Wind-Hydrogen Hybrid Power Systems on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hybrid power are combinations between different technologies to produce power.
In
Hybrid power are combinations between different technologies to produce power.
In


File:Hybrid system.jpg, Typical wind and solar hybrid system
File:Hybrid system, 2400W windturbines, 4000W solar modules, island Zirje, Croatia.jpg, Hybrid on Žirje, Croatia
File:Hybrid System.jpg, Small wind and solar hybrid system
Another example of a hybrid energy system is a photovoltaic array coupled with a  A combine use of wind-solar systems results, in many places, to a smoother power output since the resources are anti-correlated. Therefore, the combined use of wind and solar systems is crucial for a large-scale grid integration.
In 2019 in western Minnesota, a $5m hybrid system was installed. It runs 500 kW of solar power through the inverter of a 2 MW wind turbine, increasing the
A combine use of wind-solar systems results, in many places, to a smoother power output since the resources are anti-correlated. Therefore, the combined use of wind and solar systems is crucial for a large-scale grid integration.
In 2019 in western Minnesota, a $5m hybrid system was installed. It runs 500 kW of solar power through the inverter of a 2 MW wind turbine, increasing the
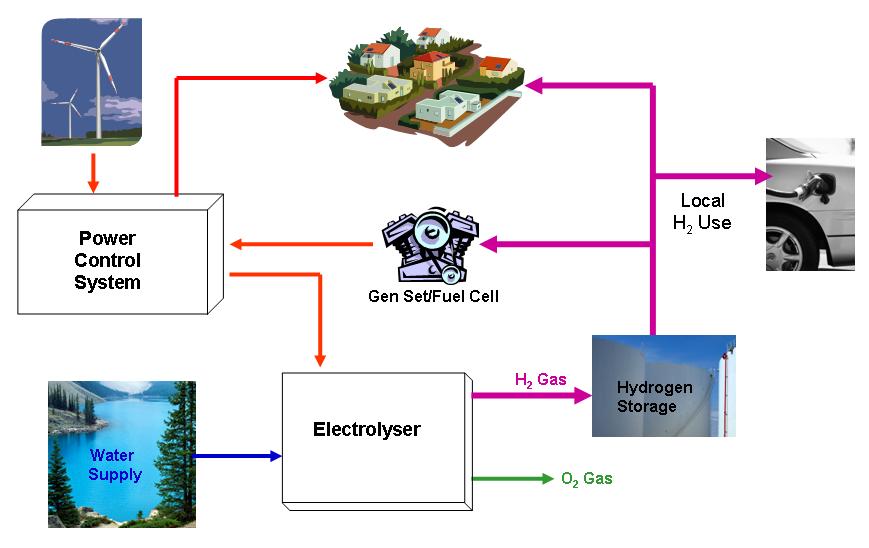 One method of storing wind energy is the production of hydrogen through the electrolysis of
One method of storing wind energy is the production of hydrogen through the electrolysis of
National Renewable Energy Laboratory usually alongside ancillary equipment such as energy storage, power converters, and various control components, to generate electricity. They are designed to increase capacity and reduce the cost and environmental impact of electrical generation in remote communities and facilities that are not linked to a
HAMILTON SPECTATOR - Integrating fuel cell technology into wind turbine structure that can produce cryo-compressed hydrogen and oxygen that is stored on-site, and used to generate electrical power when there is no wind
International Association for Hydrogen Energy
European Hydrogen Association
RES2H2
THEnergy platform "Renewables & Mining"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hybrid Power Energy storage Electric power generation Renewable energy technology Wind power Power station technology Hydrogen production
 Hybrid power are combinations between different technologies to produce power.
In
Hybrid power are combinations between different technologies to produce power.
In power engineering
Power engineering, also called power systems engineering, is a subfield of electrical engineering that deals with the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of electric power, and the electrical apparatus connected to such sy ...
, the term 'hybrid' describes a combined power and energy storage system.
Examples of power producers used in hybrid power are photovoltaics
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially ...
, wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each yea ...
s, and various types of engine-generator
An engine–generator is the combination of an electrical generator and an engine (prime mover) mounted together to form a single piece of equipment. This combination is also called an ''engine–generator set'' or a ''gen-set''. In many contexts ...
s e.g. diesel gen-sets.
