Woodheap on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Wood fuel (or fuelwood) is a fuel such as firewood, charcoal,
Wood fuel (or fuelwood) is a fuel such as firewood, charcoal,
 Wood has been used as fuel for millennia. Historically, it was limited in use only by the distribution of technology required to make a spark. Heat derived from wood is still common throughout much of the world. Early examples included a fire constructed inside a tent. Fires were constructed on the ground, and a smoke hole in the top of the tent allowed the smoke to escape by convection.
In permanent structures and in caves, hearths were constructed or established—surfaces of stone or another noncombustible material upon which a fire could be built. Smoke escaped through a smoke hole in the roof.
In contrast to civilizations in relatively arid regions (such as Mesopotamia and Egypt), the Greeks, Romans, Celts, Britons, and Gauls all had access to forests suitable for using as fuel. Over the centuries there was a partial deforestation of climax forests and the evolution of the remainder to
Wood has been used as fuel for millennia. Historically, it was limited in use only by the distribution of technology required to make a spark. Heat derived from wood is still common throughout much of the world. Early examples included a fire constructed inside a tent. Fires were constructed on the ground, and a smoke hole in the top of the tent allowed the smoke to escape by convection.
In permanent structures and in caves, hearths were constructed or established—surfaces of stone or another noncombustible material upon which a fire could be built. Smoke escaped through a smoke hole in the roof.
In contrast to civilizations in relatively arid regions (such as Mesopotamia and Egypt), the Greeks, Romans, Celts, Britons, and Gauls all had access to forests suitable for using as fuel. Over the centuries there was a partial deforestation of climax forests and the evolution of the remainder to
 The development of the chimney and the
The development of the chimney and the
 Significant quantities of
Significant quantities of
Firewood Facts
A comprehensive and fully referenced list of potentially toxic woods.
All about the health effects of biomass burning *Mike Chen {{Wood products Wood fuel,
 Wood fuel (or fuelwood) is a fuel such as firewood, charcoal,
Wood fuel (or fuelwood) is a fuel such as firewood, charcoal, chip Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is a type of immunoprecipitation experimental technique used to investigate the interaction between proteins and DNA in the cell. It aims to determine whether specific proteins are associated with specific genom ...
s, sheets, pellets, and sawdust
Sawdust (or wood dust) is a by-product or waste product of woodworking operations such as sawing, sanding, milling, planing, and routing. It is composed of small chippings of wood. These operations can be performed by woodworking machine ...
. The particular form used depends upon factors such as source, quantity, quality and application. In many areas, wood is the most easily available form of fuel, requiring no tool
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ba ...
s in the case of picking up dead wood, or few tools, although as in any industry, specialized tools, such as skidders and hydraulic wood splitters, have been developed to mechanize production. Sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes (dimensi ...
waste and construction industry by-products also include various forms of lumber tailings.
The discovery of how to make fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames a ...
for the purpose of burning wood is regarded as one of humanity's most important advances. The use of wood as a fuel source for heating is much older than civilization and is assumed to have been used by Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
s. Today, burning of wood is the largest use of energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
derived from a solid fuel biomass. Wood fuel can be used for cooking and heating
A central heating system provides warmth to a number of spaces within a building from one main source of heat. It is a component of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (short: HVAC) systems, which can both cool and warm interior spaces.
...
, and occasionally for fueling steam engines and steam turbines
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful Work (physics), work. The work produced by a turbine can be used ...
that generate electricity. Wood may be used indoors in a furnace, stove
A stove or range is a device that burns fuel or uses electricity to generate heat inside or on top of the apparatus, to be used for general warming or cooking. It has evolved highly over time, with cast-iron and induction versions being develope ...
, or fireplace
A fireplace or hearth is a structure made of brick, stone or metal designed to contain a fire. Fireplaces are used for the relaxing ambiance they create and for heating a room. Modern fireplaces vary in heat efficiency, depending on the design ...
, or outdoors in furnace, campfire
A campfire is a fire at a campsite that provides light and warmth, and heat for cooking. It can also serve as a beacon, and an insect and predator deterrent. Established campgrounds often provide a stone or steel fire ring for safety. Campfires ...
, or bonfire.
