Stanley cautioned th ...
. Similarly, Tiedens et al. have revealed that people who compared scenarios involving an angry and a sad character, attributed a higher social status
Social status is the level of social value a person is considered to possess. More specifically, it refers to the relative level of respect, honour, assumed competence, and deference accorded to people, groups, and organizations in a society. Stat ...
to the angry character. Tiedens examined in her study whether anger expression promotes status attribution. In other words, whether anger contributes to perceptions or legitimization of others' behaviors. Her findings clearly indicated that participants who were exposed to either an angry or a sad person were inclined to express support for the angry person rather than for a sad one. In addition, it was found that a reason for that decision originates from the fact that the person expressing anger was perceived as an ability owner, and was attributed a certain social status accordingly.
Showing anger during a negotiation may increase the ability of the anger expresser to succeed in negotiation. A study by Tiedens et al. indicated that the anger expressers were perceived as stubborn, dominant and powerful. In addition, it was found that people were inclined to easily give up to those who were perceived by them as powerful and stubborn, rather than soft and submissive. Based on these findings Sinaceur and Tiedens have found that people conceded more to the angry side rather than for the non-angry one.
A question raised by Van Kleef et al. based on these findings was whether expression of emotion influences others, since it is known that people use emotional information to conclude about others' limits and match their demands in negotiation accordingly. Van Kleef et al. wanted to explore whether people give up more easily to an angry opponent or to a happy opponent. Findings revealed that participants tended to be more flexible toward an angry opponent compared with a happy opponent. These results strengthen the argument that participants analyze the opponent's emotion to conclude about their limits and carry out their decisions accordingly.
Coping strategies
Therapy and behavioral strategies
According to Leland R. Beaumont, each instance of anger demands making a choice. A person can respond withhostile
Hostility is seen as form of emotionally charged aggressive behavior. In everyday speech it is more commonly used as a synonym for anger and aggression.
It appears in several psychological theories. For instance it is a facet of neuroticism in ...
action, including overt violence, or they can respond with hostile inaction, such as withdrawing or stonewalling. Other options include initiating a dominance contest; harboring resentment; or working to better understand and constructively resolve the issue.
According to Raymond Novaco, there are a multitude of steps that were researched in attempting to deal with this emotion. In order to manage anger the problems involved in the anger should be discussed, Novaco suggests. The situations leading to anger should be explored by the person.
Conventional therapies for anger involve restructuring thoughts and beliefs to bring about a reduction in anger. These therapies often come within the schools of CBT (or cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions (suc ...
) like modern systems such as REBT ( rational emotive behavior therapy). Research shows that people with excessive anger often harbor and act on dysfunctional attributions, assumptions and evaluations in specific situations. It has been shown that with therapy by a trained professional, individuals can bring their anger to more manageable levels. The therapy is followed by the so-called "stress inoculation" in which the clients are taught "relaxation skills to control their arousal and various cognitive controls to exercise on their attention, thoughts, images, and feelings. "Logic defeats anger, because anger, even when it's justified, can quickly become irrational." ( American Psychological Association). In other words, although there may be a rational reason to get angry, the frustrated actions of the subject can become irrational. Taking deep breaths is regarded as the first step to calming down. Once the anger has subsided a little, the patient will accept that they are frustrated and move on. Lingering around the source of frustration may bring the rage back.
The skills-deficit model states that poor social skills
A social skill is any competence facilitating interaction and communication with others where social rules and relations are created, communicated, and changed in verbal and nonverbal ways. The process of learning these skills is called social ...
is what renders a person incapable of expressing anger in an appropriate manner. Social skills training has been found to be an effective method for reducing exaggerated anger by offering alternative coping skills to the angry individual. Research has found that persons who are prepared for aversive events find them less threatening, and excitatory reactions are significantly reduced. In a 1981 study, that used modeling, behavior rehearsal, and videotaped feedback to increase anger control skills, showed increases in anger control among aggressive youth in the study. Research conducted with youthful offenders using a social skills training program (aggression replacement training), found significant reductions in anger, and increases in anger control. Research has also found that antisocial personalities are more likely to learn avoidance tasks when the consequences involved obtaining or losing tangible rewards. Learning among antisocial personalities also occurred better when they were involved with high intensity stimulation. Social learning theory states that positive stimulation was not compatible with hostile or aggressive reactions. Anger research has also studied the effects of reducing anger among adults with antisocial personality disorder (ASPD), with a social skills program approach that used a low fear and high arousal group setting. This research found that low fear messages were less provocative to the ASPD population, and high positive arousal stimulated their ability to concentrate, and subsequently learn new skills for anger reduction.
