Wine Database on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Wine is an
Wine is an
made 'world's oldest wine'"> Later, as
 The earliest known traces of wine are from
The earliest known traces of wine are from
made 'world's oldest wine'" /> 
 Wine is an
Wine is an alcoholic drink
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The c ...
typically made from fermented
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, ...
s. Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitut ...
consumes the sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
in the grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, ...
s and converts it to ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl ...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
, releasing heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is al ...
in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are major factors in different styles of wine. These differences result from the complex interactions between the biochemical
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology an ...
development of the grape, the reactions involved in fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
, the grape's growing environment (terroir
(, ; from ''terre'', "land") is a French term used to describe the environmental factors that affect a crop's phenotype, including unique environment contexts, farming practices and a crop's specific growth habitat. Collectively, these conte ...
), and the wine production process. Many countries enact legal appellation
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication primarily used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown, although other types of food often have appellations as well. Restrictions other than geographical boun ...
s intended to define styles and qualities of wine. These typically restrict the geographical origin and permitted varieties of grapes, as well as other aspects of wine production. Wines not made from grapes involve fermentation of other crops including rice wine
Rice wine is an alcoholic beverage fermented and distilled from rice, traditionally consumed in East Asia, Southeast Asia and South Asia. Rice wine is made by the fermentation of rice starch that has been converted to sugars. Microbes are the so ...
and other fruit wine
Fruit wines are fermented alcoholic beverages made from a variety of base ingredients (other than grapes); they may also have additional flavors taken from fruits, flowers, and herbs. This definition is sometimes broadened to include any alcohol ...
s such as plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found i ...
, cherry
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The nam ...
, pomegranate
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between tall.
The pomegranate was originally described throughout the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean re ...
, currant and elderberry
''Sambucus'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Adoxaceae. The various species are commonly called elder or elderberry. The genus was formerly placed in the honeysuckle family, Caprifoliaceae, but was reclassified as Adoxaceae due to ge ...
.
Wine has been produced for thousands of years. The earliest evidence of wine is from the Caucasus region
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
in today's Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
(6000 BCE), Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(5000 BCE), Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
and Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
(4000 BCE). New World wine has some connection to alcoholic beverages made by the indigenous peoples of the Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
, but is mainly connected to later Spanish traditions in New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
.Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...Old World wine
Old World wine refers primarily to wine made in Europe but can also include other regions of the Mediterranean basin with long histories of winemaking such as North Africa and the Near East. The phrase is often used in contrast to " New World win ...
further developed viticulture techniques, Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
would encompass three of the largest wine-producing regions. Today, the five countries with the largest wine producing regions are in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
.
Wine has long played an important role in religion. Red wine
Red wine is a type of wine made from dark-colored grape varieties. The color of the wine can range from intense violet, typical of young wines, through to brick red for mature wines and brown for older red wines. The juice from most purple grap ...
was associated with blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the c ...
by the ancient Egyptians and was used by both the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
cult of Dionysus
The cult of Dionysus was strongly associated with satyrs, centaurs, and Silenus, sileni, and its characteristic symbols were the Bull (mythology), bull, the Serpent (symbolism), serpent, tigers/leopards, ivy, and wine. The Dionysia and Lenaia f ...
and the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
in their Bacchanalia
The Bacchanalia were unofficial, privately funded popular Roman festivals of Bacchus, based on various ecstatic elements of the Greek Dionysia. They were almost certainly associated with Rome's native cult of Liber, and probably arrived in Rome ...
; Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
also incorporates it in the Kiddush
Kiddush (; he, קידוש ), literally, "sanctification", is a blessing recited over wine or grape juice to sanctify the Shabbat and Jewish holidays. Additionally, the word refers to a small repast held on Shabbat or festival mornings after t ...
, and Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
in the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
. Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
, and Israeli
Israeli may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel
* Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel
* Modern Hebrew, a language
* ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008
* Guni Israeli ...
wine cultures are still connected to these ancient roots. Similarly the largest wine regions in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
have heritages in connection to sacramental wine
Sacramental wine, Communion wine, altar wine, or wine for consecration is wine obtained from grapes and intended for use in celebration of the Eucharist (also referred to as the Lord's Supper or Holy Communion, among other names). It is usually ...
, likewise, viticulture traditions in the Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Ne ...
started within New Spain as Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
friars and monks first produced wines in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
and California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
.
History
 The earliest known traces of wine are from
The earliest known traces of wine are from Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
( BCE),Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
) ( BCE), Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
(c. 4100 BCE), and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
( BCE). Wine reached the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
by 4500 BC and was consumed and celebrated in ancient Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
and Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. Throughout history, wine has been consumed for its intoxicating effects.
The earliest archaeological and archaeobotanical evidence for grape wine and viniculture, dating to 6000–5800 BCE was found on the territory of modern Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. Both archaeological and genetic evidence suggest that the earliest production of wine elsewhere was relatively later, likely having taken place in the Southern Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
(which encompasses Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
, Georgia and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
), or the West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
n region between Eastern Turkey
The Eastern Anatolia Region ('' tr, Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi'') is a geographical region of Turkey. The most populous province in the region is Van Province. Other populous provinces are Malatya, Erzurum and Elazığ.
It is bordered by the Black Se ...
, and northern Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The earliest known winery from 4100 BCE is the Areni-1 winery
The Areni-1 winery is an ancient winery that was discovered in 2007 in the Areni-1 cave complex in the village of Areni in the Vayots Dzor province of Armenia by a team of Armenian and Irish archaeologists. The excavations were carried out by B ...
in Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
.
 A 2003 report by archaeologists indicates a possibility that grapes were mixed with
A 2003 report by archaeologists indicates a possibility that grapes were mixed with rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
to produce fermented drink
This is a list of fermented foods, which are foods produced or preserved by the action of microorganisms. In this context, Fermentation in food processing, fermentation typically refers to the fermentation of sugar to ethanol, alcohol using yeas ...
s in ancient China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
in the early years of the seventh millennium BCE. Pottery jars from the Neolithic site of Jiahu
Jiahu () was the site of a Neolithic settlement based in the central plain of ancient China, near the Yellow River. It is located between the floodplains of the Ni River to the north, and the Sha River to the south, north of the modern city ...
, Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
, contained traces of tartaric acid
Tartaric acid is a white, crystalline organic acid that occurs naturally in many fruits, most notably in grapes, but also in bananas, tamarinds, and citrus. Its salt, potassium bitartrate, commonly known as cream of tartar, develops naturally i ...
and other organic compounds commonly found in wine. However, other fruits indigenous to the region, such as hawthorn
Hawthorn or Hawthorns may refer to:
Plants
* '' Crataegus'' (hawthorn), a large genus of shrubs and trees in the family Rosaceae
* ''Rhaphiolepis'' (hawthorn), a genus of about 15 species of evergreen shrubs and small trees in the family Rosace ...
, cannot be ruled out. If these drinks, which seem to be the precursors of rice wine
Rice wine is an alcoholic beverage fermented and distilled from rice, traditionally consumed in East Asia, Southeast Asia and South Asia. Rice wine is made by the fermentation of rice starch that has been converted to sugars. Microbes are the so ...
, included grapes rather than other fruits, they would have been any of the several dozen indigenous wild species in China, rather than ''Vitis vinifera
''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are curre ...
'', which was introduced 6000 years later.
The spread of wine culture westwards was most probably due to the Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient thalassocracy, thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-st ...
who spread outward from a base of city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
s along the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
coast centered around modern day Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
(as well as including small parts of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
/Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
and coastal Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
); however, the Nuragic culture in Sardinia already had a custom of consuming wine before the arrival of the Phoenicians. The wines of Byblos
Byblos ( ; gr, Βύβλος), also known as Jbeil or Jubayl ( ar, جُبَيْل, Jubayl, locally ; phn, 𐤂𐤁𐤋, , probably ), is a city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 880 ...
were exported to Egypt during the Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth ...
and then throughout the Mediterranean. Evidence for this includes two Phoenician shipwrecks from 750 BCE, found with their cargoes of wine still intact, which were discovered by Robert Ballard
Robert Duane Ballard (born June 30, 1942) is an American retired Navy officer and a professor of oceanography at the University of Rhode Island who is most noted for his work in underwater archaeology: maritime archaeology and archaeology of ...
As the first great traders in wine (''cherem''), the Phoenicians seem to have protected it from oxidation with a layer of olive oil, followed by a seal of pinewood and resin, similar to retsina
Retsina ( el, Ρετσίνα) is a Greek white (or rosé) resinated wine, which has been made for at least 2,000 years. Its unique flavor is said to have originated from the practice of sealing wine vessels, particularly amphorae, with Alepp ...
.
The earliest remains of Apadana Palace
, native_name_lang =
, alternate_name =
, image = Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.jpg
, image_size =
, alt =
, caption = Ruins of the Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.
, map =
, map_type ...
in Persepolis
, native_name_lang =
, alternate_name =
, image = Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.jpg
, image_size =
, alt =
, caption = Ruins of the Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.
, map =
, map_type ...
dating back to 515 BCE include carvings depicting soldiers from Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
subject nations bringing gifts to the Achaemenid king, among them Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
bringing their famous wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
.
Literary references to wine are abundant in Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
(8th century BCE, but possibly relating earlier compositions), Alkman
Alcman (; grc-gre, wikt:Ἀλκμάν, Ἀλκμάν ''Alkmán''; floruit, fl. 7th century BC) was an Ancient Greek Choral poetry, choral lyric poet from Sparta. He is the earliest representative of the Alexandrian canon of the Nine Lyric ...
(7th century BCE), and others. In ancient Egypt, six of 36 wine amphora
An amphora (; grc, ἀμφορεύς, ''amphoreús''; English plural: amphorae or amphoras) is a type of container with a pointed bottom and characteristic shape and size which fit tightly (and therefore safely) against each other in storag ...
s were found in the tomb of King Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun (, egy, twt-ꜥnḫ-jmn), Egyptological pronunciation Tutankhamen () (), sometimes referred to as King Tut, was an Egyptian pharaoh who was the last of his royal family to rule during the end of the Eighteenth Dynasty (ruled ...
bearing the name "Kha'y", a royal chief vintner
A winemaker or vintner is a person engaged in winemaking. They are generally employed by wineries or wine companies, where their work includes:
*Cooperating with viticulturists
*Monitoring the maturity of grapes to ensure their quality and to deter ...
. Five of these amphoras were designated as originating from the king's personal estate, with the sixth from the estate of the royal house of Aten
Aten also Aton, Atonu, or Itn ( egy, jtn, ''reconstructed'' ) was the focus of Atenism, the religious system established in ancient Egypt by the Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh Akhenaten. The Aten was the disc of the sun and originally an aspect of ...
. Traces of wine have also been found in central Asian Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
in modern-day China, dating from the second and first millennia BCE.