Hybrid power plants often contain a renewable energy component (such as PV) that is balanced via a second form of generation or storage such as a diesel genset, fuel cell or battery storage system. They can also provide other forms of power such as heat for some applications.
Hybrid power system
Hybrid systems, as the name implies, combine two or more modes of electricity generation together, usually using renewable technologies such as solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind turbines. Hybrid systems provide a high level of energy security through the mix of generation methods, and often will incorporate a storage system (battery, fuel cell) or small fossil fueled generator to ensure maximum supply reliability and security. Hybrid renewable energy systems are becoming popular as stand-alone power systems for providing electricity in remote areas due to advances in renewable energy technologies and subsequent rise in prices ofpetroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
products. A hybrid energy system, or hybrid power, usually consists of two or more renewable energy sources used together to provide increased system efficiency as well as greater balance in energy supply.
Types
Hydro and solar
Floating solar
Floating solar or floating photovoltaics (FPV), sometimes called floatovoltaics, is solar panels mounted on a structure that floats on a body of water, typically a reservoir or a lake.
The market for this renewable energy technology has grown rap ...
is usually added to existing hydro rather than building both together.
Solar and wind


wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each yea ...
. This would create more output from the wind turbine during the winter, whereas during the summer, the solar panels would produce their peak output. Hybrid energy systems often yield greater economic and environmental returns than wind, solar, geothermal or trigeneration stand-alone systems by themselves.
 A combine use of wind-solar systems results, in many places, to a smoother power output since the resources are anti-correlated. Therefore, the combined use of wind and solar systems is crucial for a large-scale grid integration.
In 2019 in western Minnesota, a $5m hybrid system was installed. It runs 500 kW of solar power through the inverter of a 2 MW wind turbine, increasing the
A combine use of wind-solar systems results, in many places, to a smoother power output since the resources are anti-correlated. Therefore, the combined use of wind and solar systems is crucial for a large-scale grid integration.
In 2019 in western Minnesota, a $5m hybrid system was installed. It runs 500 kW of solar power through the inverter of a 2 MW wind turbine, increasing the capacity factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is def ...
and reducing costs by $150,000 per year. Purchase contracts limits the local distributor to a 5% maximum of self-generation.
The Pearl River Tower
Pearl River Tower (; or ) is a 71- story, , clean technology neofuturistic skyscraper at the junction of Jinsui Road/Zhujiang Avenue West, Tianhe District, Guangzhou, China. The tower's architecture and engineering were performed by Skidmore, Ow ...
in Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
, China, will mix solar panel on its windows and several wind turbines at different stories of its structure, allowing this tower to be energy positive.
In several parts of China & India, there are lighting pylons with combinations of solar panels and wind-turbines at their top. This allows space already used for lighting to be used more efficiently with two complementary energy productions units. Most common models use horizontal axis wind-turbines, but now models are appearing with vertical axis wind-turbines, using a helicoidal shaped, twisted-Savonius
Savonius wind turbines are a type of vertical-axis wind turbine (VAWT), used for converting the force of the wind into torque on a rotating shaft. The turbine consists of a number of aerofoils, usually—but not always—vertically mounted on a r ...
system.
Solar panels on the already existing wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each yea ...
s has been tested, but produced blinding rays of light that posed a threat to airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, Propeller (aircraft), propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurat ...
s. A solution was to produce tinted solar panels that do not reflect as much light. Another proposed design was to have a vertical axis wind turbine
A vertical-axis wind turbine (VAWT) is a type of wind turbine where the main rotor shaft is set transverse to the wind while the main components are located at the base of the turbine. This arrangement allows the generator and gearbox to be ...
coated in solar cells that are able to absorb sunlight from any angle.
Other solar hybrids include solar-wind systems. The combination of wind and solar has the advantage that the two sources complement each other because the peak operating times for each system occur at different times of the day and year. The power generation of such a hybrid system is more constant and fluctuates less than each of the two component subsystems.
Hydro and wind
A wind-hydro system generateselectric energy
Electrical energy is energy related to forces on electrically charged particles and the movement of electrically charged particles (often electrons in wires, but not always). This energy is supplied by the combination of electric current and electr ...
combining wind turbines and pumped storage
Pumping may refer to:
* The operation of a pump, for moving a liquid from one location to another
**The use of a breast pump for extraction of milk
* Pumping (audio), a creative misuse of dynamic range compression
* Pumping (computer systems), th ...
