Wisconsin River on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Wisconsin River is a
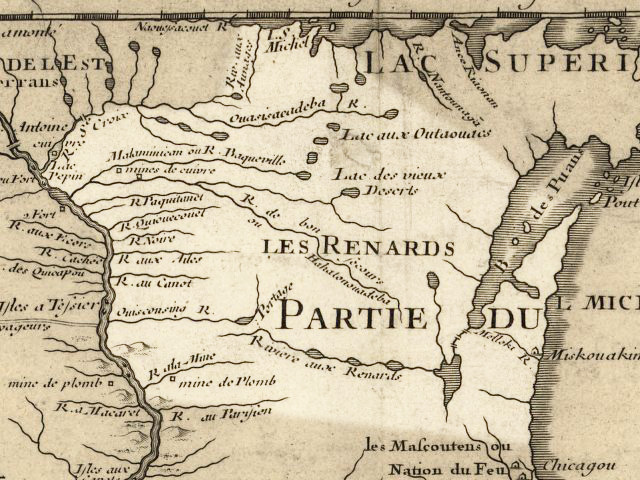 In the summer of 1673, French missionary
In the summer of 1673, French missionary
File:WisconsinDells02.jpg, Dells of the Wisconsin River, May 2002.
File:WisconsinRiverDamStevensPoint.jpg, A dam in
tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage ...
of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
in the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette
Jacques Marquette S.J. (June 1, 1637 – May 18, 1675), sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded Saint Ign ...
as "Meskousing", is rooted in the Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic languages, Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language f ...
used by the area's American Indian tribes, but its original meaning is obscure. French explorers who followed in the wake of Marquette later modified the name to "Ouisconsin", and so it appears on Guillaume de L'Isle
Guillaume Delisle, also spelled Guillaume de l'Isle, (; 28 February 1675, Paris – 25 January 1726, Paris) was a French cartographer known for his popular and accurate maps of Europe and the newly explored Americas.
Childhood and education
Desl ...
's map (Paris, 1718). This was simplified to "Wisconsin" in the early 19th century before being applied to Wisconsin Territory
The Territory of Wisconsin was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 3, 1836, until May 29, 1848, when an eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Wisconsin. Belmont was ...
and finally the state of Wisconsin.
The Wisconsin River originates in the forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
s of the North Woods
The Laurentian Mixed Forest Province, also known as the North Woods, is a forested ecoregion in eastern North America. Among others, this terminology has been adopted by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Similar, though not n ...
Lake District of northern Wisconsin, in Lac Vieux Desert
Lac Vieux Desert is a lake in the United States divided between Gogebic County, Michigan, and Vilas County, Wisconsin. Fed primarily by springs in the surrounding swamps, it is the source of the Wisconsin River, which flows out of its southwest c ...
near the border of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
. It flows south across the glacial plain of central Wisconsin, passing through Wausau, Stevens Point
Stevens Point is the county seat of Portage County, Wisconsin, United States. The city was incorporated in 1858.
Its 2020 population of 25,666 makes it the largest city in the county. Stevens Point forms the core of the United States Census Bur ...
, and Wisconsin Rapids
Wisconsin Rapids is a city in and the county seat of Wood County, Wisconsin. The population was 18,877 at the 2020 census. The city also forms one of the core areas of the United States Census Bureau's Marshfield-Wisconsin Rapids Micropolit ...
. In southern Wisconsin it encounters the terminal moraine
A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed by the front edge ...
formed during the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
, where it forms the Dells of the Wisconsin River
The Dells of the Wisconsin River, also called the Wisconsin Dells (from Old English �dæle��, modern English “dale”), meaning “valley”, is a 5-mile (8-km) gorge on the Wisconsin River in south-central Wisconsin, USA. It is noted for it ...
. North of Madison Madison may refer to:
People
* Madison (name), a given name and a surname
* James Madison (1751–1836), fourth president of the United States
Place names
* Madison, Wisconsin, the state capital of Wisconsin and the largest city known by this ...
at Portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ...
, the river turns to the west, flowing through Wisconsin's hilly Western Upland
The Western Upland is a geographical region covering much of the western half of the U.S. state of Wisconsin. It stretches from southern Polk County, Wisconsin in the north to the state border with Illinois in the south, and from Rock County i ...
and joining the Mississippi approximately 3 miles (4.8 km) south of Prairie du Chien
Prairie du Chien () is a city in and the county seat of Crawford County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 5,506 at the 2020 census. Its ZIP Code is 53821.
Often referred to as Wisconsin's second oldest city, Prairie du Chien was esta ...
.