A new integrative approach to anger treatment has been formulated by Fernandez (2010). Termed CBAT, for cognitive behavioral affective therapy, this treatment goes beyond conventional relaxation and reappraisal by adding cognitive and behavioral techniques and supplementing them with effective techniques to deal with the feeling of anger. The techniques are sequenced contingently in three phases of treatment: prevention, intervention, and postvention. In this way, people can be trained to deal with the onset of anger, its progression, and the residual features of anger.
Medication therapy
Systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
s and meta-analyses suggest that certain psychiatric medications may be effective in controlling symptoms of anger, hostility, and irritability. These include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, hea ...
s like sertraline, certain anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
mood stabilizers, antipsychotics like aripiprazole, risperidone, and olanzapine, and benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
s like midazolam, among others. Another meta-analysis of antidepressants and aggression found no change in aggression in adults and increased aggression in children. Psychostimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and inv ...
s like methylphenidate and amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
s as well as the atypical antipsychotic risperidone are useful in reducing aggression and oppositionality in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), with moderate to large effect sizes and greater effectiveness than other studied medications. Yet another meta-analysis found that methylphenidate slightly reduced irritability while amphetamines increased the risk of irritability several-fold in children with ADHD.
Suppression
Modern psychologists point out that suppression of anger may have harmful effects. The suppressed anger may find another outlet, such as a physical symptom, or become more extreme. John W. Fiero citesLos Angeles riots of 1992
The 1992 Los Angeles riots, sometimes called the 1992 Los Angeles uprising and the Los Angeles Race Riots, were a series of riots and civil disturbances that occurred in Los Angeles County, California, in April and May 1992. Unrest began in S ...
as an example of sudden, explosive release of suppressed anger. The anger was then displaced as violence against those who had nothing to do with the matter. There is also the case of Francine Hughes
Francine Moran Hughes (later Wilson; August 17, 1947 – March 22, 2017) was an American woman who, after thirteen years of domestic abuse
Domestic violence (also known as domestic abuse or family violence) is violence or other abuse that o ...
, who suffered 13 years of domestic abuse. Her suppressed anger drove her to kill her abuser husband. It is claimed that a majority of female victims of domestic violence who suppress their aggressive feelings are unable to recognize, experience, and process negative emotion and this has a destabilizing influence on their perception of agency in their relationships. Another example of widespread deflection of anger from its actual cause toward scapegoating, Fiero says, was the blaming of Jews for the economic ills of Germany by the Nazis.
Some psychologists criticized the catharsis theory of aggression, which suggests that releasing pent-up anger reduces aggression. On the other hand, there are experts who maintain that suppression does not eliminate anger since it merely forbids the expression of anger and this is also the case for repression, which merely hides anger from awareness. There are also studies that link suppressed anger and medical conditions such as hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pla ...
, and cancer. Suppressed or repressed anger is found to cause irritable bowel syndrome, eating disorder
An eating disorder is a mental disorder defined by abnormal eating behaviors that negatively affect a person's physical or mental health. Only one eating disorder can be diagnosed at a given time. Types of eating disorders include binge eating d ...
s, and depression among women. Suppression is also referred to as a form of "self-silencing", which is described as a cognitive activity wherein an individual monitors the self and eliminate thoughts and feelings that are perceived to be dangerous to relationships. Anger suppression is also associated with higher rates of suicide.
Dual threshold model
Anger expression might have negative outcomes for individuals and organizations as well, such as decrease of productivity. and increase of job stress, It could also have positive outcomes, such as increased work motivation, improved relationships and increased mutual understanding (for ex. Tiedens, 2000). A Dual Threshold Model of Anger in organizations by Geddes and Callister, (2007) provides an explanation on the valence of anger expression outcomes. The model suggests that organizational norms establish emotion thresholds that may be crossed when employees feel anger. The first "expression threshold" is crossed when an organizational member conveys felt anger to individuals at work who are associated with or able to address the anger-provoking situation. The second "impropriety threshold" is crossed if or when organizational members go too far while expressing anger such that observers and other company personnel find their actions socially and/or culturally inappropriate. The higher probability of negative outcomes from workplace anger likely will occur in either of two situations. The first is when organizational members suppress rather than express their anger—that is, they fail to cross the "expression threshold". In this instance personnel who might be able to address or resolve the anger-provoking condition or event remain unaware of the problem, allowing it to continue, along with the affected individual's anger. The second is when organizational members cross both thresholds—"double cross"— displaying anger that is perceived as deviant. In such cases the angry person is seen as the problem—increasing chances of organizational sanctions against him or her while diverting attention away from the initial anger-provoking incident. In contrast, a higher probability of positive outcomes from workplace anger expression likely will occur when one's expressed anger stays in the space between the expression and impropriety thresholds. Here, one expresses anger in a way fellow organizational members find acceptable, prompting exchanges and discussions that may help resolve concerns to the satisfaction of all parties involved. This space between the thresholds varies among different organizations and also can be changed in organization itself: when the change is directed to support anger displays; the space between the thresholds will be expanded and when the change is directed to suppressing such displays; the space will be reduced.Physiology
 Neuroscience has shown that emotions are generated by multiple structures in the brain. The rapid, minimal, and evaluative processing of the emotional significance of the sensory data is done when the data passes through the amygdala in its travel from the sensory organs along certain neural pathways towards the limbic forebrain. Emotion caused by discrimination of stimulus features, thoughts, or memories occurs when its information is relayed from the thalamus to the
Neuroscience has shown that emotions are generated by multiple structures in the brain. The rapid, minimal, and evaluative processing of the emotional significance of the sensory data is done when the data passes through the amygdala in its travel from the sensory organs along certain neural pathways towards the limbic forebrain. Emotion caused by discrimination of stimulus features, thoughts, or memories occurs when its information is relayed from the thalamus to the neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
. Based on some statistical analysis
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying distribution of probability.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical analysis infers propertie ...
