Wilhelm Bornhardt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Friedrich Wilhelm Conrad Eduard Bornhardt (20 April 1864 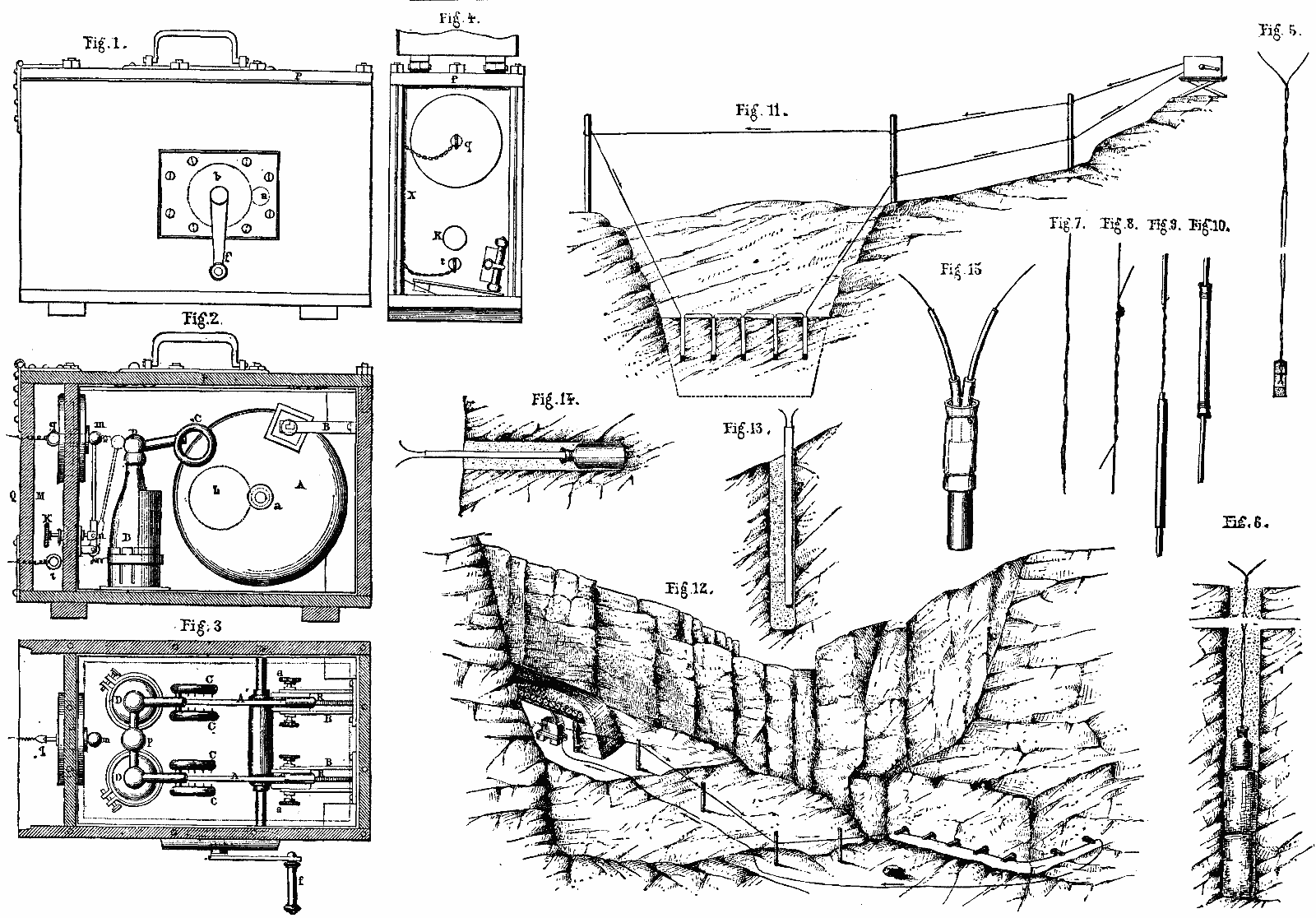 Bornhardt invented a number of applications for the mining industry. One such was a hand-powered electrical generator, much used in France, for detonating explosives in rock-blasting.