Historical development
 Wood has been used as fuel for millennia. Historically, it was limited in use only by the distribution of technology required to make a spark. Heat derived from wood is still common throughout much of the world. Early examples included a fire constructed inside a tent. Fires were constructed on the ground, and a smoke hole in the top of the tent allowed the smoke to escape by convection.
In permanent structures and in caves, hearths were constructed or established—surfaces of stone or another noncombustible material upon which a fire could be built. Smoke escaped through a smoke hole in the roof.
In contrast to civilizations in relatively arid regions (such as Mesopotamia and Egypt), the Greeks, Romans, Celts, Britons, and Gauls all had access to forests suitable for using as fuel. Over the centuries there was a partial deforestation of climax forests and the evolution of the remainder to
Wood has been used as fuel for millennia. Historically, it was limited in use only by the distribution of technology required to make a spark. Heat derived from wood is still common throughout much of the world. Early examples included a fire constructed inside a tent. Fires were constructed on the ground, and a smoke hole in the top of the tent allowed the smoke to escape by convection.
In permanent structures and in caves, hearths were constructed or established—surfaces of stone or another noncombustible material upon which a fire could be built. Smoke escaped through a smoke hole in the roof.
In contrast to civilizations in relatively arid regions (such as Mesopotamia and Egypt), the Greeks, Romans, Celts, Britons, and Gauls all had access to forests suitable for using as fuel. Over the centuries there was a partial deforestation of climax forests and the evolution of the remainder to coppice with standards
Coppicing is a traditional method of woodland management which exploits the capacity of many species of trees to put out new shoots from their stump or roots if cut down. In a coppiced wood, which is called a copse, young tree stems are repeate ...
woodland as the primary source of wood fuel. These woodlands involved a continuous cycle of new stems harvested from old stumps, on rotations between seven and thirty years. One of the earliest printed books on woodland management, in English, was John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's diary, or ...
's "Sylva, or a discourse on forest trees" (1664) advising landowners on the proper management of forest estates. H. L. Edlin, in "Woodland Crafts in Britain", 1949 outlines the extraordinary techniques employed, and range of wood products that have been produced from these managed forests since pre-Roman times. And throughout this time the preferred form of wood fuel was the branches of cut coppice stems bundled into faggots. Larger, bent or deformed stems that were of no other use to the woodland craftsmen were converted to charcoal.
As with most of Europe, these managed woodlands continued to supply their markets right up to the end of World War Two. Since then much of these woodlands have been converted to broadscale agriculture. Total demand for fuel increased considerably with the industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
but most of this increased demand was met by the new fuel source coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
, which was more compact and more suited to the larger scale of the new industries.
During the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characte ...
of Japan, wood was used for many purposes, and the consumption of wood led Japan to develop a forest management Forest management is a branch of forestry concerned with overall administrative, legal, economic, and social aspects, as well as scientific and technical aspects, such as silviculture, protection, and forest regulation. This includes management fo ...
policy during that era. Demand for timber resources was on the rise not only for fuel, but also for construction of ships and buildings, and consequently deforestation was widespread. As a result, forest fires occurred, along with floods and soil erosion. Around 1666, the shōgun made it a policy to reduce logging and increase the planting of trees. This policy decreed that only the shōgun, or a ''daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominal ...
'', could authorize the use of wood. By the 18th century, Japan had developed detailed scientific knowledge about silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, and quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production.
The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests and wo ...
and plantation forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. ...
.
Fireplaces and stoves
fireplace
A fireplace or hearth is a structure made of brick, stone or metal designed to contain a fire. Fireplaces are used for the relaxing ambiance they create and for heating a room. Modern fireplaces vary in heat efficiency, depending on the design ...
allowed for more effective exhaustion of the smoke. Masonry heater
A masonry heater (also called a masonry stove) is a device for warming an interior space through radiant heating, by capturing the heat from periodic burning of fuel (usually wood), and then radiating the heat at a fairly constant temperature ...
s or stoves went a step further by capturing much of the heat of the fire and exhaust in a large thermal mass, becoming much more efficient than a fireplace alone.