. The combination has been the subject of long-term discussion, and an experimental plant, which also tested wind turbines, was implemented by Nova Scotia Power
Nova Scotia Power Inc. is a vertically integrated electric utility in Nova Scotia, Canada. It is privately owned by Emera and regulated by the provincial government via the Nova Scotia Utility and Review Board (NSUARB). Nova Scotia Power Inc pr ...
at its Wreck Cove hydro electric power site in the late 1970s, but was decommissioned within ten years. Since, no other system has been implemented at a single location as of late 2010.
Wind-hydro stations dedicate all, or a significant portion, of their wind power resources to pumping water into pumped storage reservoirs. These reservoirs are an implementation of grid energy storage.
Wind and its generation potential is inherently variable. However, when this energy source is used to pump water into reservoirs at an elevation (the principle behind pumped storage), the potential energy of the water is relatively stable and can be used to generate electrical power by releasing it into a hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a w ...
plant when needed. The combination has been described as particularly suited to islands that are not connected to larger grids.
During the 1980s, an installation was proposed in the Netherlands. The IJsselmeer would be used as the reservoir, with wind turbines located on its dike. Feasibility studies have been conducted for installations on the island of Ramea
Ramea is a small village in Newfoundland and Labrador located on Northwest Island, one of a group of five major islands located off the south coast of Newfoundland, Canada. The island is approximately 3.14 km long by 0.93 km wide (1.9 ...
(Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic Canada, Atlantic region. The province comprises t ...
) and on the Lower Brule Indian Reservation
The Lower Brulé Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation that belongs to the Lower Brulé Lakota Tribe. It is located on the west bank of the Missouri River in Lyman and Stanley counties in central South Dakota in the United States. It i ...
(South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large porti ...
).
An installation at Ikaria Island, Greece, had entered the construction phase as of 2010.
The island of El Hierro
El Hierro, nicknamed ''Isla del Meridiano'' (the "Meridian Island"), is the second-smallest and farthest-south and -west of the Canary Islands (an autonomous community of Spain), in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa, with a populatio ...
is where the first world's first wind-hydro power station is expected to be complete. Current TV
Current TV was an American television channel which broadcast from August 1, 2005, to August 20, 2013. Prior INdTV founders Al Gore and Joel Hyatt, with Ronald Burkle, each held a sizable stake in Current TV. Comcast and DirecTV each held a smalle ...
called this "a blueprint for a sustainable future on planet Earth". It was designed to cover between 80-100% of the island's power and was set to be operational in 2012. However, these expectations were not realized in practice, probably due to inadequate reservoir volume and persistent problems with grid stability.
100% renewable energy
100% renewable energy means getting all energy from renewable resources. The endeavor to use 100% renewable energy for electricity, heating, cooling and transport is motivated by climate change, pollution and other environmental issues ...
systems require an over-capacity of wind or solar power.
Solar PV and solar thermal
ThoughSolar PV
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and co ...
generates cheaper intermittent power during the day light time, it needs the support of sustainable power generation sources to provide round the clock power. Solar thermal
Solar thermal energy (STE) is a form of energy and a technology for harnessing solar energy to generate thermal energy for use in industry, and in the residential and commercial sectors.
Solar thermal collectors are classified by the United S ...
plants with thermal storage are clean sustainable power generation to supply electricity round the clock. They can cater the load demand perfectly and work as base load power plants when the extracted solar energy is found excess in a day. Proper mix of solar thermal (thermal storage type) and solar PV
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and co ...
can fully match the load fluctuations without the need of costly battery storage.
During the day time, the additional auxiliary power consumption of a solar thermal storage power plant is nearly 10% of its rated capacity for the process of extracting solar energy in the form of thermal energy. This auxiliary power requirement can be made available from cheaper solar PV plant by envisaging hybrid solar plant with a mix of solar thermal and solar PV plants at a site. Also to optimise the cost of power, generation can be from the cheaper solar PV plant (33% generation) during the day light whereas the rest of the time in a day is from the solar thermal storage plant (67% generation from Solar power tower
A solar power tower, also known as 'central tower' power plant or ' heliostat' power plant, is a type of solar furnace using a tower to receive focused sunlight. It uses an array of flat, movable mirrors (called heliostats) to focus the sun's r ...
