Wood–Ljungdahl Pathway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
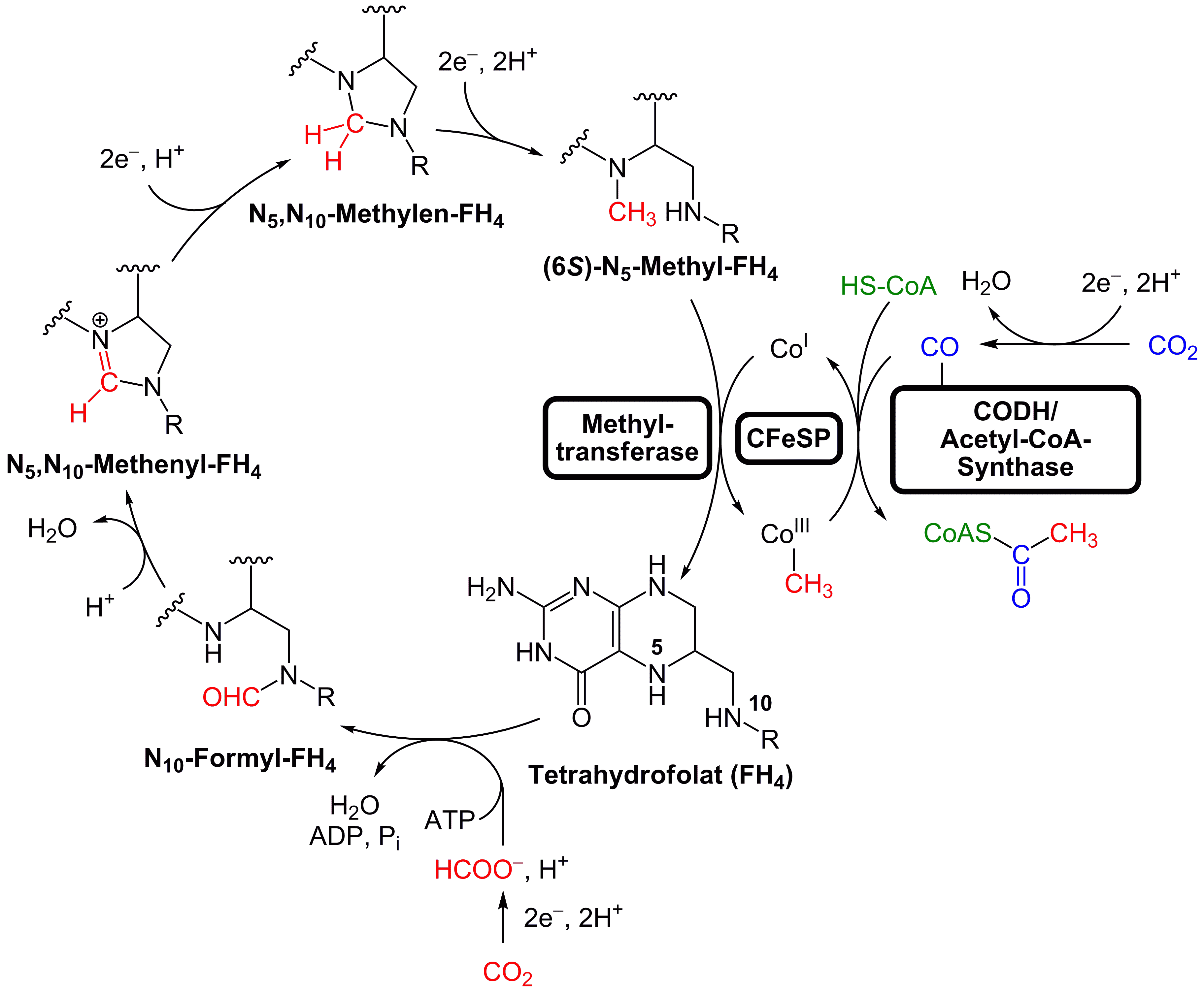 The Wood–Ljungdahl pathway is a set of biochemical reactions used by some
The Wood–Ljungdahl pathway is a set of biochemical reactions used by some
 The Wood–Ljungdahl pathway is a set of biochemical reactions used by some
The Wood–Ljungdahl pathway is a set of biochemical reactions used by some bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
. It is also known as the reductive acetyl-coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
) pathway. This pathway enables these organisms to use hydrogen as an electron donor
In chemistry, an electron donor is a chemical entity that donates electrons to another compound. It is a reducing agent that, by virtue of its donating electrons, is itself oxidized in the process.