The metal stove
A stove or range is a device that burns fuel or uses electricity to generate heat inside or on top of the apparatus, to be used for general warming or cooking. It has evolved highly over time, with cast-iron and induction versions being develope ...
was a technological development concurrent with the industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
. Stoves were manufactured or constructed pieces of equipment that contained the fire on all sides and provided a means for controlling the draft—the amount of air allowed to reach the fire. Stoves have been made of a variety of materials. Cast iron is among the more common. Soapstone (talc
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral, composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent a ...
), tile
Tiles are usually thin, square or rectangular coverings manufactured from hard-wearing material such as ceramic, stone, metal, baked clay, or even glass. They are generally fixed in place in an array to cover roofs, floors, walls, edges, or o ...
, and steel have all been used. Metal stoves are often lined with refractory materials such as firebrick
A fire brick, firebrick, or refractory is a block of ceramic material used in lining furnaces, kilns, fireboxes, and fireplaces. A refractory brick is built primarily to withstand high temperature, but will also usually have a low thermal con ...
, since the hottest part of a woodburning fire will burn away steel over the course of several years' use.
The Franklin stove was developed in the United States by Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
. More a manufactured fireplace than a stove, it had an open front and a heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct conta ...
in the back that was designed to draw air from the cellar and heat it before releasing it out the sides. The heat exchanger was never a popular feature and was omitted in later versions. So-called "Franklin" stoves today are made in a great variety of styles, though none resembles the original design.
The 1800s became the high point of the cast iron stove. Each local foundry would make their own design, and stoves were built for myriads of purposes—parlour stoves, box stoves, camp stoves, railroad stoves, portable stoves, cooking stoves and so on. Elaborate nickel and
chrome edged models took designs to the edge, with cast ornaments, feet and doors. Wood or coal could be burnt in the stoves and
thus they were popular for over one hundred years. The action of the fire, combined with the causticity of the ash, ensured that the stove would eventually disintegrate or crack over time. Thus a steady supply of stoves was needed. The maintenance of stoves, needing to be blacked, their smokiness, and the need to split wood meant that oil or electric heat found favour.
The airtight stove, originally made of steel, allowed greater control of combustion, being more tightly fitted than other stoves of the day. Airtight stoves became common in the 19th century.
Use of wood heat declined in popularity with the growing availability of other, less labor-intensive fuels. Wood heat was gradually replaced by coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
and later by fuel oil, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
and propane heating except in rural areas with available forests.
After the 1967 Oil Embargo
The 1967 Oil Embargo began on June 6, 1967, the second day of the Six-Day War, with a joint Arab decision to deter any countries from supporting Israel militarily. Several Middle Eastern countries eventually limited their oil shipments, some emba ...
, many people in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
used wood as fuel for the first time. The EPA provided information on clean stoves, which burned much more efficiently.
1970s
A brief resurgence in popularity occurred during and after the 1973 energy crisis, when some believed that fossil fuels would become so expensive as to preclude their use. A period of innovation followed, with many small manufacturers producing stoves based on designs old and new. Notable innovations from that era include the Ashley heater, a thermostatically controlled stove with an optional perforated steel enclosure that prevented accidental contact with hot surfaces. The decade also saw a number of dual-fuel furnaces and boilers made, which utilized ductwork and piping to deliver heat throughout a house or other building.1980s
The growth in popularity of wood heat also led to the development and marketing of a greater variety of equipment for cutting, splitting and processing firewood. Consumer grade hydrauliclog splitter
A log splitter is a piece of machinery or equipment used for splitting firewood from softwood or hardwood logs that have been pre-cut into sections (rounds), usually by chainsaw or on a saw bench. Many log splitters consist of a hydraulic pump or ...
s were developed to be powered by electricity, gasoline, or PTO of farm tractors. In 1987 the US Department of Agriculture published a method for producing kiln dried firewood, on the basis that better heat output and increased combustion efficiency can be achieved with logs containing lower moisture content.
The magazine "Wood Burning Quarterly" was published for several years before changing its name to "Home Energy Digest" and, subsequently, disappearing.
Today
Apellet stove
A pellet stove is a stove that burns compressed wood or biomass pellets to create a source of heat for residential and sometimes industrial spaces. By steadily feeding fuel from a storage container (hopper) into a burn pot area, it produces a con ...
is an appliance that burns compressed wood or biomass pellets.