, some scholars have suggested that the tendency for anger may be genetic. Distinguishing between genetic and environmental factors requires further research and actual measurement of specific genes and environments.
In neuroimaging studies of anger, the most consistently activated region of the brain was the lateral orbitofrontal cortex. This region is associated with approach motivation and positive affective processes.
The external expression of anger can be found in physiological responses, facial expressions, body language, and at times in public acts of aggression. The rib cage tenses and breathing
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular ...
through the nose becomes faster, deeper, and irregular. Anger activates the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. The catecholamine activation is more strongly norepinephrine than epinephrin
Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, is a medication and hormone. As a medication, it is used to treat several conditions, including anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, asthma, and superficial bleeding. Inhaled epinephrine may be used to improve th ...
e. Heart rate and blood pressure increase. Blood flows to the hands. Perspiration increases (particularly when the anger is intense). The face flushes. The nostrils flare. The jaw tenses. The brow muscles move inward and downward, fixing a hard stare on the target. The arms are raised and a squared-off stance is adopted. The body is mobilized for immediate action, often manifesting as a subjective sense of strength, self-assurance, and potency. This may encourage the impulse to strike out.
Measuring Anger
The Gallup World Poll
Every year,Gallup
Gallup may refer to:
*Gallup, Inc., a firm founded by George Gallup, well known for its opinion poll
*Gallup (surname), a surname
*Gallup, New Mexico, a city in New Mexico, United States
**Gallup station, an Amtrak train in downtown Gallup, New Me ...
asks people in over 140 countries, "did you experience anger during a lot of the day yesterday?" In 2021, Gallup found that 23% of adults experienced a lot of anger, which is up from 18% in 2014. The countries that experienced the most anger were Lebanon, Turkey, Armenia, Iraq, and Afghanistan; the countries that experience the least anger were Finland, Mauritius, Estonia, Portugal, and the Netherlands.
Philosophical perspectives

Ancient history
Ancient Greek philosophers, describing and commenting on the uncontrolled anger, particularly toward slaves, in their society generally showed a hostile attitude towards anger. Galen and Seneca regarded anger as a kind of madness. They all rejected the spontaneous, uncontrolled fits of anger and agreed on both the possibility and value of controlling anger. There were disagreements regarding the value of anger. For Seneca, anger was "worthless even for war". Seneca believed that the disciplinedRoman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval continu ...
was regularly able to beat the Germans, who were known for their fury. He argued that "...in sporting contests, it is a mistake to become angry".
Aristotle on the other hand, ascribed some value to anger that has arisen from perceived injustice because it is useful for preventing injustice. Furthermore, the opposite of anger is a kind of insensibility, Aristotle stated. The difference in people's temperaments was generally viewed as a result of the different mix of qualities or humors people contained. Seneca held that "red-haired and red-faced people are hot-tempered because of excessive hot and dry humors". Ancient philosophers rarely refer to women's anger at all, according to Simon Kemp and K.T. Strongman perhaps because their works were not intended for women. Some of them that discuss it, such as Seneca, considered women to be more prone to anger than men.