The highest waterfall on the river is Grandfather Falls
Grandfather Falls is the highest waterfall on the Wisconsin River. The total drop is 89 feet, spread out in a series of cascades over about one mile. The upper third of the falls and most of the flow, except in the spring, is diverted through a ...
in Lincoln County. It creates the borders between Adams, Juneau, Columbia, Sauk, Dane, Iowa, Richland, Grant, and Crawford Counties, creating the only natural county borders within the state (excluding the Mississippi River and the Great Lakes).
Geology
The modern Wisconsin River was formed in several stages. The lower, westward-flowing portion of the river is located in the unglaciatedDriftless Area
The Driftless Area, a topographical and cultural region in the American Midwest, comprises southwestern Wisconsin, southeastern Minnesota, northeastern Iowa, and the extreme northwestern corner of Illinois.
Never covered by ice during the las ...
, and this section of the river's course likely predates the rest by several million years. The lower reach of the river is narrower than its upstream valley, leading to the suggestion that the upper portions of the ancestor of the river flowed east before the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
. The remaining length of the river was formed gradually as glaciers advanced and retreated over Wisconsin. The stretch of river from Stevens Point north to Merrill Merrill may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Merrill Field, Anchorage, Alaska
* Merrill, Iowa
*Merrill, Maine
* Merrill, Michigan
*Merrill, Mississippi, an unincorporated community near Lucedale in George County
*Merrill, Oregon
*Merrill, W ...
was a drainage route for meltwater flowing away from the glaciers which covered northern Wisconsin during the Wisconsin Glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cord ...
. As the glaciers retreated further northward, the river also grew in that direction. South from Stevens Point, the meltwater would have flowed into Glacial Lake Wisconsin
Glacial Lake Wisconsin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed from approximately 18,000 to 14,000 years ago, at the end of the last ice age, in the central part of present-day Wisconsin in the United States.
Formation and demise
Before t ...
, a prehistoric proglacial lake
In geology, a proglacial lake is a lake formed either by the damming action of a moraine during the retreat of a melting glacier, a glacial ice dam, or by meltwater trapped against an ice sheet due to isostatic depression of the crust around th ...
that existed in the central part of the state. As temperatures warmed around 15,000 years ago, the ice dam holding the lake in place burst, unleashing a catastrophic flood that carved the Dells of the Wisconsin River
The Dells of the Wisconsin River, also called the Wisconsin Dells (from Old English �dæle��, modern English “dale”), meaning “valley”, is a 5-mile (8-km) gorge on the Wisconsin River in south-central Wisconsin, USA. It is noted for it ...
and joined the upper stretches of the river with the pre-existing lower river valley that today flows from Portage to Prairie du Chien.
History
 In the summer of 1673, French missionary
In the summer of 1673, French missionary Jacques Marquette
Jacques Marquette S.J. (June 1, 1637 – May 18, 1675), sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded Saint Ign ...
, French-Canadian explorer Louis Joliet
Louis Jolliet (September 21, 1645after May 1700) was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore and ...
, and their crew of five Metis
Metis or Métis may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Métis, recognized Indigenous communities in Canada and America whose distinct culture and language emerged after early intermarriage between First Nations peoples and early European settlers, prima ...
arrived near the headwaters of the Fox River. From there, they were told to portage their two canoes a distance of slightly less than two miles through marsh and oak plains to the Wisconsin River.
The first documented exploration of the Wisconsin River by Europeans took place in 1673, when Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet
Louis Jolliet (September 21, 1645after May 1700) was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore and ...
of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
canoed from Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
up the Fox River until they reached the present-day site of Portage in early June. At this location the Wisconsin and Fox rivers are only 2 miles (3.2 km) apart, so the explorers could portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ...
from the Fox to the Wisconsin River. They then continued downstream 200 miles (320 km) to the Wisconsin's mouth, entering the Mississippi on June 17. Other explorers and traders would follow the same route, and for the next 150 years the Wisconsin and Fox rivers, collectively known as the Fox-Wisconsin Waterway, formed a major transportation route between the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
and the Mississippi River.
Industry began to form on the Wisconsin in the early 19th century, as loggers
Lumberjacks are mostly North American workers in the logging industry who perform the initial harvesting and transport of trees for ultimate processing into forest products. The term usually refers to loggers in the era (before 1945 in the Unite ...
started using the river to raft logs downstream from northern forests to sawmills in new cities like Wausau. By the 1880s, logging companies were dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
ming the river to ensure the river had enough capacity for the logs being floated downstream. Later, at the start of the 20th century, more dams were constructed to provide for flood control and hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other Renewabl ...
. The dams also spurred tourism, creating reservoirs such as Lake Wisconsin
Lake Wisconsin is a reservoir on the Wisconsin River in southern Wisconsin in the United States. It is located in Columbia and Sauk counties, approximately southeast of Baraboo and NNW of Madison. Today it is home to the Wisconsin wine appella ...
that are popular areas for recreational boating and fishing. Today the Wisconsin River is the hardest working river in the nation. There are 25 operating Hydroelectric Power Plants on the Wisconsin River. The "hydros" harness 645 feet of the rivers fall to generate nearly one billion kilowatt hours of renewable electricity a year — enough energy to supply the residential needs of over 300,000 people without creating any pollution.