 The first known mention of
The first known mention of grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, ...
-based wines in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
is from the late 4th-century BCE writings of Chanakya
Chanakya (Sanskrit: चाणक्य; IAST: ', ; 375–283 BCE) was an ancient Indian polymath who was active as a teacher, author, strategist, philosopher, economist, jurist, and royal advisor. He is traditionally identified as Kauṭilya o ...
, the chief minister of Emperor Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (350-295 BCE) was a ruler in Ancient India who expanded a geographically-extensive kingdom based in Magadha and founded the Maurya dynasty. He reigned from 320 BCE to 298 BCE. The Maurya kingdom expanded to become an empi ...
. In his writings, Chanakya condemns the use of alcohol while chronicling the emperor and his court's frequent indulgence of a style of wine known as ''madhu''.
The ancient Romans
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom ...
planted vineyards near garrison towns so wine could be produced locally rather than shipped over long distances. Some of these areas are now world-renowned for wine production. The Romans discovered that burning sulfur candles inside empty wine vessels kept them fresh and free from a vinegar smell. In medieval Europe
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
supported wine because the clergy required it for the Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
. Monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
s in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
made wine for years, aging it in caves. An old English recipe that survived in various forms until the 19th century calls for refining white wine from bastard—bad or tainted '' bastardo'' wine.
Later, the descendants of the sacramental wine were refined for a more palatable taste. This gave rise to modern viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for ''vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ran ...
in French wine
French wine is produced all throughout France, in quantities between 50 and 60 million hectolitres per year, or 7–8 billion bottles. France is one of the largest wine producers in the world, along with Italian, Spanish, and America ...
, Italian wine
Italian wine is produced in every region of Italy. Italy is the world's largest producer of wine, with an area of under vineyard cultivation, and contributing a 2013–2017 annual average of 48.3 million hl of wine. In 2018 Italy accounted for ...
, Spanish wine
Spanish wine () includes red, white, and sparkling wines produced throughout the country. Located on the Iberian Peninsula, Spain has over 1.2 million hectares (2.9 million acres) planted in wine grapes, making it the most widely pla ...
, and these wine grape traditions were brought into New World wine. For example, Mission grapes were brought by Franciscan monks to New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
in 1628 beginning the New Mexico wine
New Mexico has a long history of wine production, within American wine, especially along the Rio Grande, from its capital Santa Fe, the city of Albuquerque with its surrounding metropolitan area, and in valleys like the Mesilla and the Mimbres ...
heritage, these grapes were also brought to California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
which started the California wine
California wine production has a rich viticulture history since 1680 when
Spanish Jesuit missionaries planted ''Vitis vinifera'' vines native to the Mediterranean region in their established missions to produce wine for religious services. I ...
industry. Thanks to Spanish wine culture, these two regions eventually evolved into the oldest and largest producers, respectively, of wine of the United States
Wine has been produced in the United States since the 1500s, with the first widespread production beginning in New Mexico wine, New Mexico in 1628. Today, wine production is undertaken in all fifty states, with California wine, California producin ...
. Viking sagas earlier mentioned a fantastic land filled with wild grapes and high-quality wine called precisely Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland ( non, Vínland ᚠᛁᚾᛚᛅᚾᛏ) was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and John ...
. Prior to the Spanish establishing their American wine grape traditions in California and New Mexico, both France and Britain had unsuccessfully attempted to establish grapevines in Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
respectively.
In East Asia, the first modern wine industry was Japanese wine
Although viticulture and the cultivation of grapes for table consumption has a long history in Japan, domestic wine production using locally produced grapes only really began with the adoption of Western culture during the Meiji restoration in th ...
, developed in 1874 after grapevines were brought back from Europe.
Etymology
Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic branc ...
''*winam'', an early borrowing from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''vinum'', Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
''ღვინო'' (''ghvee-no''), "wine", itself derived from the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
stem *''win-o-'' (cf. hy, գինի, '' gini''; Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
: ''oinos''; Aeolic Greek
In linguistics, Aeolic Greek (), also known as Aeolian (), Lesbian or Lesbic dialect, is the set of dialects of Ancient Greek spoken mainly in Boeotia; in Thessaly; in the Aegean island of Lesbos; and in the Greek colonies of Aeolis in Anatolia ...
: ''woinos''; Hittite: ''wiyana''; Lycian: ''oino''). The earliest attested terms referring to wine are the Mycenaean Greek
Mycenaean Greek is the most ancient attested form of the Greek language, on the Greek mainland and Crete in Mycenaean Greece (16th to 12th centuries BC), before the hypothesised Dorian invasion, often cited as the ''terminus ad quem'' for the ...
''me-tu-wo ne-wo'' (*), meaning "in (the month)" or "(festival) of the new wine", and ''wo-no-wa-ti-si'', meaning "wine garden", written in Linear B
Linear B was a syllabic script used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest attested form of Greek. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries. The oldest Mycenaean writing dates to about 1400 BC. It is descended from ...
inscriptions. Linear B also includes, inter alia, an ideogram
An ideogram or ideograph (from Greek "idea" and "to write") is a graphic symbol that represents an idea or concept, independent of any particular language, and specific words or phrases. Some ideograms are comprehensible only by familiarit ...
for wine, i.e. .
The ultimate Indo-European origin of the word is the subject of some continued debate. Some scholars have noted the similarities between the words for wine in Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
(e.g. Armenian '' gini'', Latin ''vinum'', Ancient Greek οἶνος, Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
вино ), Kartvelian Kartvelian may refer to:
* Anything coming from or related to Georgia (country)
* Kartvelian languages
* Kartvelian alphabet, see Georgian alphabet
* Kartvelian studies
* Georgians
{{disambig
Language and nationality disambiguation pages ...
(e.g. Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
ღვინო ), and Semitic (''*wayn''; Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
יין ), pointing to the possibility of a common origin of the word denoting "wine" in these language families. The Georgian word goes back to Proto-Kartvelian
The Proto-Kartvelian language, or Common Kartvelian ( ka, წინარექართველური ენა, tr), is the linguistic reconstruction of the common ancestor of the Kartvelian languages, which was spoken by the ancestors of th ...
*''ɣwino''-, which is either a borrowing from Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
The Sound of Indo-European: Phonetics, Phonemics, and Morphophonemics, p. 505+ or the lexeme was specifically borrowed from
Proto-Armenian
Proto-Armenian is the earlier, unattested stage of the Armenian language which has been reconstructed by linguists. As Armenian is the only known language of its branch of the Indo-European languages, the comparative method cannot be used to rec ...
*''ɣʷeinyo''-, whence Armenian ''gini''. An alternate hypothesis by Fähnrich supposes *''ɣwino''-, a native Kartvelian word derived from the verbal root *''ɣun''- ('to bend'). See *''ɣwino''- for more. All these theories place the origin of the word in the same geographical location, South Caucasus, that has been established based on archeological and biomolecular studies as the origin of viticulture.
Types of wine
Wine types: *Red wine
Red wine is a type of wine made from dark-colored grape varieties. The color of the wine can range from intense violet, typical of young wines, through to brick red for mature wines and brown for older red wines. The juice from most purple grap ...
, made from blue grapes with skins.
* White wine
White wine is a wine that is Fermentation in winemaking, fermented without skin contact. The wine color, colour can be straw-yellow, yellow-green, or yellow-gold. It is produced by the alcoholic fermentation of the non-coloured Juice vesicles, ...
, made from green grapes or destemmed blue grapes.
* Rosé wine
A rosé () is a type of wine that incorporates some of the color from the grape skins, but not enough to qualify it as a red wine. It may be the oldest known type of wine, as it is the most straightforward to make with the skin contact method. ...
, made from blue grapes, where the skins are sorted from early in the fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
process or rosé wine can also be made from rosé wine grape varieties.
* Sparkling wine
Sparkling wine is a wine with significant levels of carbon dioxide in it, making it fizzy. While the phrase commonly refers to champagne, European Union countries legally reserve that term for products exclusively produced in the Champagne regi ...
, made from both green and blue grapes. Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
is made from pinot noir
Pinot Noir () is a red-wine grape variety of the species ''Vitis vinifera''. The name may also refer to wines created predominantly from pinot noir grapes. The name is derived from the French language, French words for ''pine'' and ''black.' ...
, meunier
Meunier is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Christian Meunier (born 1967), French automotive businessman
* Claude Meunier (born 1951), Canadian actor and film director
* Claude Marie Meunier (1770–1846), French general du ...
and chardonnay
Chardonnay (, , ) is a green-skinned grape variety used in the production of white wine. The variety originated in the Burgundy wine region of eastern French wine, France, but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from English wine, Englan ...
around Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
.
* Hard wine
Hard may refer to:
* Hardness, resistance of physical materials to deformation or fracture
* Hard water, water with high mineral content
Arts and entertainment
* ''Hard'' (TV series), a French TV series
* Hard (band), a Hungarian hard rock super ...
da, wine with a higher alcohol content than the other types.
* Ice wine
Ice wine (or icewine; german: Eiswein) is a type of dessert wine produced from grapes that have been frozen while still on the vine. The sugars and other dissolved solids do not freeze, but the water does, allowing for a more concentrated grape ...
, wine with a characteristically sweet taste and low alcohol content.
* Dessert wine
Dessert wines, sometimes called pudding wines in the United Kingdom, are sweet wines typically served with dessert.
There is no simple definition of a dessert wine. In the UK, a dessert wine is considered to be any sweet wine drunk with a meal ...
, are sweet wines that are typically served with a dessert.
The types have such different properties that in practice they are considered different drinks.
Styles
Wine is made in many ways from different fruits, with grapes being the most common.From grapes
The type of grape used and the amount ofskin contact
Maceration is the winemaking process where the phenolic materials of the grape—tannins, coloring agents (anthocyanins) and flavor compounds—are leached from the grape skins, seeds and stems into the must. To macerate is to soften by soaking, ...
while the juice is being extracted determines the color and general style of the wine. The color has no relation to a wine's sweetness
Sweetness is a Taste#Basic tastes, basic taste most commonly Perception, perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasure, pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds ...
—all may be made sweet or dry.
Red
Red wine gains its color and flavor (notably,tannins
Tannins (or tannoids) are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
The term ''tannin'' (from Anglo-Norman ''tanner'', f ...
) from the grape skin, by allowing the grapes to soak in the extracted juice. Red wine is made from dark-colored red grape varieties. The actual color of the wine
The color of wine is one of the most easily recognizable characteristics of wines. Color is also an element in wine tasting since heavy wines generally have a deeper color. The accessory traditionally used to judge the wine color was the tastevin, ...
can range from violet, typical of young wines, through red for mature wines, to brown for older red wines. The juice from most red grapes is actually greenish-white; the red color comes from anthocyanin
Anthocyanins (), also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart gave the name Anthokyan to a chemical compo ...
s present in the skin of the grape. A notable exception is the family of rare ''teinturier
Teinturier grapes are grapes whose flesh and juice is red in colour due to anthocyanin pigments accumulating within the pulp of the grape berry itself. In most cases, anthocyanin pigments are confined to the outer skin tissue only, and the squee ...