Control methods
Seneca addresses the question of mastering anger in three parts: 1. how to avoid becoming angry in the first place 2. how to cease being angry and 3. how to deal with anger in others. Seneca suggests, to avoid becoming angry in the first place, that the many faults of anger should be repeatedly remembered. One should avoid being too busy or dealing with anger-provoking people. Unnecessary hunger or thirst should be avoided and soothing music be listened to. To cease being angry, Seneca suggests Seneca further advises daily self-inquisition about one's bad habit. To deal with anger in others, Seneca suggests that the best reaction is to keep calm. A certain kind of deception, Seneca says, is necessary in dealing with angry people. Galen repeats Seneca's points but adds a new one: finding a guide and teacher can help the person in controlling their passions. Galen also gives some hints for finding a good teacher. Both Seneca and Galen (and later philosophers) agree that the process of controlling anger should start in childhood on grounds of malleability. Seneca warns that this education should not blunt the spirit of the children nor should they be humiliated or treated severely. At the same time, they should not be pampered. Children, Seneca says, should learn not to beat their playmates and not to become angry with them. Seneca also advises that children's requests should not be granted when they are angry.Post-classical history
During the period of the Roman Empire and the Middle Ages, philosophers elaborated on the existing conception of anger, many of whom did not make major contributions to the concept. For example, many medieval philosophers such asIbn Sina
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
(Avicenna), Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empiri ...
and Thomas Aquinas agreed with ancient philosophers that animals cannot become angry. On the other hand, al-Ghazali (Algazel), who often disagreed with Aristotle and Ibn Sina on many issues, argued that animals do possess anger as one of the three "powers" in their heart, the other two being appetite
Appetite is the desire to eat food items, usually due to hunger. Appealing foods can stimulate appetite even when hunger is absent, although appetite can be greatly reduced by satiety. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to regu ...
and impulse. He also argued that animal will
Will may refer to:
Common meanings
* Will and testament, instructions for the disposition of one's property after death
* Will (philosophy), or willpower
* Will (sociology)
* Will, volition (psychology)
* Will, a modal verb - see Shall and will
...
is "conditioned by anger and appetite" in contrast to human will which is "conditioned by the intellect
In the study of the human mind, intellect refers to, describes, and identifies the ability of the human mind to reach correct conclusions about what is true and what is false in reality; and how to solve problems. Derived from the Ancient Gree ...
". A common medieval belief was that those prone to anger had an excess of yellow bile or choler (hence the word "choleric"). This belief was related to Seneca's belief that "red-haired and red-faced people are hot-tempered because of excessive hot and dry humors".
By gender
Wrath was sinful because of the social problems it caused, sometimes even homicide. It served to ignore those who are present, contradicts those who are absent, producesinsult
An insult is an expression or statement (or sometimes behavior) which is disrespectful or scornful. Insults may be intentional or accidental. An insult may be factual, but at the same time pejorative, such as the word "inbred".
Jocular exc ...
s, and responds harshly to insults that are received. Aristotle felt that anger or wrath was a natural outburst of self-defense in situations where people felt they had been wronged. Aquinas felt that if anger was justified, it was not a sin. For example, "He that is angry without cause, shall be in danger; but he that is angry with cause, shall not be in danger: for without anger, teaching will be useless, judgments unstable, crimes unchecked. Therefore to be angry is not always an evil."
The concept of wrath contributed to a definition of gender and power. Many medieval authors in 1200 agreed the differences between men and women were based on complexion, shape, and disposition. Complexion involved the balance of the four fundamental qualities of heat, coldness, moistness, and dryness. When various combinations of these qualities are made they define groups of certain people as well as individuals. Hippocrates, Aristotle, and Galen all agreed on that, in terms of biology and sexual differentiation, heat was the most important of the qualities because it determined shape and disposition. Disposition included a balance of the previous four qualities, the four elements and the four humors. For example, the element of fire shared the qualities of heat and dryness: fire dominated in yellow bile or choler, meaning a choleric person was more or hot and dry than others. Hot and dry individuals were active, dominant, and aggressive. The opposite was true with the element of water. Water, is cold and moist, related closely to phlegm: people with more phlegmatic personalities were passive and submissive. While these trait clusters varied from individual to individual most authors in the Middle Ages assumed certain clusters of traits characterized men more than women and vice versa.In the Garden of Evil: Vices and Culture in the Middle Ages. Richard Newhauser. PIMS, 2005
=Women
= Scholars posted that females were seen by authors in the Middle Ages to be more phlegmatic (cold and wet) than males, meaning females were more sedentary and passive than males. Women's passive nature appeared "natural" due to their lack of power when compared to men. Aristotle identified traits he believed women shared: female, feminine, passive, focused on matter, inactive, and inferior. Thus medieval women were supposed to act submissively toward men and relinquish control to their husbands. Hildegard of Bingen believed women were fully capable of anger. While most women were phlegmatic, individual women under certain circumstances could also be choleric.=Men
= Medieval scholars believed most men were choleric, or hot and dry. Thus they were dominant and aggressive. (Barton) Aristotle also identified characteristics of men: male, masculine, active, focused on form, potent, outstanding, and superior. Men were aware of the power they held. Given their choleric "nature", men exhibited hot temperatures and were quick to anger. Peter of Albano once said, "The male's spirit, is lively, given to violent impulse; t isslow getting angry and slower being calmed." Medieval ideas of gender assumed men were more rational than women. Masculinity involved a wide range of possible behaviors, and men were not angry all the time. Every man's humoral balance was different, some men were strong, others weak, also some more prone to wrath then others. There are those who view anger as a manly act. For instance, David Brakke maintained:Control methods
Maimonides considered being given to uncontrollable passions as a kind of illness. Like Galen, Maimonides suggested seeking out a philosopher for curing this illness just as one seeks out a physician for curing bodily illnesses. Roger Bacon elaborates Seneca's advices. Many medieval writers discuss at length the evils of anger and the virtues of temperance. In a discussion of confession,John Mirk
John Mirk was an Augustinian Canon Regular, active in the late 14th and early 15th centuries in Shropshire. He is noted as the author of widely copied, and later printed, books intended to aid parish priests and other clergy in their work. The ...
