|
Mawson Station
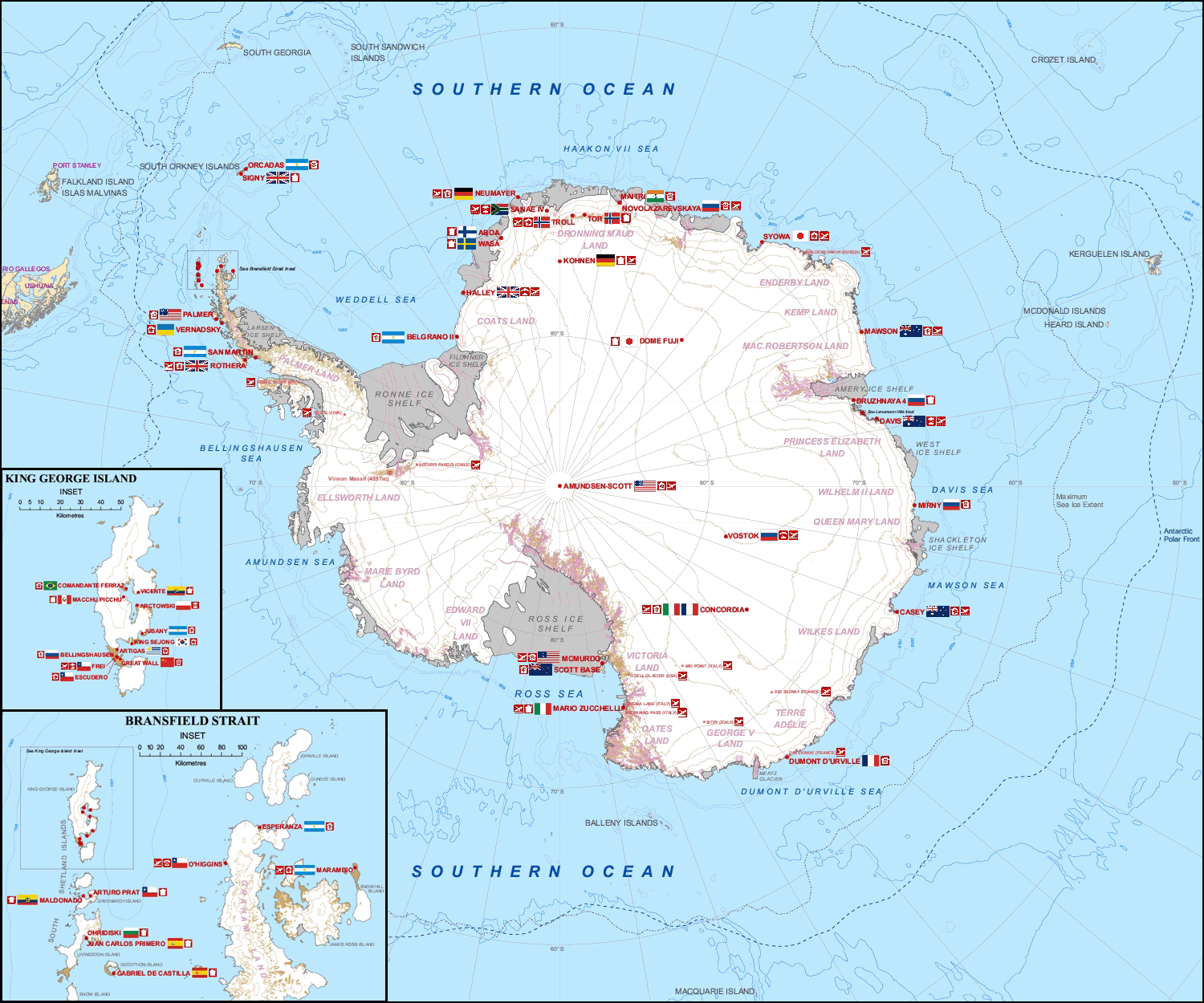
The Mawson Station, commonly called Mawson, is one of three permanent bases and research outposts in Antarctica managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). Mawson lies in Holme Bay in Mac. Robertson Land, East Antarctica in the Australian Antarctic Territory, a territory claimed by Australia. Established in 1954, Mawson is Australia's oldest Antarctic station and the oldest continuously inhabited Antarctic station south of the Antarctic Circle. Mawson was named in honour of the Australian Antarctic explorer Sir Douglas Mawson. Mawson was listed on the Register of the National Estate in 2001 and listed on the Commonwealth Heritage List on 22 June 2004, reflecting the post-World War Two revival of Australia's scientific research and territorial interests in Antarctica. Purpose Mawson Station is a base for scientific research programs including an underground cosmic ray detector, various long-term meteorological aeronomy and geomagnetic studies, as well as ongoing con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Stations In Antarctica
Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rock or on ice that is (for practical purposes) fixed in place. Many of the stations are staffed throughout the year. A total of 42 countries (as of October 2006), all signatories to the Antarctic Treaty, operate seasonal (summer) and year-round research stations on the continent. The population of people performing and supporting scientific research on the continent and nearby islands varies from approximately 4,000 during the summer season to 1,000 during winter (June). In addition to these permanent stations, approximately 30 field camps are established each summer to support specific projects. History First bases During the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration in the late 19th century, the first bases on the continent were established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk is deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Australian And New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition
The British Australian (and) New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) was a research expedition into Antarctica between 1929 and 1931, involving two voyages over consecutive Austral summers. It was a British Commonwealth initiative, driven more by geopolitics than science, and funded by the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand. The leader of the BANZARE was Sir Douglas Mawson and there were several subcommanders (Captain K.N. MacKenzie, who replaced Captain John King Davis for the second summer) on board the RRS Discovery, the ship previously used by Robert Falcon Scott. The BANZARE, which also made several short flights in a small plane, mapped the coastline of Antarctica and discovered Mac. Robertson Land and Princess Elizabeth Land (which later was claimed as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory). The voyages primarily comprised an "acquisitive exploratory expedition", with Mawson making proclamations of British sovereignty over Antarctic lands at each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Stations In Australia
A number of historic and current Earth (or ground) stations in Australia are used to communicate and track human-made satellites. Many of the sites are associated with overseas government partnerships established generally with the United States, European Union, and Japan. They are generally run by various Australian Government agencies along with NASA, European Space Agency or the US Military. List of sites Treaties A number of treaties A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ... and other instruments associated with the stations: References {{reflist, 30em * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANARESAT
ANARESAT or ''Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions Satellite'' is a communication solution using Intelsat Geostationary communication satellites to allow Australian Antarctic Division sites to communicate. The installation includes a 7.3 m dish antenna, and a large dark dome to protect the satellite from the harsh weather conditions. It was installed at: * Davis Station in March 1987, * Mawson Station in January 1988, * Casey Station in March 1988, and * Macquarie Island Station The Macquarie Island Station is a permanent Australian subantarctic research base on Macquarie Island, commonly called Macca, situated in the Southern Ocean and located approximately halfway between mainland Australia and Antarctica, managed b ... in December 1988. References {{reflist Satellite telephony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Fuel
Diesel fuel , also called diesel oil, is any liquid fuel specifically designed for use in a diesel engine, a type of internal combustion engine in which fuel ignition takes place without a spark as a result of compression of the inlet air and then injection of fuel. Therefore, diesel fuel needs good compression ignition characteristics. The most common type of diesel fuel is a specific fractional distillate of petroleum fuel oil, but alternatives that are not derived from petroleum, such as biodiesel, biomass to liquid (BTL) or gas to liquid (GTL) diesel are increasingly being developed and adopted. To distinguish these types, petroleum-derived diesel is sometimes called petrodiesel in some academic circles. In many countries, diesel fuel is standardised. For example, in the European Union, the standard for diesel fuel is EN 590. Diesel fuel has many colloquial names; most commonly, it is simply referred to as ''diesel''. In the United Kingdom, diesel fuel for on-road use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Generator
A wind turbine is a device that wind power, converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of list of most powerful wind turbines, large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. Wind turbines are an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy, and are used in many countries to lower energy costs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. One study claimed that, wind had the "lowest relative greenhouse gas emissions, the least water consumption demands and the most favorable social impacts" compared to photovoltaic, hydroelectricity, hydro, geothermal power, geothermal, coal power, coal and gas-fired power plant, gas energy sources. Smaller wind turbines are used for applications such as battery charging for auxiliary power for boats or caravan (towed trailer), caravans, and to power traffic warning signs. Larger turbines can contribute to a domestic power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
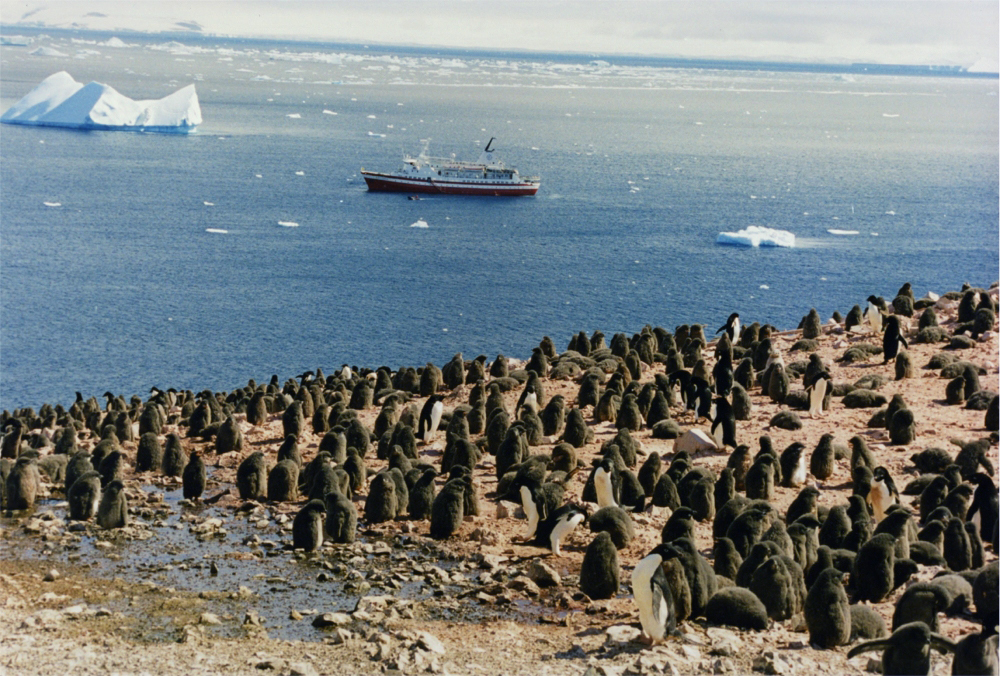
Adélie Penguin
The Adélie penguin (''Pygoscelis adeliae'') is a species of penguin common along the entire coast of the Antarctic continent, which is the only place where it is found. It is the most widespread penguin species, and, along with the emperor penguin, is the most southerly distributed of all penguins. It is named after Adélie Land, in turn named for Adèle Dumont d'Urville, who was married to French explorer Jules Dumont d'Urville, who first discovered this penguin in 1840. Adélie penguins obtain their food by both predation and foraging, with a diet of mainly krill and fish. Taxonomy and systematics The first Adélie penguin specimens were collected by crew members of French explorer Jules Dumont d'Urville on his expedition to Antarctica in the late 1830s and early 1840s. Jacques Bernard Hombron and Honoré Jacquinot, two French surgeons who doubled as naturalists on the journey, described the bird for science in 1841, giving it the scientific name ''Catarrhactes adeliæ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Penguin