and parabolic trough
A parabolic trough is a type of solar thermal collector that is straight in one dimension and curved as a parabola in the other two, lined with a polished metal mirror. The sunlight which enters the mirror parallel to its plane of symmetry is foc ...
types) for meeting 24 hours base load operation. When solar thermal storage plant is forced to idle due to lack of sunlight locally during cloudy days in monsoon season, it is also possible to consume (similar to a lesser efficient, huge capacity and low cost battery storage system) the cheap surplus / infirm power from solar PV, wind and hydro power plants by heating the hot molten salt to higher temperature for converting stored thermal energy in to electricity during the peak demand hours when the electricity sale price is profitable.
Solar PV, battery and grid
Solar PV gives variable output which can be buffered with battery storage. However, large variations exist in production over the day, as well in many places seasonally. The battery helps match the power with the load. A ''hybrid solar inverter'' additionally allows the storage of low cost electricity drawn down on cheap tariffs.Wind-hydrogen system
water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
. This hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
is subsequently used to generate electricity during periods when demand can not be matched by wind alone. The energy in the stored hydrogen can be converted into electrical power through fuel cell technology or a combustion engine linked to an electrical generator
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy) or fuel-based power ( chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, g ...
.
Successfully storing hydrogen has many issues which need to be overcome, such as embrittlement
Embrittlement is a significant decrease of ductility of a material, which makes the material brittle. Embrittlement is used to describe any phenomena where the environment compromises a stressed material's mechanical performance, such as temperatu ...
of the materials used in the power system.
This technology is being developed in many countries. In 2007 there was an IPO of an Australian firm called Wind Hydrogen that aimed to commercialise this technology in both Australia and the UK. In 2008 the company changed its name and turned its operations to fossil fuel exploration.
In 2007, technology test sites included:
Wind and diesel
A wind-diesel hybrid power system combinesdiesel generator
A diesel generator (DG) (also known as a diesel Genset) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator (often an alternator) to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine generator. A diesel compression-ig ...
s and wind turbines,Wales, Alaska High-Penetration Wind-Diesel Hybrid Power SystemNational Renewable Energy Laboratory usually alongside ancillary equipment such as energy storage, power converters, and various control components, to generate electricity. They are designed to increase capacity and reduce the cost and environmental impact of electrical generation in remote communities and facilities that are not linked to a
power grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
. Wind-diesel hybrid systems reduce reliance on diesel fuel, which creates pollution and is costly to transport.
Wind-diesel generating systems have been under development and trialled in a number of locations during the latter part of the 20th century. A growing number of viable sites have been developed with increased reliability and minimized technical support costs in remote communities.
The successful integration of wind energy with diesel generating sets relies on complex controls to ensure correct sharing of intermittent wind energy and controllable diesel generation to meet the demand of the usually variable load. The common measure of performance for wind diesel systems is Wind Penetration which is the ratio between Wind Power and Total Power delivered, e.g. 60% wind penetration implies that 60% of the system power comes from the wind. Wind Penetration figures can be either peak or long term. Sites such as Mawson Station
The Mawson Station, commonly called Mawson, is one of three permanent bases and research outposts in Antarctica managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). Mawson lies in Holme Bay in Mac. Robertson Land, East Antarctica in the Austra ...
, Antarctica, as well as Coral Bay and Bremer Bay Bremer may refer to:
People
*Bremer (surname)
* Bremer Ehrler (born 1914), American politician
* Bremer (born 1997), Brazilian footballer
Places
;Australia
*Bremer Bay, Western Australia
* Bremer Marine Park
*Bremer Island
* Bremer River (disambig ...
in Australia have peak wind penetrations of around 90%. Technical solutions to the varying wind output include controlling wind output using variable speed wind turbines (e.g. Enercon
Enercon GmbH is a wind turbine manufacturer based in Aurich, Lower Saxony, Germany. It has been the market leader in Germany since the mid-1990s. Enercon has production facilities in Germany (Aurich, Emden and Magdeburg), Brazil, India, Canada, ...
, Denham, Western Australia), controlling demand such as the heating load (e.g. Mawson), storing energy in a flywheel (e.g. Powercorp, Coral Bay). Some installations are now being converted to wind hydrogen systems such as on Ramea
Ramea is a small village in Newfoundland and Labrador located on Northwest Island, one of a group of five major islands located off the south coast of Newfoundland, Canada. The island is approximately 3.14 km long by 0.93 km wide (1.9 ...
in Canada which is due for completion in 2010.