, an English 14th-century Augustinian writer, tells priests how to advise the penitent
Penance is any act or a set of actions done out of repentance for sins committed, as well as an alternate name for the Catholic, Lutheran, Eastern Orthodox, and Oriental Orthodox sacrament of Reconciliation or Confession. It also plays a part i ...
by considering the spiritual and social consequences of anger:
In '' The Canon of Medicine'', Ibn Sina
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
(Avicenna) modified the theory of temperaments and argued that anger heralded the transition of melancholia to mania, and explained that humidity inside the head can contribute to such mood disorders.
On the other hand, Ahmed ibn Sahl al-Balkhi classified anger (along with aggression) as a type of neurosis, while al-Ghazali argued that anger takes form in rage, indignation and revenge, and that "the powers of the soul become balanced if it keeps anger under control".
Modern perspectives
Immanuel Kant rejects revenge as vicious. Regarding the latter, David Hume argues that because "anger andhatred
Hatred is an intense negative emotional response towards certain people, things or ideas, usually related to opposition or revulsion toward something. Hatred is often associated with intense feelings of anger, contempt, and disgust. Hatred is s ...
are passions inherent in our very frame and constitution, the lack of them is sometimes evidence of weakness and imbecility". Martha Nussbaum
Martha Craven Nussbaum (; born May 6, 1947) is an American philosopher and the current Ernst Freund Distinguished Service Professor of Law and Ethics at the University of Chicago, where she is jointly appointed in the law school and the philosoph ...
has also agreed that even "great injustice" is no "excuse for childish and undisciplined behavior". Two main differences between the modern understanding and ancient understanding of anger can be detected, Kemp and Strongman state: one is that early philosophers were not concerned with possible harmful effects of the suppression of anger; the other is that, recently, studies of anger take the issue of gender differences into account. Soraya Chemaly has in contrast argued that anger is "a critically useful and positive emotion" which "warns us, as humans, that something is wrong and needs to change" when "being threatened with indignity, physical harm, humiliation and unfairness" and therefore "a powerful force for political good". Furthermore, she argues that women and minorities are not allowed to be angry to the same extent as white men. In a similar vein, Rebecca Traister has argued that holding back anger has been an impediment to the progress of women's rights.
The American psychologist Albert Ellis has suggested that anger, rage, and fury partly have roots in the philosophical meanings and assumptions through which human beings interpret transgression
Transgression may refer to:
Legal, religious and social
*Sin, a violation of God's Ten Commandments or other elements of God's moral law
*Crime, legal transgression, usually created by a violation of social or economic boundary
**In civil law ju ...
. According to Ellis, these emotions are often associated and related to the leaning humans have to absolutistically depreciating and damning other peoples' humanity when their personal rules and domain are transgressed.
Religious perspectives
Judaism
In Judaism, anger is a negative trait. In the Book of Genesis, Jacob condemned the anger that had arisen in his sons Simon and Levi: "Cursed be their anger, for it was fierce; and their wrath, for it was cruel." Kaufmann KohlerAnger
Jewish Encyclopedia
''The Jewish Encyclopedia: A Descriptive Record of the History, Religion, Literature, and Customs of the Jewish People from the Earliest Times to the Present Day'' is an English-language encyclopedia containing over 15,000 articles on th ...
Restraining oneself from anger is seen as noble and desirable, as Ethics of the Fathers states:
Maimonides rules that one who becomes angry is as though that person had worshipped idols. Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi explains that the parallel between anger and idol worship is that by becoming angry, one shows a disregard of Divine Providence
In theology, Divine Providence, or simply Providence, is God's intervention in the Universe. The term ''Divine Providence'' (usually capitalized) is also used as a title of God. A distinction is usually made between "general providence", which ...
– whatever had caused the anger was ultimately ordained from Above – and that through coming to anger one thereby denies the hand of God in one's life.
In its section dealing with ethical traits a person should adopt, the '' Kitzur Shulchan Aruch'' states: "Anger is also a very evil trait and it should be avoided at all costs. You should train yourself not to become angry even if you have a good reason to be angry."