Wood heat continues to be used in areas where firewood is abundant. For serious attempts at heating, rather than mere ambience (open fireplaces), stoves, fireplace inserts, and furnaces are most commonly used today. In rural, forested parts of the U.S., freestanding boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, centr ...
s are increasingly common. They are installed outdoors, some distance from the house, and connected to a heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct conta ...
in the house using underground piping. The mess of wood, bark, smoke, and ashes is kept outside and the risk of fire is reduced. The boilers are large enough to hold a fire all night, and can burn larger pieces of wood, so that less cutting and splitting is required. There is no need to retrofit a chimney in the house. However, outdoor wood boilers emit more wood smoke and associated pollutants than other wood-burning appliances. This is due to design characteristics such as the water-filled jacket surrounding the firebox, which acts to cool the fire and leads to incomplete combustion. Outdoor wood boilers also typically have short stack heights in comparison to other wood-burning appliances, contributing to ambient levels of particulates at ground level. An alternative that is increasing in popularity are wood gasification boilers, which burn wood at very high efficiencies (85-91%) and can be placed indoors or in an outbuilding. There are plenty of ways to process wood fuel and the inventions today are maximizing by the minute.
Wood is still used today for cooking in many places, either in a stove or an open fire. It is also used as a fuel in many industrial processes, including smoking meat and making maple syrup.
As a sustainable energy source, wood fuel also remains viable for generating electricity in areas with easy access to forest products and by-products.
Measurement of firewood
In themetric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the Interna ...
, firewood is normally sold by the cubic metre or stere (1 m³ = ~0.276 cords).
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
and Canada, firewood is usually sold by the cord
Cord or CORD may refer to:
People
* Alex Cord (1933–2021), American actor and writer
* Chris Cord (born 1940), American racing driver
* Errett Lobban Cord (1894–1974) American industrialist
* Ronnie Cord (1943–1986), Brazilian singer
* Co ...
, 128 ft³ (3.62 m³), corresponding to a woodpile 8 ft wide × 4 ft high of 4 ft-long logs. The cord is legally defined by statute in most U.S. states. A "thrown cord" is firewood that has not been stacked and is defined as 4 ft wide x 4 ft tall x 10 ft long. The additional volume is to make it equivalent to a standard stacked cord, where there is less void space. It is also common to see wood sold by the "face cord", which is usually ''not'' legally defined, and varies from one area to another. For example, in one state a pile of wood 8 feet wide × 4 feet high of 16"-long logs will often be sold as a "face cord", though its volume is only one-third of a cord. In another state, or even another area of the same state, the volume of a face cord may be considerably different. Hence, it is risky to buy wood sold in this manner, as the transaction is not based on a legally enforceable unit of measure.
In Australia, it is normally sold by the tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
but is commonly advertised as sold by the barrowload (wheelbarrow), bucket (1/3 of a m3 bucket of a typical skid-steer
A skid loader, skid-steer loader, SSLs or skidsteer is a small, rigid-frame, engine-powered machine with lift arms that can attach to a wide variety of buckets and other labor-saving tools or attachments.
Skid-steer loaders are typically four-whee ...
), ute-load or bag (roughly 15–20 kg).
Energy content
A common hardwood, red oak, has an energy content ( heat value) of 14.9mega
Mega or MEGA may refer to:
Science
* mega-, a metric prefix denoting 106
* Mega (number), a certain very large integer in Steinhaus–Moser notation
* "mega-" a prefix meaning "large" that is used in taxonomy
* Gravity assist, for ''Moon-Eart ...
joules
The joule ( , ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). It is equal to the amount of work done when a force of 1 newton displaces a mass through a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force applied. ...
per kilogram (6,388 BTU
The British thermal unit (BTU or Btu) is a unit of heat; it is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It is also part of the United States customary units. The modern SI u ...
per pound), and 10.4 mega
Mega or MEGA may refer to:
Science
* mega-, a metric prefix denoting 106
* Mega (number), a certain very large integer in Steinhaus–Moser notation
* "mega-" a prefix meaning "large" that is used in taxonomy
* Gravity assist, for ''Moon-Eart ...
joules
The joule ( , ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). It is equal to the amount of work done when a force of 1 newton displaces a mass through a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force applied. ...
recoverable if burned at 70% efficiency.