Recently, in Northern Canada wind-diesel hybrid power systems were built by the mining industry. In remote locations at Lac de Gras, in Canada's Northwest Territories, and Katinniq, Ungava Peninsula, Nunavik, two systems are used to save fuel at mines. There is another system in Argentina.
Other hybrid power systems
At power stations that usecompressed air energy storage
Compressed-air energy storage (CAES) is a way to store energy for later use using compressed air. At a utility scale, energy generated during periods of low demand can be released during peak load periods.Wild, Matthew, LWind Drives Growing Use o ...
(CAES), electrical energy is used to compress air and store it in underground facilities such as caverns or abandoned mines. During later periods of high electrical demand, the air is released to power turbines, generally using supplemental natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
. Power stations that make significant use of CAES are operational in McIntosh, Alabama
McIntosh is a town located in Washington County, Alabama, United States along U.S. Route 43. It is south of Wagarville and north of Mobile. It was named for William McIntosh, a prominent Creek chief of the nineteenth century. The town was inc ...
, Germany, and Japan. System disadvantages include some energy losses in the CAES process; also, the need for supplemental use of fossil fuels such as natural gas means that these systems do not completely make use of renewable energy.
The Iowa Stored Energy Park, projected to begin commercial operation in 2015, will use wind farms in Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
as an energy source in conjunction with CAES.
Combining solar and geothermal is also possible.
Solar and diesel
A common type is a photovoltaic diesel hybrid system, combiningphotovoltaics
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially ...
(PV) and diesel generator
A diesel generator (DG) (also known as a diesel Genset) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator (often an alternator) to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine generator. A diesel compression-ig ...
s, or diesel gensets, as PV has hardly any marginal cost and is treated with priority on the grid
Grid, The Grid, or GRID may refer to:
Common usage
* Cattle grid or stock grid, a type of obstacle is used to prevent livestock from crossing the road
* Grid reference, used to define a location on a map
Arts, entertainment, and media
* News ...
. The diesel gensets are used to constantly fill in the gap between the present load and the actual generated power by the PV system.
As solar energy is fluctuating, and the generation capacity of the diesel genesets is limited to a certain range, it is often a viable option to include battery storage
A battery storage power station is a type of energy storage power station that uses a group of batteries to store electrical energy. Battery storage is the fastest responding dispatchable source of power on electric grids, and it is used to stab ...
in order to optimize solar's contribution to the overall generation of the hybrid system.
The best business cases for diesel reduction with solar and wind energy can normally be found in remote locations because these sites are often not connected to the grid and transport of diesel over long distances is expensive. Many of these applications can be found in the mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic ...
sector and on islands
In 2015, a case-study conducted in seven countries concluded that in all cases generating costs can be reduced by hybridising mini-grids and isolated grids. However, financing costs for diesel-powered electricity grids with solar photovoltaics are crucial and largely depend on the ownership structure of the power plant. While cost reductions for state-owned utilities can be significant, the study also identified short-term economic benefits to be insignificant or even negative for non-public utilities, such as independent power producers, given historical costs at the time of the study.
More than 2 sources
Adding wave power to wind and solar may be possible.See also
* Stand-alone power system *List of energy storage projects
This is a list of energy storage power plants worldwide, other than pumped hydro storage.
Many individual energy storage plants augment electrical grids by capturing excess electrical energy during periods of low demand and storing it in o ...
*Distributed generation
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to ...
*Photovoltaic thermal hybrid solar collector
Photovoltaic thermal collectors, typically abbreviated as PVT collectors and also known as hybrid solar collectors, photovoltaic thermal solar collectors, PV/T collectors or solar cogeneration systems, are power generation technologies that conver ...
References
External links
HAMILTON SPECTATOR - Integrating fuel cell technology into wind turbine structure that can produce cryo-compressed hydrogen and oxygen that is stored on-site, and used to generate electrical power when there is no wind
International Association for Hydrogen Energy
European Hydrogen Association
RES2H2
THEnergy platform "Renewables & Mining"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hybrid Power Energy storage Electric power generation Renewable energy technology Wind power Power station technology Hydrogen production