The emperor penguin (''Aptenodytes forsteri'') is the tallest and heaviest of all living penguin species and is endemic to Antarctica. The male and female are similar in plumage and size, reaching in length and weighing from . Feathers of the head and back are black and sharply delineated from the white belly, pale-yellow breast and bright-yellow ear patches. Like all penguins, it is flightless, with a streamlined body, and wings stiffened and flattened into flippers for a marine habitat. Its diet consists primarily of fish, but also includes crustaceans, such as krill, and cephalopods, such as squid. While hunting, the species can remain submerged around 20 minutes, diving to a depth of . It has several adaptations to facilitate this, including an unusually structured haemoglobin to allow it to function at low oxygen levels, solid bones to reduce barotrauma, and the ability to reduce its metabolism and shut down non-essential organ functions. The only penguin specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rookery
A rookery is a colony of breeding animals, generally gregarious birds. Coming from the nesting habits of rooks, the term is used for corvids and the breeding grounds of colony-forming seabirds, marine mammals ( true seals and sea lions), and even some turtles. Rooks (northern-European and central-Asian members of the crow family) have multiple nests in prominent colonies at the tops of trees. Paleontological evidence points to the existence of rookery-like colonies in the pterosaur ''Pterodaustro''. The term '' rookery'' was also borrowed as a name for dense slum housing in nineteenth-century cities, especially in London. See also * Auca Mahuevo, for a titanosaurid sauropod dinosaur rookery *Bird colony A bird colony is a large congregation of individuals of one or more species of bird that nest or roost in proximity at a particular location. Many kinds of birds are known to congregate in groups of varying size; a congregation of nesting bi ... * Heronry * Rook sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auster Rookery
Auster Rookery is an Emperor penguin rookery on sea-ice, sheltered by grounded icebergs, east of the Auster Islands, and about ENE of Mawson Station in Antarctica. It was discovered in August 1957 by Flying Officer D. Johnston, RAAF, from an ANARE Auster Auster Aircraft Limited was a British aircraft manufacturer from 1938 to 1961.Willis, issue 122, p.55 History The company began in 1938 at the Britannia Works, Thurmaston near Leicester, England, as Taylorcraft Aeroplanes (England) Limited, ma ... aircraft, after which it was named. The rookery was estimated in 2009 to contain 7,855 individual emperor penguins, and has been designated an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International. References Important Bird Areas of Antarctica Penguin colonies Mac. Robertson Land {{MacRobertsonLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Biology
Conservation biology is the study of the conservation of nature and of Earth's biodiversity with the aim of protecting species, their habitats, and ecosystems from excessive rates of extinction and the erosion of biotic interactions. It is an interdisciplinary subject drawing on natural and social sciences, and the practice of natural resource management. The conservation ethic is based on the findings of conservation biology. Origins The term conservation biology and its conception as a new field originated with the convening of "The First International Conference on Research in Conservation Biology" held at the University of California, San Diego in La Jolla, California, in 1978 led by American biologists Bruce A. Wilcox and Michael E. Soulé with a group of leading university and zoo researchers and conservationists including Kurt Benirschke, Sir Otto Frankel, Thomas Lovejoy, and Jared Diamond. The meeting was prompted due to concern over tropical deforestation, disappe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)