The Sustainable Energy Development Office (SEDO), part of the Government of Western Australia states that the energy content of wood is 16.2 megajoules per kilogram (4.5 kWh/kg).
According to ''The Bioenergy Knowledge Centre'', the energy content of wood is more closely related to its moisture content than its species. The energy content improves as moisture content decreases.
In 2008, wood for fuel cost $15.15 per 1 million BTUs (0.041 EUR per kWh).
Environmental impacts
Combustion by-products
As with anyfire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames a ...
, burning wood fuel creates numerous by-products, some of which may be useful (heat and steam), and others that are undesirable, irritating or dangerous.
One by-product of wood burning is wood ash
Wood ash is the powdery residue remaining after the combustion of wood, such as burning wood in a fireplace, bonfire, or an industrial power plant. It is largely composed of calcium compounds along with other non-combustible trace elements presen ...
, which in moderate amounts is a fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
(mainly potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
), contributing minerals, but is strongly alkaline as it contains potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
(lye). Wood ash can also be used to manufacture soap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
.
Smoke
Smoke is a suspension of airborne particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-produc ...
, containing water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
and other chemicals and aerosol particulates, including caustic alkali fly ash, which can be an irritating (and potentially dangerous) by-product of partially burnt wood fuel. A major component of wood smoke is fine particles that may account for a large portion of particulate air pollution in some regions. During cooler months, wood heating accounts for as much as 60% of fine particles in Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
, Australia.Environment Protection Authority (2002) Wood heaters, open fires and air quality. Publication 851 EPA Victoria.
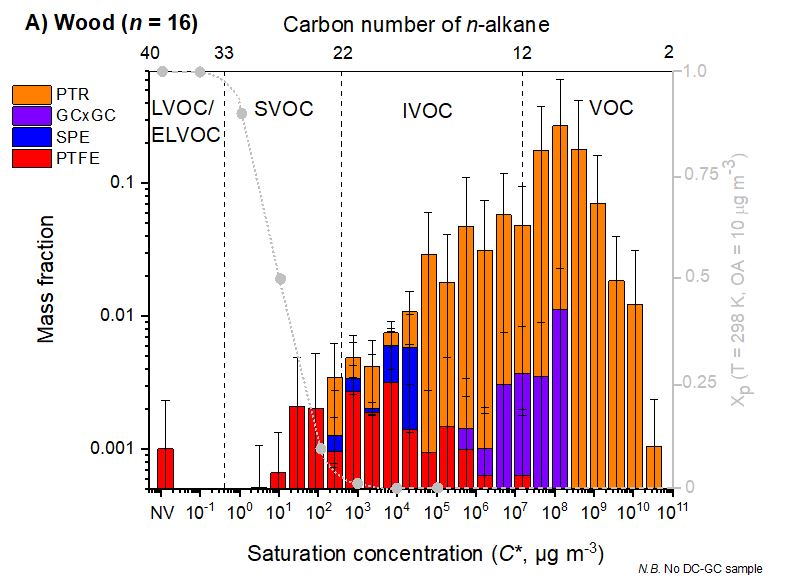
 Significant quantities of
Significant quantities of volatile organic compound
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapour pressure at room temperature. High vapor pressure correlates with a low boiling point, which relates to the number of the sample's molecules in the surrounding air, a ...
s are released from the combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combus ...
of fuel wood
Firewood is any wooden material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not highly processed and is in some sort of recognizable log or branch form, compared to other forms of wood fuel like pellets or chips. Firewood can ...
. Large quantities of smaller oxygenate species are released during the combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combus ...
process, as well as organics formed from the depolymerisation reaction of lignin such as phenolics, furans and furanones. The combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combus ...
of fuel wood
Firewood is any wooden material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not highly processed and is in some sort of recognizable log or branch form, compared to other forms of wood fuel like pellets or chips. Firewood can ...
has also been shown to release many organic compounds into the aerosol phase. The burning of fuel woods has been shown to release organic components over a range of volatilities, over effective saturation concentrations, ''C''*, from 101-1011 μg m−3. The emissions from fuel wood
Firewood is any wooden material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not highly processed and is in some sort of recognizable log or branch form, compared to other forms of wood fuel like pellets or chips. Firewood can ...
samples collected from the Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
area of India were shown to be 30 times more reactive with the hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydro ...
radical than emissions from liquefied petroleum gas. Furthermore, when comparing 21 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. ...
s emitted from the same fuel wood
Firewood is any wooden material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not highly processed and is in some sort of recognizable log or branch form, compared to other forms of wood fuel like pellets or chips. Firewood can ...
samples from Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
, emissions from fuel wood were around 20 times more toxic than emissions from liquefied petroleum gas.