'' varieties, which actually have red flesh and produce red juice.
White
To make white wine, grapes are pressed quickly with the juice immediately drained away from the grape skins. The grapes used are typically white grape varieties, though red grapes may be used if the winemaker is careful not to let the skin stain thewort
Wort () is the liquid extracted from the mashing process during the brewing of beer or whisky. Wort contains the sugars, the most important being maltose and maltotriose, that will be fermented by the brewing yeast to produce alcohol. Wort ...
during the separation of the pulp-juice. For example, pinot noir
Pinot Noir () is a red-wine grape variety of the species ''Vitis vinifera''. The name may also refer to wines created predominantly from pinot noir grapes. The name is derived from the French language, French words for ''pine'' and ''black.' ...
(a red grape) is commonly used in champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
.
Dry (low sugar) white wine is the most common, derived from the complete fermentation of the juice, however sweet white wines such as Moscato d'Asti
Moscato d'Asti is a DOCG sparkling white wine made from the Moscato bianco grape and produced mainly in the province of Asti, northwest Italy, and in smaller nearby regions in the provinces of Alessandria and Cuneo. The wine is sweet and low in a ...
are also made.
Rosé
A rosé wine gainscolor
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
from red grape skins, but not enough to qualify it as a red wine
Red wine is a type of wine made from dark-colored grape varieties. The color of the wine can range from intense violet, typical of young wines, through to brick red for mature wines and brown for older red wines. The juice from most purple grap ...
. It may be the oldest known type of wine, as it is the most straightforward to make with the skin contact method. The color can range from a pale orange to a vivid near-purple, depending on the varietals used and wine-making techniques.
There are three primary ways to produce rosé wine: Skin contact (allowing dark grape skins to stain the wort
Wort () is the liquid extracted from the mashing process during the brewing of beer or whisky. Wort contains the sugars, the most important being maltose and maltotriose, that will be fermented by the brewing yeast to produce alcohol. Wort ...
), saignée (removing juice from the must
Must (from the Latin ''vinum mustum'', "young wine") is freshly crushed fruit juice (usually grape juice) that contains the skins, seeds, and stems of the fruit. The solid portion of the must is called pomace and typically makes up 7–23% of t ...
early in fermentation and continuing fermentation of the juice separately), and blending of a red and white wine (uncommon and discouraged in most wine growing regions). Rosé wines have a wide range of sweetness levels from dry Provençal rosé to sweet White Zinfandel
White Zinfandel is an off-dry to sweet rosé wine. Originally the result of a stuck fermentation and fortuitous accident, White Zinfandel is made from the Zinfandel wine grape that would otherwise produce a bold and spicy red wine.
White Zinfan ...
s and blushes. Rosé wines are made from a wide variety of grapes all over the world.J. Robinson (ed) ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'' Third Edition pg 593 Oxford University Press 2006 O. Clarke ''Oz Clarke's Encyclopedia of Wine'' pgs 15, 225, 320, 360 Time Warner Books, London 2003
Orange
Sometimes called amber wines, these are wines made with white grapes but with the skins allowed tosoak
Soak may refer to:
* Steeping
* Bathing
* Soakage (source of water), a source of water in Australian deserts
* Soak dike, ditch or drain
* Soak testing, a method of system testing in computing and electronics
* Soak (singer), Irish singer-songwrit ...
during pressing, similar to red and rosé wine production. They are notably tannic, and usually made dry.
Sparkling
These areeffervescent
Effervescence is the escape of gas from an aqueous solution and the foaming or fizzing that results from that release. The word effervescence is derived from the Latin verb ''fervere'' (to boil), preceded by the adverb ''ex''. It has the same li ...
wines, made in any of the above styles (ie, orange, red, rosé, white). They must undergo secondary fermentation to create carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
, which creates the bubbles.
Two common methods of accomplishing this are the traditional method
The traditional method is the process used in the Champagne region of France to produce Champagne. It is also the method used in various French regions to produce sparkling wines (not called “Champagne”), in Spain to produce Cava, in Portu ...
, used for Cava, Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
, and more expensive sparkling wines, and the Charmat method
Sparkling wine production is the method of winemaking used to produce sparkling wine. The oldest known production of sparkling wine took place in 1531 with the ''ancestral method''.
Pressure and terminology
In popular parlance and also in the ...
, used for Prosecco
Prosecco (; Italian: ) is an Italian DOC or DOCG white wine produced in a large area spanning nine provinces in the Veneto and Friuli Venezia Giulia regions, and named after the village of Prosecco which is in the province of Trieste, Italy. It ...
, Asti
Asti ( , , ; pms, Ast ) is a ''comune'' of 74,348 inhabitants (1-1-2021) located in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy, about east of Turin in the plain of the Tanaro River. It is the capital of the province of Asti and it is deemed t ...
, and less expensive wines. A hybrid ''transfer method'' is also used, yielding intermediate results, and simple addition of carbon dioxide is used in the cheapest of wines.
The bottles used for sparkling wine must be thick to withstand the pressure of the gas behind the cork
Cork or CORK may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Cork (plug), a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
***Wine cork
Places Ireland
* Cork (city)
** Metropolitan Cork, also known as G ...
, which can be up to .
Dessert
This refers to sweet wines that have a high level ofsugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
remaining after fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
. There are various ways of increasing the amount of sugar in a wine, yielding products with different strengths and names. Icewine
Ice wine (or icewine; german: Eiswein) is a type of dessert wine produced from grapes that have been frozen while still on the vine. The sugars and other dissolved solids do not freeze, but the water does, allowing for a more concentrated grape ...
, Port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
, Sauternes, Tokaji Aszú, Trockenbeerenauslese
''Trockenbeerenauslese'' (literal meaning: 'dried berry selection') is a German language wine term for a medium to full body dessert wine.
''Trockenbeerenauslese'' is the highest in sugar content in the ''Prädikatswein'' category of the Austrian ...
, and Vin Santo
Vin Santo ("holy wine") is a style of Italian dessert wine. Traditional in Tuscany, these wines are often made from white grape varieties such as Trebbiano and Malvasia, though Sangiovese may be used to produce a ''rosé'' style known as "Occ ...
are some examples.
From other fruits and foods
Fruit
Wines from other fruits, such as apples and berries, are usually named after the fruit from which they are produced, and combined with the word "wine" (for example,apple wine
''Apfelwein'' ( German, 'apple wine'), or ''Viez'' ( Moselfranken, Saarland, Trier, ''vice'') or ''Most'' ( Austria, Switzerland, South Germany, ''must'') are German words for cider. It is made from a mix of sour tasting apples, such as "Bohna ...
and elderberry wine
Fruit wines are Ethanol fermentation, fermented alcoholic beverages made from a variety of base ingredients (other than grapes); they may also have additional flavors taken from fruits, flowers, and herbs. This definition is sometimes broadened t ...
) and are generically called fruit wine
Fruit wines are fermented alcoholic beverages made from a variety of base ingredients (other than grapes); they may also have additional flavors taken from fruits, flowers, and herbs. This definition is sometimes broadened to include any alcohol ...
or country wine (similar to French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
term ''vin de pays
''Vin de pays'' (, "country wine") was a French wine classification that was above the ''vin de table'' classification, but below the ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) classification and below the former ''vin délimité de qualité s ...
''). Other than the grape varieties
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
traditionally used for wine-making, most fruits naturally lack either sufficient fermentable sugars, proper amount of acidity, yeast amounts needed to promote or maintain fermentation, or a combination of these three materials. This is probably one of the main reasons why wine derived from grapes has historically been more prevalent by far than other types, and why specific types of fruit wines have generally been confined to the regions in which the fruits were native or introduced for other reasons.
Honey
Mead, also called honey wine, is created by fermentinghoney
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
with water, sometimes with various fruits, spices, grains, or hops
Hops are the flowers (also called seed cones or strobiles) of the hop plant ''Humulus lupulus'', a member of the Cannabaceae family of flowering plants. They are used primarily as a bittering, flavouring, and stability agent in beer, to whi ...
. As long as the primary substance fermented is honey, the drink is considered mead. Mead was produced in ancient history throughout Europe, Africa and Asia, and was known in Europe before grape wine.
Starch
Other drinks called "wine", such asbarley wine
Barley wine is a strong ale between 6–12% alcohol by volume."Barley wine"
 Wine is usually made from one or more
Wine is usually made from one or more
 Regulations govern the classification and sale of wine in many regions of the world. European wines tend to be classified by region (e.g.
Regulations govern the classification and sale of wine in many regions of the world. European wines tend to be classified by region (e.g.
 France has various
France has various
 In the United States, for a wine to be vintage-dated and labeled with a country of origin or
In the United States, for a wine to be vintage-dated and labeled with a country of origin or
If a wine is not labeled with a country of origin or AVA the percentage requirement is lowered to 85%. Vintage wines are generally bottled in a single batch so that each bottle will have a similar taste. Climate's impact on the character of a wine can be significant enough to cause different vintages from the same vineyard to vary dramatically in flavor and quality. Thus, vintage wines are produced to be individually characteristic of the particular vintage and to serve as the flagship wines of the producer. Superior vintages from reputable producers and regions will often command much higher prices than their average ones. Some vintage wines (e.g. Brunello), are only made in better-than-average years. For consistency, non-vintage wines can be blended from more than one vintage, which helps wine-makers sustain a reliable market image and maintain sales even in bad years. One recent study suggests that for the average wine drinker, the vintage year may not be as significant for perceived quality as had been thought, although wine connoisseurs continue to place great importance on it.

 Outstanding vintages from the best vineyards may sell for thousands of
Outstanding vintages from the best vineyards may sell for thousands of

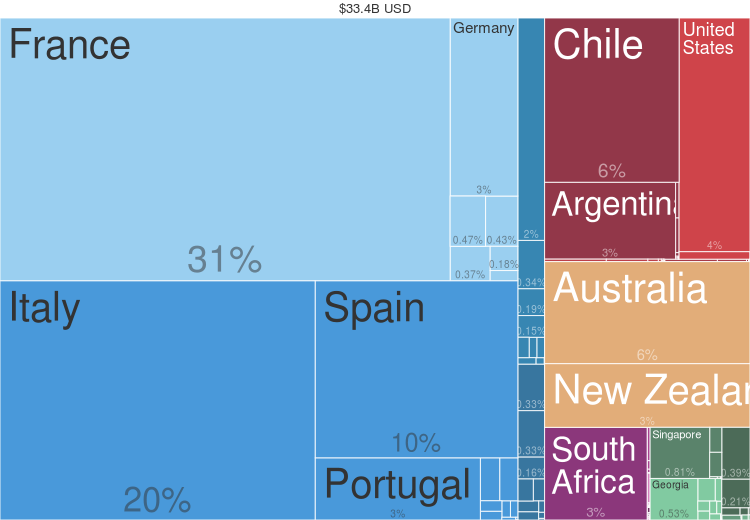
* May include official, semi-official or estimated data.