In modern writing s, Rabbi Harold Kushner
Harold Samuel Kushner (born April 3, 1935) is a prominent American rabbi and author. He is a member of the Rabbinical Assembly of Conservative Judaism and served as the congregational rabbi of Temple Israel of Natick, in Natick, Massachusetts, ...
finds no grounds for anger toward God because "our misfortunes are none of His doing". In contrast to Kushner's reading of the Bible, David Blumenthal finds an "abusing God" whose "sometimes evil" actions evoke vigorous protest, but without severing the protester's relationship with God.
Christianity
Both Catholic and Protestant writers have addressed anger In different perspectives.Catholic
 Wrath is one of the Seven Deadly Sins in Catholicism; and yet the
Wrath is one of the Seven Deadly Sins in Catholicism; and yet the Catechism of the Catholic Church
The ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'' ( la, Catechismus Catholicae Ecclesiae; commonly called the ''Catechism'' or the ''CCC'') is a catechism promulgated for the Catholic Church by Pope John Paul II in 1992. It aims to summarize, in book for ...
states (canons 1772 and 1773) that anger is among the passions, and that "in the passions, as movements of the sensitive appetite, there is neither good nor evil". The neutral act of anger becomes the sin of wrath when it's directed against an innocent person, when it's unduly unbending or long-lasting, or when it desires excessive punishment. "If anger reaches the point of a deliberate desire to kill or seriously wound a neighbor, it is gravely against charity; it is a mortal sin" (CCC 2302). Hatred is the sin of desiring that someone else may suffer misfortune or evil, and is a mortal sin when one desires grave harm (CCC 2302-03).
Medieval Christianity
Christianity in the Middle Ages covers the history of Christianity from the fall of the Western Roman Empire (). The end of the period is variously defined. Depending on the context, events such as the conquest of Constantinople by the Ottoman ...
vigorously denounced wrath as one of the seven cardinal, or deadly sins Deadly Sins may refer to:
*Seven deadly sins
The seven deadly sins, also known as the capital vices or cardinal sins, is a grouping and classification of vices within Christian teachings. Although they are not directly mentioned in the Bibl ...
, but some Christian writers at times regarded the anger caused by injustice as having some value.Simon Kemp, K.T. Strongman, ''Anger theory and management: A historical analysis'', The American Journal of Psychology, Vol. 108, No. 3. (Autumn, 1995), pp. 397–417 Saint Basil viewed anger as a "reprehensible temporary madness". Joseph F. Delany in the Catholic Encyclopedia (1914) defines anger as "the desire of vengeance" and states that a reasonable vengeance and passion is ethical and praiseworthy. Vengeance is sinful when it exceeds its limits in which case it becomes opposed to justice and charity. For example, "vengeance upon one who has not deserved it, or to a greater extent than it has been deserved, or in conflict with the dispositions of law, or from an improper motive" are all sinful. An unduly vehement vengeance is considered a venial sin unless it seriously goes counter to the love of God or of one's neighbor.
A more positive view of anger is espoused by Roman Catholic pastoral theologian Henri J.M. Nouwen. Father Nouwen points to the spiritual benefits in anger toward God as found in both the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
and New Testament of the Bible. In the Bible, says Father Nouwen, "it is clear that only by expressing our anger and hatred directly to God will we come to know the fullness of both his love and our freedom".
Georges Bernanos illustrates Nouwen's position in his novel ''The Diary of a Country Priest''. The countess gave birth to the son she had long wanted, but the child died. She was fiercely angry. When the priest called, the countess vented her anger toward her daughter and husband, then at the priest who responded gently, "open your heart to od. The countess rejoined, "I've ceased to bother about God. When you've forced me to admit that I hate Him, will you be any better off?" The priest continued, "you no longer hate Him. Hate is indifference and contempt. Now at last you're face to face with Him... Shake your fist at Him, spit in His face, scourge Him." The countess did what the priest counseled. By confessing her hate, she was enabled to say, "all's well".
Protestant
 Everyone experiences anger, Andrew D. Lester observes, and furthermore anger can serve as "a spiritual friend, a spiritual guide, and a spiritual ally". Denying and suppressing anger is contrary to St. Paul's admonition in his
Everyone experiences anger, Andrew D. Lester observes, and furthermore anger can serve as "a spiritual friend, a spiritual guide, and a spiritual ally". Denying and suppressing anger is contrary to St. Paul's admonition in his Epistle to the Ephesians
The Epistle to the Ephesians is the tenth book of the New Testament. Its authorship has traditionally been attributed to Paul the Apostle but starting in 1792, this has been challenged as Deutero-Pauline, that is, pseudepigrapha written in Pau ...