Slow combustion stoves increase efficiency of wood heaters burning logs, but also increase particulate production. Low pollution/slow combustion stoves are a current area of research. An alternative approach is to use pyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''py ...
to produce several useful biochemical byproducts, and clean burning charcoal, or to burn fuel extremely quickly inside a large thermal mass, such as a masonry heater. This has the effect of allowing the fuel to burn completely without producing particulates while maintaining the efficiency of the system.
In some of the most efficient burners, the temperature of the smoke is raised to a much higher temperature where the smoke will itself burn (e.g. 609 °C for igniting carbon monoxide gas). This may result in significant reduction of smoke hazards while also providing additional heat from the process. By using a catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an vehicle emissions control, exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis, catalyzing a redox chemic ...
, the temperature for obtaining cleaner smoke can be reduced. Some U.S. jurisdictions prohibit sale or installation of stoves that do not incorporate catalytic converters.
Combustion by-product effects on human health
Depending on population density, topography, climatic conditions and combustion equipment used, wood heating may substantially contribute toair pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different typ ...
, particularly particulate
Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) – are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The te ...
s. The conditions in which wood is burnt will greatly influence the content of the emission. Particulate air pollution can contribute to human health problems and increased hospital admissions for asthma & heart diseases.
The technique of compressing wood pulp into pellets or artificial logs can reduce emissions. The combustion is cleaner, and the increased wood density and reduced water content can eliminate some of the transport bulk. The fossil energy consumed in transport is reduced and represents a small fraction of the fossil fuel consumed in producing and distributing heating oil or gas.
Harvesting operations
Much wood fuel comes fromnative
Native may refer to:
People
* Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Native Americans (disambiguation)
In arts and entert ...
forests
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
around the world. Plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The ...
wood is rarely used for firewood, as it is more valuable as timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, w ...
or wood pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw mate ...
, however, some wood fuel is gathered from trees planted amongst crops, also known as agroforestry. The collection or harvesting of this wood can have serious environmental implications for the collection area. The concerns are often specific to the particular area, but can include all the problems that regular logging create. The heavy removal of wood from forests can cause habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
and soil erosion.
However, in many countries, for example in Europe and Canada, the forest residues are being collected and turned into useful wood fuels with minimal impact on the environment. Consideration is given to soil nutrition as well as erosion.
The environmental impact of using wood as a fuel depends on how it is burnt. Higher temperatures result in more complete combustion and less noxious gases as a result of pyrolysis. Some may regard the burning of wood from a sustainable source as carbon-neutral
Carbon neutrality is a state of net-zero carbon dioxide emissions. This can be achieved by balancing emissions of carbon dioxide with its removal (often through carbon offsetting) or by eliminating emissions from society (the transition to the "p ...
. A tree, over the course of its lifetime, absorbs as much carbon (or carbon dioxide) as it releases when burnt.
Some firewood is harvested in "woodlot A woodlot is a parcel of a woodland or forest capable of small-scale production of forest products (such as wood fuel, sap for maple syrup, sawlogs, and pulpwood) as well as recreational uses like bird watching, bushwalking, and wildflower appr ...
s" managed for that purpose, but in heavily wooded areas it is more often harvested as a byproduct of natural forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
s. Deadfall that has not started to rot is preferred, since it is already partly seasoned. Standing dead timber is considered better still, as it is both seasoned, and has less rot. Harvesting this form of timber reduces the speed and intensity of bushfire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire ...
s. Harvesting timber for firewood is normally carried out by hand with chainsaw
A chainsaw (or chain saw) is a portable gasoline-, electric-, or battery-powered saw that cuts with a set of teeth attached to a rotating chain driven along a guide bar. It is used in activities such as tree felling, limbing, bucking, pru ...
s. Thus, longer pieces - requiring less manual labor, and less chainsaw fuel - are less expensive and only limited by the size of their firebox. Prices also vary considerably with the distance from wood lots, and quality of the wood.