Wine grapes grow almost exclusively between 30 and 50 degrees latitude north and south of the
* May include official, semi-official or estimated data.
 ]
The UK was the world's largest importer of wine in 2007.
]
The UK was the world's largest importer of wine in 2007.

 Wine-consumption data from a
Wine-consumption data from a
 Wine is a popular and important
Wine is a popular and important
 In
In
 Alcoholic drinks, including wine, are forbidden under most interpretations of
Alcoholic drinks, including wine, are forbidden under most interpretations of
 The main active ingredient of wine is ethanol. A 2016 systematic review and meta-analysis found that moderate ethanol consumption brought no mortality benefit compared with lifetime abstention from ethanol consumption. A systematic analysis of data from the Global Burden of Disease study found that consumption of ethanol increases the risk of cancer and increases the risk of all-cause mortality, and that the most healthful dose of ethanol is zero consumption. Some studies have concluded that drinking small quantities of alcohol (less than one drink daily in women and two drinks daily in men) is associated with a decreased risk of
The main active ingredient of wine is ethanol. A 2016 systematic review and meta-analysis found that moderate ethanol consumption brought no mortality benefit compared with lifetime abstention from ethanol consumption. A systematic analysis of data from the Global Burden of Disease study found that consumption of ethanol increases the risk of cancer and increases the risk of all-cause mortality, and that the most healthful dose of ethanol is zero consumption. Some studies have concluded that drinking small quantities of alcohol (less than one drink daily in women and two drinks daily in men) is associated with a decreased risk of
 Most wines are sold in wine bottle, glass bottles and sealed with cork (material), corks (50% of which come from
Most wines are sold in wine bottle, glass bottles and sealed with cork (material), corks (50% of which come from
 Wine cellars, or wine rooms, if they are above-ground, are places designed specifically for the storage and aging of wine. Fine restaurants and some private homes have wine cellars. In an active wine cellar, temperature and humidity are maintained by a climate-control system. Passive wine cellars are not climate-controlled, and so must be carefully located. Because wine is a natural, perishable food product, all types—including red, white, sparkling, and fortified—can spoil when exposed to heat, light, vibration or fluctuations in temperature and humidity. When properly stored, wines can maintain their quality and in some cases improve in aroma, flavor, and complexity as they age. Some wine experts contend that the optimal temperature for aging wine is , others .
Wine refrigerators offer a smaller alternative to wine cellars and are available in capacities ranging from small, 16-bottle units to furniture-quality pieces that can contain 500 bottles. Wine refrigerators are not ideal for aging, but rather serve to chill wine to the proper temperature for drinking. These refrigerators keep the humidity low (usually under 50%), below the optimal humidity of 50% to 70%. Lower humidity levels can dry out corks over time, allowing oxygen to enter the bottle, which reduces the wine's quality through oxidation. While some types of alcohol are sometimes stored in the freezer, such as vodka, it is not possible to safely freeze wine in the bottle, as there is insufficient room for it to expand as it freezes and the bottle will usually crack. Certain shapes of bottle may allow the cork to be pushed out by the ice, but if the bottle is frozen on its side, the wine in the narrower neck will invariably freeze first, preventing this.
Wine cellars, or wine rooms, if they are above-ground, are places designed specifically for the storage and aging of wine. Fine restaurants and some private homes have wine cellars. In an active wine cellar, temperature and humidity are maintained by a climate-control system. Passive wine cellars are not climate-controlled, and so must be carefully located. Because wine is a natural, perishable food product, all types—including red, white, sparkling, and fortified—can spoil when exposed to heat, light, vibration or fluctuations in temperature and humidity. When properly stored, wines can maintain their quality and in some cases improve in aroma, flavor, and complexity as they age. Some wine experts contend that the optimal temperature for aging wine is , others .
Wine refrigerators offer a smaller alternative to wine cellars and are available in capacities ranging from small, 16-bottle units to furniture-quality pieces that can contain 500 bottles. Wine refrigerators are not ideal for aging, but rather serve to chill wine to the proper temperature for drinking. These refrigerators keep the humidity low (usually under 50%), below the optimal humidity of 50% to 70%. Lower humidity levels can dry out corks over time, allowing oxygen to enter the bottle, which reduces the wine's quality through oxidation. While some types of alcohol are sometimes stored in the freezer, such as vodka, it is not possible to safely freeze wine in the bottle, as there is insufficient room for it to expand as it freezes and the bottle will usually crack. Certain shapes of bottle may allow the cork to be pushed out by the ice, but if the bottle is frozen on its side, the wine in the narrower neck will invariably freeze first, preventing this.
online review
*
''The Guardian'' & ''Observer'' Guide to Wine
{{Authority control Wine, Alcoholic drinks Ceremonial food and drink Cooking Fermented drinks Grape
rice wine
Rice wine is an alcoholic beverage fermented and distilled from rice, traditionally consumed in East Asia, Southeast Asia and South Asia. Rice wine is made by the fermentation of rice starch that has been converted to sugars. Microbes are the so ...
(e.g. sake
Sake, also spelled saké ( ; also referred to as Japanese rice wine), is an alcoholic beverage of Japanese origin made by fermenting rice that has been polished to remove the bran. Despite the name ''Japanese rice wine'', sake, and indee ...
, huangjiu
''Huangjiu'' (), meaning yellow wine, is a Chinese alcoholic beverage, and is most popular in the Jiangnan area. ''Huangjiu'' is brewed by mixing boiled grains including rice, glutinous rice or millet with qū as starter culture, followed by ...
and cheongju
Cheongju () is the capital and largest List of cities in South Korea, city of North Chungcheong Province in South Korea.
History
Cheongju has been an important provincial town since ancient times. In the Cheongju Mountains, specifically in the ...
), are made from starch-based materials and resemble beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
more than traditional wine, while ginger wine
Ginger wine is a fortified wine often made from a fermented blend of ginger, raisins, sugar and yeast, that is often fortified by being blended with brandy. It is one of the main ingredients of the Whisky Mac cocktail.
Ginger wine originated in ...
is fortified with brandy
Brandy is a liquor produced by distilling wine. Brandy generally contains 35–60% alcohol by volume (70–120 US proof) and is typically consumed as an after-dinner digestif. Some brandies are aged in wooden casks. Others are coloured with ...
. In these latter cases, the term "wine" refers to the similarity in alcohol content rather than to the production process. The commercial use of the English word "wine" (and its equivalent in other languages) is protected by law in many jurisdictions.
Grape varieties
 Wine is usually made from one or more
Wine is usually made from one or more varieties
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
of the European species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
''Vitis vinifera
''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are curre ...
'', such as Pinot noir
Pinot Noir () is a red-wine grape variety of the species ''Vitis vinifera''. The name may also refer to wines created predominantly from pinot noir grapes. The name is derived from the French language, French words for ''pine'' and ''black.' ...
, Chardonnay
Chardonnay (, , ) is a green-skinned grape variety used in the production of white wine. The variety originated in the Burgundy wine region of eastern French wine, France, but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from English wine, Englan ...
, Cabernet Sauvignon
Cabernet Sauvignon () is one of the world's most widely recognized red wine grape varieties. It is grown in nearly every major wine producing country among a diverse spectrum of climates from Australia and British Columbia, Canada to Lebanon' ...
, Gamay
Gamay is a purple-colored grape variety used to make red wines, most notably grown in Beaujolais and in the Loire Valley around Tours. Its full name is Gamay Noir à Jus Blanc. It is a very old cultivar, mentioned as long ago as the 15th centu ...
and Merlot
Merlot is a dark blue–colored wine grape variety, that is used as both a blending grape and for varietal wines. The name ''Merlot'' is thought to be a diminutive of ''merle'', the French name for the blackbird, probably a reference to the ...
. When one of these varieties is used as the predominant grape (usually defined by law as minimums of 75% to 85%), the result is a "varietal
A varietal wine is a wine made primarily from a single named grape variety, and which typically displays the name of that variety on the wine label.The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000.winepros.com.au. ...
" as opposed to a "blended" wine. Blended wines are not necessarily inferior to varietal wines, rather they are a different style of wine-making.
Wine can also be made from other species of grape or from hybrids, created by the genetic crossing of two species. '' V. labrusca'' (of which the Concord grape
The Concord grape is a cultivar derived from the grape species ''Vitis labrusca'' (also known as fox grape) that are used as table grapes, wine grapes and juice grapes. They are often used to make grape jelly, grape juice, grape pies, grape-fl ...
is a cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture, ...
), '' V. aestivalis'', '' V. rupestris'', '' V. rotundifolia'' and '' V. riparia'' are native North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
n grapes usually grown to eat fresh or for grape juice, jam, or jelly, and only occasionally made into wine.
Hybridization is different from grafting
Grafting or graftage is a horticultural technique whereby tissues of plants are joined so as to continue their growth together. The upper part of the combined plant is called the scion () while the lower part is called the rootstock. The succ ...
. Most of the world's vineyards are planted with European ''Vitis vinifera'' vines that have been grafted onto North American species' rootstock, a common practice due to their resistance to phylloxera
Grape phylloxera is an insect pest of commercial grapevines worldwide, originally native to eastern North America. Grape phylloxera (''Daktulosphaira vitifoliae'' (Fitch 1855) belong to the family Phylloxeridae, within the order Hemiptera, bugs ...
, a root louse that eventually kills the vine. In the late 19th century, most of Europe's vineyards (excluding some of the driest in the south) were devastated by the infestation, leading to widespread vine deaths and eventual replanting. Grafting is done in every wine-producing region in the world except in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
and the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
– the only places not yet exposed to the insect.
In the context of wine production, ''terroir
(, ; from ''terre'', "land") is a French term used to describe the environmental factors that affect a crop's phenotype, including unique environment contexts, farming practices and a crop's specific growth habitat. Collectively, these conte ...
'' is a concept that encompasses the varieties of grapes used, elevation and shape of the vineyard, type and chemistry of soil, climate and seasonal conditions, and the local yeast cultures. The range of possible combinations of these factors can result in great differences among wines, influencing the fermentation, finishing, and aging processes as well. Many wineries use growing and production methods that preserve or accentuate the aroma
An odor (American English) or odour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds that are generally found in low concentrations that humans and animals can perceive via their sense ...
and taste influences of their unique ''terroir''. However, flavor differences are less desirable for producers of mass-market table wine
Table wine (rarely abbreviated TW) is a wine term with two different meanings: a style of wine and a quality level within wine classification.