4:26. When anger toward God is denied and suppressed, it interferes with an individual's relation with God. Expressing one's anger toward God can deepen the relationship. C. FitzSimons Allison
Christopher FitzSimons Allison (born March 5, 1927) is a retired American Anglican bishop and an author. He is known for his role in the Anglican realignment, which led to his participation in the controversial consecration in 2000 of two bishops ...
holds that "we worship God by expressing our honest anger at him".
Biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
scholar Leonard Pine concludes from his studies in the Book of Habakkuk
The Book of Habakkuk is the eighth book of the 12 minor prophets of the Bible. It is attributed to the prophet Habakkuk, and was probably composed in the late 7th century BC.
Of the three chapters in the book, the first two are a dialogue betwee ...
that "far from being a sin, proper remonstration with God is the activity of a healthy faith relationship with Him". Other biblical examples of anger toward God include the following:
* Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
was angry with God for mistreating his people: "Lord, why have you mistreated 'lit.'' done evil tothis people?" ( Book of Exodus 5:22).
* Naomi was angry with God after the death of her husband and two sons: "The Almighty has dealt bitterly with me. The Almighty has brought calamity upon me" (Book of Ruth
The Book of Ruth ( he, מגילת רות, ''Megilath Ruth'', "the Scroll of Ruth", one of the Five Megillot) is included in the third division, or the Writings (Ketuvim), of the Hebrew Bible. In most Christian canons it is treated as one of the ...
1:20–21 ''abr'').
* Elijah was angry with God after the son of the widow died: "O Lord my God, have you brought calamity even upon the widow with whom I am staying, by killing her son?" (1 Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books ...
17:20).
* Job was angry with God: "You have turned cruel to me; with the might of your hand you persecute me" (Book of Job
The Book of Job (; hbo, אִיּוֹב, ʾIyyōḇ), or simply Job, is a book found in the Ketuvim ("Writings") section of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh), and is the first of the Poetic Books in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. Scholars ar ...
30:21).
* Jeremiah was angry with God for deceiving his people: "Ah, Lord God, how utterly you have deceived this people and Jerusalem" (Book of Jeremiah
The Book of Jeremiah ( he, ספר יִרְמְיָהוּ) is the second of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible, and the second of the Prophets in the Christian Old Testament. The superscription at chapter Jeremiah 1:1–3 identifies the boo ...
4:10).
Hinduism
In Hinduism, anger is equated with sorrow as a form of unrequited desire. The objects of anger are perceived as a hindrance to the gratification of the desires of the angry person. Alternatively if one thinks one is superior, the result is grief. Anger is considered to be packed with more evil power than desire. In theBhagavad Gita
The Bhagavad Gita (; sa, श्रीमद्भगवद्गीता, lit=The Song by God, translit=śrīmadbhagavadgītā;), often referred to as the Gita (), is a 700- verse Hindu scripture that is part of the epic ''Mahabharata'' (c ...
, Krishna regards greed, anger, and lust as signs of ignorance that lead to perpetual bondage. As for the agitations of the bickering mind, they are divided into two divisions. The first is called avirodha-prīti, or unrestricted attachment, and the other is called virodha-yukta-krodha, anger arising from frustration. Adherence to the philosophy of the Māyāvādīs, belief in the fruitive results of the karma-vādīs, and belief in plans based on materialistic desires are called avirodha-prīti.
Jñānīs, karmīs and materialistic planmakers generally attract the attention of conditioned souls, but when the materialists cannot fulfill their plans and when their devices are frustrated, they become angry. Frustration of material desires produces anger.
Buddhism
Anger is defined in Buddhism as: "being unable to bear the object, or the intention to cause harm to the object". Anger is seen as aversion with a stronger exaggeration, and is listed as one of the five hindrances. Buddhist monks, such as Dalai Lama, the spiritual leader of Tibetans in exile, sometimes get angry.The Urban Dharma NewsletterMarch 9, 2004 Most often a spiritual person is aware of the emotion and the way it can be handled. Thus, in response to the question: "Is any anger acceptable in Buddhism?' the Dalai Lama answered: Buddhist scholar and author Geshe Kelsang Gyatso has also explained Buddha's teaching on the spiritual imperative to identify anger and overcome it by transforming difficulties: The Buddha himself on anger:"Kodhana Sutta: An Angry Person"(AN 7.60), translated from the Pali by Thanissaro Bhikkhu. Access to Insight
June 8, 2010
Islam
A verse in the third surah of the Quran instructs people to restrain their anger. Anger (Arabic:غضب, ''ghadab'') in Islam is considered to be instigated by Satan (''Shaitan
' (; ''devils'' or ''demons''), singular: (شَيْطَان) are evil spirits in Islam, inciting humans (and jinn) to sin by "whispering" (وَسْوَسَة, “waswasah”) to their qalb, hearts (قَلْب ''qalb''). Folklore suggests that t ...