Firewood usually relates to timber or trees unsuitable for building or construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form Physical object, objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Pr ...
. Firewood is a renewable resource
A renewable resource, also known as a flow resource, is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of ti ...
provided the consumption rate is controlled to sustainable levels. The shortage of suitable firewood in some places has seen local populations damaging huge tracts of bush possibly leading to further desertification.
Greenhouse gases
Wood burning creates more atmospheric CO2 than biodegradation of wood in a forest (in a given period of time) because by the time the bark of a dead tree has rotted, the log has already been occupied by other plants and micro-organisms which continue to sequester the CO2 by integrating the hydrocarbons of the wood into their own life cycle. Wood harvesting and transport operations produce varying degrees of greenhouse gas pollution. Inefficient and incomplete combustion of wood can result in elevated levels of greenhouse gases other than CO2, which may result in positive emissions where the byproducts have greaterCarbon dioxide equivalent
Global warming potential (GWP) is the heat absorbed by any greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, as a multiple of the heat that would be absorbed by the same mass of carbon dioxide (). GWP is 1 for . For other gases it depends on the gas and the time ...
values. In an attempt to provide quantitative information about the relative output of CO2 to produce electricity or domestic heating, the United Kingdom Department of Energy and Climate Change ( DECC) has published a comprehensive model comparing the burning of wood (wood chip) and other fuels, based on 33 scenarios. The model's output is kilogram of CO2 produced per Megawatt hour of delivered energy. Scenario 33 for example, which concerns the production of heat from wood chips produced from UK small roundwood produced from bringing neglected broadleaf forests back into production, shows that burning oil releases 377 kg of CO2 while burning woodchip releases 1501 kg of CO2 per MW h delivered energy. On the other hand, scenario 32 in that same reference, which concerns production of heat from wood chips that would otherwise be made into particleboard, releases only 239 kg of CO2 per MW h delivered energy. Therefore, the relative greenhouse effects of biomass energy production very much depends on the usage model.
The intentional and controlled charring of wood and its incorporation into the soil is an effective method for carbon sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. Carbon dioxide () is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. These changes can be accelerated through changes in lan ...
as well as an important technique to improve soil conditions for agriculture, particularly in heavily forested regions. It forms the basis of the rich soils known as Terra preta
''Terra preta'' (, locally , literally "black soil" in Portuguese) is a type of very dark, fertile anthropogenic soil ( anthrosol) found in the Amazon Basin. It is also known as "Amazonian dark earth" or "Indian black earth". In Portuguese its f ...
.
Regulation and Legislation
The environmental impact of burning wood fuel is debatable. Several cities have moved towards setting standards of use and/or bans of wood burning fireplaces. For example, the city of Montréal, Québec passed a resolution to ban wood fireplace installation in new construction. Wood burning advocates claim that properly harvested wood is carbon-neutral, therefore off-setting the negative impact of by-product particles given off during the burning process. In the context of forest wildfires, wood removed from the forest setting for use as wood fuel can reduce overall emissions by decreasing the quantity of open burned wood and the severity of the burn while combusting the remaining material under regulated conditions. On March 7, 2018, theUnited States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
passed a bill that would delay for three years the
implementation of more stringent emission standards for new residential wood heaters.
Potential use in renewable energy technologies
*Efficient stove for developing nations *Pellet stove
A pellet stove is a stove that burns compressed wood or biomass pellets to create a source of heat for residential and sometimes industrial spaces. By steadily feeding fuel from a storage container (hopper) into a burn pot area, it produces a con ...
*Sawdust
Sawdust (or wood dust) is a by-product or waste product of woodworking operations such as sawing, sanding, milling, planing, and routing. It is composed of small chippings of wood. These operations can be performed by woodworking machine ...
can be pelletized
*Wood pellets
Pellet fuels (or pellets) are biofuels made from compressed organic matter or biomass. Pellets can be made from any one of five general categories of biomass: industrial waste and co-products, food waste, agricultural residues, energy crops, and ...