Despite this, a 93-mile (150 km) stretch of the Wisconsin between its mouth and the Prairie du Sac Dam is free of any dams or barriers and is relatively free-flowing. In the late 1980s, this portion of the river was designated as a state riverway, and development alongside the river has been limited to preserve its scenic integrity.
Stevens Point
Stevens Point is the county seat of Portage County, Wisconsin, United States. The city was incorporated in 1858.
Its 2020 population of 25,666 makes it the largest city in the county. Stevens Point forms the core of the United States Census Bur ...
File:WisconsinRiverBridge.WIS82.jpg, Highway 82 bridge over the Wisconsin River
File:WisconsinRiverBoating.jpg, Boating on the Wisconsin River
File:WyalusingStateParkWisconsinRiverIntoMississippiRiver.jpg, Delta at the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
, seen from Wyalusing State Park
Navigable river of the United States
The Wisconsin River is a "navigable river of the United States." This designation primarily means that the federal government has jurisdiction for dams on the river. Dams that include hydropower facilities are regulated by theFederal Energy Regulatory Commission
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) is the United States federal agency that regulates the transmission and wholesale sale of electricity and natural gas in interstate commerce and regulates the transportation of oil by pipeline in ...
. Courts have ruled that despite the fact that the river lies entirely in one state, it nevertheless historically carried goods to markets in other states and therefore is subject to the commerce clause
The Commerce Clause describes an enumerated power listed in the United States Constitution ( Article I, Section 8, Clause 3). The clause states that the United States Congress shall have power "to regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and amon ...
of the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
. Courts have also ruled that raw logs, even if merely carried via log drives to mills within the state, constitute commerce. On the basis of these judgments, the Wisconsin River is considered a navigable waterway throughout its entire length. This designation does not generally have bearing on recreational use of the river. Boat registrations and fishing licenses are obtained through the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources
The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR) is a government agency of the U.S. state of Wisconsin charged with conserving and managing Wisconsin's natural resources. The Wisconsin Natural Resources Board has the authority to set policy ...
, for example.
Lower Wisconsin River State Riverway
The Lower Wisconsin River State Riverway is a state-funded project designed to protect the southern portion of the Wisconsin River. It extends fromSauk City
Sauk City is a village in Sauk County, Wisconsin, United States, North America. The population was 3,518 as of the 2020 census. The first incorporated village in the state, the community was founded by Agoston Haraszthy and his business partner, R ...
to the point where the Wisconsin River empties into the Mississippi, about south of the city of Prairie du Chien
Prairie du Chien () is a city in and the county seat of Crawford County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 5,506 at the 2020 census. Its ZIP Code is 53821.
Often referred to as Wisconsin's second oldest city, Prairie du Chien was esta ...
. The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources
The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR) is a government agency of the U.S. state of Wisconsin charged with conserving and managing Wisconsin's natural resources. The Wisconsin Natural Resources Board has the authority to set policy ...
manages protected lands of over , including the river itself, islands, and some lands adjacent to the river. In 2020 the riverway was designated as a protected Ramsar site
A Ramsar site is a wetland site designated to be of international importance under the Ramsar Convention,8 ha (O)
*** Permanent 8 ha (P)
*** Seasonal Intermittent < 8 ha(Ts)
**
There are no dams or man-made obstructions to the natural flow of water between the hydroelectric dam just north of Sauk City and the confluence of the Wisconsin and the Mississippi. This long stretch of free-flowing river provides important natural habitats for a variety of wildlife, including
River Alliance of Wisconsin
Wisconsin's Name: Where It Came From and What It Means
, Wisconsin Historical Society
Lower Wisconsin State Riverway Board
Pictures and Information of the Northern Stretch of the Wisconsin River
Current Wisconsin River Conditions
Lower Wisconsin River Maps and Mileage
* * Kent, Paul G. and Dudiak, Tamara A
''Wisconsin Water Law: A Guide to Water rights and Regulations, Second Edition''
(University of Wisconsin Extension, 2001). {{authority control Rivers of Wisconsin Tributaries of the Mississippi River Driftless Area Bodies of water of Wood County, Wisconsin Rivers of Grant County, Wisconsin Rivers of Lincoln County, Wisconsin Rivers of Sauk County, Wisconsin Rivers of Columbia County, Wisconsin Bodies of water of Portage County, Wisconsin Rivers of Oneida County, Wisconsin Rivers of Marathon County, Wisconsin Mississippi River watershed Ramsar sites in the United States
white-tail deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced t ...