In the United States, the term primarily designates a wine style: an ordinary wine which is not fortif ...
or other cheaper wines, where consistency takes precedence. Such producers try to minimize differences in sources of grapes through production techniques such as micro-oxygenation Micro-oxygenation is a process used in winemaking to introduce oxygen into wine in a controlled manner. Developed in 1991 by Patrick DuCournau, working with the exceptionally grape tannins, tannic grape Tannat in Madiran AOC, Madiran, the process ga ...
, tannin filtration, cross-flow filtration, thin-film evaporation,
and spinning cones.
About 700 grapes go into one bottle of wine, approximately 2.6 pounds.
Classification
 Regulations govern the classification and sale of wine in many regions of the world. European wines tend to be classified by region (e.g.
Regulations govern the classification and sale of wine in many regions of the world. European wines tend to be classified by region (e.g. Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefectur ...
, Rioja and Chianti
A Chianti wine (, also , ) is any wine produced in the Chianti region of central Tuscany. It was historically associated with a squat bottle enclosed in a straw basket, called a ''fiasco'' ("flask"; ''pl. fiaschi''). However, the ''fiasco'' is ...
), while non-European wines are most often classified by grape (e.g. Pinot noir
Pinot Noir () is a red-wine grape variety of the species ''Vitis vinifera''. The name may also refer to wines created predominantly from pinot noir grapes. The name is derived from the French language, French words for ''pine'' and ''black.' ...
and Merlot
Merlot is a dark blue–colored wine grape variety, that is used as both a blending grape and for varietal wines. The name ''Merlot'' is thought to be a diminutive of ''merle'', the French name for the blackbird, probably a reference to the ...
). Market recognition of particular regions has recently been leading to their increased prominence on non-European wine labels. Examples of recognized non-European locales include Napa Valley
Napa Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in Napa County in California's Wine Country. It was established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) on January 27, 1981. Napa Valley is considered one of the premier ...
, Santa Clara Valley, Sonoma Valley
Sonoma Valley is a valley located in southeastern Sonoma County, California, in the North Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. Known as the birthplace of the California wine industry, the valley is home to some of the earliest vineyards an ...
, Anderson Valley, and Mendocino County
Mendocino County (; ''Mendocino'', Spanish language, Spanish for "of Antonio de Mendoza, Mendoza) is a County (United States), county located on the North Coast (California), North Coast of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 United Sta ...
in California; Willamette Valley
The Willamette Valley ( ) is a long valley in Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. The Willamette River flows the entire length of the valley and is surrounded by mountains on three sides: the Cascade Range to the east, ...
and Rogue Valley
The Rogue Valley is a valley region in southwestern Oregon in the United States. Located along the middle Rogue River and its tributaries in Josephine and Jackson counties, the valley forms the cultural and economic heart of Southern Oregon nea ...
in Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
; Columbia Valley
The Columbia Valley is the name used for a region in the Rocky Mountain Trench near the headwaters of the Columbia River between the town of Golden and the Canal Flats. The main hub of the valley is the town of Invermere. Other towns include Rad ...
in Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on ...
; Barossa Valley
The Barossa Valley ( Barossa German: ''Barossa Tal'') is a valley in South Australia located northeast of Adelaide city centre. The valley is formed by the North Para River. It is notable as a major wine-producing region and tourist destinati ...
in South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
; Hunter Valley
The Hunter Region, also commonly known as the Hunter Valley, is a region of New South Wales, Australia, extending from approximately to north of Sydney. It contains the Hunter River and its tributaries with highland areas to the north and so ...
in New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
; Luján de Cuyo in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
; Vale dos Vinhedos in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
; Hawke's Bay
Hawke's Bay ( mi, Te Matau-a-Māui) is a local government region on the east coast of New Zealand's North Island. The region's name derives from Hawke Bay, which was named by Captain James Cook in honour of Admiral Edward Hawke. The region is ...
and Marlborough
Marlborough may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Marlborough, Wiltshire, England
** Marlborough College, public school
* Marlborough School, Woodstock in Oxfordshire, England
* The Marlborough Science Academy in Hertfordshire, England
Austral ...
in New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
; Central Valley in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
; and in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, the Okanagan Valley
The Okanagan ( ), also known as the Okanagan Valley and sometimes as the Okanagan Country, is a region in the Canadian province of British Columbia defined by the basin of Okanagan Lake and the Canadian portion of the Okanagan River. It is part ...
of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, and the Niagara Peninsula
The Niagara Peninsula is an area of land lying between the southwestern shore of Lake Ontario and the northeastern shore of Lake Erie, in Ontario, Canada. Technically an isthmus rather than a peninsula, it stretches from the Niagara River in the ...
and Essex County regions of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
are the three largest producers.
Some blended wine names are marketing terms whose use is governed by trademark
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a type of intellectual property consisting of a recognizable sign, design, or expression that identifies products or services from a particular source and distinguishes them from others ...
law rather than by specific wine laws. For example, Meritage
Meritage is a name for red and white Bordeaux-style wines without infringing on the Bordeaux (France) region's legally protected designation of origin. Winemakers must license the Meritage trademark from its owner, the California-based Meritage A ...
is generally a Bordeaux-style blend of Cabernet Sauvignon
Cabernet Sauvignon () is one of the world's most widely recognized red wine grape varieties. It is grown in nearly every major wine producing country among a diverse spectrum of climates from Australia and British Columbia, Canada to Lebanon' ...
and Merlot, but may also include Cabernet Franc
Cabernet Franc is one of the major black grape varieties worldwide. It is principally grown for blending with Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot in the Bordeaux style, but can also be vinified alone, as in the Loire's Chinon. In addition to being us ...
, Petit Verdot
Petit Verdot is a variety of red wine grape, principally used in classic Bordeaux blends. It ripens much later than the other varieties in Bordeaux, often too late, so it fell out of favour in its home region. When it does ripen it adds tannin, c ...
, and Malbec
Malbec () is a purple grape variety used in making red wine. The grapes tend to have an inky dark color and robust tannins, and are known as one of the six grapes allowed in the blend of red Bordeaux wine. In France, plantations of Malbec are n ...
. Commercial use of the term Meritage is allowed only via licensing agreements with the Meritage Association.
European classifications
 France has various
France has various appellation
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication primarily used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown, although other types of food often have appellations as well. Restrictions other than geographical boun ...
systems based on the concept of ''terroir'', with classifications ranging from ''Vin de Table
Table wine (rarely abbreviated TW) is a wine term with two different meanings: a style of wine and a quality level within wine classification.
In the United States, the term primarily designates a wine style: an ordinary wine which is not fortif ...
'' ("table wine") at the bottom, through ''Vin de Pays
''Vin de pays'' (, "country wine") was a French wine classification that was above the ''vin de table'' classification, but below the ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) classification and below the former ''vin délimité de qualité s ...
'' and ''Appellation d'Origine Vin Délimité de Qualité Supérieure
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication primarily used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown, although other types of food often have appellations as well. Restrictions other than geographical boun ...
'' (AOVDQS), up to ''Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication primarily used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown, although other types of food often have appellations as well. Restrictions other than geographical boun ...
'' (AOC) or similar, depending on the region. Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
has developed a system resembling that of France and, in fact, pioneered this concept in 1756 with a royal charter creating the Demarcated Douro Region and regulating the production and trade of wine. Germany created a similar scheme in 2002, although it has not yet achieved the authority of the other countries' classification systems. Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
have classifications based on a dual system of region of origin and product quality.
Beyond Europe
New World wines—those made outside the traditional wine regions of Europe—are usually classified by grape rather than by ''terroir'' or region of origin, although there have been unofficial attempts to classify them by quality. According to Canadian Food and Drug Regulations, wine in Canada is an alcoholic drink that is produced by the complete or partial alcoholic fermentation of fresh grapes, grape must, products derived solely from fresh grapes, or any combination of them. There are many materials added during the course of the manufacture, such as yeast, concentrated grape juice,dextrose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
, fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
, glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
or glucose solids, invert sugar
Inverted sugar syrup, also called invert syrup, invert sugar, simple syrup, sugar syrup, sugar water, bar syrup, syrup USP, or sucrose inversion, is a syrup mixture of the monosaccharides glucose and fructose, that is made by hydrolytic sacch ...
, sugar, or aqueous solutions. Calcium sulphate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Pari ...
in such quantity that the content of soluble sulphates in the finished wine shall not exceed 0.2 percent weight by volume calculated as potassium sulphate. Calcium carbonate in such quantity that the content of tartaric acid
Tartaric acid is a white, crystalline organic acid that occurs naturally in many fruits, most notably in grapes, but also in bananas, tamarinds, and citrus. Its salt, potassium bitartrate, commonly known as cream of tartar, develops naturally i ...
in the finished wine shall not be less than 0.15 percent weight by volume. Also, sulphurous acid
Sulfurous acid (also sulfuric(IV) acid, sulphurous acid (UK), sulphuric(IV) acid (UK)) is the chemical compound with the formula . There is no evidence that sulfurous acid exists in solution, but the molecule has been detected in the gas phase. ...
, including salts thereof, in such quantity that its content in the finished wine shall not exceed 70 parts per million in the free state, or 350 parts per million in the combined state, calculated as sulphur dioxide. Caramel, amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of ...
and pectinase
Pectinases are a group of enzymes that breaks down pectin, a polysaccharide found in plant cell walls, through hydrolysis, transelimination and deesterification reactions. Commonly referred to as pectic enzymes, they include pectolyase, pectozym ...
at a maximum level of use consistent with good manufacturing practice. Brandy, fruit spirit or alcohol derived from the alcoholic fermentation of a food source distilled to not less than 94 percent alcohol by volume. Prior to final filtration may be treated with a strongly acid cation exchange resin in the sodium ion form, or a weakly basic anion exchange resin in the hydroxyl ion form.
Vintages
American Viticultural Area
An American Viticultural Area (AVA) is a designated wine grape-growing region in the United States, providing an official appellation for the mutual benefit of winery, wineries and consumers. Winemakers frequently want their consumers to know abo ...
(AVA; e.g., Sonoma Valley
Sonoma Valley is a valley located in southeastern Sonoma County, California, in the North Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. Known as the birthplace of the California wine industry, the valley is home to some of the earliest vineyards an ...
), 95% of its volume must be from grapes harvested in that year.Title 27 of the United States Code
Title 27 of the United States Code outlines the role of intoxicating liquors in the United States Code.