Usage
Some European countries produce a significant fraction of their electricity needs from wood or wood wastes. In Scandinavian countries the costs of manual labor to process firewood is very high. Therefore, it is common to import firewood from countries with cheap labor and natural resources. The main exporters to Scandinavia are theBaltic countries
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone ...
(Estonia, Lithuania, and Latvia). In Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
, there is a growing interest in using wood waste as fuel for home and industrial heating, in the form of compacted pellets.
In the United States, wood fuel is the second-leading form of renewable energy (behind hydro-electric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
).
Australia
About 1.5 million households in Australia use firewood as the main form of domestic heating. As of 1995, approximately 1.85 million cubic metres of firewood (1m³ equals approximately one car trailer load) was used inVictoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
annually, with half being consumed in Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
. This amount is comparable to the wood consumed by all of Victoria's sawlog and pulplog forestry operations (1.9 million m³).
Species used as sources of firewood include:
* Red Gum, from forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
s along the Murray River
The Murray River (in South Australia: River Murray) (Ngarrindjeri: ''Millewa'', Yorta Yorta: ''Tongala'') is a river in Southeastern Australia. It is Australia's longest river at extent. Its tributaries include five of the next six longest ...
(the Mid-Murray Forest Management Area, including the Barmah and Gunbower forests, provides about 80% of Victoria's red gum timber).NRE 2002 Forest Management Plan for the Mid-Murray Forest Management Area
*Box and Messmate Stringybark, in southern Australia.
* Sugar gum, a wood with high thermal efficiency
In thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency (\eta_) is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc.
For a ...
that usually comes from small plantations.
*Jarrah
''Eucalyptus marginata'', commonly known as jarrah, djarraly in Noongar language and historically as Swan River mahogany, is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a tree with rou ...
, in the Southwest of Western Australia. It generates a greater heat than most other available woods and is usually sold by the tonne.
Europe
In 2014, the construction of the biggest pellet plant in the Baltic region was started inVõrumaa
Võrumaa (german: Kreis Werro; vro, Võromaa) was a historical county in Estonia. The historical Võrumaa includes the areas of the present counties of Võru, Põlva, Valga and Tartu.
Regions of Estonia
Historical regions in Estonia
Ancient p ...
, Sõmerpalu
Sõmerpalu ( vro, Sõmmõrpalo, german: Sommerpahlen) is a small borough ( et, alevik) in Võru County, Estonia. Between 1991–2017, until the administrative reform of Estonian local governments, the small town was the administrative center of ...
, Estonia, with an expected output of 110,000 tons of pellet / year. Different types of wood will be used in the process of pellet making (firewood, woodchips, shavings). The Warmeston OÜ plant started its activity by the end of 2014.
In 2013, the main pellet consumers in Europe were the UK, Denmark, the Netherlands, Sweden, Germany and Belgium, as U.E.'s annual report on biofuels states. In Denmark and Sweden, pellets are used by power plants, households and medium scale consumers for district heating, compared to Austria and Italy, where pellets are mainly used as small - scale private residential and industrial boilers for heating.
The UK is the single largest consuming market for industrial wood pellets, in large part due to its major biomass-fueled power stations such as Drax, MGT and Lynemouth
Lynemouth is a village in Northumberland, England, northeast of Ashington, close to the village of Ellington to the north west. It was built close to coal mines, including Lynemouth Colliery.
Lynemouth and the surrounding industrial area feat ...
.
Asia
Japan andSouth Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eas ...
are both growing markets for industrial wood pellets, and as of 2017, were expected to become the second and third largest global markets for wood pellets due to government policies favoring the use of biomass in power generation.
North America
Demand for wood fuel in theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
is principally driven by residential and commercial heating customers. Canada was not a major consumer of industrial wood pellets as of 2017, but has relatively aggressive de-carbonization policies and may become a significant consumer of industrial wood pellets by the 2020s.
See also
* Biofuel * Biomass * Forestry * Outdoor wood-fired boiler, Outdoor wood furnace * Renewable heat * Woodchips * Wood-fired oven * Wood gasReferences
External links
Firewood Facts
A comprehensive and fully referenced list of potentially toxic woods.
All about the health effects of biomass burning *Mike Chen {{Wood products Wood fuel,