Bornhardt invented a number of applications for the mining industry. One such was a hand-powered electrical generator, much used in France, for detonating explosives in rock-blasting.
Braunschweig
Braunschweig () or Brunswick ( ; from Low German , local dialect: ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in Lower Saxony, Germany, north of the Harz Mountains at the farthest navigable point of the river Oker, which connects it to the ...
- 2 December 1946 Goslar
Goslar (; Eastphalian dialect, Eastphalian: ''Goslär'') is a historic town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the administrative centre of the Goslar (district), district of Goslar and is located on the northwestern wikt:slope, slopes of the Harz ...
) was a German geologist, engineer and explorer, and was Director of the Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
College of Mines (Bergakademie) from 1907 to 1916.
He explored and set out the groundwork of the geology of German East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; ) was a German colonial empire, German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Portugu ...
. His published work consisted of two parts – an account of his travels and his geological findings. In 1896 he set out from Lindi
Lindi is a historic coastal town in southern Tanzania and the administrative center of the Lindi Region, the least populated region in the country. Situated at the head of Lindi Bay along the Indian Ocean, the town is located approximately 10 ...
to Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, () is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.
It is ...
where he stayed for ten months undertaking eight exploratory trips of the region. Afterwards he returned to the coast to write up his geology journals.
In 1897 he explored the protectorate of Dar es Salaam
Dar es Salaam (, ; from ) is the largest city and financial hub of Tanzania. It is also the capital of the Dar es Salaam Region. With a population of over 7 million people, Dar es Salaam is the largest city in East Africa by population and the ...
as far as the Ruvuma Region
Ruvuma Region (''Mkoa wa Ruvuma'' in Swahili language, Swahili) is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative Regions of Tanzania, regions. The region covers a land area of , comparable in size to the nation state of Latvia. The region is also bordered ...
, the Zanzibar Archipelago
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. The c ...
and the Usambara Mountains
The Usambara Mountains of northeastern Tanzania in tropical East Africa, comprise the easternmost ranges of the Eastern Arc Mountains. The ranges are approximately long and about half that wide, and they are situated in the Lushoto District ...
, carrying out some thirteen journeys. In all he covered about and prepared maps of the geology and vegetation of the regions he traversed. Bornhardt documented the existence of coal reserves in present-day Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
in 1896 when he explored the Songwe Kiwira area, described the Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe Khoemana (also known as !Orakobab or Korana) word is a semidesert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is ...
stratigraphy and surveyed several coal fields.
The rose-red mineral ''bornhardtite'' from Lautenthal
The formerly free mining town ('' Bergstadt'') of Lautenthal in Germany is a state-recognised, climatic spa with around 1,570 inhabitants and has been part of the borough of Langelsheim since 1972.
Geography
Lautenthal lies in the Innerste ...
in the Harz Mountains
The Harz (), also called the Harz Mountains, is a Mittelgebirge, highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The nam ...
of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Re ...
, is named in his honour. He first coined the term "inselberg
An inselberg or monadnock ( ) is an isolated rock hill, knob, ridge, or small mountain that rises abruptly from a gently sloping or virtually level surrounding plain.
In Southern Africa, a similar formation of granite is known as a koppie, an ...
" to describe an isolated massif, while the term "bornhardt
A bornhardt () is a dome-shaped, steep-sided, bald rock outcropping at least in height and several hundred metres in width. They are named after Wilhelm Bornhardt (1864–1946), a German geologist and explorer of German East Africa, who firs ...
", describing a particular type of mountain, is used in his honour.
 Bornhardt invented a number of applications for the mining industry. One such was a hand-powered electrical generator, much used in France, for detonating explosives in rock-blasting.
Bornhardt invented a number of applications for the mining industry. One such was a hand-powered electrical generator, much used in France, for detonating explosives in rock-blasting.
Publications
* * * *References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bornhardt, Friedrich Wilhelm Conrad Eduard 1864 births 1946 deaths Scientists from Braunschweig People from the Duchy of Brunswick 20th-century German geologists 19th-century German explorers Members of the Göttingen Academy of Sciences and Humanities German people in German East Africa