* —General Provisions
* — Prohibition of Intoxicating Beverages
* — Beer, Ale, Porter, and Similar Fermented Liquor
* —Industrial Alco ...
, Code of Federal Regulations
In the law of the United States, the ''Code of Federal Regulations'' (''CFR'') is the codification of the general and permanent regulations promulgated by the executive departments and agencies of the federal government of the United States. ...
br>§ 4.27If a wine is not labeled with a country of origin or AVA the percentage requirement is lowered to 85%. Vintage wines are generally bottled in a single batch so that each bottle will have a similar taste. Climate's impact on the character of a wine can be significant enough to cause different vintages from the same vineyard to vary dramatically in flavor and quality. Thus, vintage wines are produced to be individually characteristic of the particular vintage and to serve as the flagship wines of the producer. Superior vintages from reputable producers and regions will often command much higher prices than their average ones. Some vintage wines (e.g. Brunello), are only made in better-than-average years. For consistency, non-vintage wines can be blended from more than one vintage, which helps wine-makers sustain a reliable market image and maintain sales even in bad years. One recent study suggests that for the average wine drinker, the vintage year may not be as significant for perceived quality as had been thought, although wine connoisseurs continue to place great importance on it.
Tasting

Wine tasting
Wine tasting is the sensory examination and evaluation of wine. While the practice of wine tasting is as ancient as its production, a more formalized methodology has slowly become established from the 14th century onward. Modern, professional w ...
is the sensory examination and evaluation of wine. Wines contain many chemical compounds similar or identical to those in fruits, vegetables, and spice
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices a ...
s. The sweetness of wine
The subjective sweetness of a wine is determined by the interaction of several factors, including the amount of sugar in the wine, but also the relative levels of alcohol, acids, and tannins. Sugars and alcohol enhance a wine's sweetness, whil ...
is determined by the amount of residual sugar in the wine after fermentation, relative to the acidity present in the wine. Dry wine
The subjective sweetness of a wine is determined by the interaction of several factors, including the amount of sugar in the wine, but also the relative levels of alcohol, acids, and tannins. Sugars and alcohol enhance a wine's sweetness, wh ...
, for example, has only a small amount of residual sugar. Some wine labels suggest opening the bottle and letting the wine "breathe" for a couple of hours before serving, while others recommend drinking it immediately. Decanting (the act of pouring a wine into a special container just for breathing) is a controversial subject among wine enthusiasts. In addition to aeration, decanting with a filter allows the removal of bitter sediments that may have formed in the wine. Sediment is more common in older bottles, but aeration may benefit younger wines.
During aeration, a younger wine's exposure to air often "relaxes" the drink, making it smoother and better integrated in aroma, texture, and flavor. Older wines generally fade (lose their character and flavor intensity) with extended aeration. Despite these general rules, breathing does not necessarily benefit all wines. Wine may be tasted as soon as the bottle is opened to determine how long it should be aerated, if at all. When tasting wine, individual flavors may also be detected, due to the complex mix of organic molecules (e.g. ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
s and terpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n > 1. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes ar ...
s) that grape juice and wine can contain. Experienced tasters can distinguish between flavors characteristic of a specific grape and flavors that result from other factors in wine-making. Typical intentional flavor elements in wine—chocolate, vanilla, or coffee—are those imparted by aging in oak casks rather than the grape itself.
Vertical and horizontal tasting involves a range of vintages within the same grape and vineyard, or the latter in which there is one vintage from multiple vineyards. "Banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguis ...
" flavors (isoamyl acetate
Isoamyl acetate, also known as isopentyl acetate, is an organic compound that is the ester formed from isoamyl alcohol and acetic acid, with the molecular formula
C7H14O2.It is a colorless liquid that is only slightly soluble in water, but very s ...
) are the product of yeast metabolism, as are spoilage aromas such as "medicinal" or "Band-Aid" (4-ethylphenol
Ethylphenol (4-EP) is an organic compound with the formula C2H5C6H4OH. It is one of three isomeric ethylphenols. A white solid, it occurs as an impurity in xylenols and as such is used in the production of some commercial phenolic resins. It is ...
), "spicy" or "smoky" ( 4-ethylguaiacol), and rotten egg (hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
). Some varieties can also exhibit a mineral flavor due to the presence of water-soluble salts as a result of limestone's presence in the vineyard's soil. Wine aroma comes from volatile compounds released into the air. Vaporization of these compounds can be accelerated by twirling the wine glass or serving at room temperature. Many drinkers prefer to chill red wines that are already highly aromatic, like Chinon
Chinon () is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department, Centre-Val de Loire, France.
The traditional province around Chinon, Touraine, became a favorite resort of French kings and their nobles beginning in the late 15th and early 16th centuri ...
and Beaujolais
Beaujolais ( , ) is a French ''Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée'' (AOC) wine generally made of the Gamay grape, which has a thin skin and is low in tannins. Like most AOC wines they are not labeled varietally. Whites from the region, which mak ...
.
The ideal temperature for serving a particular wine is a matter of debate by wine enthusiasts and sommeliers, but some broad guidelines have emerged that will generally enhance the experience of tasting certain common wines. White wine should foster a sense of coolness, achieved by serving at "cellar temperature" (). Light red wines drunk young should also be brought to the table at this temperature, where they will quickly rise a few degrees. Red wines are generally perceived best when served ''chambré'' ("at room temperature"). However, this does not mean the temperature of the dining room—often around —but rather the coolest room in the house and, therefore, always slightly cooler than the dining room itself. Pinot noir should be brought to the table for serving at and will reach its full bouquet at . Cabernet Sauvignon, zinfandel, and Rhone varieties should be served at and allowed to warm on the table to for best aroma.
Collecting
 Outstanding vintages from the best vineyards may sell for thousands of
Outstanding vintages from the best vineyards may sell for thousands of dollars
Dollar is the name of more than 20 currencies. They include the Australian dollar, Brunei dollar, Canadian dollar, Hong Kong dollar, Jamaican dollar, Liberian dollar, Namibian dollar, New Taiwan dollar, New Zealand dollar, Singapore dollar, Un ...
per bottle, though the broader term "fine wine" covers those typically retailing in excess of US$30–50. "Investment wine
Investment wine, like gold bullion, rare coins, fine art, and tulip bulbs, is seen by some as an alternative investment other than the more traditional investment holdings of stocks, bonds, cash, or real estate. While most wine is purchased ...
s" are considered by some to be Veblen good
A Veblen good is a type of luxury good for which the demand increases as the price increases, in apparent (but not actual) contradiction of the law of demand, resulting in an upward-sloping demand curve. The higher prices of Veblen goods may mak ...
s: those for which demand increases rather than decreases as their prices rise.
Particular selections such as "Verticals", which span multiple vintages of a specific grape and vineyard, may be highly valued. The most notable was a Château d'Yquem
Château d'Yquem () is a '' Premier Cru Supérieur'' ( Fr: "Superior First Growth") wine from the Sauternes, Gironde region in the southern part of the Bordeaux vineyards known as Graves. In the Bordeaux Wine Official Classification of 1855, Ch� ...
135-year vertical containing every vintage from 1860 to 2003 sold for $1.5 million.
The most common wines purchased for investment include those from Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefectur ...
and Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
; cult wine
Cult wines are wines for which dedicated groups of committed enthusiasts will pay large sums of money.
Cult wines are often seen as trophy wines to be collected or as investment wine to be held rather than consumed. Because price is often seen ...
s from Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and elsewhere; and vintage port
Port wine (also known as vinho do Porto, , or simply port) is a Portuguese fortified wine produced in the Douro Valley of northern Portugal. It is typically a sweet red wine, often served with dessert, although it also comes in dry, semi-dry ...
. Characteristics of highly collectible wines include:
# A proven track record of holding well over time
# A drinking-window plateau (i.e., the period for maturity and approachability) that is many years long
# A consensus among experts as to the quality of the wines
# Rigorous production methods at every stage, including grape selection and appropriate barrel aging
Investment in fine wine has attracted those who take advantage of their victims' relative ignorance of this wine market sector. Such wine fraud
Wine fraud relates to the commercial aspects of wine. The most prevalent type of fraud is one where wines are adulterated, usually with the addition of cheaper products (e.g. juices) and sometimes with harmful chemicals and sweeteners (compensati ...
sters often profit by charging excessively high prices for off-vintage or lower-status wines from well-known wine regions, while claiming that they are offering a sound investment unaffected by economic cycle
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examini ...
s. As with any investment, thorough research is essential to making an informed decision.
Production

equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
. The world's southernmost vineyards are in the Central Otago
Central Otago is located in the inland part of the Otago region in the South Island of New Zealand. The motto for the area is "A World of Difference".
The area is dominated by mountain ranges and the upper reaches of the Clutha River and tributa ...
region of New Zealand's South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman ...
near the 45th parallel south
The 45th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 45 ° south of the Earth's equator.
It is the line that marks the theoretical halfway point between the equator and the South Pole. The true halfway point is south of this parallel becau ...
, and the northernmost are in Flen
Flen (local pronunciation ''Flén'') is a locality and the seat of Flen Municipality, Södermanland County, Sweden with 6,229 inhabitants in 2010.
Flen evolved as a railway junction and got the title of a city in 1949. Since 1971 it is the seat of ...
, Sweden, just north of the 59th parallel north
The 59th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 59 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
At this latitude the Sun is visible for 18 hours, 30 ...
.
Exporting countries
 ]
The UK was the world's largest importer of wine in 2007.
]
The UK was the world's largest importer of wine in 2007.
Consumption
list of countries by alcohol consumption
This is a list of countries by alcohol consumption measured in equivalent litres of pure alcohol (ethanol) consumed per capita per year.
World Health Organization (WHO) data
The World Health Organization periodically publishes ''The Global Statu ...
measured in liters of pure ethyl alcohol consumed per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". The term is used in a wide variety of social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistic ...
in a given year, according to the most recent data from the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
. The methodology includes persons 15 years of age or older. About 40% of individuals above the legal drinking age consider themselves "wine drinkers", which is higher than all other alcoholic beverages combined (34%) and those who do not drink at all (26%).
Culinary uses
 Wine is a popular and important
Wine is a popular and important drink
A drink or beverage is a liquid intended for human consumption. In addition to their basic function of satisfying thirst, drinks play important roles in human culture. Common types of drinks include plain drinking water, milk, juice, smoothies a ...
that accompanies and enhances a wide range of cuisines, from the simple and traditional stew
A stew is a combination of solid food ingredients that have been cooked in liquid and served in the resultant gravy. A stew needs to have raw ingredients added to the gravy. Ingredients in a stew can include any combination of vegetables and ...
s to the most sophisticated and complex haute cuisine
''Haute cuisine'' (; ) or ''grande cuisine'' is the cuisine of "high-level" establishments, gourmet restaurants, and luxury hotels. ''Haute cuisine'' is characterized by the meticulous preparation and careful presentation of food at a high pri ...
s. Wine is often served with dinner. Sweet dessert wine
Dessert wines, sometimes called pudding wines in the United Kingdom, are sweet wines typically served with dessert.