, North American river otter
The North American river otter (''Lontra canadensis''), also known as the northern river otter and river otter, is a semiaquatic mammal that only lives on the North American continent, along its waterways and coasts. An adult North American rive ...
s, beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers ar ...
s, turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked tu ...
s, sandhill crane
The sandhill crane (''Antigone canadensis'') is a species of large crane of North America and extreme northeastern Siberia. The common name of this bird refers to habitat like that at the Platte River, on the edge of Nebraska's Sandhills on ...
s, eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just ...
s, hawk
Hawks are bird of prey, birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are widely distributed and are found on all continents except Antarctica.
* The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks and others. Th ...
s, and a variety of fish species.
Recreational opportunities on the lower Wisconsin River range from fishing and canoeing to tubing and camping. Canoe camping is particularly popular because of the abundance of suitable sandbars along the riverway and because no permits are required. On summer weekends, naturists
Naturism is a lifestyle of practising non-sexual social nudity in private and in public; the word also refers to the cultural movement which advocates and defends that lifestyle. Both may alternatively be called nudism. Though the two terms a ...
can be found on Mazo Beach which is north of the village of Mazomanie. According to the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, two thirds of river users can be found on the stretch between Prairie du Sac and Spring Green.
Cities and villages along the river
* Biron * Boscobel * Brokaw * Eagle River * Kronenwetter *Merrill Merrill may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Merrill Field, Anchorage, Alaska
* Merrill, Iowa
*Merrill, Maine
* Merrill, Michigan
*Merrill, Mississippi, an unincorporated community near Lucedale in George County
*Merrill, Oregon
*Merrill, W ...
* Merrimac
* Mosinee
*Muscoda
Muscoda is a village in Grant and Iowa counties in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The population was 1,299 at the 2010 census. Of this, 1,249 were in Grant County and 50 were in Iowa County. The Grant County part of the village is adjacent to the T ...
* Nekoosa
* Okee
*Plover
Plovers ( , ) are a widely distributed group of wading birds belonging to the subfamily Charadriinae.
Description
There are about 66 species in the subfamily, most of them called "plover" or "dotterel". The closely related lapwing subf ...
* Port Edwards
*Portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ...
* Prairie du Sac
* Rhinelander
*Rothschild
Rothschild () is a name derived from the German ''zum rothen Schild'' (with the old spelling "th"), meaning "with the red sign", in reference to the houses where these family members lived or had lived. At the time, houses were designated by sign ...
*Sauk City
Sauk City is a village in Sauk County, Wisconsin, United States, North America. The population was 3,518 as of the 2020 census. The first incorporated village in the state, the community was founded by Agoston Haraszthy and his business partner, R ...
* Schofield
* Spring Green
*Stevens Point
Stevens Point is the county seat of Portage County, Wisconsin, United States. The city was incorporated in 1858.
Its 2020 population of 25,666 makes it the largest city in the county. Stevens Point forms the core of the United States Census Bur ...
*Tomahawk
A tomahawk is a type of single-handed axe used by the many Indigenous peoples and nations of North America. It traditionally resembles a hatchet with a straight shaft. In pre-colonial times the head was made of stone, bone, or antler, and Eur ...
* Wausau
* Whiting
* Wisconsin Dells
*Wisconsin Rapids
Wisconsin Rapids is a city in and the county seat of Wood County, Wisconsin. The population was 18,877 at the 2020 census. The city also forms one of the core areas of the United States Census Bureau's Marshfield-Wisconsin Rapids Micropolit ...
See also
*List of Wisconsin rivers
This is a list of rivers in the U.S. state of Wisconsin.
By drainage basin
This list is arranged by drainage basin, with respective tributaries indented under each larger stream's name.
Great Lakes Drainage
Lake Michigan
*Menominee River
* ...
References
External links
River Alliance of Wisconsin
Wisconsin's Name: Where It Came From and What It Means
, Wisconsin Historical Society
Lower Wisconsin State Riverway Board
Pictures and Information of the Northern Stretch of the Wisconsin River
Current Wisconsin River Conditions
Lower Wisconsin River Maps and Mileage
* * Kent, Paul G. and Dudiak, Tamara A
''Wisconsin Water Law: A Guide to Water rights and Regulations, Second Edition''
(University of Wisconsin Extension, 2001). {{authority control Rivers of Wisconsin Tributaries of the Mississippi River Driftless Area Bodies of water of Wood County, Wisconsin Rivers of Grant County, Wisconsin Rivers of Lincoln County, Wisconsin Rivers of Sauk County, Wisconsin Rivers of Columbia County, Wisconsin Bodies of water of Portage County, Wisconsin Rivers of Oneida County, Wisconsin Rivers of Marathon County, Wisconsin Mississippi River watershed Ramsar sites in the United States