Typical reducing agents undergo permanent chem ...
, and carbon dioxide as an electron acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process. Electron acceptors are sometimes mista ...
and as a building block for biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. ...
.
In this pathway carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
is reduced to carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
and formic acid
Formic acid (), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid, and has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure . It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some ants. Es ...
or directly into a formyl group
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group ...
, the formyl group is reduced to a methyl group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many ...
and then combined with the carbon monoxide and Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a subs ...
to produce acetyl-CoA. Two specific enzymes participate on the carbon monoxide side of the pathway: CO Dehydrogenase and acetyl-CoA synthase. The former catalyzes the reduction of the CO2 and the latter combines the resulting CO with a methyl group to give acetyl-CoA.
Some anaerobic
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to:
* Anaerobic adhesive, a bonding a ...
bacteria use the Wood–Ljungdahl pathway in reverse to break down acetate
An acetate is a salt (chemistry), salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. Alkali metal, alkaline, Alkaline earth metal, earthy, Transition metal, metallic, nonmetallic or radical Radical (chemistry), base). "Acetate" als ...
. For example, Sulfate reducing bacteria
Sulfate-reducing microorganisms (SRM) or sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) are a group composed of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfate-reducing archaea (SRA), both of which can perform anaerobic respiration utilizing sulfate () as termina ...
oxidize acetate completely to CO2 and H2 coupled with the reduction of sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ar ...
to sulfide
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds lar ...
. When operating in the reverse direction, the acetyl-CoA synthase is sometimes called acetyl-CoA decarbonylase.
Not to be confused with the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway, an evolutionarily related but biochemically distinct pathway named the Wolfe Cycle occurs exclusively in some methanogenic archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
called methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are com ...
s. In these anaerobic
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to:
* Anaerobic adhesive, a bonding a ...
archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
, the Wolfe Cycle functions as a methanogenesis
Methanogenesis or biomethanation is the formation of methane coupled to energy conservation by microbes known as methanogens. Organisms capable of producing methane for energy conservation have been identified only from the domain Archaea, a group ...
pathway to reduce CO2 into methane with electron donors such as hydrogen and formate. Similar to the Reverse Krebs cycle
The reverse Krebs cycle (also known as the reverse tricarboxylic acid cycle, the reverse TCA cycle, or the reverse citric acid cycle, or the reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle, or the reductive TCA cycle)
is a sequence of chemical reactions that ...
and the Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
, the Wolfe Cycle is cyclic, but the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway is not.
Evolution
Last universal common ancestor
A 2016 study of the genomes of a set of bacteria and archaea suggested that the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) of all cells was using an ancient Wood–Ljungdahl pathway in a hydrothermal setting, but more recent work challenges this conclusion. Phylometabolic reconstructions also support this. However, recent experiments have tried to replicate this pathway by attempting to reduce CO2, with very little pyruvate observed using native iron as a reducing agent (<0.03 mM), and even less so under hydrothermal settings with H2 (10 μM).See also
*Carbon fixation
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon (particularly in the form of carbon dioxide) is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as ...
* Carbon monoxide dehydrogenase
In enzymology, carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CODH) () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:CO + H2O + A \rightleftharpoons CO2 + AH2
The chemical process catalyzed by carbon monoxide dehydrogenase is similar to the water-gas shif ...
* Syngas fermentation Syngas fermentation, also known as synthesis gas fermentation, is a microbial process. In this process, a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide, known as syngas, is used as carbon and energy sources, and then converted into fuel ...
* Methanogenesis
Methanogenesis or biomethanation is the formation of methane coupled to energy conservation by microbes known as methanogens. Organisms capable of producing methane for energy conservation have been identified only from the domain Archaea, a group ...
References
Other reading
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Reductive Acetyl-Coa Pathway Metabolic pathways