There is no simple definition of a dessert wine. In the UK, a dessert wine is considered to be any sweet wine drunk with a meal ...
s may be served with the dessert
Dessert is a course (food), course that concludes a meal. The course consists of sweet foods, such as confections, and possibly a beverage such as dessert wine and liqueur. In some parts of the world, such as much of Greece and West Africa, and ...
course. In fine restaurants in Western countries, wine typically accompanies dinner. At a restaurant, patrons are helped to make good food-wine pairings by the restaurant's sommelier
A sommelier ( or or ; ), or wine steward, is a trained and knowledgeable wine professional, normally working in fine restaurants, who specializes in all aspects of wine service as well as wine and food pairing. The role of the wine steward in hau ...
or wine waiter. Individuals dining at home may use wine guides to help make food–wine pairings. Wine is also drunk without the accompaniment of a meal in wine bar
A wine bar is a tavern-like business focusing on selling wine, rather than liquor or beer. A typical feature of many wine bars is a wide selection of wines available by the glass. Some wine bars are profiled on wines of a certain type of origin, ...
s or with a selection of cheeses (at a wine and cheese party). Wines are also used as a theme for organizing various events such as festival
A festival is an event ordinarily celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, mela, or eid. A festival c ...
s around the world; the city of Kuopio
Kuopio (, ) is a Finnish city and municipality located in the region of Northern Savonia. It has a population of , which makes it the most populous municipality in Finland. Along with Joensuu, Kuopio is one of the major urban, economic, and cult ...
in North Savonia
North Savo (or Northern Savonia; fi, Pohjois-Savo; sv, Norra Savolax) is a region in eastern Finland. It borders the regions of South Savo, Central Finland, North Ostrobothnia, Kainuu, and North Karelia. Kuopio is the largest city in the regio ...
, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
is known for its annual Kuopio Wine Festivals (''Kuopion viinijuhlat'').
Wine is important in cuisine not just for its value as a drink, but as a flavor agent, primarily in stocks
Stocks are feet restraining devices that were used as a form of corporal punishment and public humiliation. The use of stocks is seen as early as Ancient Greece, where they are described as being in use in Solon's law code. The law describing ...
and braising
Braising (from the French word ''braiser'') is a combination-cooking method that uses both wet and dry heats: typically, the food is first browned at a high temperature, then simmered in a covered pot in cooking liquid (such as wine, broth, coc ...
, since its acidity lends balance to rich savory
Savory or Savoury may refer to:
Common usage
* Herbs of the genus ''Satureja'', particularly:
** Summer savory (''Satureja hortensis''), an annual herb, used to flavor food
** Winter savory (''Satureja montana''), a perennial herb, also used to ...
or sweet
Sweetness is a basic taste most commonly perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds are sweet, including aldehydes, ketones ...
dishes. Wine sauce
Wine sauce is a Culinary art, culinary sauce prepared with wine as a primary ingredient, heated and mixed with stock, butter, herbs, spices, onions, garlic and other ingredients. Several types of wines may be used, including red wine, white wine ...
is an example of a culinary sauce that uses wine as a primary ingredient. Natural wines may exhibit a broad range of alcohol content, from below 9% to above 16% ABV
Alcohol by volume (abbreviated as ABV, abv, or alc/vol) is a standard measure of how much alcohol (ethanol) is contained in a given volume of an alcoholic beverage (expressed as a volume percent). It is defined as the number of millilitres (mL) o ...
, with most wines being in the 12.5–14.5% range. Fortified wine
Fortified wine is a wine to which a distilled spirit, usually brandy, has been added. In the course of some centuries, winemakers have developed many different styles of fortified wine, including port, sherry, madeira, Marsala, Commanda ...
s (usually with brandy) may contain 20% alcohol or more.
Religious significance
Ancient religions
The use of wine in ancientNear Eastern
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
and Ancient Egyptian religious ceremonies was common. Libation
A libation is a ritual pouring of a liquid, or grains such as rice, as an offering to a deity or spirit, or in memory of the dead. It was common in many religions of antiquity and continues to be offered in cultures today.
Various substa ...
s often included wine, and the religious mysteries of Dionysus used wine as a sacramental entheogen
Entheogens are psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood (psychology), mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior for the purposes of engendering spiritual development or otherwiseRätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclop ...
to induce a mind-altering state.
Judaism
Wine is an integral part of Jewish laws and traditions. The ''Kiddush
Kiddush (; he, קידוש ), literally, "sanctification", is a blessing recited over wine or grape juice to sanctify the Shabbat and Jewish holidays. Additionally, the word refers to a small repast held on Shabbat or festival mornings after t ...
'' is a blessing recited over wine or grape juice to sanctify the Shabbat
Shabbat (, , or ; he, שַׁבָּת, Šabbāṯ, , ) or the Sabbath (), also called Shabbos (, ) by Ashkenazim, is Judaism's day of rest on the seventh day of the week—i.e., Saturday. On this day, religious Jews remember the biblical storie ...
. On Pesach (Passover
Passover, also called Pesach (; ), is a major Jewish holidays, Jewish holiday that celebrates the The Exodus, Biblical story of the Israelites escape from slavery in Ancient Egypt, Egypt, which occurs on the 15th day of the Hebrew calendar, He ...
) during the Seder, it is a Rabbinic
Rabbinic Judaism ( he, יהדות רבנית, Yahadut Rabanit), also called Rabbinism, Rabbinicism, or Judaism espoused by the Rabbanites, has been the mainstream form of Judaism since the 6th century Common era, CE, after the codification of the ...
obligation of adults to drink four cups of wine. In the Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
and in the Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusa ...
, the libation of wine was part of the sacrificial service. Note that this does not mean that wine is a symbol of blood, a common misconception that contributes to the Christian beliefs of the blood libel
Blood libel or ritual murder libel (also blood accusation) is an antisemitic canardTurvey, Brent E. ''Criminal Profiling: An Introduction to Behavioral Evidence Analysis'', Academic Press, 2008, p. 3. "Blood libel: An accusation of ritual mur ...
.
"It has been one of history's cruel ironies that the blood libel—accusations against Jews using the blood of murdered gentile children for the making of wine and matzot—became the false pretext for numerous pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russia ...
s. And due to the danger, those who live in a place where blood libels occur are halachically exempted from using red wine, lest it be seized as "evidence" against them."
Christianity
 In
In Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, wine is used in a sacred rite called the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
, which originates in the Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words an ...
account of the Last Supper
Image:The Last Supper - Leonardo Da Vinci - High Resolution 32x16.jpg, 400px, alt=''The Last Supper'' by Leonardo da Vinci - Clickable Image, Depictions of the Last Supper in Christian art have been undertaken by artistic masters for centuries, ...
(Gospel of Luke
The Gospel of Luke), or simply Luke (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). tells of the origins, birth, ministry, death, resurrection, and ascension of Jesus Christ. Together with the Acts of the Apostles, it makes up a two-volu ...
22:19) describing Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
sharing bread and wine with his disciples and commanding them to "do this in remembrance of me." Beliefs about the nature of the Eucharist vary among denominations (see Eucharistic theologies contrasted
Eucharistic theology is a branch of Christian theology which treats doctrines concerning the Holy Eucharist, also commonly known as the Lord's Supper. It exists exclusively in Christianity and related religions, as others generally do not cont ...
).
While some Christians consider the use of wine from the grape as essential for the validity of the sacrament
A sacrament is a Christianity, Christian Rite (Christianity), rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments ...
, many Protestants also allow (or require) pasteurized
Pasteurization American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), or pasteurisation is a process of food preservation in which packaged and non-packaged foods (such as milk and fruit juices) are treated with mi ...
grape juice as a substitute. Wine was used in Eucharistic rites by all Protestant groups until an alternative arose in the late 19th century. Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's b ...
dentist
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry (the diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases and conditions of the mouth, oral cavity and other aspects of the craniofaci ...
and prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic ...
ist Thomas Bramwell Welch
Thomas Bramwell Welch (December 31, 1825 – December 29, 1903) was a British–American Methodist minister and dentist. He pioneered the use of pasteurization as a means of preventing the fermentation of grape juice. He persuaded local ...
applied new pasteurization techniques to stop the natural fermentation process of grape juice
Grape juice is obtained from crushing and blending grapes into a liquid. In the wine industry, grape juice that contains 7–23 percent of pulp, skins, stems and seeds is often referred to as ''must''. The sugars in grape juice allow it to be u ...
. Some Christians who were part of the growing temperance movement
The temperance movement is a social movement promoting temperance or complete abstinence from consumption of alcoholic beverages. Participants in the movement typically criticize alcohol intoxication or promote teetotalism, and its leaders emph ...
pressed for a switch from wine to grape juice, and the substitution spread quickly over much of the United States, as well as to other countries to a lesser degree. There remains an ongoing debate between some American Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
denominations as to whether wine can and should be used for the Eucharist or allowed as an ordinary drink, with Catholics and some mainline Protestants allowing wine drinking in moderation, and some conservative Protestant groups opposing consumption of alcohol altogether.
The earliest viticulture tradition in the Southwestern United States starts with sacramental wine
Sacramental wine, Communion wine, altar wine, or wine for consecration is wine obtained from grapes and intended for use in celebration of the Eucharist (also referred to as the Lord's Supper or Holy Communion, among other names). It is usually ...
, beginning in the 1600s, with Christian friars and monks producing New Mexico wine
New Mexico has a long history of wine production, within American wine, especially along the Rio Grande, from its capital Santa Fe, the city of Albuquerque with its surrounding metropolitan area, and in valleys like the Mesilla and the Mimbres ...
.
Islam
 Alcoholic drinks, including wine, are forbidden under most interpretations of
Alcoholic drinks, including wine, are forbidden under most interpretations of Islamic law
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the ...
. In many Muslim countries, possession or consumption of alcoholic drinks carry legal penalties. Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
had previously had a thriving wine industry that disappeared after the Islamic Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dyna ...
in 1979. In Greater Persia
Greater Iran ( fa, ایران بزرگ, translit=Irān-e Bozorg) refers to a region covering parts of Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Xinjiang, and the Caucasus, where both Iranian culture and Iranian languages have had a si ...
, '' mey'' (Persian wine) was a central theme of poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
for more than a thousand years, long before the advent of Islam. Some Alevi
Alevism or Anatolian Alevism (; tr, Alevilik, ''Anadolu Aleviliği'' or ''Kızılbaşlık''; ; az, Ələvilik) is a local Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Alevi Islamic ( ''bāṭenī'') teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, w ...
sects – one of the two main branches of Islam in Turkey (the other being Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
) – use wine in their religious services.