''). Factors stated to lead to anger include selfishness, arrogance and excessive ambition. Islamic teachings also state that anger hinders the faith (''iman
Iman, Imann, Imaan, Eman, Emaan, or Imman may refer to:
Places
* Iman, Iran, a village in Kalashi District, Kermanshah Province
* The Iman River, the former name of the Bolshaya Ussurka River, a tributary of the Ussuri River in Russia's Primors ...
'') of a person. The Quran attributes anger to prophets and believers as well as Muhammad's enemies. It mentions the anger of Moses ('' Musa'') against his people for worshiping a golden calf
According to the Bible, the golden calf (עֵגֶל הַזָּהָב '' ‘ēgel hazzāhāv'') was an idol (a cult image) made by the Israelites when Moses went up to Mount Sinai. In Hebrew, the incident is known as ''ḥēṭə’ hā‘ēgel'' ...
and at the moment when Moses strikes an Egyptian for fighting against an Israelite. The anger of Jonah (''Yunus
Yunus ibn Matta ( ar, يُونُس ٱبْن مَتّىٰ, Yūnus ibn Mattā) is a prophet and messenger of God (Allah). Yunus is traditionally viewed as highly important in Islam as a prophet who was faithful to God and delivered his messages. Y ...
'') is also mentioned in the Quran, which led to his departure from the people of Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ban ...
and his eventual realization of his error and his repentance. The removal of anger from the hearts of believers by God ( Arabic: ') after the fighting against Muhammad's enemies is over. In general, suppression of anger (Arabic: کاظم, ''kazm'') is deemed a praiseworthy quality in the hadis.Bashir, Shahzad. ''Anger'', Encyclopaedia of the Qur'an, Brill, 2007.Mohammed Abu-Nimer, ''Non-Violence, Peacebuilding, Conflict Resolution and Human Rights in Islam:A Framework for Nonviolence and Peacebuilding in Islam'', Journal of Law and Religion, Vol. 15, No. 1/2. (2000–2001), pp. 217–265. Ibn Abdil Barr, the Andalusian Maliki jurist explains that controlling anger is the door way for restraining other blameworthy traits ego and envy, since these two are less powerful than anger. The hadis state various ways to diminish, prevent and control anger. One of these methods is to perform a ritual ablution
Ritual purification is the ritual prescribed by a religion by which a person is considered to be free of ''uncleanliness'', especially prior to the worship of a deity, and ritual purity is a state of ritual cleanliness. Ritual purification ma ...
, a different narration states that the angry person should lie down and other narrations instruct the angry person to invoke God and seek refuge from the Devil, by reciting ''I take refuge with Allah/God from the accursed Devil.''
It has also been stated by the Imam Ali, the "Commander of the faithful" and the son-in-law of prophet Muhammad that "A moment of patience in a moment of anger saves a thousand moments of regret." As well as "Anger begins with madness, and ends in regret."
Divine retribution
 In many religions, anger is frequently attributed to God or gods. Primitive people held that gods were subject to anger and revenge in anthropomorphic fashion. The Hebrew Bible says that opposition to God's will results in God's anger.Shailer Mathews, Gerald Birney Smith, A Dictionary of Religion and Ethics, Kessinger Publishing, p.17 Reform
In many religions, anger is frequently attributed to God or gods. Primitive people held that gods were subject to anger and revenge in anthropomorphic fashion. The Hebrew Bible says that opposition to God's will results in God's anger.Shailer Mathews, Gerald Birney Smith, A Dictionary of Religion and Ethics, Kessinger Publishing, p.17 Reform rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as '' semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form o ...
Kaufmann Kohler explains:
Christians believe in God's anger at the sight of evil. This anger is not inconsistent with God's love, as demonstrated in the Gospel where the righteous indignation of Christ is shown in the Cleansing of the Temple.
See also
*Angry Cognitions Scale The Angry Cognitions Scale (ACS) is a psychometric measure of how anger is acted out. It measures cognitive processes and their relation to attributes of anger, including misattributing causation, overgeneralizing, catastrophizing, demandingness, i ...
* Fear
* Indignation
* Moral emotions
* Outrage (emotion)
* Rage (emotion)
References
Further reading
Books
* * * * * * *Articles
Maintaining A Good and Healthy Anger
Managing emotions in the workplace
What Your Anger May Be Hiding – Leon F Seltzer Ph.D.
The Interpersonal Effects of Anger and Happiness in Negotiations
Get mad and get more than even: When and why anger expression is effective in negotiations
How To Manage Anger, Stay Calm And Live A Good Life
Anger and advancement versus sadness and subjugation: the effect of negative emotion expressions on social status conferral
{{Authority control Emotions Seven deadly sins Violence