Certain exceptions to the ban on alcohol apply. Alcohol derived from a source other than the grape (or its byproducts) and the date is allowed in "very small quantities" (loosely defined as a quantity that does not cause intoxication) under the Sunni Hanafi
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools ( maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named aft ...
''madhab'', for specific purposes (such as medicines), where the goal is not intoxication. However, modern Hanafi scholars regard alcohol consumption as totally forbidden.
Health effects
Short-term
Wine containsethyl alcohol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hyd ...
, the chemical in beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
and distilled spirits
Liquor (or a spirit) is an alcoholic drink produced by distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar, that have already gone through alcoholic fermentation. Other terms for liquor include: spirit drink, distilled beverage or hard li ...
. The effects of wine depend on the amount consumed, the span of time over which consumption occurs, and the amount of alcohol in the wine, among other factors. Drinking enough to reach a blood alcohol concentration
Blood alcohol content (BAC), also called blood alcohol concentration or blood alcohol level, is a measurement of alcohol intoxication used for legal or medical purposes; it is expressed as mass of alcohol per volume or mass of blood. For example ...
(BAC) of 0.03%-0.12% may cause an overall improvement in mood, increase self-confidence and sociability, decrease anxiety, flushing of the face, and impair judgment and fine motor coordination Motor coordination is the orchestrated movement of multiple body parts as required to accomplish intended actions, like walking. This coordination is achieved by adjusting kinematic and kinetic parameters associated with each body part involved in t ...
. A BAC of 0.09% to 0.25% causes lethargy
Lethargy is a state of tiredness, sleepiness, weariness, fatigue, sluggishness or lack of energy. It can be accompanied by depression, decreased motivation, or apathy. Lethargy can be a normal response to inadequate sleep, overexertion, overwo ...
, sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ether, ...
, balance problems and blurred vision. A BAC from 0.18% to 0.30% causes profound confusion, impaired speech (e.g. slurred speech), staggering, dizziness and vomiting. A BAC from 0.25% to 0.40% causes stupor
Stupor is the lack of critical mental function and a level of consciousness, in which an affected person is almost entirely unresponsive and responds only to intense stimuli such as pain. The word derives from the Latin '' stupor'' ("numbness, inse ...
, unconsciousness, anterograde amnesia
In neurology, anterograde amnesia is the inability to create new memories after the event that caused amnesia, leading to a partial or complete inability to recall the recent past, while long-term memories from before the event remain intact. T ...
, vomiting, and death may occur due to respiratory depression
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapnia ...
and inhalation of vomit during unconsciousness. A BAC from 0.35% to 0.80% causes coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
, life-threatening respiratory depression and possibly fatal alcohol poisoning
Alcohol intoxication, also known as alcohol poisoning, commonly described as drunkenness or inebriation, is the negative behavior and physical effects caused by a recent consumption of alcohol. In addition to the toxicity of ethanol, the main ps ...
. The operation of vehicles or machinery while drunk can increase the risk of accident, and many countries have laws against drinking and driving
Drunk driving (or drink-driving in British English) is the act of driving under the influence of alcohol. A small increase in the blood alcohol content increases the relative risk of a motor vehicle crash.
In the United States, alcohol is in ...
. The social context and quality of wine can affect the mood and emotions.
Long-term
heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
, stroke, diabetes mellitus, and early death. Ethanol consumption increases the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, and stroke. Some studies that reported benefits of moderate ethanol consumption erred by lumping former drinkers and life-long abstainers into a single group of nondrinkers, hiding the health benefits of life-long abstention from ethanol. Risk is greater in younger people due to binge drinking which may result in violence or accidents. About 3.3 million deaths (5.9% of all deaths) annually are due to ethanol use.
Alcoholism, Alcohol use disorder is the inability to stop or control alcohol use despite harmful consequences to health, job, or relationships; alternative terms include alcoholism, alcohol abuse, alcohol dependence, or alcohol addiction. and alcohol use is the third leading cause of early death in the United States. No professional medical association recommends that people who are nondrinkers should start drinking wine.
Excessive consumption of alcohol can cause liver cirrhosis and alcoholism. The American Heart Association "cautions people NOT to start drinking ... if they do not already drink alcohol. Consult your doctor on the benefits and risks of consuming alcohol in moderation."
Although red wine contains more of the stilbene resveratrol and of other polyphenols than white wine, the evidence for a cardiac health benefit is of poor quality and at most, the benefit is trivial. Grape skins naturally produce resveratrol in response to fungal infection, including exposure to yeast during Fermentation (wine), fermentation. White wine generally contains lower levels of the chemical as it has minimal contact with grape skins during this process.
Forgery and manipulation
Incidents of fraud, such as mislabeling the origin or quality of wines, have resulted in regulations on labeling. "Wine scandals" that have received media attention include: * The 1985 diethylene glycol wine scandal, in which diethylene glycol was used as a sweetener in some Austrian wines. * Wine fraud#Hazardous materials, In 1986, methanol (a toxic type of alcohol) was used to alter certain wines manufactured in Italy. * In 2008, some Italian wines were found to include sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid. * In 2010, some Chinese red wines were found to be adulterated, and as a consequence China's Hebei province shut down nearly 30 wineries. * In 2018, million bottles of French wine was falsely sold as high quality Côtes-du-Rhône winePackaging
 Most wines are sold in wine bottle, glass bottles and sealed with cork (material), corks (50% of which come from
Most wines are sold in wine bottle, glass bottles and sealed with cork (material), corks (50% of which come from Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
). An increasing number of wine producers have been using Alternative wine closure, alternative closures such as Screw cap (wine), screwcaps and synthetic plastic "corks". Although alternative closures are less expensive and prevent cork taint, they have been blamed for such problems as excessive redox, reduction.
Some wines are packaged in thick plastic bags within corrugated fiberboard boxes, and are called "box wines", or "cask wine". Tucked inside the package is a tap affixed to the bag in box, or bladder, that is later extended by the consumer for serving the contents. Box wine can stay acceptably fresh for up to a month after opening because the bladder collapses as wine is dispensed, limiting contact with air and, thus, slowing the rate of oxidation. In contrast, bottled wine oxidizes more rapidly after opening because of the increasing ratio of air to wine as the contents are dispensed; it can degrade considerably in a few days. Canned wine is one of the fastest-growing forms of alternative wine packaging on the market.
Environmental considerations of wine packaging reveal the benefits and drawbacks of both bottled and box wines. The glass used to make bottles is a nontoxic, naturally occurring substance that is completely recyclable, whereas the plastics used for box-wine containers are typically much less environmentally friendly. However, wine-bottle manufacturers have been cited for Clean Air Act (United States), Clean Air Act violations. A ''New York Times'' editorial suggested that box wine, being lighter in package weight, has a reduced carbon footprint from its distribution; however, box-wine plastics, even though possibly recyclable, can be more labor-intensive (and therefore expensive) to process than glass bottles. In addition, while a wine box is recyclable, its plastic bladder most likely is not. Some people are drawn to canned wine due to its portability and recyclable packaging.
Some wine is sold in stainless steel kegs and is referred to as wine on tap.
Storage
 Wine cellars, or wine rooms, if they are above-ground, are places designed specifically for the storage and aging of wine. Fine restaurants and some private homes have wine cellars. In an active wine cellar, temperature and humidity are maintained by a climate-control system. Passive wine cellars are not climate-controlled, and so must be carefully located. Because wine is a natural, perishable food product, all types—including red, white, sparkling, and fortified—can spoil when exposed to heat, light, vibration or fluctuations in temperature and humidity. When properly stored, wines can maintain their quality and in some cases improve in aroma, flavor, and complexity as they age. Some wine experts contend that the optimal temperature for aging wine is , others .
Wine refrigerators offer a smaller alternative to wine cellars and are available in capacities ranging from small, 16-bottle units to furniture-quality pieces that can contain 500 bottles. Wine refrigerators are not ideal for aging, but rather serve to chill wine to the proper temperature for drinking. These refrigerators keep the humidity low (usually under 50%), below the optimal humidity of 50% to 70%. Lower humidity levels can dry out corks over time, allowing oxygen to enter the bottle, which reduces the wine's quality through oxidation. While some types of alcohol are sometimes stored in the freezer, such as vodka, it is not possible to safely freeze wine in the bottle, as there is insufficient room for it to expand as it freezes and the bottle will usually crack. Certain shapes of bottle may allow the cork to be pushed out by the ice, but if the bottle is frozen on its side, the wine in the narrower neck will invariably freeze first, preventing this.
Wine cellars, or wine rooms, if they are above-ground, are places designed specifically for the storage and aging of wine. Fine restaurants and some private homes have wine cellars. In an active wine cellar, temperature and humidity are maintained by a climate-control system. Passive wine cellars are not climate-controlled, and so must be carefully located. Because wine is a natural, perishable food product, all types—including red, white, sparkling, and fortified—can spoil when exposed to heat, light, vibration or fluctuations in temperature and humidity. When properly stored, wines can maintain their quality and in some cases improve in aroma, flavor, and complexity as they age. Some wine experts contend that the optimal temperature for aging wine is , others .
Wine refrigerators offer a smaller alternative to wine cellars and are available in capacities ranging from small, 16-bottle units to furniture-quality pieces that can contain 500 bottles. Wine refrigerators are not ideal for aging, but rather serve to chill wine to the proper temperature for drinking. These refrigerators keep the humidity low (usually under 50%), below the optimal humidity of 50% to 70%. Lower humidity levels can dry out corks over time, allowing oxygen to enter the bottle, which reduces the wine's quality through oxidation. While some types of alcohol are sometimes stored in the freezer, such as vodka, it is not possible to safely freeze wine in the bottle, as there is insufficient room for it to expand as it freezes and the bottle will usually crack. Certain shapes of bottle may allow the cork to be pushed out by the ice, but if the bottle is frozen on its side, the wine in the narrower neck will invariably freeze first, preventing this.
Professions
There are a large number of occupations and professions that are part of the wine industry, ranging from the individuals who grow the grapes, prepare the wine, bottle it, sell it, assess it, market it and finally make recommendations to clients and serve the wine.See also
* Outline of wine * Glossary of wine terms * Classification of wine * Winemaking * List of grape varieties * Health effects of wine * Storage of wine * Maceration (wine) * Pressing (wine) * Vidal blanc * Hybrid grapeReferences
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * *online review
*
External links
''The Guardian'' & ''Observer'' Guide to Wine
{{Authority control Wine, Alcoholic drinks Ceremonial food and drink Cooking Fermented drinks Grape